SpringBoot系列——@Async优雅的异步调用
前言
众所周知,java的代码是同步顺序执行,当我们需要执行异步操作时我们需要创建一个新线程去执行,以往我们是这样操作的:
/**
* 任务类
*/
class Task implements Runnable { @Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":异步任务");
}
}
//新建线程并执行任务类
new Thread(new Task()).start();
jdk1.8之后可以使用Lambda 表达式
//新建线程并执行任务类
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":异步任务");
}).start();
当然,除了显式的new Thread,我们一般通过线程池获取线程,这里就不再展开
Spring 3.0之后提供了一个@Async注解,使用@Async注解进行优雅的异步调用,我们先看一下API对这个注解的定义:https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/javadoc-api/org/springframework/scheduling/annotation/Async.html
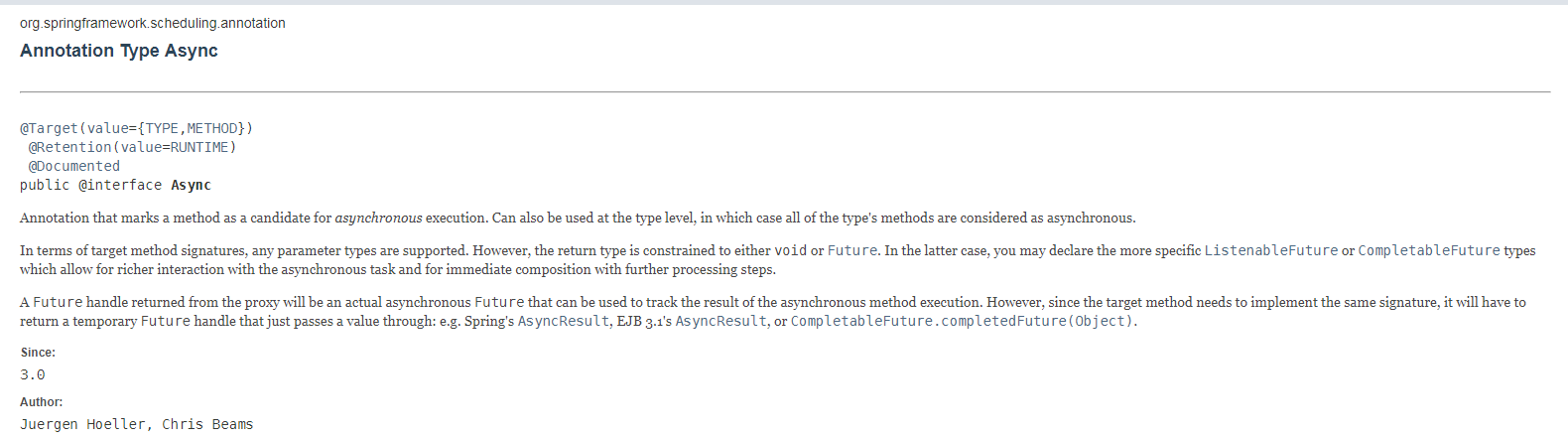
本文记录在SpringBoot项目中使用@Async注解,实现优雅的异步调用
代码与测试
项目工程结构
因为要测试事务,所以需要引入
<!--添加springdata-jpa依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency> <!--添加MySQL驱动依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
在启动类开启启用异步调用,同时注入ApplicationRunner对象在启动类进行调用测试
package cn.huanzi.qch.springbootasync; import cn.huanzi.qch.springbootasync.service.TestService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component
@EnableAsync//开启异步调用
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootAsyncApplication { @Autowired
private TestService testService; public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootAsyncApplication.class, args);
} /**
* 启动成功
*/
@Bean
public ApplicationRunner applicationRunner() {
return applicationArguments -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":开始调用异步业务");
//无返回值
// testService.asyncTask(); //有返回值,但主线程不需要用到返回值
// Future<String> future = testService.asyncTask("huanzi-qch");
//有返回值,且主线程需要用到返回值
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":返回值:" + testService.asyncTask("huanzi-qch").get()); //事务测试,事务正常提交
// testService.asyncTaskForTransaction(false);
//事务测试,模拟异常事务回滚
// testService.asyncTaskForTransaction(true); long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":调用异步业务结束,耗时:" + (endTime - startTime));
};
}
}
看一下我们的测试业务类TestService
package cn.huanzi.qch.springbootasync.service;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
public interface TestService {
/**
* 异步调用,无返回值
*/
void asyncTask();
/**
* 异步调用,有返回值
*/
Future<String> asyncTask(String s);
/**
* 异步调用,无返回值,事务测试
*/
void asyncTaskForTransaction(Boolean exFlag);
}
package cn.huanzi.qch.springbootasync.service; import cn.huanzi.qch.springbootasync.pojo.TbUser;
