201871010109-胡欢欢《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十六周学习总结
|
项目 |
内容 |
|
这个作业属于哪个课程 |
https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ |
|
这个作业的要求在哪里 |
https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p/11435127.html |
|
作业学习目标 |
(1) 掌握Java应用程序的打包操作; (2) 掌握线程概念; (3) 掌握线程创建的两种技术。 (4) 学习设计应用程序的GUI。 |
实验十四 应用程序归档与线程初步
第一部分:理论知识总结
14.1 什么是线程
1、程序、进程与线程
程序是一段静态的代码,它是应用程序执行的蓝本。 进程是程序的一次动态执行,它对应了从代码加载、执行至执行完毕的一个完整过程。 线程是进程执行过程中产生的多条执行线索。 线程是比进程执行更小的单位。
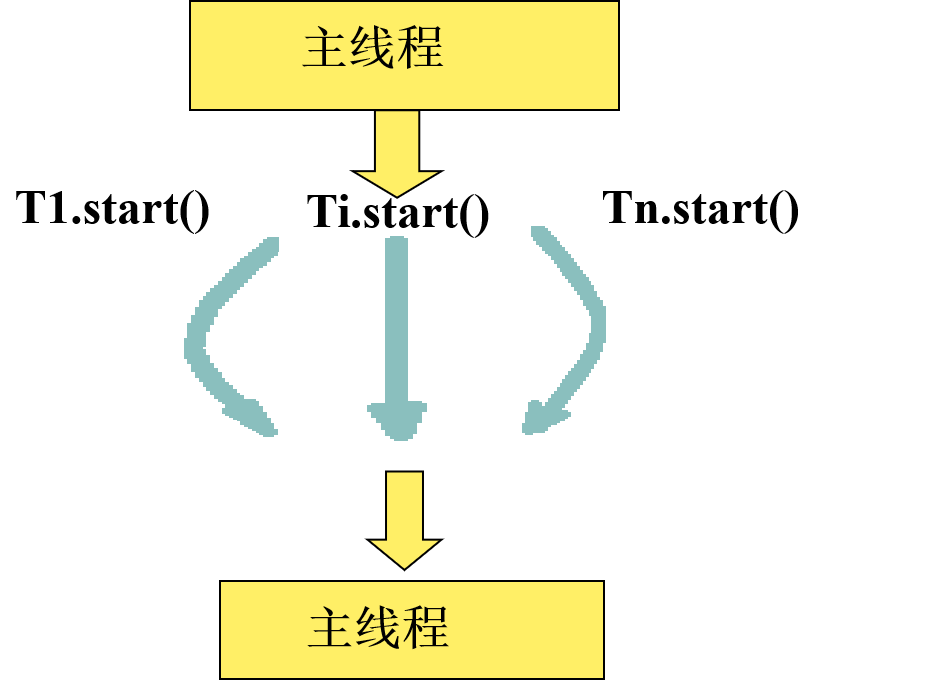
2、Java中实现多线程应用有两种途径:
(1)创建Thread类的子类
用Thread类的子类创建线程
只需从Thread类派生出一个子类,在类中一定要实现run()。
例: class hand extends Thread
{
public void run()
{…….}
}
案例:
class Lefthand extends Thread {
public void run(){
for(int i=0;i<=5;i++)
{
System.out.println("You are Students!");
try{
sleep(500);
}
catch(InterruptedException e) {… }
}
}
}
(2)在程序中实现Runnable接口
用Runnable()接口实现多线程时,必须实现run()方法,也用start()启动线程。
用Runnable()接口实现多线程时,常用Thread类的构造方法来创建线程对象。
class BallRunnable implements Runnable
{
public void run(){
try {
for (int i = 1; i <= STEPS; i++) {
ball.move(component.getBounds());
component.repaint();
Thread.sleep(DELAY);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e){}
}
API:java.lang.Thread Thread(Runnable r) Runnable r = new BallRunnable(b, comp);
Thread t = new Thread(r);
创建一个新线程,它调用r的run(), r是一个实现了Runnable接口的类的实例。
14.2 中断线程
当线程的run方法执行方法体中最后一条语句后,并经由执行return语句返回时,或者出现了在方法中没有捕获的异常时,线程将终止。 在程序中常常调用interrupt()来终止线程,interrupt()不仅可中断正在运行的线程,而且也能中断处于blocked状态的线程,此时interrupt()会抛出一个InterruptedException异常。 Java提供了几个用于测试线程是否被中断的方法。
void interrupt()
向一个线程发送一个中断请求,同时把这个线程的“interrupted”状态置为true。 若该线程处于blocked状态,会抛出InterruptedException。
static boolean interrupted()
