吴裕雄 python 神经网络——TensorFlow实现AlexNet模型处理手写数字识别MNIST数据集
import tensorflow as tf # 输入数据
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("E:\\MNIST_data", one_hot=True) # 定义网络的超参数
learning_rate = 0.001
training_iters = 200000
batch_size = 128
display_step = 5 # 定义网络的参数
# 输入的维度 (img shape: 28*28)
n_input = 784
# 标记的维度 (0-9 digits)
n_classes = 10
# Dropout的概率,输出的可能性
dropout = 0.75 # 输入占位符
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_input])
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_classes])
#dropout (keep probability)
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) # 定义卷积操作
def conv2d(name,x, W, b, strides=1):
# Conv2D wrapper, with bias and relu activation
x = tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, strides, strides, 1], padding='SAME')
x = tf.nn.bias_add(x, b)
# 使用relu激活函数
return tf.nn.relu(x,name=name) # 定义池化层操作
def maxpool2d(name,x, k=2):
# MaxPool2D wrapper
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, k, k, 1], strides=[1, k, k, 1],padding='SAME',name=name) # 规范化操作
def norm(name, l_input, lsize=4):
return tf.nn.lrn(l_input, lsize, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9.0,beta=0.75, name=name) # 定义所有的网络参数
weights = {
'wc1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([11, 11, 1, 96])),
'wc2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([5, 5, 96, 256])),
'wc3': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 256, 384])),
'wc4': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 384, 384])),
'wc5': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 384, 256])),
'wd1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([4*4*256, 4096])),
'wd2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([4096, 1024])),
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024, n_classes]))
}
biases = {
'bc1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([96])),
'bc2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([256])),
'bc3': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([384])),
'bc4': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([384])),
'bc5': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([256])),
'bd1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([4096])),
'bd2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024])),
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_classes]))
} # 定义整个网络
def alex_net(x, weights, biases, dropout):
# 向量转为矩阵 Reshape input picture
x = tf.reshape(x, shape=[-1, 28, 28, 1]) # 第一层卷积
# 卷积
conv1 = conv2d('conv1', x, weights['wc1'], biases['bc1'])
# 下采样
pool1 = maxpool2d('pool1', conv1, k=2)
# 规范化
norm1 = norm('norm1', pool1, lsize=4) # 第二层卷积
# 卷积
conv2 = conv2d('conv2', norm1, weights['wc2'], biases['bc2'])
# 最大池化(向下采样)
pool2 = maxpool2d('pool2', conv2, k=2)
# 规范化
norm2 = norm('norm2', pool2, lsize=4) # 第三层卷积
# 卷积
conv3 = conv2d('conv3', norm2, weights['wc3'], biases['bc3'])
# 规范化
norm3 = norm('norm3', conv3, lsize=4) # 第四层卷积
conv4 = conv2d('conv4', norm3, weights['wc4'], biases['bc4']) # 第五层卷积
conv5 = conv2d('conv5', conv4, weights['wc5'], biases['bc5'])
# 最大池化(向下采样)
pool5 = maxpool2d('pool5', conv5, k=2)
# 规范化
norm5 = norm('norm5', pool5, lsize=4) # 全连接层1
fc1 = tf.reshape(norm5, [-1, weights['wd1'].get_shape().as_list()[0]])
fc1 =tf.add(tf.matmul(fc1, weights['wd1']),biases['bd1'])
fc1 = tf.nn.relu(fc1)
# dropout
fc1=tf.nn.dropout(fc1,dropout) # 全连接层2
fc2 = tf.reshape(fc1, [-1, weights['wd2'].get_shape().as_list()[0]])
fc2 =tf.add(tf.matmul(fc2, weights['wd2']),biases['bd2'])
fc2 = tf.nn.relu(fc2)
# dropout
fc2=tf.nn.dropout(fc2,dropout) # 输出层
out = tf.add(tf.matmul(fc2, weights['out']) ,biases['out'])
return out # 构建模型
pred = alex_net(x, weights, biases, keep_prob) # 定义损失函数和优化器
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=pred, labels=y)) optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(cost) # 评估函数
correct_pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred,1), tf.argmax(y,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred, tf.float32)) # 初始化变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer() # 开启一个训练
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
step = 1
# 开始训练,直到达到training_iters,即200000
while step * batch_size < training_iters:
#获取批量数据
batch_x, batch_y = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={x: batch_x, y: batch_y, keep_prob: dropout})
if step % display_step == 0:
# 计算损失值和准确度,输出
loss,acc = sess.run([cost,accuracy], feed_dict={x: batch_x, y: batch_y, keep_prob: 1.})
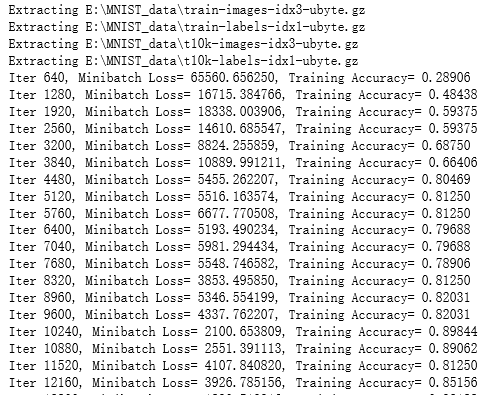
print ("Iter " + str(step*batch_size) + ", Minibatch Loss= " + "{:.6f}".format(loss) + ", Training Accuracy= " + "{:.5f}".format(acc))
step += 1
print ("Optimization Finished!")
