Java笔记 - 线程与并行API
一、线程简介
1、线程与进程
每个进程都具有独立的代码和数据空间,进程间的切换会有较大的开销。线程是轻量级的进程,同一类线程共享代码和数据空间,每个线程有独立的运行栈和程序计数器(PC),线程切换的开销小。
多进程:在操作系统中能同时运行多个任务(程序)
多线程:在同一应用程序中有多个顺序流同时执行
2、线程的应用
二、线程状态控制
线程具有创建、就绪、运行、阻塞、终止,五种状,详细的状态转换如下图所示:
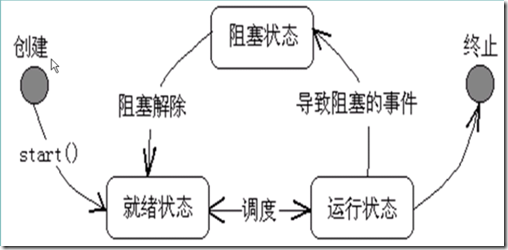
1、线程的创建与启动
JVM启动时会有一个由主方法所定义的线程,程序员可以通过实现 Runable接口的类 或 Thread类 的实例创建新的线程,每个线程对象都是通过方法run()来完成其操作,通过start()方法来启动一个线程。
(1)定义线程类实现Runable接口【建议】
使用Runable接口可以更灵活的定义多线程,如:为多个线程提供共享的数据(线程同步问题),另外,在实现Runable接口的类的run方法定义中可以使用Thread的静态方法。
1 public class Main {
2 public static void main(String args[]) {
3 Runner1 r = new Runner1();
4 Thread t = new Thread(r);
5
6 t.start();//r.run()是方法调用,而非线程启动
7
8 for(int i=0; i<100; i++) {
9 System.out.println("Main Thread:------" + i);
10 }
11 }
12 }
13
14 //同一个Runable可以创建多个Thread
15 class Runner1 implements Runnable {
16 public int a = 0;
17 public void run() {//定义线程体
18 for(int i=0; i<100; i++) {
19 System.out.println("Runner1 :" + i);
20 }
21 }
22 }
(2)定义Thread的子类,并重写run()方法
1 public class Main {
2 public static void main(String args[]) {
3
4 Runner1 r = new Runner1();
5 r.start();
6
7 for(int i=0; i<100; i++) {
8 System.out.println("Main Thread:------" + i);
9 }
10 }
11 }
12
13 //Thread类已经实现了Runable接口
14 class Runner1 extends Thread {
15 public void run() {
16 for(int i=0; i<100; i++) {
17 System.out.println("Runner1 :" + i);
18 }
19 }
20 }
21
(3)如何关闭一个线程
1 public class Main {
2 public static void main(String args[]){
3 Runner r = new Runner();
4 Thread t = new Thread(r);
5 t.start(); //线程启动
6
7 for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
8 if(i%2==0 & i>0)
9 System.out.println("in thread main i=" + i);
10 }
11 System.out.println("Thread main is over");
12
13 //stop()与interrupt()会立即关闭线程,造成正在打开的资源无法关闭,不建议使用
14 r.shutDown();
15 }
16 }
17 //设置flag标志位,表示线程是否关闭
18 class Runner implements Runnable {
19 private boolean flag=true;
20
21 public void run() {
22 int i = 0;
23 while (flag==true) {
24 System.out.println(" " + i++);
25 }
26 }
27
28 public void shutDown() {
29 flag = false;
30 }
31 }
2、线程的基本操作
线程控制基本方法如下:
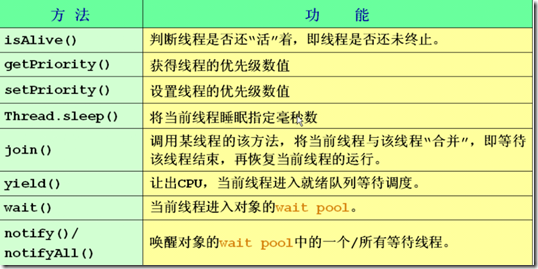
(1)线程优先级
JAVA提供一个线程调度器来监视程序中启动后进入就绪状态的所有线程。线程调度器按照线程的优先级决定调度那个线程来执行。线程的优先级用户数字表示,范围从1到10,线程的缺省优先级是5。
Thread.MIN_PRIORITY = 1
Thread.NORM_PRIORITY = 5
Thread.MAX_PRIORITY = 10
1 public class Main {
2 public static void main(String[] args) {
3 Thread t1 = new Thread(new T1());
4 Thread t2 = new Thread(new T2());
5
6 System.out.println(t1.getPriority()); //获取线程对象的优先级
7 t1.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY + 3);//设置线程对象的优先级
8 t1.start();
9 t2.start();
10 }
11 }
12
13 class T1 implements Runnable {
14 public void run() {
15 for(int i=0; i<100; i++) {
16 System.out.println("T1: " + i);
17 }
18 }
19 }
20
21 class T2 implements Runnable {
22 public void run() {
23 for(int i=0; i<100; i++) {
24 System.out.println("------T2: " + i);
25 }
26 }
27 }
