SpringBoot与缓存
一、Spring Boot与缓存、
JSR-107、Spring缓存抽象、整合Redis
一、JSR107
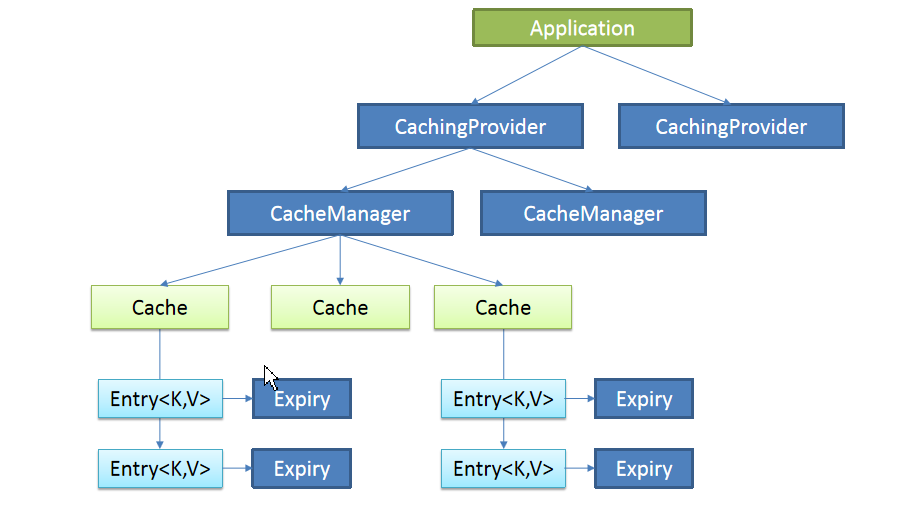
Java Caching定义了5个核心接口,分别是CachingProvider, CacheManager, Cache, Entry 和 Expiry。
1.CachingProvider定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个CacheManager。一个应用可以在运行期访问多个CachingProvider。
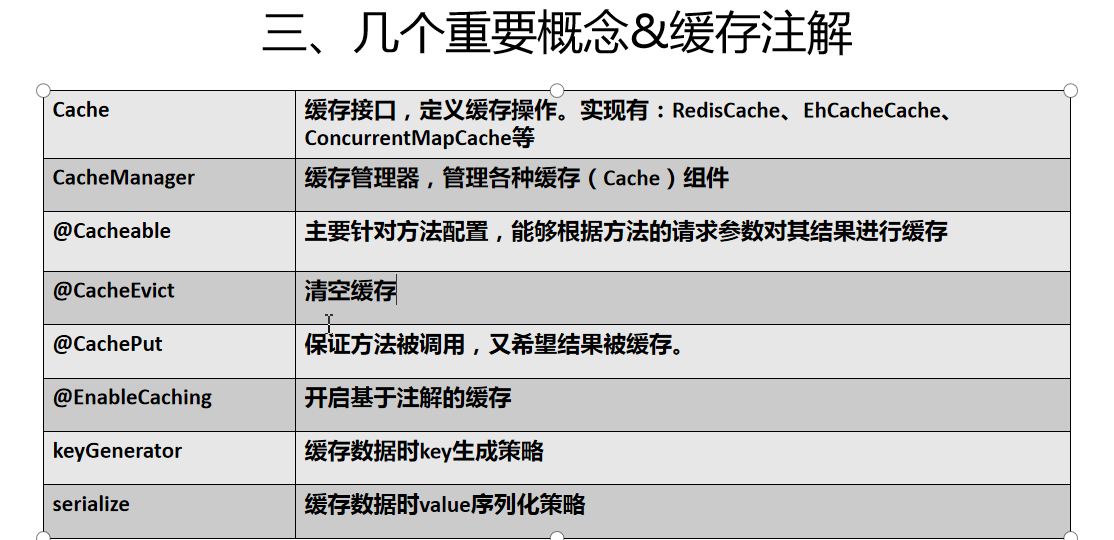
2.CacheManager定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个唯一命名的Cache,这些Cache存在于CacheManager的上下文中。
一个CacheManager仅被一个CachingProvider所拥有。
3.Cache是一个类似Map的数据结构并临时存储以Key为索引的值。一个Cache仅被一个CacheManager所拥有。
4.Entry是一个存储在Cache中的key-value对。
5.Expiry 每一个存储在Cache中的条目有一个定义的有效期。一旦超过这个时间,条目为过期的状态。一旦过期,条目将不可访问、更新和删除。
缓存有效期可以通过ExpiryPolicy设置。
二、Spring缓存抽象
Spring从3.1开始定义了org.springframework.cache.Cache
和org.springframework.cache.CacheManager接口来统一不同的缓存技术;
并支持使用JCache(JSR-107)注解简化我们开发; 1.Cache接口为缓存的组件规范定义,包含缓存的各种操作集合;
2.Cache接口下Spring提供了各种xxxCache的实现;如RedisCache,EhCacheCache , ConcurrentMapCache等; 3.每次调用需要缓存功能的方法时,Spring会检查检查指定参数的指定的目标方法是否已经被调用过;如果有就直接从缓存中获取方法调用后的结果,
如果没有就调用方法并缓存结果后返回给用户。下次调用直接从缓存中获取。
4.使用Spring缓存抽象时我们需要关注以下两点;
1、确定方法需要被缓存以及他们的缓存策略
2、从缓存中读取之前缓存存储的数据



四、缓存使用
1、引入spring-boot-starter-cache模块
2、@EnableCaching开启缓存
3、使用缓存注解
4、切换为其他缓存
第一步:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
第二步:
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching; /**
* 一、搭建基本环境
* 1、导入数据库文件 创建出department和employee表
* 2、创建javaBean封装数据
* 3、整合MyBatis操作数据库
* 1.配置数据源信息
* 2.使用注解版的MyBatis;
* 1)、@MapperScan指定需要扫描的mapper接口所在的包
* 二、快速体验缓存
* 步骤:
* 1、开启基于注解的缓存 @EnableCaching
* 2、标注缓存注解即可
* @Cacheable
* @CacheEvict
* @CachePut
* 默认使用的是ConcurrentMapCacheManager==ConcurrentMapCache;将数据保存在 ConcurrentMap<Object, Object>中
* 开发中使用缓存中间件;redis、memcached、ehcache;
* 三、整合redis作为缓存
* Redis 是一个开源(BSD许可)的,内存中的数据结构存储系统,它可以用作数据库、缓存和消息中间件。
* 1、安装redis:使用docker;
* 2、引入redis的starter
* 3、配置redis
* 4、测试缓存
* 原理:CacheManager===Cache 缓存组件来实际给缓存中存取数据
* 1)、引入redis的starter,容器中保存的是 RedisCacheManager;
* 2)、RedisCacheManager 帮我们创建 RedisCache 来作为缓存组件;RedisCache通过操作redis缓存数据的
