Linux防火墙之iptables常用扩展匹配条件(一)
上一篇博文讲了iptables的基本匹配条件和隐式匹配条件,回顾请参考https://www.cnblogs.com/qiuhom-1874/p/12269717.html;今天在来说说iptabels的一些常用的显示扩展匹配条件,何谓显示扩展匹配条件呢?显示扩展匹配条件就是我们需要用到一些扩展的模块,用-m选项去指定动态加载它。要用iptabels的扩展匹配条件的前提是,我们的系统上要有对应的扩展模块。在Linux主机上/usr/lib64/xtables/这个目录用来存放iptables的模块的,这里面的模块以libip6t开头的,表示适用于ipv6,其余的是ipv4协议版本的模块。这个目录下的模块命名是这样的,libipt_或者libip6t_后面的名字如果全是大写,则该模块用于处理动作扩展模块,如果是小写就是匹配条件的扩展模块。对于这些模块的帮助信息,在centos上用man iptables命令就可以找到相应的模块说明和用法,以及模块的选项等等,在centos7上我们要查看扩展模块的用法帮助,需要用man iptables-extensions命令来查看;了解了iptables的扩展模块,我们接下来说说常用的几种扩展模块的使用和说明
1、multiport扩展,这个扩展模块主要用于匹配多个源端口或目标端口,前面我们了解了tcp和udp他们都有两个隐式扩展来指定连续或单个源端口或目标端口,它不能同时指定多个离散的端口,multiport这个模块就可以以离散方式定义多端口匹配,当然它也支持连续的端口匹配,连续端口匹配同tcp/udp的连续端口匹配用法和写法一直,它也支持,连续和非连续端口的混合匹配,但这个模块最多匹配15个端口。这里的15个端口不同于我们理解的15个端口,这里的15个端口是说用逗号隔开的离散端口,也就是说连续的端口,在这里只算一个。
[!] --source-ports,--sports port[,port|,port:port]...,这个选项表示匹配多个源端口
[root@test ~]# iptables -F
[root@test ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 18 packets, 1292 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain FORWARD (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 13 packets, 1212 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain my_chain (0 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@test ~]# iptables -A INPUT -s 172.16.0.0/16 -d 192.168.0.99 -p tcp -m multiport --sports 20:50,80,3306,9000 -j ACCEPT
[root@test ~]# iptables -A my_chain -s 172.16.0.0/16 -d 192.168.0.99 -p tcp -m multiport ! --sports 53,123,323 -j DROP
[root@test ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 24 packets, 1740 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 172.16.0.0/16 192.168.0.99 multiport sports 20:50,80,3306,9000 Chain FORWARD (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 17 packets, 1580 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain my_chain (0 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 DROP tcp -- * * 172.16.0.0/16 192.168.0.99 multiport sports !53,123,323
[root@test ~]#
提示:--sports支持对指定端口取反,表示匹配除了指定端口以外的其他端口。
[!] --destination-ports,--dports port[,port|,port:port]...,这个选项表示匹配多个目标端口
[root@test ~]# iptables -F
[root@test ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 8 packets, 528 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain FORWARD (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 5 packets, 620 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain my_chain (0 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@test ~]# iptables -A INPUT -d 192.168.0.99 -p tcp -m multiport --dports 22,80,3306,41319 -j ACCEPT
[root@test ~]# iptables -A INPUT -d 192.168.0.99 -p tcp -m multiport ! --dports 22,80,3306,41319 -j DROP
[root@test ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
152 12112 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.0.99 multiport dports 22,80,3306,41319
0 0 DROP tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.0.99 multiport dports !22,80,3306,41319 Chain FORWARD (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 17 packets, 1580 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain my_chain (0 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@test ~]#
[!] --ports port[,port|,port:port]...多个源或目标端口
[root@test ~]# iptables -F