检测当前线程是否已被中断,并重置状态“interrupted”值为false。
boolean isInterrupted()
检测当前线程是否已被中断,不改变状态“interrupted”值 。
14.3 线程状态
1、线程一共有如下6种状态:
New (新建)
Runnable (可运行)
Blocked (被阻塞)
Waiting (等待)
Timed waiting (计时等待)
Terminated (被终止)
2、新创建线程
new(新建) 线程对象刚刚创建,还没有启动,此时还处于不可运行状态。
Thread thread=new Thread(“test”) 此时线程thread处于新建状态,但已有了相应的内存空间以及其它资源。
3、可运行线程
runnable(可运行状态) 此时的线程已经启动,处于线程的run()方法之中。 此时的线程可能运行,也可能不运行,只要CPU一空闲,马上就会运行。 调用线程的start()方法可使线程处于“可运行”状态。
thread.start()
blocked (被阻塞) 一个正在执行的线程因特殊原因,被暂停执行,进入阻塞状态。 阻塞时线程不能进入队列排队,必须等到引起阻塞的原因消除,
才可重新进入排队队列。 引起阻塞的原因很多,不同原因要用不同的方法解除。
sleep(),wait()是两个常用引起阻塞的方法。
Terminated (被终止) 线程被终止的原因有二: 一是run()方法中最后一个语句执行完毕,因而自然死亡。 二是因为一个没有捕获的异常终止了run
方法,从而意外死亡。 thread.stop() 可以调用线程的stop方法杀死一个线程,但是,stop方法已过时,不要在自己的代码中调用它。
4、线程的挂起和恢复
suspend() 和 resume() 方法:两个方法配套使用,suspend()使得线程进入阻塞状态,并且不会自动恢复,必须其对应的 resume() 被调用,才能
使得线程重新进入可执行状态。 suspend() 和 resume() 被用在等待另一个线程产生的结果的情形:测试发现结果还没有产生后,让线程阻塞,另
一个线程产生了结果后,调用 resume() 使其恢复。但suspend()方法很容易引起死锁问题,已经不推荐使用了。
第二部分:实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第13章示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材585页程序13-1,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 将所生成的JAR文件移到另外一个不同的目录中,再运行该归档文件,以便确认程序是从JAR文件中,而不是从当前目录中读取的资源。
l 掌握创建JAR文件的方法;
实验代码:
package 线程; import java.awt.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* @version 1.41 2015-06-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class ResourceTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{ //设置图像界面窗口
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new ResourceTestFrame();
frame.setTitle("ResourceTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
} /**
* A frame that loads image and text resources.