* 3)、默认保存数据 k-v 都是Object;利用序列化保存;如何保存为json
* 1、引入了redis的starter,cacheManager变为 RedisCacheManager;
* 2、默认创建的 RedisCacheManager 操作redis的时候使用的是 RedisTemplate<Object, Object>
* 3、RedisTemplate<Object, Object> 是 默认使用jdk的序列化机制
* 4)、自定义CacheManager;
*
*/
@MapperScan("com.atguigu.cache.mapper")
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching
public class Springboot01CacheApplication { public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Springboot01CacheApplication.class, args);
}
}
Controller层:
@RestController
public class EmployeeController { @Autowired
EmployeeService employeeService; @GetMapping("/emp/{id}")
public Employee getEmployee(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
Employee employee = employeeService.getEmp(id);
return employee;
} @GetMapping("/emp")
public Employee update(Employee employee){
Employee emp = employeeService.updateEmp(employee); return emp;
} @GetMapping("/delemp")
public String deleteEmp(Integer id){
employeeService.deleteEmp(id);
return "success";
} @GetMapping("/emp/lastname/{lastName}")
public Employee getEmpByLastName(@PathVariable("lastName") String lastName){
return employeeService.getEmpByLastName(lastName);
} }
Sercvice层:
@CacheConfig(cacheNames="emp"/*,cacheManager = "employeeCacheManager"*/) //抽取缓存的公共配置
@Service
public class EmployeeService { @Autowired
EmployeeMapper employeeMapper; /**
* 将方法的运行结果进行缓存;以后再要相同的数据,直接从缓存中获取,不用调用方法;
* CacheManager管理多个Cache组件的,对缓存的真正CRUD操作在Cache组件中,每一个缓存组件有自己唯一一个名字;
* *
* 原理:
* 1、自动配置类;CacheAutoConfiguration
* 2、缓存的配置类
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.GenericCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.JCacheCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.EhCacheCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.HazelcastCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.InfinispanCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CouchbaseCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CaffeineCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.GuavaCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.SimpleCacheConfiguration【默认】
