python27期day02:while循环、break、格式化、运算符、编码初始、作业题。
1、while循环:不断的重复着某件事就是循环
2、while循环图解:
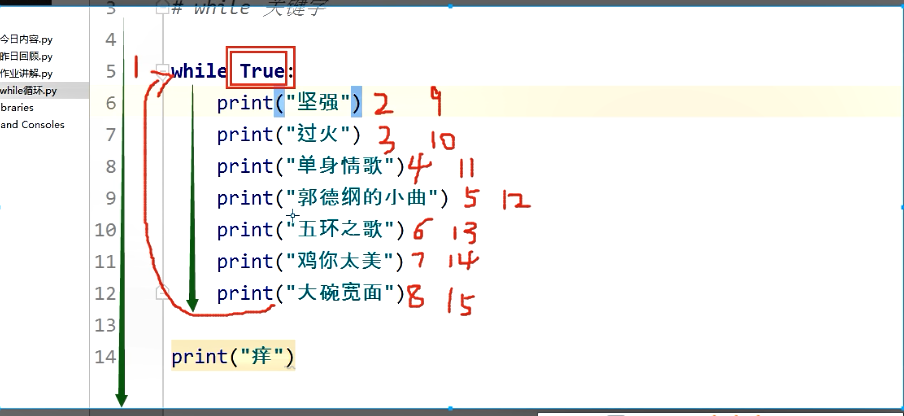
3、break:终止当前循环。
4、continue就是跳出本次循环、继续下次循环。
下方代码都不会执行。
改变循环条件来终止循环。
5、打印4-67写法一:
count = 4
while True:
print(count)
if count == 67 :
break
count += 1
打印4-67写法二:
count = 4
while count < 68 :
print(count)
count += 1
打印4-67写法三:
for i in range(4,68):
print(i)
6、打印100-6写法一:
count = 100
while True :
print(count)
if count == 6 :
break
count -= 1
打印100-6写法二:
count = 100
while count > 5 :
print(count)
count -= 1
打印100-6写法三:
for i in range(100,5,-1):
print(i)
7、打印1,3,5,7,9写法一:
count = 1
while True:
if count % 2 == 1 :
print(count)
if count == 9 :
break
count += 1
打印1,3,5,7,9写法二:
count = 1
while count < 10 :
if count % 2 == 1 :
print(count)
count += 1
打印1,3,5,7,9写法三:
count = 1
while count < 10:
if not count % 2 == 0:
print(count)
count += 1
打印1,3,5,7,9写法四:
count = 1
while count < 10:
print(count)
count += 2
8、打印2,4,6,8,10写法一:
count = 2
while count < 11:
print(count)
count += 2
9、while else(是一体的)条件成立走while不成立走else:
print(222)
count = 0
while count < 3:
print(count)
count += 1
else:
print(111)
10、格式化:%s是占位符(字符串)、%d/%i占的是整型、按照位置顺序一一对应(占几个位置就填几个位置)、可以填充字符串也可以填充数字、整型必须填充数字、两个%%转义变成普通的%
name = input("name")
age = input("age")
sex = input("sex")
hobby = input("hobby")
msg = """
------info------
name:%s
age:%s
sex:%s
hobby:%s
------end------
"""
print(msg%(name,age,sex,hobby))
11、%%:
msg = "山哥,目前的学习进度为%s%%"
print(msg%(2))
12、单双引号配合使用:
msg = "my name is %s I'm %s years old" #单双引号配合使用
print(msg%(input("name:"),input("age:")))
13、小f:f - strings python3.6版本及以上才能使用
msg = f"my name is {input('name:')} I'm {input('age:')} years old"
print(msg)
14、运算符:比较运算符、算术运算符、赋值运算符、逻辑运算符、成员运算符、
比较运算符:> < >= <= == !=
算术运算符:+ - * / //(整除/地板除(向下取整)) **次方/幂 %取余/模
print(5/2)--2.5
print(5//2)--2
print(2**0)--1
print(5 % 2)--1
赋值运算符:= += -= *= /= //= **= %=
a = 10
b = 2
b += 1
print(b)
a -= 1 --9
a *= 2 --20
a /= 2 --5.0
a //= 2 --5
a **= 2 --100
a %= 2 --0
逻辑运算符:与(and)或(or)非(not)
True and False--False
True or False--True
True and not False--True
优先级:() > not > and > or--首先是括号大于not、然后not大于and、然后and大于or
查找顺序:从左向右查找:True and False or True and not False and True--True
and数字进行逻辑运算时:
数字不为0时和不为false: and运算选择and后边的内容