import cn.huanzi.qch.springbootasync.repository.TbUserRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncResult;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; import java.util.concurrent.Future; @Service
public class TestServiceImpl implements TestService { @Autowired
private TbUserRepository tbUserRepository; @Async
@Override
public void asyncTask() {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
//模拟耗时
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":void asyncTask(),耗时:" + (endTime - startTime));
} @Async("asyncTaskExecutor")
@Override
public Future<String> asyncTask(String s) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
//模拟耗时
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":Future<String> asyncTask(String s),耗时:" + (endTime - startTime));
return AsyncResult.forValue(s);
} @Async("asyncTaskExecutor")
@Transactional
@Override
public void asyncTaskForTransaction(Boolean exFlag) {
//新增一个用户
TbUser tbUser = new TbUser();
tbUser.setUsername("huanzi-qch");
tbUser.setPassword("123456");
tbUserRepository.save(tbUser); if(exFlag){
//模拟异常
throw new RuntimeException("模拟异常");
}
}
}
配置线程池
package cn.huanzi.qch.springbootasync.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.task.AsyncTaskExecutor;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor; /**
* 线程池的配置
*/
@Configuration
public class AsyncConfig { private static final int MAX_POOL_SIZE = 50; private static final int CORE_POOL_SIZE = 20; @Bean("asyncTaskExecutor")
public AsyncTaskExecutor asyncTaskExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor asyncTaskExecutor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
asyncTaskExecutor.setMaxPoolSize(MAX_POOL_SIZE);
asyncTaskExecutor.setCorePoolSize(CORE_POOL_SIZE);
asyncTaskExecutor.setThreadNamePrefix("async-task-thread-pool-");
asyncTaskExecutor.initialize();
return asyncTaskExecutor;
}
}
配置好后,@Async会默认从线程池获取线程,当然也可以显式的指定@Async("asyncTaskExecutor")
无返回值
/**
* 启动成功
*/
@Bean
public ApplicationRunner applicationRunner() {
return applicationArguments -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":开始调用异步业务");
//无返回值
testService.asyncTask();
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":调用异步业务结束,耗时:" + (endTime - startTime));
};
}

有返回值
有返回值,但主线程不需要用到返回值
/**
* 启动成功
*/
@Bean
public ApplicationRunner applicationRunner() {
return applicationArguments -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":开始调用异步业务");//有返回值,但主线程不需要用到返回值