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.NoOpCacheConfiguration
* 3、哪个配置类默认生效:SimpleCacheConfiguration;
*
* 4、给容器中注册了一个CacheManager:ConcurrentMapCacheManager
* 5、可以获取和创建ConcurrentMapCache类型的缓存组件;他的作用将数据保存在ConcurrentMap中;
*
* 运行流程:
* @Cacheable:
* 1、方法运行之前,先去查询Cache(缓存组件),按照cacheNames指定的名字获取;
* (CacheManager先获取相应的缓存),第一次获取缓存如果没有Cache组件会自动创建。
* 2、去Cache中查找缓存的内容,使用一个key,默认就是方法的参数;
* key是按照某种策略生成的;默认是使用keyGenerator生成的,默认使用SimpleKeyGenerator生成key;
* SimpleKeyGenerator生成key的默认策略;
* 如果没有参数;key=new SimpleKey();
* 如果有一个参数:key=参数的值
* 如果有多个参数:key=new SimpleKey(params);
* 3、没有查到缓存就调用目标方法;
* 4、将目标方法返回的结果,放进缓存中
*
* @Cacheable标注的方法执行之前先来检查缓存中有没有这个数据,默认按照参数的值作为key去查询缓存,
* 如果没有就运行方法并将结果放入缓存;以后再来调用就可以直接使用缓存中的数据;
*
* 核心:
* 1)、使用CacheManager【ConcurrentMapCacheManager】按照名字得到Cache【ConcurrentMapCache】组件
* 2)、key使用keyGenerator生成的,默认是SimpleKeyGenerator
*
*
* 几个属性:
* cacheNames/value:指定缓存组件的名字;将方法的返回结果放在哪个缓存中,是数组的方式,可以指定多个缓存;
*
* key:缓存数据使用的key;可以用它来指定。默认是使用方法参数的值 1-方法的返回值
* 编写SpEL; #i d;参数id的值 #a0 #p0 #root.args[0]
* getEmp[2]
*
* keyGenerator:key的生成器;可以自己指定key的生成器的组件id
* key/keyGenerator:二选一使用;
*
*
* cacheManager:指定缓存管理器;或者cacheResolver指定获取解析器
*
* condition:指定符合条件的情况下才缓存;
* ,condition = "#id>0"
* condition = "#a0>1":第一个参数的值》1的时候才进行缓存
*
* unless:否定缓存;当unless指定的条件为true,方法的返回值就不会被缓存;可以获取到结果进行判断
* unless = "#result == null"
* unless = "#a0==2":如果第一个参数的值是2,结果不缓存;
* sync:是否使用异步模式
* @param id
* @return
*
*/
@Cacheable(value = {"emp"}/*,keyGenerator = "myKeyGenerator",condition = "#a0>1",unless = "#a0==2"*/)
public Employee getEmp(Integer id){
System.out.println("查询"+id+"号员工");
Employee emp = employeeMapper.getEmpById(id);
return emp;
} /**
* @CachePut:既调用方法,又更新缓存数据;同步更新缓存
* 修改了数据库的某个数据,同时更新缓存;
* 运行时机:
* 1、先调用目标方法
* 2、将目标方法的结果缓存起来
*
* 测试步骤:
* 1、查询1号员工;查到的结果会放在缓存中;
* key:1 value:lastName:张三
* 2、以后查询还是之前的结果
* 3、更新1号员工;【lastName:zhangsan;gender:0】
* 将方法的返回值也放进缓存了;
* key:传入的employee对象 值:返回的employee对象;
* 4、查询1号员工?