数字为0或False时 and运算都为假时选择and前的内容
and运算一真一假选择假
or数字进行逻辑运算时:
数字不为0时和不为false or运算选择or前边的内容
数字为0或False时 or运算都为假时选择or后边的内容
or运算一真一假选择真
成员运算符:in(在)、not in(不在)
name = "zd"
msg = input("请输入名字:")
if name in msg:
print(111)
else:
print(222)
15、编码初始:所有编码底层都是ascii码
编码集(密码本)
ascii: 不支持中文 a、b、c字母都有 英文:1个字符占8位 gbk: 包含ascii码 国标 英文:1个字符占8位
中文:1个中文两个字节1个字符占16位(1个字节、1位就是1个字节) Unicode: 兼容所有国家编码 英文:4个字节 32位
中文:4个字节 32位 utf-8 最流行的编码集(按地区) 英文:1个字节 8位
欧洲:2个字节 16位
亚洲:一个中文3字节 24位
逗号:1个逗号1个字节 单位转换: 1字节 = 8位
1Bytes = 8bit
1024bytes = 1kb
1024kb = 1MB
1024MB = 1GB
1024GB = 1TB
1024TB = 1PB
16、while循环:
while 关键字
17、while条件:
循环体
18、while else
while 条件: 当条件成立时、不执行else、当条件不成立时执行else。
循环体 出现break else就不会被执行了。
else:
结果
19、作业题:
#20、True and False是来判断选择True还是False
print (True and False) # False
#21、True or False 是来判断选择True还是False
print (True or False) # True
#22、数字中不是零的都为True?
#是的
#23、1 and 3是为了验证都为真时会选择and那边的内容
print(1 and 3) #3
#24、1 or 3 是为了验证都为真时会选择or那边的内容
print (1 or 3) # 1
#25、判断下列逻辑语句的结果,一定要自己先分析 (3<4这种是一体)?
# 1 > 1 or 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 and 9 > 8 or 7 < 6
print (1 > 1 or 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 and 9 > 8 or 7 < 6) #True
# not 2 > 1 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 and 9 > 8 or 7 < 6
print (not 2 > 1 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 and 9 > 8 or 7 < 6) #False
#26、求出下列逻辑语句的值,一定要自己分析
# 8 or 3 and 4 or 2 and 0 or 9 and 7
print (8 or 3 and 4 or 2 and 0 or 9 and 7) #8
# 0 or 2 and 3 and 4 or 6 and 0 or 3
print(0 or 2 and 3 and 4 or 6 and 0 or 3) #4
# 1 and 0 or 8 and 9 and 5 or 2
print(1 and 0 or 8 and 9 and 5 or 2) #5
# 4 or 8 and not False and 8 or 9
print(4 or 8 and not False and 8 or 9) #4
#27、下列结果是什么? (2>1这种是一体)
# 6 or 2 > 1
print("-"*60)
print(6 or 2 > 1) #6
# 3 or 2 > 1
print(3 or 2 > 1) #3
# 0 or 5 < 4
print(0 or 5 < 4) #False
# 5 < 4 or 3
print(5 < 4 or 3) #3
# 2 > 1 or 6
print(2 > 1 or 6) #True
# 3 and 2 > 1
print(3 and 2 > 1) #True
# 0 and 3 > 1
print(0 and 3 > 1) #0
# 2 > 1 and 3
print(2 > 1 and 3) #3
# 3 > 1 and 0
print(3 > 1 and 0) #0
# 3 > 1 and 2 or 2 < 3 and 3 and 4 or 3 > 2
print("/"*60)
print(3 > 1 and 2 or 2 < 3 and 3 and 4 or 3 > 2) #2
#28、简述ASCII、Unicode、utf-8编码
# ascii:不支持中文、字母:1个字节8位
# unicode:
# utf-8:
#29、简述位和字节的关系?