[root@test ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 18 packets, 1292 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain FORWARD (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 13 packets, 1212 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain my_chain (0 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@test ~]# iptables -A INPUT -d 192.168.0.99 -p tcp -m multiport --ports 22,3306,41319 -j ACCEPT
[root@test ~]# iptables -A INPUT -d 192.168.0.99 -p tcp -m multiport ! --ports 22,3306,41319 -j DROP
[root@test ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
121 9468 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.0.99 multiport ports 22,3306,41319
6 304 DROP tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.0.99 multiport ports !22,3306,41319 Chain FORWARD (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 25 packets, 3120 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain my_chain (0 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@test ~]#
提示:--ports表示匹配到的端口不管是源还是目标,只要是指定的端口都能匹配得到,然后做出相应的处理动作
2、iprange扩展,此扩展模块主要用于匹配连续的ip地址范围
[!] --src-range from[-to] 此选项表示匹配源ip地址范围
[root@test ~]# iptables -F
[root@test ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 25 packets, 1832 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain FORWARD (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 19 packets, 1832 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain my_chain (0 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@test ~]# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m iprange --src-range 192.168.0.200-192.168.0.245 -j ACCEPT
[root@test ~]# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m iprange ! --src-range 192.168.0.200-192.168.0.245 -j DROP
[root@test ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
144 12000 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 source IP range 192.168.0.200-192.168.0.245
0 0 DROP tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 source IP range ! 192.168.0.200-192.168.0.245 Chain FORWARD (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 15 packets, 1396 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain my_chain (0 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@test ~]#
[!] --dst-range from[-to],此选项表示匹配目标地址范围
[root@test ~]# iptables -F
[root@test ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 29 packets, 2096 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain FORWARD (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 20 packets, 1856 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain my_chain (0 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@test ~]# iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp -m iprange --dst-range 192.168.0.100-192.168.0.245 -j ACCEPT
[root@test ~]# iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp -m iprange ! --dst-range 192.168.0.100-192.168.0.245 -j DROP
[root@test ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 103 packets, 7240 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain FORWARD (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
175 16212 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 destination IP range 192.168.0.100-192.168.0.245