(2)线程wait与sleep方法
wait是Object的方法,调用wait方法时必须锁定对象,wait时别的线程可以访问锁定的对象,wait需要notify或notifyALL方法唤醒。
sleep是Thread静态方法,sleep时别的方法不能访问锁定的对象,sleep方法等睡眠时间到了,可以自己苏醒。
1 import java.util.*;
2 public class Main {
3 public static void main(String[] args) {
4 MyThread thread = new MyThread();
5 thread.start();//每隔一秒输出一次时间
6
7 try {
8 //在未继承Thread类的方法在可以调用Thread的静态方法sleep暂停进程
9 Thread.sleep(10000);
10 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
11 e.printStackTrace();
12 }//主线程等待10s
13
14 thread.interrupt();//不建议使用interrupt和stop
15 }
16 }
17
18 class MyThread extends Thread {
19 boolean flag = true;
20 public void run(){
21 while(flag){
22 //若调用该线程的主线程还“活着”
23 if(Thread.currentThread().isAlive()) {
24 System.out.println("==="+new Date()+"===");
25 }
26
27 try {
28 //public static sleep(long millis)throw InterruptedException
29 //使得当前线程休眠,暂停执行millis毫秒
30 sleep(1000); //1000毫秒,即1s
31 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
32 //重写的方法不能抛出比被重写的方法不同的异常
33 //此处只能写try catch,不能写throws
34 return;
35 }
36 }
37 }
38 }
(3)线程合并
1 public class Main {
2 public static void main(String[] args) {
3 MyThread2 t1 = new MyThread2("myThread");
4 t1.start();
5 try {
6 t1.join();
7 } catch (InterruptedException e) {}
8
9 for(int i=1;i<=3;i++){
10 System.out.println("i am main thread");
11 }
12 }
13 }
14 class MyThread2 extends Thread {
15 MyThread2(String s){
16 super(s);//设置当前线程名为 s
17 }
18
19 public void run(){
20 for(int i =1;i<=3;i++){
21 System.out.println("i am "+getName());//输出线程名
22 }
23 }
24 }//线程合并结果,相当于方法调用
三、线程同步与死锁
1、线程同步
Java引入了对象互斥锁的概念,使用synchronized修饰符修饰方法和代码块,表明在某一时间段内,只能有一个线程访问被锁住的同步对象或同步方法,以保证共享数据的完整性;但其他线程仍可以访问没有锁定的方法,所以,要想保证数据同步,需将所有改变该属性值的方法都加锁,但锁加的越多,执行效率会被降低。建议对于读属性的方法无需加锁 。
1 public class Main implements Runnable {
2
3 private static int num = 100;
4
5 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
6 Main test = new Main();
7 Thread t1 = new Thread(test);
8 Thread t2 = new Thread(test);
9 //设置线程名字
10 t1.setName("t1");
11 t2.setName("t2");
12 //启动线程
13 t1.start();
14 t2.start();
15
16 // test.m2();//使t1和t2同步
17 // test.m3();//使t1、t2和主线程 同步
18 // System.out.println("Main"+" : "+(num));
19 }
20 //在某一时间段,保证只有一个线程访问被锁住的方法
21 public synchronized void m1(){
22 //若不使用死锁,num++和num输出 的原子性过程可能会打断,结果是都是102或101
23 num++;
24 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +": "+ num);
25 }
26
27 //其他线程仍可以访问没有锁定的方法,导致数据有可能不同步
28 public void m2() {
29 num++;
30 }
31
32 //要想保证数据同步,需将所有改变该属性值的方法都加锁
33 public void m3() {
34 synchronized (this) {//互斥锁
35 num++;
36 }
37 }
38
39 public void run() {
40 try {
41 m1();
42 } catch(Exception e) {
43 e.printStackTrace();
44 }
45 }
46 }
2、线程死锁
(1)死锁实例
1 public class Main implements Runnable {
2 public int flag = 1;
3 static Object o1 = new Object(), o2 = new Object();
4
5 public static void main(String[] args) {
6 Main td1 = new Main();
7 Main td2 = new Main();