*/
class ResourceTestFrame extends JFrame
{
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 300; public ResourceTestFrame()
{
setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT);//设置框架大小
URL aboutURL = getClass().getResource("about.gif"); //利用about.gif图像文件制作图标
Image img = new ImageIcon(aboutURL).getImage();
setIconImage(img); JTextArea textArea = new JTextArea();//创建一个文本空白框
InputStream stream = getClass().getResourceAsStream("about.txt");//读取about.txt文件
try (Scanner in = new Scanner(stream, "UTF-8"))
{
while (in.hasNext())//判断读取文件的该行是否有数据
textArea.append(in.nextLine() + "\n");
}
add(textArea);//将读取的文件添加到文本域中
}
}
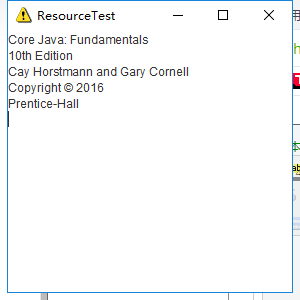
实验结果:
点击后:
测试程序2:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行ThreadTest,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握线程概念;
l 掌握用Thread的扩展类实现线程的方法;
利用Runnable接口改造程序,掌握用Runnable接口创建线程的方法。
class Lefthand extends Thread {
public void run()
{
for(int i=0;i<=5;i++)
{ System.out.println("You are Students!");
try{ sleep(500); }
catch(InterruptedException e)
{ System.out.println("Lefthand error.");}
}
}
}
class Righthand extends Thread {
public void run()
{
for(int i=0;i<=5;i++)
{ System.out.println("I am a Teacher!");
try{ sleep(300); }
catch(InterruptedException e)
{ System.out.println("Righthand error.");}
}
}
}
public class ThreadTest
{
static Lefthand left;
static Righthand right;
public static void main(String[] args)
{ left=new Lefthand();
right=new Righthand();
left.start();
right.start();
}
}
利用Runnable接口改造程序后
package 线程;
//线程的接口Runnable
class Lefthand implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run()
{
for(int i=0;i<=5;i++)
{ System.out.println("You are Students!");
try{ Thread.sleep(500); }
catch(InterruptedException e)
{ System.out.println("Lefthand error.");}
}
}
}
class Righthand implements Runnable {
public void run()
{
for(int i=0;i<=5;i++)
{ System.out.println("I am a Teacher!");
try{ Thread.sleep(300); }
catch(InterruptedException e)
{ System.out.println("Righthand error.");}
}
}
}
public class ThreadTest
{
static Lefthand left;
static Righthand right;
public static void main(String[] args)
{ left=new Lefthand();
right=new Righthand();
new Thread(left).start();
new Thread(right).start(); }
}
运行结果:
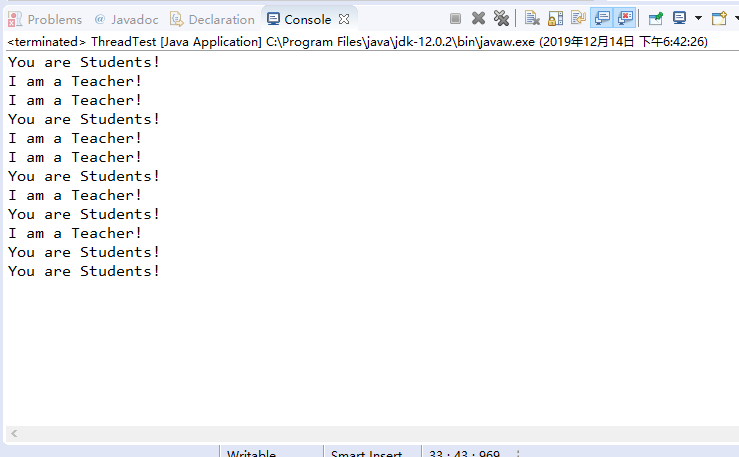
测试程序3:
l 在Elipse环境下调试教材625页程序14-1、14-2 、14-3,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 在Elipse环境下调试教材631页程序14-4,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 对比两个程序,理解线程的概念和用途;
l 掌握线程创建的两种技术。
14-1
package 线程; import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* Shows an animated bouncing ball.
* @version 1.34 2015-06-21
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Bounce
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new BounceFrame();
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});//创建一个GUI界面
}
} /**
* The frame with ball component and buttons.