0 0 DROP tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 destination IP range ! 192.168.0.100-192.168.0.245 Chain my_chain (0 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@test ~]#
3、mac扩展,该模块用于匹配主机的MAC地址,适用于PREROUTING和FORWARD,INPUT链上
[!] --mac-source XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX,此选项表示匹配源MAC地址
[root@test ~]# iptables -F
[root@test ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 19 packets, 1332 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain FORWARD (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 13 packets, 1212 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain my_chain (0 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@test ~]# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m mac --mac-source 00:24:81:68:ce:45 -j ACCEPT
[root@test ~]# iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.0.151 -p tcp -j DROP
[root@test ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 65 packets, 16202 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
18 1480 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 MAC 00:24:81:68:CE:45
0 0 DROP tcp -- * * 192.168.0.151 0.0.0.0/0 Chain FORWARD (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 70 packets, 19646 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain my_chain (0 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@test ~]#
4、string扩展,此模块主要对报文中的应用层数据做字符串模式匹配检测
--algo {bm|kmp} ,指定字符串匹配检测算法,这个必须指定
--from offset:从第几个字节开始匹配
--to offset :到底几个字节结束
[!] --string pattern 指定要检测到字符串模式
[!] --hex-string pattern 知道那个要检测字符串模式,16进制格式
示例:入站报文有loganalyzer的字眼的报文,给予丢弃
在没有设置规则的是可以正常访问的
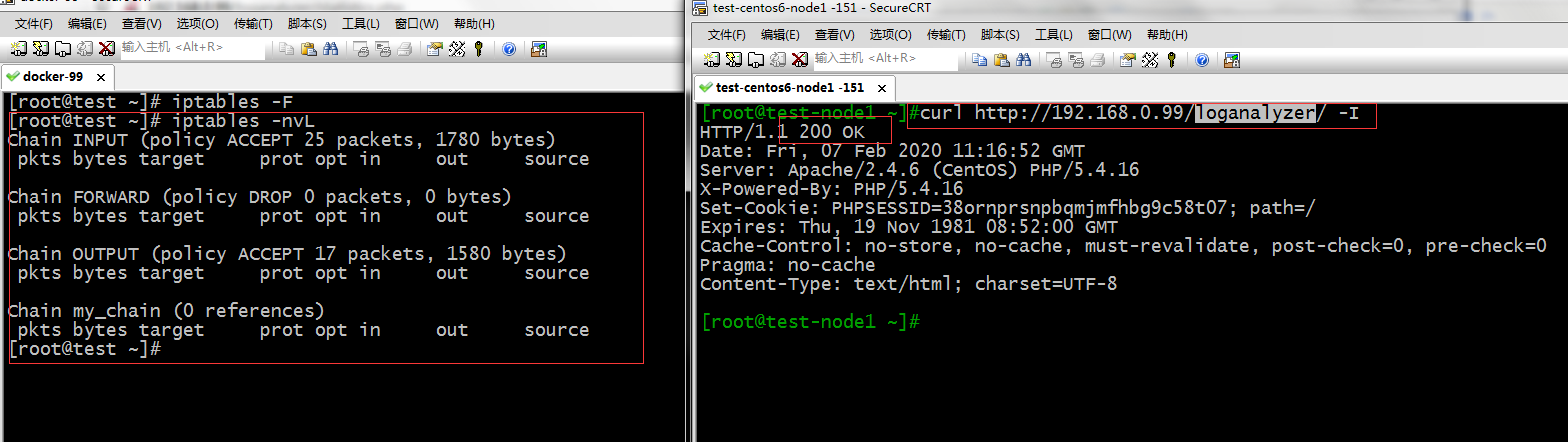
添加如下规则
[root@test ~]# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -m string --algo bm --string "loganalyzer" -j DROP
[root@test ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 35 packets, 2328 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
8 1840 DROP tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:80 STRING match "loganalyzer" ALGO name bm TO 65535 Chain FORWARD (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 28 packets, 3200 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain my_chain (0 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@test ~]#
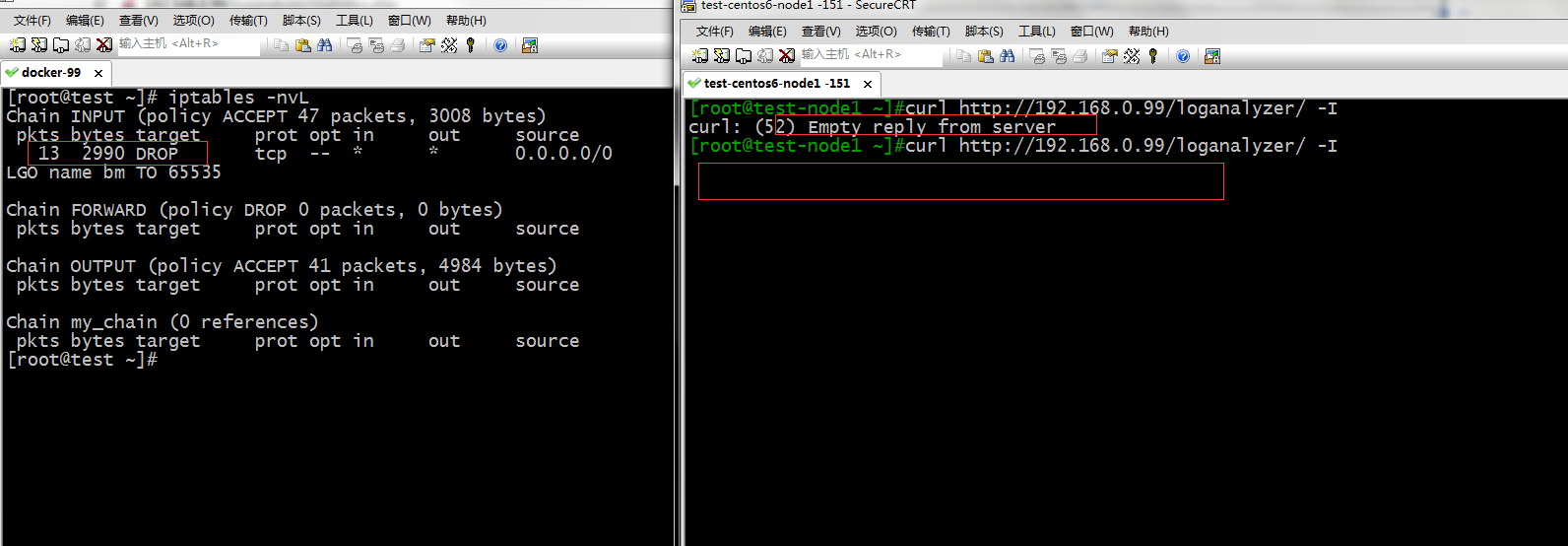
提示:可以看到添加了规则后,我们客户端就不能再访问我们的网站了,这个就是通过过滤字符串来实现控制用户的访问
5、time扩展,此模块根据将报文到达的时间与指定的时间范围进行匹配
--datestart YYYY[-MM[-DD[Thh[:mm[:ss]]]]] 指定开始日期
--datestop YYYY[-MM[-DD[Thh[:mm[:ss]]]]] 指定结束日期
--timestart hh:mm[:ss] 指定开始时间
--timestop hh:mm[:ss] 指定结束时间
[!] --monthdays day[,day...] 指定每个月的几号
[!] --weekdays day[,day...] 指定星期几,1 – 7 分别表示星期一到星期日
--kerneltz:使用内核配置的时区而非默认的UTC,CentOS7系统默认为UTC;注意: centos6 不支持kerneltz ,--localtz指定本地时区(默认)
通常情况我们用--mouthdays 和--timestart 、--timestop结合或者--weekdays day 和--timestart 、--timestop来结合使用很少和--datastart 、datastop使用;最后我们还有指定为使用的时区,如果我们不指定,它默认使用的是UTC时区,在centos6 上需要用--localtz来指定时区
示例:允许任何客户端在晚上的20:00:00 到20:50:00 通过telnet 来访问我们服务器
[root@test ~]# iptables -F