Future<String> future = testService.asyncTask("huanzi-qch"); long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":调用异步业务结束,耗时:" + (endTime - startTime));
};
}
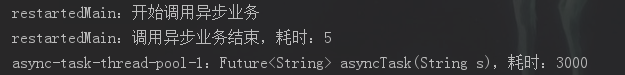
有返回值,且主线程需要用到返回值
/**
* 启动成功
*/
@Bean
public ApplicationRunner applicationRunner() {
return applicationArguments -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":开始调用异步业务");
//有返回值,且主线程需要用到返回值
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":返回值:" + testService.asyncTask("huanzi-qch").get()); long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":调用异步业务结束,耗时:" + (endTime - startTime));
};
}
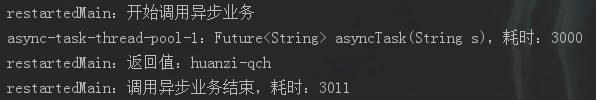
可以发现,有返回值的情况下,虽然异步业务逻辑是由新线程执行,但如果在主线程操作返回值对象,主线程会等待,还是顺序执行
事务测试
为了方便观察、测试,我们在配置文件中将日志级别设置成debug
#修改日志登记,方便调试
logging.level.root=debug
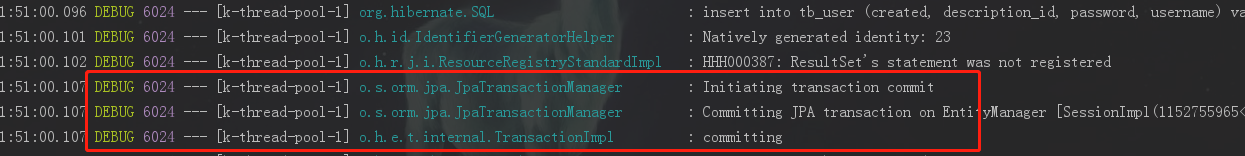
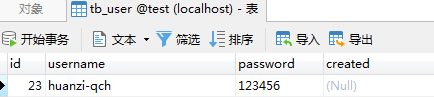
事务提交
/**
* 启动成功
*/
@Bean
public ApplicationRunner applicationRunner() {
return applicationArguments -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":开始调用异步业务");//事务测试,事务正常提交
testService.asyncTaskForTransaction(false); long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":调用异步业务结束,耗时:" + (endTime - startTime));
};
}

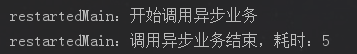
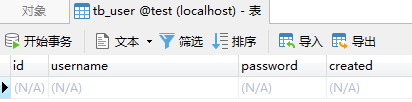
模拟异常,事务回滚
/**
* 启动成功
*/
@Bean
public ApplicationRunner applicationRunner() {
return applicationArguments -> {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":开始调用异步业务");
//事务测试,模拟异常事务回滚
testService.asyncTaskForTransaction(true); long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":调用异步业务结束,耗时:" + (endTime - startTime));
};
}

后记
SpringBoot使用@Async优雅的异步调用就暂时记录到这里,以后再进行补充
代码开源
代码已经开源、托管到我的GitHub、码云:
GitHub:https://github.com/huanzi-qch/springBoot
码云:https://gitee.com/huanzi-qch/springBoot
SpringBoot系列——@Async优雅的异步调用的更多相关文章
- SpringBoot系列:Spring Boot异步调用@Async
在实际开发中,有时候为了及时处理请求和进行响应,我们可能会多任务同时执行,或者先处理主任务,也就是异步调用,异步调用的实现有很多,例如多线程.定时任务.消息队列等, 这一章节,我们就来讲讲@Async ...
- 使用Spring中@Async注解实现异步调用
异步调用? 在解释异步调用之前,我们先来看同步调用的定义:同步就是整个处理过程顺序执行,当各个过程都执行完毕,并返回结果. 异步调用则是只是发送了调用的指令,调用者无需等待被调用的方法完全执行完毕,继 ...
- 【JDK8】Java8 优雅的异步调用API CompletableFuture
1.CompletableFuture是什么? CompletableFuture是JDK8的新特性之一,是异步调用相关的API,用于简化异步调用,提高异步调用的效率 2.CompletableFut ...
- WCF系列教程之客户端异步调用服务
本文参考自http://www.cnblogs.com/wangweimutou/p/4409227.html,纯属读书笔记,加深记忆 一.简介 在前面的随笔中,详细的介绍了WCF客户端服务的调用方法 ...
- SpringBoot系列: 如何优雅停止服务
============================背景============================在系统生命周期中, 免不了要做升级部署, 对于关键服务, 我们应该能做到不停服务完成 ...