*/
class BounceFrame extends JFrame
{
private BallComponent comp;
public static final int STEPS = 1000;
public static final int DELAY = 3; /*构造包含用于显示弹跳球和启动和关闭按钮*/
public BounceFrame()
{
setTitle("Bounce");
comp = new BallComponent();
add(comp, BorderLayout.CENTER);//设置组件在页面的布局为边框布局的中央
JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel();
addButton(buttonPanel, "Start", event -> addBall());//添加按钮到按钮面板中,并为其添加事件监听器addBall方法
addButton(buttonPanel, "Close", event -> System.exit(0));
add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);//
pack();
} /**
* Adds a button to a container.
* @param c the container
* @param title the button title
* @param listener the action listener for the button
*/
public void addButton(Container c, String title, ActionListener listener)
{
JButton button = new JButton(title);
c.add(button);
button.addActionListener(listener);
} /* 在面板中添加一个弹跳球,使其弹跳1000次。
*/
public void addBall()
{
try
{
Ball ball = new Ball();
comp.add(ball); for (int i = 1; i <= STEPS; i++)
{
ball.move(comp.getBounds());
comp.paint(comp.getGraphics());
Thread.sleep(DELAY);//调用线程当中的Thread.sleep方法。用于暂停当前的线程活动
}
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
}
}
}
14-2
package 线程; import java.awt.geom.*; /* 在长方形边缘上移动和反弹的球*/
public class Ball
{
private static final int XSIZE = 15;
private static final int YSIZE = 15;
private double x = 0;
private double y = 0;
private double dx = 1;
private double dy = 1; // 将球移动到下一个位置,如果球碰到其中一个边,则反转方向
public void move(Rectangle2D bounds)
{
x += dx;
y += dy;
if (x < bounds.getMinX())
{
x = bounds.getMinX();
dx = -dx;
}
if (x + XSIZE >= bounds.getMaxX())
{
x = bounds.getMaxX() - XSIZE;
dx = -dx;
}
if (y < bounds.getMinY())
{
y = bounds.getMinY();
dy = -dy;
}
if (y + YSIZE >= bounds.getMaxY())
{
y = bounds.getMaxY() - YSIZE;
dy = -dy;
}
} //获取球在其当前位置的形状
public Ellipse2D getShape()
{
return new Ellipse2D.Double(x, y, XSIZE, YSIZE);
}
}
14-3
package 线程; import java.awt.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class BallComponent extends JPanel
{
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 450;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 350; private java.util.List<Ball> balls = new ArrayList<>(); //在面板上添加一个球
public void add(Ball b)
{
balls.add(b);
} public void paintComponent(Graphics g)
{
super.paintComponent(g); // erase background
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g;
for (Ball b : balls)
{
g2.fill(b.getShape());
}
} public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); }
}
运行结果:
14-4
package Main; import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; /**
* Shows animated bouncing balls.