[root@test ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 19 packets, 1332 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain FORWARD (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 13 packets, 1212 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain my_chain (0 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@test ~]# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 23 -m time --timestart 20:00:00 --timestop 20:50:00 --kerneltz -j ACCEPT
[root@test ~]# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 23 -j DROP
[root@test ~]# iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --sport 23 -m time --timestart 20:00:00 --timestop 20:50:00 --kerneltz -j ACCEPT
[root@test ~]# iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --sport 23 -j DROP
[root@test ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 19 packets, 1332 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:23 TIME from 20:00:00 to 20:50:00
0 0 DROP tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:23 Chain FORWARD (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 13 packets, 1212 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp spt:23 TIME from 20:00:00 to 20:50:00
0 0 DROP tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp spt:23 Chain my_chain (0 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@test ~]#
测试:在允许的时间内通过Telnet访问服务器
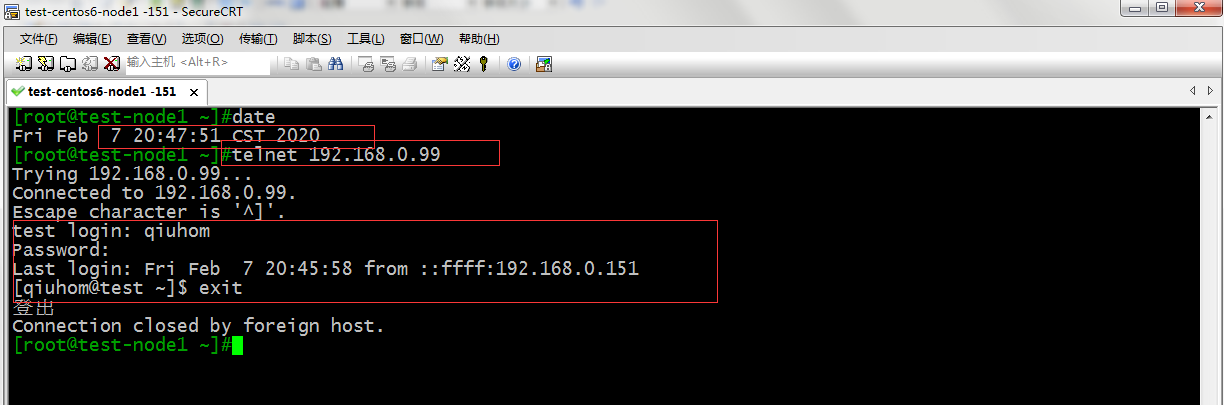
提示:可以看到在允许的时间访问服务器上没有问题,我们等会不再允许的时间范围内在访问下,看看是不是可以正常访问呢
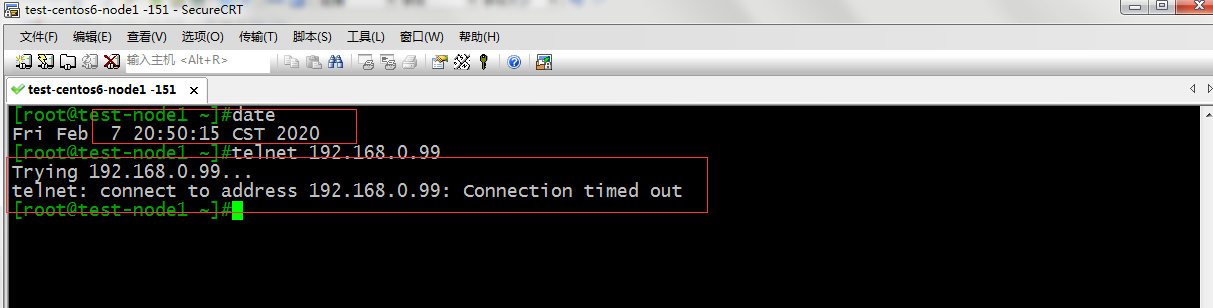
提示:可以看到不在允许的时间范围呢 是不可以访问的
通过time模块我们可以做到在某个时间允许或拒绝客户端的访问,时间可以用上面的三种时间组合来确定一个范围,也可以同其他扩展模块联合使用,比如我们又要控制时间,又要控制部分源ip 来访问我们服务器,我们可以用-m指定iprange 的范围,iptables里的一条规则匹配条件都是取并集,也就说一条规则是否匹配到报文,要看这条规则里的匹配条件是否对数据包都匹配,换句话说就是一个数据要通过某一条规则,那么这个数据包需要满足我们给定规则的所有条件。
示例2:允许192.168.0.10-192.168.0.200 的服务器在21:00:00到21:20:00 允许通过Telnet访问我们服务器
[root@test ~]# iptables -F
[root@test ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 20 packets, 1372 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain FORWARD (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 13 packets, 1212 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain my_chain (0 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@test ~]# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 23 -m iprange --src-range 192.168.0.10-192.168.0.200 -m time --timestart 21:00:00 --timestop 21:20:00 --kerneltz -j ACCEPT
[root@test ~]# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 23 -j DROP
[root@test ~]# iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --sport 23 -m iprange --dst-range 192.168.0.10-192.168.0.200 -m time --timestart 21:00:00 --timestop 21:20:00 --kerneltz -j ACCEPT
[root@test ~]# iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --dport 23 -j DROP
[root@test ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 14 packets, 924 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:23 source IP range 192.168.0.10-192.168.0.200 TIME from 21:00:00 to 21:20:00
0 0 DROP tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:23 Chain FORWARD (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 11 packets, 1908 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp spt:23 destination IP range 192.168.0.10-192.168.0.200 TIME from 21:00:00 to 21:20:00
0 0 DROP tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:23 Chain my_chain (0 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@test ~]#
测试:不在允许范围的主机和在允许范围的主机都在允许时间是否能访问服务器?