8 td1.flag = 1;
9 td2.flag = 0;
10 Thread t1 = new Thread(td1);
11 Thread t2 = new Thread(td2);
12 t1.start();
13 t2.start();
14 }
15
16 public void run() {
17 System.out.println("flag=" + flag);
18 if(flag == 1) {
19 synchronized(o1) {
20 try {
21 Thread.sleep(500);
22 } catch (Exception e) {
23 e.printStackTrace();
24 }
25 synchronized(o2) {
26 System.out.println("1");
27 }
28 }
29 }
30 if(flag == 0) {
31 synchronized(o2) {
32 try {
33 Thread.sleep(500);
34 } catch (Exception e) {
35 e.printStackTrace();
36 }
37 synchronized(o1) {
38 System.out.println("0");
39 }
40 }
41 }
42 }
43 }
四、经典同步问题
1、生产者消费者
1
2 public class Main {
3 public static void main(String[] args) {
4 SyncStack ss = new SyncStack();
5
6 //生成者
7 Producer p = new Producer(ss);
8 new Thread(p).start();
9
10 //消费者
11 Consumer c = new Consumer(ss);
12 new Thread(c).start();
13 }
14 }
15
16 class WoTou {
17 int id;
18 WoTou(int id) {
19 this.id = id;
20 }
21 public String toString() {
22 return "WoTou : " + id;
23 }
24 }
25
26 //支持多线程同步操作的堆栈的实现
27 class SyncStack {
28 private int index = 0;
29 private WoTou[] arrWT = new WoTou[6];
30
31 public synchronized void push(WoTou wt) {
32 while(index == arrWT.length) {
33 try {
34 //Object的wait只能在synchronized修饰的方法中使用
35 //让当前正在访问的线程wait
36 this.wait();
37 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
38 e.printStackTrace();
39 }
40 }
41 this.notifyAll();//唤醒所有线程,此处也可使用notify()唤醒一个线程;
42
43 arrWT[index] = wt;
44 index ++;
45 }
46
47 public synchronized WoTou pop() {
48 //不能写if,在发生异常后还需在判断index值
49 while(index == 0) {
50 try {
51 this.wait();
52 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
53 e.printStackTrace();
54 }
55 }
56 this.notifyAll();// notify();
57 index--;
58 return arrWT[index];
59 }
60 }
61
62 class Producer implements Runnable {
63 SyncStack ss = null;
64 Producer(SyncStack ss) {
65 this.ss = ss;
66 }
67
68 public void run() {
69 for(int i=0; i<20; i++) {
70 WoTou wt = new WoTou(i);
71 ss.push(wt);
72 System.out.println("生产了:" + wt);
73
74 try {
75 Thread.sleep((int)(Math.random() * 200));
76 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
77 e.printStackTrace();
78 }
79 }
80 }
81 }
82
83 class Consumer implements Runnable {
84 SyncStack ss = null;
85 Consumer(SyncStack ss) {
86 this.ss = ss;
87 }
88
89 public void run() {
90 for(int i=0; i<20; i++) {
91 WoTou wt = ss.pop();
92 System.out.println("消费了: " + wt);
93 try {
94 Thread.sleep((int)(Math.random() * 1000));
95 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
96 e.printStackTrace();
97 }
98 }
99 }
100 }
2、银行家算法
Java笔记 - 线程与并行API的更多相关文章
- java JDK8 学习笔记——第11章 线程和并行API
第11章 线程与并行API 11.1 线程 11.1.1 线程 在java中,如果想在main()以外独立设计流程,可以撰写类操作java.lang.Runnable接口,流程的进入点是操作在run( ...
- JavaSE中线程与并行API框架学习笔记——线程为什么会不安全?
前言:休整一个多月之后,终于开始投简历了.这段时间休息了一阵子,又病了几天,真正用来复习准备的时间其实并不多.说实话,心里不是非常有底气. 这可能是学生时代遗留的思维惯性--总想着做好万全准备才去做事 ...