* @version 1.34 2015-06-21
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class BounceThread
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new BounceFrame();
frame.setTitle("BounceThread");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
} //在框架上添加面板和按钮
class BounceFrame extends JFrame
{
private BallComponent comp;
public static final int STEPS = 1000;
public static final int DELAY = 5; //构造包含用于显示弹跳球和启动和关闭按钮
public BounceFrame()
{
comp = new BallComponent();
add(comp, BorderLayout.CENTER);
JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel();
addButton(buttonPanel, "Start", event -> addBall());
addButton(buttonPanel, "Close", event -> System.exit(0));
add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
pack();
} public void addButton(Container c, String title, ActionListener listener)
{
JButton button = new JButton(title);
c.add(button);
button.addActionListener(listener);
} // 在画布上添加一个弹跳球并开始一条线使其弹跳
public void addBall()
{
Ball ball = new Ball();
comp.add(ball);
Runnable r = () -> {
try
{
for (int i = 1; i <= STEPS; i++)
{
ball.move(comp.getBounds());
comp.repaint();
Thread.sleep(DELAY);
}
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
}
};
Thread t = new Thread(r);
t.start();
}
}
运行结果:

第三部分:结对编程练习
采用GUI界面设计以下程序,并创建程序归档文件。
设计一个100以内整数小学生四则运算练习程序,由计算机随机产生10道加减乘除练习题,学生输入答案,由程序检查答案是否正确,每道题正确计10分,错误不计分,10道题测试结束后给出测试总分;
将程序中测试练习题及学生答题结果输出到文件,文件名为test.txt。
代码如下:
package jsq;
import java.awt.EventQueue;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class jsq {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventQueue.invokeLater(()->{
JFrame g = new gui();
g.setVisible(true);
g.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
new jisuan();
});
}
}
package jsq;
import java.io.*;
import java.math.*; import javax.swing.JTextArea; public class jisuan {
char fh;
public int m() {
int m = (int)(1+Math.random()*100);
return m;
}
public int n() {
int n = (int)(1+Math.random()*100);
return n;
}
public char fh() {
int x = (int)(1+Math.random()*4);
switch (x) {
case 1:
fh='+';
break;
case 2:
fh='-';
break;
case 3:
fh='*';
break;
case 4:
fh='/';
break;
}
return fh;
}
public int pd(int m, char fh ,int n) {
int jg=0 ;
switch (fh) {
case '+':
jg = m+n;
break;
case '-':
jg = m-n;
break;
case '*':
jg = m*n;
break;
case '/':
jg = m/n;
break;
}
return jg;
}
public void wfile(String str) {
File f = new File("C:\\Users\\huhuanhuan\\Desktop\\test.txt");
try {
BufferedWriter b = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("C:\\Users\\huhuanhuan\\Desktop\\test.txt"));
b.write(str);
b.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package jsq; import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import javax.swing.*; public class gui extends JFrame {
int m,n,jg,cj,jsq,btcj,sj,sjjg=1;
char fh;
public static int width=600;
public static int height=400;
JPanel JP0 = new JPanel();
JPanel JP1 = new JPanel();
JPanel JP2 = new JPanel();
JLabel L1 = new JLabel();
JLabel L2 = new JLabel();
JLabel L3 = new JLabel();
JLabel L4 = new JLabel();
JLabel L5 = new JLabel();
JLabel L6 = new JLabel();
JTextField text = new JTextField();
JTextField text1 = new JTextField();
JTextArea Are = new JTextArea();
JButton ks = new JButton("开始答题");
JButton xyt = new JButton("下一题");
JButton jc = new JButton("检查");
JButton jj = new JButton("交卷");
jisuan j = new jisuan();
JOptionPane o;
ActionListener listener1 = new time();
Timer t = new Timer(1000,listener1);
public gui() { Dimension scrSize=Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getScreenSize();