#1个字节等于8位
#30、while循环语句基本结构?
# while 循环:
# while 关键字
# while 条件:
# 循环体
# while 条件: 当条件成立时不执行else
# 当条件不成立时执行else
# 出现break else就不会执行
# else:
# 结果
#31、利用while语句写出猜大小的游戏:设定一个理想数字比如:66,让用户输入数字,如果比66大,则显示猜测的结果大了;如果比66小,则显示猜测的结果小了;只有等于66,显示猜测结果正确,然后退出循环。
while True:
sum = input ( "请输入数字:" )
if int(sum) == 66:
print("猜测结果正确")
break
if int(sum) > 66:
print("猜测的结果大了")
elif int(sum) < 66 :
print("测试的结果小了")
#32、在7题的基础上进行升级:给用户三次猜测机会,如果三次之内猜测对了,则显示猜测正确,退出循环,如果三次之内没有猜测正确,则自动退出循环,并显示‘太笨了你....’。
count = 0
while count < 3:
sum = input("请输入数字:")
if int(sum) == 66:
print("猜对了")
break
if count == 2:
print("太笨了你")
count += 1
#33、使用while循环输出 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 10
count = 1
while count < 11:
print(count)
count += 1
#34、求1-100的所有数的和
#range写法:
x=0
for y in range (1,101):
x=x+y
print(x)
#普通写法:
count = 1 #第一次count=1 #返回上以后count = 2
sum1 = 0 #第一次count=0 #返回上以后sum1 = 1
while count < 101:
sum1 = count + sum1 #第一次sum1 = count + sum1 = 1 + 0 = 1 #第二次sum1 = 上面返回的count的值2 + sum1的值1就等于3
count += 1 #第一次count += 1等于1 + 1 = 2 #第二次count等于上面的count值2加上1就等于3
print(sum1)
#35、输出 1-100 内的所有奇数
for i in range(101):
if not i % 2 == 0:
print(i)
#36、输出 1-100 内的所有偶数
for i in range ( 101 ):
if i % 2 == 0:
print ( i )
#37、求1-2+3-4+5 ... 99的所有数的和
print("*"*60)
count = 1
sum2 = 0
while count < 100:
if count % 2 == 0:
sum2 = sum2 - count
else:
sum2 = sum2 + count
count += 1
print("$"*60)
print(sum2)
#38、⽤户登陆(三次输错机会)且每次输错误时显示剩余错误次数(提示:使⽤字符串格式化)
count = 3
while count:
username = input("请输入账号:")
password = input("请输入密码:")
if username == "zd" and int(password) == 1:
print("登陆成功")
break
else:
count -= 1
print("账号或密码错误,请重新输入剩余次数:%s" % count)
#39、本周作业
# 整理这一周的笔记
# 将这一周所学的知识整理成思维导图
# 将这一周的知识点搞明白后预习下周要讲的内容
# 将以上的笔记和思维导图上传到码云
python27期day02:while循环、break、格式化、运算符、编码初始、作业题。的更多相关文章
- python 中的while循环、格式化、编码初始
while循环 循环:不断重复着某件事就是循环 while 关键字 死循环:while True: 循环体 while True: # 死循环# print("坚强")# pr ...
- python while 格式化 运算符 编码
#######################总结############# 1. 循环 while 条件: 循环体(break, continue) 循环的执行过程: 执行到while的时候. 首先 ...