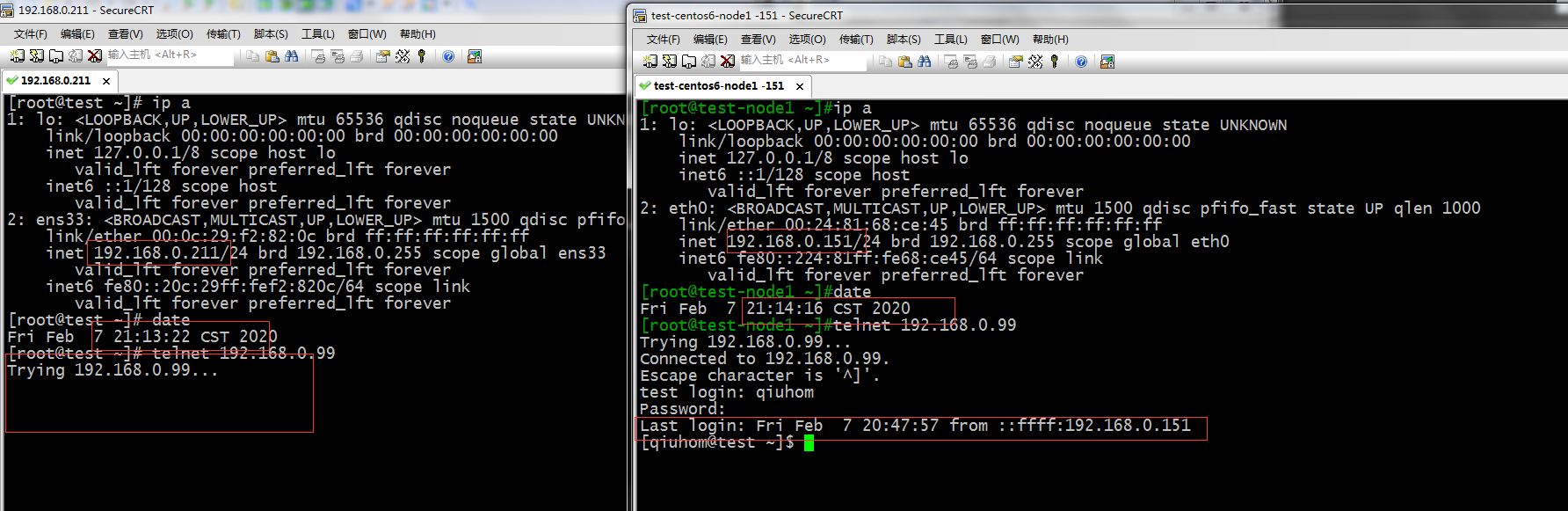
提示:可以看到虽然都是在允许的时间,在允许范围的主机是可以访问的,不在允许范围的主机上不能访问的。
测试:允许的主机和不允许的主机,都在不在允许的时间是否可以访问服务器?