* 应该是更新后的员工;
* key = "#employee.id":使用传入的参数的员工id;
* key = "#result.id":使用返回后的id
* @Cacheable的key是不能用#result
* 为什么是没更新前的?【1号员工没有在缓存中更新】
*
*/
@CachePut(/*value = "emp",*/key = "#result.id")
public Employee updateEmp(Employee employee){
System.out.println("updateEmp:"+employee);
employeeMapper.updateEmp(employee);
return employee;
} /**
* @CacheEvict:缓存清除
* key:指定要清除的数据
* allEntries = true:指定清除这个缓存中所有的数据
* beforeInvocation = false:缓存的清除是否在方法之前执行
* 默认代表缓存清除操作是在方法执行之后执行;如果出现异常缓存就不会清除
*
* beforeInvocation = true:
* 代表清除缓存操作是在方法运行之前执行,无论方法是否出现异常,缓存都清除
*
*
*/
@CacheEvict(value="emp",beforeInvocation = true/*key = "#id",*/)
public void deleteEmp(Integer id){
System.out.println("deleteEmp:"+id);
//employeeMapper.deleteEmpById(id);
int i = 10/0;
} // @Caching 定义复杂的缓存规则
@Caching(
cacheable = {
@Cacheable(/*value="emp",*/key = "#lastName")
},
put = {
@CachePut(/*value="emp",*/key = "#result.id"),
@CachePut(/*value="emp",*/key = "#result.email")
}
)
public Employee getEmpByLastName(String lastName){
return employeeMapper.getEmpByLastName(lastName);
} }
@Service
public class DeptService { @Autowired
DepartmentMapper departmentMapper; @Qualifier("deptCacheManager")
@Autowired
RedisCacheManager deptCacheManager; /**
* 缓存的数据能存入redis;
* 第二次从缓存中查询就不能反序列化回来;
* 存的是dept的json数据;CacheManager默认使用RedisTemplate<Object, Employee>操作Redis
*
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
// @Cacheable(cacheNames = "dept",cacheManager = "deptCacheManager")
// public Department getDeptById(Integer id){
// System.out.println("查询部门"+id);
// Department department = departmentMapper.getDeptById(id);
// return department;
// } // 使用缓存管理器得到缓存,进行api调用
public Department getDeptById(Integer id){
System.out.println("查询部门"+id);
Department department = departmentMapper.getDeptById(id); //获取某个缓存
Cache dept = deptCacheManager.getCache("dept");
dept.put("dept:1",department); return department;
} }
Mapper层:
@Mapper
public interface EmployeeMapper { @Select("SELECT * FROM employee WHERE id = #{id}")
public Employee getEmpById(Integer id); @Update("UPDATE employee SET lastName=#{lastName},email=#{email},gender=#{gender},d_id=#{dId} WHERE id=#{id}")
public void updateEmp(Employee employee); @Delete("DELETE FROM employee WHERE id=#{id}")
public void deleteEmpById(Integer id); @Insert("INSERT INTO employee(lastName,email,gender,d_id) VALUES(#{lastName},#{email},#{gender},#{dId})")
public void insertEmployee(Employee employee); @Select("SELECT * FROM employee WHERE lastName = #{lastName}")
Employee getEmpByLastName(String lastName);
}
五、整合redis实现缓存
1.引入spring-boot-starter-data-redis
2.application.yml配置redis连接地址
3.使用ReditTemplate操作redis
redisTemplate.opsForValue();//操作字符串
redisTemplate.opsForHash();//操作hash
redisTemplate.opsForList();//操作list
redisTemplate.opsForSet();//操作set
redisTemplate.opsForZSet();//操作有序set
4.配置缓存、CacheManagerCustomizers
5.测试使用缓存、切换缓存、 CompositeCacheManager
第一步:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
第二步:
spring.redis.host=118.24.44.**
第三步:
测试类:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class Springboot01CacheApplicationTests {
@Autowired
EmployeeMapper employeeMapper; @Autowired
StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate; //操作k-v都是字符串的 @Autowired
RedisTemplate redisTemplate; //k-v都是对象的 @Autowired
RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> empRedisTemplate; /**
* Redis常见的五大数据类型
* String(字符串)、List(列表)、Set(集合)、Hash(散列)、ZSet(有序集合)
* stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue()[String(字符串)]
* stringRedisTemplate.opsForList()[List(列表)]
* stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet()[Set(集合)]
* stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash()[Hash(散列)]
* stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet()[ZSet(有序集合)]
*/
@Test
public void test01(){
//给redis中保存数据
//stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().append("msg","hello");
// String msg = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("msg");
// System.out.println(msg); // stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush("mylist","1");
// stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush("mylist","2");
} //测试保存对象
@Test
public void test02(){
Employee empById = employeeMapper.getEmpById(1);
//默认如果保存对象,使用jdk序列化机制,序列化后的数据保存到redis中
//redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("emp-01",empById);
//1、将数据以json的方式保存
//(1)自己将对象转为json
//(2)redisTemplate默认的序列化规则;改变默认的序列化规则;
empRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("emp-01",empById);
} @Test
public void contextLoads() { Employee empById = employeeMapper.getEmpById(1);
System.out.println(empById); } }
Config配置类: 前提是Employee类实现了序列化。
@Configuration
public class MyRedisConfig { @Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> empRedisTemplate(
RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory)
throws UnknownHostException {
RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> template = new RedisTemplate<Object, Employee>();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Employee> ser = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Employee>(Employee.class);
template.setDefaultSerializer(ser);
return template;
}
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Department> deptRedisTemplate(
RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory)
throws UnknownHostException {
RedisTemplate<Object, Department> template = new RedisTemplate<Object, Department>();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Department> ser = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Department>(Department.class);
template.setDefaultSerializer(ser);
return template;
} //CacheManagerCustomizers可以来定制缓存的一些规则
@Primary //将某个缓存管理器作为默认的
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager employeeCacheManager(RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> empRedisTemplate){
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = new RedisCacheManager(empRedisTemplate);
//key多了一个前缀 //使用前缀,默认会将CacheName作为key的前缀
cacheManager.setUsePrefix(true); return cacheManager;
} @Bean
public RedisCacheManager deptCacheManager(RedisTemplate<Object, Department> deptRedisTemplate){
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = new RedisCacheManager(deptRedisTemplate);
//key多了一个前缀 //使用前缀,默认会将CacheName作为key的前缀
cacheManager.setUsePrefix(true); return cacheManager;
} }
注意:
1.当有多个缓存管理器的时候,必须指定一个默认的。@Primary
//CacheManagerCustomizers可以来定制缓存的一些规则
@Primary //将某个缓存管理器作为默认的
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager employeeCacheManager(RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> empRedisTemplate){
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = new RedisCacheManager(empRedisTemplate);
//key多了一个前缀 //使用前缀,默认会将CacheName作为key的前缀
cacheManager.setUsePrefix(true); return cacheManager;
}
2. 编码的方式使用缓存;
// 使用缓存管理器得到缓存,进行api调用
public Department getDeptById(Integer id){
System.out.println("查询部门"+id);
Department department = departmentMapper.getDeptById(id); //获取某个缓存
Cache dept = deptCacheManager.getCache("dept");
dept.put("dept:1",department); return department;
}
SpringBoot与缓存的更多相关文章
- 带着新人学springboot的应用03(springboot+mybatis+缓存 下)
springboot+mybatis+缓存,基本的用法想必是会了,现在说一说内部大概的原理. 稍微提一下mybatis,只要导入了mybatis的依赖,那么有个自动配置类就会生效,你可以去mybati ...