- 老贾的幸福生活day5 while循环 格式化 运算符 编码初识
while 循环 死循环 while 条件: print(结果) while 条件: print(结果) else: print(结果) break 终止当前循环 continue 跳出当前循环,进行 ...
- python27期day04:列表、元组、range、作业题。
1.for循环套for循环: for i in "abc": for x in "egf: print(x) 结果是:e g f e g f e g f 2.99乘法表 ...
- day02 循环、格式化输出、运算符、编码
01 昨日内容回顾 python2x python3x区别: python2x:源码重复,不规范. python3x:源码规范,优美,清晰,简单. 编译型:将代码一次性全部转化成字节码. 代表语言:C ...
- day02——while、字符串格式化、运算符、编码初识
day02 while--关键字(死循环) 格式:while 条件: 循环体 print(1) while True: print("痒") print("鸡你太美& ...
- while循环 格式化输出 运算符 编码
一.while循环 1.基本结构 while 条件: 循环体 流程: 判断条件是否为真. 如果真, 执行代码块. 然后再次判断条件是否为真 .如果真继续执行代码块.... ...
- python 基础(while 循环、格式化输出、运算符、编码初识)
while循环 break 终止当前循环 count = 1 while count < 3: print(count) count += 1 break # while循环中一旦代码执行到br ...
- day_02 循环格式化输出编码运算符
1.while循环 语法 while 条件: 循环体 else: 当条件不成立的时候执行这里,和break没关系 如果循环是通过break退出的. 那么while后面的else将不会被执行, 只有在w ...
随机推荐
- ESP8266 LUA脚本语言开发: 外设篇-串口
https://nodemcu.readthedocs.io/en/master/modules/uart/ 串口发送数据 发送一个16进制到串口 uart.write(0, 0xaa) 注: 之所以 ...
- C 函数与指针(function & pointer)
C 函数与指针(function & pointer) /* * function.c * 函数在C中的使用 * */ #include <stdio.h> int noswap( ...
- CSS使用知识点
1.空白符 2.字符间距 3.省略号样式 4.水平垂直居中用法 5.CSS角标实现 空格符 1. 相当于键盘按下的空格,区别是 是可以累加的空格,键盘敲下的空格不会累加 2. ...
- 领域驱动设计(DDD)编码实践
写在前面 Martin Fowler在<企业应用架构模式>一书中写道: I found this(business logic) a curious term because there ...
- 在Azure DevOps Server (TFS)的流水线中编译和测试Xcode移动应用(iPhone)
概述 Xcode是开发基于苹果macOS系统的桌面应用和移动应用的主要IDE工具.使用Azure DevOps Server (原名TFS)系统中的pipelines流水线功能,可以方便的集成Xcod ...
- 1+x证书Web前端开发CSS3详细教程
web 前端开发之 CSS3 新特性 http://blog.zh66.club/index.php/archives/189/ web 前端开发之 html5 新特性 http://blog.zh6 ...
- Shell基本运算符之算术、关系运算符
Shell 运算符 =============================摘自菜鸟教程================================= Shell和其他编程语言一样,支持多种运算 ...
- 我在生产项目里是如何使用Redis发布订阅的?(一)使用场景
转载请注明出处! 导语 Redis是我们很常用的一款nosql数据库产品,我们通常会用Redis来配合关系型数据库一起使用,弥补关系型数据库的不足. 其中,Redis的发布订阅功能也是它的一大亮点.虽 ...
- python asyncio call_soon, call_at, call_later
1. call_soon, 协程一运行就马上运行 def callback(sleep_times): print("success time {}".format(sleep_t ...
- AngleSharp 实战(05)之遍历内部子元素(x)元素,尝试着获取元素的 Attr 和 InnerText
直接贴代码了: using System; using System.Linq; using System.Threading.Tasks; using AngleSharp; using Angle ...