- Java 8的新并行API - 魅力与炫目背后
这是一篇译文,原文链接见这里. 本文同时发表在ImportNew上,转载请注明出处. 我很擅长同时处理多项任务.就算是在写这篇博客的此刻,我仍然在为昨天在聚会上发表了一个让大家都感到诧异的评论而觉得尴 ...
- JavaSE中线程与并行API框架学习笔记1——线程是什么?
前言:虽然工作了三年,但是几乎没有使用到多线程之类的内容.这其实是工作与学习的矛盾.我们在公司上班,很多时候都只是在处理业务代码,很少接触底层技术. 可是你不可能一辈子都写业务代码,而且跳槽之后新单位 ...
- java笔记--线程休眠sleep()的运用
线程休眠sleep()方法的运用 在多线程编程中,有时需要让某个线程优先执行.除了可以设置这个线程的优先级为最高外,更加理想的方法是休眠其他线程,若有线程中断了正在休眠的线程,则抛出Interrupt ...
- java笔记线程电影院卖票最终版
* 如何解决线程安全问题呢? * * 要想解决问题,就要知道哪些原因会导致出问题:(而且这些原因也是以后我们判断一个程序是否会有线程安全问题的标准) * A:是否是多线程环境 * B:是否有共享数据 ...
- java笔记----线程状态转换函数
注意:stop().suspend()和 resume()方法现在已经不提倡使用,这些方法在虚拟机中可能引起“死锁”现象.suspend()和 resume()方法的替代方法是 wait()和 sle ...
- java笔记--线程的插队行为
对线程的插队行为的理解 在编写多线程时,会遇到让一个线程优先于其他线程运行的情况, 此时除了可以设置其优先级高于其他线程外,更直接的方式是使用Thread类的join()方法 --如果朋友您想转载本文 ...
- java笔记线程电影院卖票改进版
通过加入延迟后,就产生了连个问题: * A:相同的票卖了多次 * CPU的一次操作必须是原子性的 * B:出现了负数票 * 随机性和延迟导致的 public class SellTicketD ...
随机推荐
- 三层(3-tier architecture)基础
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主同意不得转载. https://blog.csdn.net/lhc2207221755/article/details/24802053 之前看过非常多关 ...
- Vue+Iview+Node 安装环境 运行测试Vue
1.运行环境及设置 备注:建议设置 npm config set registry https://registry.npm.taobao.org 2.全局安装vue/cli 3.创建vue 项目 v ...
- Spring整合Dubbo框架
Dubbo作为一个RPC框架,其最核心的功能就是要实现跨网络的远程调用.演示过程创建两个小工程,一个作为服务的提供者,一个作为服务的消费者.通过Dubbo来实现服务消费者远程调用服务提供者的方法. d ...
- iOS开发之SceneKit框架--SCNNode.h
1.SCNNode简介 SCNNode是场景图的结构元素,表示3D坐标空间中的位置和变换,您可以将模型,灯光,相机或其他可显示内容附加到该元素.也可以对其做动画. 2.相关API简介 初始化方法 // ...
- mavlink 笔记1
Packet Anatomy This is the anatomy of one packet. It is inspired by the CAN and SAE AS-4 standards. ...
- PHP面向对象魔术方法之__clone函数
l 基本介绍 : 当我们需要将一个对象完全的赋值一份, 保证两个对象的属性和属性值一样,但是他们的数据库空间独立,则可以使用对象克隆. <?php header('content-type:te ...
- PAT甲级——A1110 Complete Binary Tree【25】
Given a tree, you are supposed to tell if it is a complete binary tree. Input Specification: Each in ...
- ie9 jscript7 内存不足 页面无响应
花了我差不多一天时间 我是加载一个datagrid ,多表联查,查询几遍(不一定,又是1遍就死了)后 就卡死了...后台日志都是过的.... 后来我发现数据库某个表的数据很多有一模一样的两条,把一份删 ...
- markdown实现页内目录跳转
1.实现页内目录跳转 语法: 页面首部添加目录:[目录](#jump_id) 页面内部锚点:<span id='jump_id'>标题</span>
- 批量处理数据 SqlBulkCopy
string connectionString = new PublicDBHelper().GetCon(System.Configuration.ConfigurationManager.AppS ...