# 计算测试集的精确度
print ("Testing Accuracy:",sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: mnist.test.images[:256],y: mnist.test.labels[:256],keep_prob: 1.}))
吴裕雄 python 神经网络——TensorFlow实现AlexNet模型处理手写数字识别MNIST数据集的更多相关文章
- 吴裕雄 python 神经网络TensorFlow实现LeNet模型处理手写数字识别MNIST数据集
import tensorflow as tf tf.reset_default_graph() # 配置神经网络的参数 INPUT_NODE = 784 OUTPUT_NODE = 10 IMAGE ...
- 吴裕雄 python 神经网络——TensorFlow实现回归模型训练预测MNIST手写数据集
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data mnist = input_dat ...
- 吴裕雄 PYTHON 神经网络——TENSORFLOW 滑动平均模型
import tensorflow as tf v1 = tf.Variable(0, dtype=tf.float32) step = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False) ...
- 吴裕雄 python 神经网络——TensorFlow 实现LeNet-5模型处理MNIST手写数据集
import os import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import ...
- TensorFlow 之 手写数字识别MNIST
官方文档: MNIST For ML Beginners - https://www.tensorflow.org/get_started/mnist/beginners Deep MNIST for ...
- 吴裕雄 python 神经网络——TensorFlow训练神经网络:全模型
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data INPUT_NODE = 784 ...
- 吴裕雄 python 神经网络——TensorFlow 循环神经网络处理MNIST手写数字数据集
#加载TF并导入数据集 import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.contrib import rnn from tensorflow.examples.tuto ...
- 吴裕雄 python 神经网络——TensorFlow 使用卷积神经网络训练和预测MNIST手写数据集
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_dat ...
- 吴裕雄 python 神经网络——TensorFlow 训练过程的可视化 TensorBoard的应用
#训练过程的可视化 ,TensorBoard的应用 #导入模块并下载数据集 import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mni ...
随机推荐
- 比较一下数据结构的链表和linux i2c驱动难度比较
- print format
python基础_格式化输出(%用法和format用法) name = 'jack' age = 18 sex = 'man' job = "IT" salary = 9999.9 ...
- eclipse查看jar包源代码乱码问题解决
文章来源 今天在eclipse中查看java的jar包中的源代码时,显示的全部是乱码.起初只设置了content types还不行,还是乱码.不过问题最后解决了,配置步骤如下: 首先要知道你需要配置的 ...
- mybatis(六):设计模式 - 责任链模式
- AcWing 285. 没有上司的舞会
//f[u][0]是所有以u为根的子树中选择,并且不选u这个点的方案 //f[u][1]是所有以u为根的子树中选择,并且 选u这个点的方案 #include <cstring> #incl ...
- SpringMVC项目使用elastic search搜索
项目需要,引入了elastic search(后续简称es),后面将介绍本地对es的安装,使用以及java连接es查询的整个过程. 1.es索引字段建立与修改,以curl新增一个索引字段示例 curl ...
- angularJS 十六进制与字符串相互转换
angular 将字符串数据转换为十六进制数据 /** * @Description: TODO 字符串转16进制方法 * @author wjw * @date 2019年9月18日16:35:32 ...
- pudn免费下载账号 codeforge积分账号 pudn共享账号 codeforge下载账号
www.pudn.com和www.codeforge.cn网站下载代码很好,没有积分怎么办?那么多好的matlab代码,matlab程序,C,JAVA等等,都要充值啊!!! 下面的账号积分都用完了,大 ...
- 【转载】C/C++编译过程分析
转自:http://www.360doc.com/content/14/0109/16/835125_343879650.shtml C/C++编译过程 C/C++编译过程主要分为4个过程 1) 编译 ...
- Codeforces C. Almost Equal (数学规律)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/1206/problem/C 题解 : 观察可以发现当n为偶数时,1 - 2n是不满足题意的,可以举例n = 2,n = 4试一试 ...