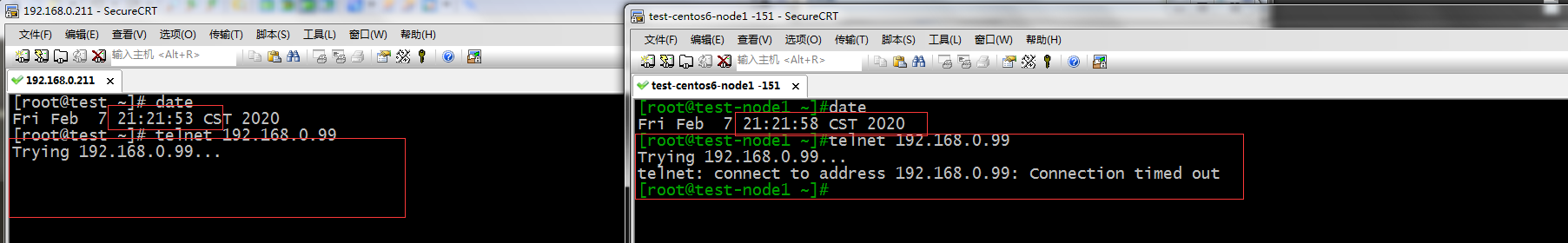
提示:可以看到都不在允许的时间,它俩是都不能访问的,所以要满足在允许的时间内的同时还要满足是允许的主机才可以,它俩条件必须是交集。
6、connlimit扩展,此模块可根据每客户端IP做并发连接数数量匹配,可防止CC(Challenge Collapsar挑战黑洞)攻击
--connlimit-upto #:连接的数量小于等于#时匹配
[root@test ~]# iptables -F
[root@test ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 14 packets, 1004 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain FORWARD (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 11 packets, 996 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain my_chain (0 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@test ~]# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 23 -m connlimit --connlimit-upto 2 -j ACCEPT
[root@test ~]# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 23 -j DROP
[root@test ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 23 packets, 1668 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:23 #conn src/32 <= 2
0 0 DROP tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:23 Chain FORWARD (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 17 packets, 1548 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain my_chain (0 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@test ~]#
提示:以上规则表示,同一客户端连接我本机服务器上的23号端口(Telnet服务),如果连接数小于等于2 允许连接。
测试:同一主机开三个窗口对服务器,看看第三个连接是否可以连接
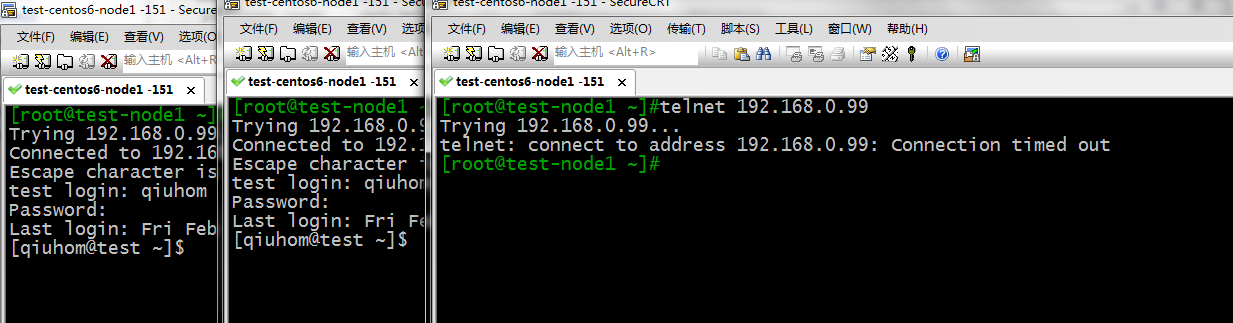
提示:可以看到当192.168.0.151 的第三个连接是被服务器拒绝了
--connlimit-above #:连接的数量大于#时匹配
[root@test ~]# iptables -F