setBounds((scrSize.width-width)/2,(scrSize.height-height)/2,width,height);
JP1.setBounds(0,0,width,height/2);
JP2.setBounds(0,200,width,height/2);
JP0.setBounds(0, 0, width, height);
add(JP1);
add(JP2);
JP1.setLayout(null);
JP2.setLayout(null);
L1.setBounds(150, 40, width/10, height/8);
L1.setText("题目:");
JP1.add(L1);
L2.setBounds(150, 83, width/10, height/8);
L2.setText("答案:");
JP1.add(L2);
L3.setBounds(210, 40, width/6, height/8);
JP1.add(L3);
L4.setBounds(310, 40, width/6, height/8);
JP1.add(L4);
L5.setBounds(230, 10, 220, height/12);
L5.setVisible(false);
Font font = new Font("Default",Font.PLAIN,30);
L5.setFont(font);
L5.setForeground(Color.red);
JP1.add(L5);
L6.setBounds(103, 10, 90, height/12);
L6.setText("输入倒计时/s:");
JP1.add(L6);
text.setBounds(190, 95, 220, height/12);
JP1.add(text);
text1.setBounds(190, 10, 220, height/12);
JP1.add(text1);
ks.setBounds(240, 200, 120, 45);
JP2.add(ks);
jc.setBounds(170, 200, 120, 45);
xyt.setBounds(310, 200, 120, 45);
jj.setBounds(310, 200, 120, 45);
jc.setVisible(false);
xyt.setVisible(false);
jj.setVisible(false);
JP2.add(jc);
JP2.add(xyt);
JP2.add(jj);
ks.addActionListener(event->{
ks.setVisible(false);
jc.setVisible(true);
xyt.setVisible(true);
// var j = new jisuan();
m = j.m();
n = j.n();
fh = j.fh();
L3.setText(m+" "+fh+" "+n+" "+"=");
L6.setVisible(false);
text1.setVisible(false);
L5.setVisible(true);
sj=Integer.parseInt(text1.getText());
t.start();
});
xyt.addActionListener(event->{
jsq++;
Are.append(m+" "+fh+" "+n+" "+"="+" "+jg+" 本题得分:"+btcj+'\n');
m = j.m();
n = j.n();
fh = j.fh();
L3.setText(m+" "+fh+" "+n+" "+"=");
text.setText("");
L4.setText("");
btcj=0;
jg=0;
if(jsq==9)
{
xyt.setVisible(false);
jj.setVisible(true);
}
});
jc.addActionListener(event->{
jg = (Integer.parseInt(text.getText()));
if((j.pd(m, fh, n))==(jg)) {
L4.setText(jg+" "+"√");
L4.setForeground(Color.green);
btcj=10;
}
else
{
L4.setText(jg+" "+"×");
L4.setForeground(Color.red);
btcj=0;
}
cj=cj+btcj;
});
jj.addActionListener(event->{
JP1.setVisible(false);
JP2.setVisible(false);
Are.setSize(width, height);
add(Are);
Are.append(m+" "+fh+" "+n+" "+"="+" "+jg+" 本题得分:"+btcj+'\n');
Are.append("总分:"+cj);
j.wfile(Are.getText());
}); }
class time implements ActionListener{ @Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(sj==0) {
o.showMessageDialog(gui.this, "时间到");;
t.stop();
text.setEditable(false);
}
L5.setText(" "+sj);
sj--;
Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().beep();
} }
}
运行界面及导出的jar文件如下:
运行时截图:

倒计时结束弹出提示并设置文本框为禁止输入:


运行完截图及输出test.txt文件截图:


结对编程照片:

第四部分:实验总结
通过本次实验,我初步理解了程序、进程和线程的概念,以及创建线程和中断线程的方法,还有线程的几种状态,并且完成了结对编程练习,此次结对编程练习对我的帮助很大,在结对编程中我复习了很多前面的知识,对lambda表达式,事件处理,布局管理器等的运用更加得心应手,编程能力有所提高,我会继续努力。
201871010109-胡欢欢《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十六周学习总结的更多相关文章
- 201571030332 扎西平措 《面向对象程序设计Java》第八周学习总结
<面向对象程序设计Java>第八周学习总结 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https: ...
- 201771010118马昕璐《面向对象程序设计java》第八周学习总结
第一部分:理论知识学习部分 1.接口 在Java程序设计语言中,接口不是类,而是对类的一组需求描述,由常量和一组抽象方法组成.Java为了克服单继承的缺点,Java使用了接口,一个类可以实现一个或多个 ...
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第八周学习总结
第八周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 一.接口.lambda和内部类: Comparator与comparable接口: 1.comparable接口的方法是compareTo,只有一个参数:comp ...
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第七周学习总结
第七周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 1.继承是面向对象程序设计(Object Oriented Programming-OOP)中软件重用的关键技术.继承机制使用已经定义的类作为基础建立新的类定义,新 ...