- SpringBoot系列——事件发布与监听
前言 日常开发中,我们经常会碰到这样的业务场景:用户注册,注册成功后需要发送邮箱.短信提示用户,通常我们都是这样写: /** * 用户注册 */ @GetMapping("/userRegi ...
- SpringBoot学习笔记(十七:异步调用)
@ 目录 1.@EnableAsync 2.@Async 2.1.无返回值的异步方法 2.1.有返回值的异步方法 3. Executor 3.1.方法级别重写Executor 3.2.应用级别重写Ex ...
- dubbo同步调用、异步调用和是否返回结果源码分析和实例
0. dubbo同步调用.异步调用和是否返回结果配置 (1)dubbo默认为同步调用,并且有返回结果. (2)dubbo异步调用配置,设置 async="true",异步调用可以提 ...
- springboot 异步调用Async使用方法
引言: 在Java应用中,绝大多数情况下都是通过同步的方式来实现交互处理的:但是在处理与第三方系统交互的时候,容易造成响应迟缓的情况,之前大部分都是使用多线程来完成此类任务,其实,在spring 3. ...
随机推荐
- Delphi berlin ShowMessage的改进与使用
这个版本的delphi对ShowMessage进行了重新实现,更好的适应移动跨平台,即在移动平台下是异步执行的,而在Windows及os X下是同步执行的,如果自己控制是否异步显示对话框,也可以通过T ...
- Java实现Qt的SIGNAL-SLOT机制(保存到Map中,从而将它们关联起来,收到信号进行解析,最后反射调用)
SIGNAL-SLOT是Qt的一大特色,使用起来十分方便.在传统的AWT和Swing编程中,我们都是为要在 监听的对象上添加Listener监听器.被监听对象中保存有Listener的列表,当相关事件 ...
- impala学习笔记
impala学习笔记 -- 建库 CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS database_name; -- 在HDFS文件系统中创建数据库,需要指定要创建数据库的位置. CREA ...
- java多线程之线程安全
线程安全和非线程安全是多线程的经典问题,非线程安全会在多个线程对同一个对象并发访问时发生. 注意1: 非线程安全的问题存在于实例变量中,如果是方法内部的私有变量,则不存在非线程安全问题. 实例变量是对 ...
- 使用spring容器干掉if-else
spring容器干掉if-else 场景说明 最近新做一个项目,需要对不同店铺的商品做不同处理.例如storeA需要进行handleA操作,storeB需要进行handleB操作,如此类推 大家很容易 ...
- sql一关联多查询时否定筛选出现的问题的解决
问题:一方关联多方查询时执行否定筛选,结果包含未通过筛选的项. 我们规定一方为父,多方为子,我们希望子未通过筛选时,结果也不出现对应的父. 查询部门及部门下的所有员工. SELECT * FROM d ...
- Ubuntu --- 【转】安装lamp(php7.0)
本篇转自:http://www.laozuo.org/8303.html.以防丢失,再次记录 PHP7已经出来有一段时间,根据网友的实践测试比之前的版本效率会高不少,而且应用到网站中打开速度会有明显的 ...
- Mac上使用brew update会卡住的问题
Mac上使用brew update会卡住的问题 brew默认的源是Github,会非常慢,建议换为国内的源.推荐中科大的镜像源,比较全面. 解决方案 Homebrew Homebrew源代码仓库 替换 ...
- navicat12.0.29破解操作步骤
navicat12.0.29破解操作步骤 2018年07月11日 22:21:17 xijian0521 阅读数:1620 我的百度网盘地址: 下载点这里 以管理员身份运行 此注册机: 打开注册 ...
- C语言版数据结构笔记
现在把以前学的数据结构知识再理一遍,上机测试.首先最重要的是链表.在我看来,链表其实就是由一个个结构体连接而成的,创建一个链表有多种方式,头插法,尾插法等,这里采用的是尾插法.表述有不对的地方,欢迎更 ...