[root@test ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 20 packets, 1372 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain FORWARD (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 13 packets, 1212 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain my_chain (0 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@test ~]# iptables -A INPUT -d 192.168.0.99 -p tcp --dport 23 -m connlimit --connlimit-above 2 -j DROP
[root@test ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 23 packets, 1596 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 DROP tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.0.99 tcp dpt:23 #conn src/32 > 2 Chain FORWARD (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 15 packets, 1396 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain my_chain (0 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@test ~]#
提示:我们把上面的规则更改为同一主机连接数大于2时 就丢弃,其他连接走默认同意放行连接,也就是说只要同一ip 连接数大于2 就拒绝
测试:同一主机开三个窗口对服务器,看看第三个连接是否可以连接
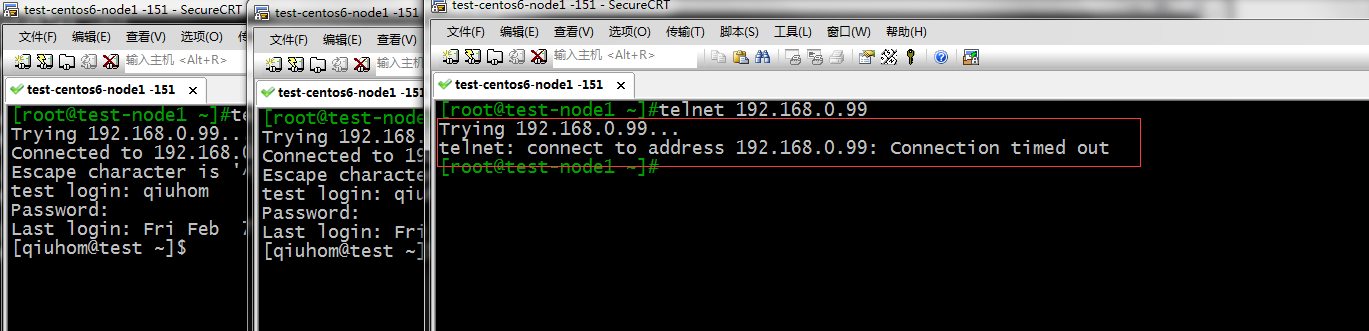
提示:可以看到同一主机连接大于2时就拒绝链接了
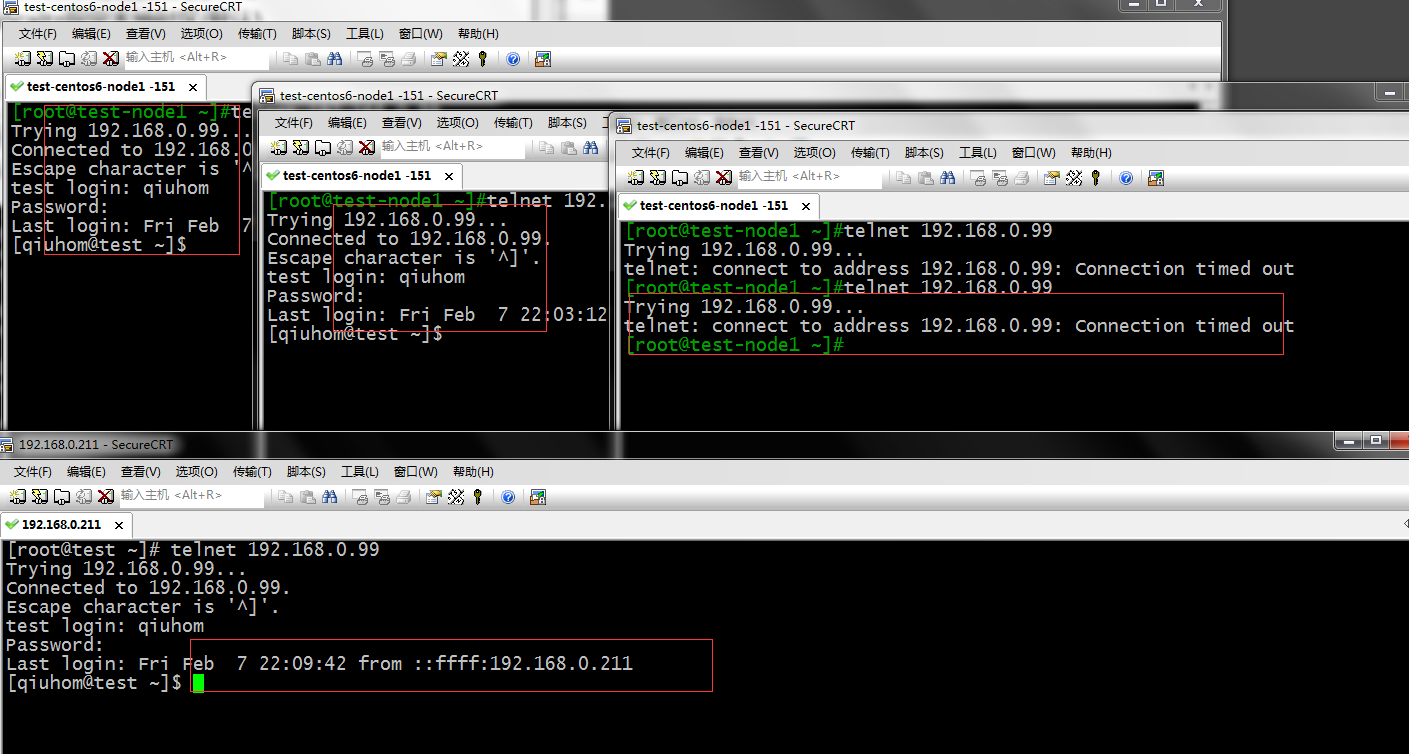
提示:在同一主机连接数大于2时 用另外的主机去连接是不受影响的
从以上测试看,connlimit模块可以控制单台客户端的并发连接数,并且不对其他客户端产生影响,通常情况--connlimit-upto 和--connlimit-above 和默认策略结合使用,如果默认策略是允许所有不匹配的报文,那么我就用--connlimit-above 来控制连接上限,然后再拒绝。如果默认策略是拒绝所有不匹配的报文那么我们就用--connlimit-upto来允许连接数小于等于某个数来控制连接请求。
Linux防火墙之iptables常用扩展匹配条件(一)的更多相关文章
- Linux防火墙之iptables常用扩展匹配条件(二)
上一篇博文我们讲到了iptables的一些常用的扩展匹配模块以及扩展模块的一些选项的说明,回顾请参考https://www.cnblogs.com/qiuhom-1874/p/12273755.htm ...