- 201771010128 王玉兰《面象对象程序设计 (Java) 》第六周学习总结
---恢复内容开始--- 第一部分:基础知识总结: 1.继承 A:用已有类来构建新类的一种机制,当定义了一个新类继承一个类时,这个新类就继承了这个类的方法和域以适应新的情况: B:特点:具有层次结构. ...
- 201871010126 王亚涛《面向对象程序设计 JAVA》 第十三周学习总结
内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p/ ...
- 201777010217-金云馨《面向对象程序设计Java》第八周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201871010126 王亚涛 《面向对象程序设计 (Java)》第十七周学习总结
内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p/12 ...
- 马凯军201771010116《面向对象程序设计Java》第八周学习总结
一,理论知识学习部分 6.1.1 接口概念 两种含义:一,Java接口,Java语言中存在的结构,有特定的语法和结构:二,一个类所具有的方法的特征集合,是一种逻辑上的抽象.前者叫做“Java接口”,后 ...
- 周强201771010141《面向对象程序设计Java》第八周学习总结
一.理论知识学习部分 Java为了克服单继承的缺点,Java使用了接口,一个类可以实现一个或多个接口. 接口体中包含常量定义和方法定义,接口中只进行方法的声明,不提供方法的实现. 类似建立类的继承关系 ...
随机推荐
- Java设计模式 - - 单例模式 装饰者模式
Java设计模式 单例模式 装饰者模式 作者 : Stanley 罗昊 [转载请注明出处和署名,谢谢!] 静态代理模式:https://www.cnblogs.com/StanleyBlogs/p/1 ...
- C#封装继承
面向对象开发有三大特性(特点 / 特征) : 封装, 继承, 多态.我们今天主要讨论封装和继承,多态会在下篇中讨论. 一.封装: 所谓封装,也就是把客观事物封装成抽象的类,并且类可以把自己的数据和方法 ...
- (转)两种高效过滤敏感词算法--DFA算法和AC自动机算法
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/u013421629/article/details/83178970 一道bat面试题:快速替换10亿条标题中的5万个敏感词,有哪些解决思路? 有十 ...
- ES-结构化查询
参考: https://es.xiaoleilu.com/054_Query_DSL/55_Request_body_search.html 请求体查询 GET /_search {} 分页 GET ...
- MySQL数据库:子查询的应用
子查询 子查询是一种常用计算机语言SELECT-SQL语言中嵌套查询下层的程序模块.当一个查询是另一个查询的条件时,称之为子查询. # 子查询的用法 # 在字段 select (select cNam ...
- 012.MongoDB读写分离
一 读写分离概述 1.1 读写分离描述 从应用程序角度来看,使用Replica Set 和使用单台mongo很像.默认的驱动程序会连接primary节点,并且将所有读写请求都路由到主节点.但也可以通过 ...
- TypeScript初体验
第一次运行TypeScript 1.创建文件夹并初始化项目 mkdir ts-demo cd ts-demo npm init -y 2.安装typescript与ts-node # 局部安装 npm ...
- 编辑器之神vim的一些常用快捷键整理
yy:复制 光标所在的这一行 4yy:复制 光标所在行开始向下的4行 p:粘贴 dd:剪切(删除) 光标所在的这一行 4dd:剪切(删除) 光标所在行向下的4行 D:从当前的光标开始向后剪切,一直到行 ...
- C语言程序设计100例之(24):数制转换
例24 数制转换 题目描述 请你编一程序实现两种不同进制之间的数据转换. 输入格式 共三行,第一行是一个正整数,表示需要转换的数的进制n(2≤n≤16),第二行是一个n进制数,若n>10则用 ...
- 前端小白webpack学习(一)
俗话说得好,好记性不如烂笔头. 之前就在学习中看过webpack的教程,然而一段时间没用,火速的忘光了.写这篇博文,做个总结,也让自己以后有个地方回顾. 看webpack之前,我先去看了一下官方文档, ...