- iptables详解(6):iptables扩展匹配条件之’–tcp-flags’
如果你看过前文,那么你一定知道,前文已经对"tcp扩展模块"做过总结,但是只总结了tcp扩展模块中的"--sport"与"--dport"选 ...
- Linux防火墙之iptables基本匹配条件和隐式扩展匹配条件
一.iptables的基本匹配条件 上一篇博文我们说到了iptables的基本工作原理.数据报文在内核的走向和管理链.管理规则.以及查看规则.导入和导出规则:回顾请参考https://www.cnbl ...
- linux防火墙(三)—— iptables语法之匹配条件
一.iptables规则的匹配条件类型有三类 1.通用匹配:可直接使用,不依赖于其他条件或扩展,包括网络协议.IP地址.网络接口等条件 2.隐含匹配:要求以特定的协议匹配作为前提,包括端口.TCP标记 ...
- Linux防火墙之iptables扩展处理动作
前文我们讲了iptables的扩展匹配,一些常用的扩展模块以及它的专有选项的使用和说明,回顾请参考https://www.cnblogs.com/qiuhom-1874/p/12285152.html ...
- Linux防火墙(iptables/firewalld)
Linux防火墙(iptables/firewalld) 目录 Linux防火墙(iptables/firewalld) 一.iptables 1. iptables概述 2. netfilter和i ...
- Linux防火墙简介 – iptables配置策略
Linux防火墙简介 – iptables配置策略 Netfilter/iptables简介 要想真正掌握Linux防火墙体系,首先要搞清楚Netfilter和iptables的关系,Netfilte ...
- Linux防火墙之iptables入门
一.防火墙的概念 什么是防火墙?防火墙是一台或一组设备,用以在网络间实施访问控制策略:事实上一个防火墙能够包含OSI模型中的很多层,并且可能会涉及进行数据包过滤的设备,它可以实施数据包检查和过滤,在更 ...
- linux防火墙之iptables
linux防火墙之iptables 1.1.1 关于iptables简介 IPTABLES 是与最新的 3.5 版本 Linux 内核集成的 IP 信息包过滤系统.如果 Linux 系统连接到因特网或 ...
随机推荐
- 别怕,"卷积"其实很简单(下)
文章来自我的CSDN同名博客,欢迎文末扫码关注~ 定义 基于上一篇文章的通俗化例子,我们从基本概念上了解了卷积,那么更严格的定义是怎样的呢? 从数学上讲,卷积只不过是一种运算,对于很多没有 ...
- 解决echarts中的点击事件点击后走多次接口
使用echarts图点击图之后,走了很多次接口,后来发现添加一个off事件就可以解决了,具体如下:
- $51nod\ 1522$ 上下序列 $dp$
正解:$dp$ 解题报告: 传送门$QwQ$ 一年过去了$gql$还是不咋会这题,,,好菜昂我的$NOIp$必将惨败了$kk$ 考虑从大到小枚举两个相同的数填哪儿,根据那个限制,十分显然的是这两个数必 ...
- python中的enumerate、map、filter和zip函数
引入 python内置了很多可以供我们直接调用的函数,这些函数的效率往往都非常高.我们在自己造轮子的同时,也非常有必要了解并且正确使用python给我们提供的大量的内置函数.在前面的博客里面我已经介绍 ...
- 端口扫描器--利用socket协议
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:UTF-8 -*- import optparse import socket import threading # 用法 pyt ...
- (数据科学学习手札72)用pdpipe搭建pandas数据分析流水线
1 简介 在数据分析任务中,从原始数据读入,到最后分析结果出炉,中间绝大部分时间都是在对数据进行一步又一步的加工规整,以流水线(pipeline)的方式完成此过程更有利于梳理分析脉络,也更有利于查错改 ...
- 最强常用开发库总结 - JSON库详解
最强常用开发库总结 - JSON库详解 JSON应用非常广泛,对于Java常用的JSON库要完全掌握.@pdai JSON简介 JSON是什么 JSON 指的是 JavaScript 对象表示法(Ja ...
- BeanUtils 如何拷贝 List?
BeanUtils 如何拷贝 List? 一.背景 我们在DO.Model.VO层数据间可能经常转换数据: Entity对应的是持久层数据结构(一般是数据库表的映射模型); Model 对应的是业务层 ...
- Scala与Mongodb实践4-----数据库操具体应用
目的:在实践3中搭建了运算环境,这里学会如何使用该环境进行具体的运算和相关的排序组合等. 由数据库mongodb操作如find,aggregate等可知它们的返回类型是FindObservable.A ...
- Java配置文件读取中文乱码问题
背景 这是我之前在做的用友服务对接开发,昨天领导拿给财务测试时告诉我有乱码,当时我第一想法是用友那边的编码格式有问题,因为还在做其他任务,我说等问一下用友他们用的什么编码格式我们这边改一下,然后今天早 ...