- SpringBoot 与缓存
1. JSR107 Java Caching 定义了5个核心接口: CachingProvider:定义了创建,配置,获取,管理和控制多个CacheManager; CacheManager:定义了创 ...
- SpringBoot 整合缓存Cacheable实战详细使用
前言 我知道在接口api项目中,频繁的调用接口获取数据,查询数据库是非常耗费资源的,于是就有了缓存技术,可以把一些不常更新,或者经常使用的数据,缓存起来,然后下次再请求时候,就直接从缓存中获取,不需要 ...
- springboot redis 缓存对象
只要加入spring-boot-starter-data-redis , springboot 会自动识别并使用redis作为缓存容器,使用方式如下 gradle加入依赖 compile(" ...
- springboot~hazelcast缓存中间件
缓存来了 在dotnet平台有自己的缓存框架,在java springboot里当然了集成了很多,而且缓存的中间件也可以进行多种选择,向redis, hazelcast都是分布式的缓存中间件,今天主要 ...
- 带着新人学springboot的应用02(springboot+mybatis+缓存 中)
继续接着上一节,大家应该知道驼峰命名法吧!就是我们javabean中属性一般命名是lastName,userName这种类型的,而数据库中列名一般都是last_name,user_name这种的,要让 ...
- 带着新人学springboot的应用01(springboot+mybatis+缓存 上)
上一篇结束,第一次做一个这么长的系列,很多东西我也是没有说到,也许是还没有想到,哈哈哈,不过基本的东西还是说的差不多了的.假如以后碰到了不会的,随便查查资料配置一下就ok. 咳,还有大家如果把我前面的 ...
- SpringBoot Redis缓存 @Cacheable、@CacheEvict、@CachePut
文章来源 https://blog.csdn.net/u010588262/article/details/81003493 1. pom.xml <dependency> <gro ...
- springboot Redis 缓存
1,先整合 redis 和 mybatis 步骤一: springboot 整合 redis 步骤二: springboot 整合 mybatis 2,启动类添加 @EnableCaching 注解, ...
- SpringBoot学习笔记(6) SpringBoot数据缓存Cache [Guava和Redis实现]
https://blog.csdn.net/a67474506/article/details/52608855 Spring定义了org.springframework.cache.CacheMan ...
随机推荐
- 【35.53%】【POJ 2912】Rochambeau
Time Limit: 5000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 2837 Accepted: 1008 Description N childre ...
- buerdepepeqi 的模版
buerdepepeqi的模板 头文件 #include <set> #include <map> #include <deque> #include <qu ...
- 清晰架构(Clean Architecture)的Go微服务: 设计原则
我最近写了一个Go微服务应用程序,这个程序的设计来自三个灵感: 清晰架构"Clean Architecture"¹ and SOLID (面向对象设计)² 设计 原则³ Sprin ...
- QT信号和槽函数学习笔记
//connect 函数有4个参数 分别是 发送者 信号.接受者 ,槽 //connect(sender,signal,receiver,slot) /* * 信号和槽 * 信号 就是一个普通的函数 ...
- 使用 Python 中 re 模块对测试用例参数化,进行搜索 search、替换 sub
自动化测试用例,如果一百个接口要在Excel写100个sheet表单,每个接口有10个字段,里面有5个都可能是变化的,需要使用参数化,先试用特定的字符进行站位,在构造参数时在进行替换占位符: 一.用力 ...
- Django 单表查询
前言 如何只单独测试django中的某一个py文件呢?或者说如何书写测试脚本? 我们可以在任意一个py文件(应用下的tests或者自己新建一个)中书写以下代码: 前期准备 创建一个电影表 class ...
- 用markdown写博客,看这一篇就够了
0. 前言 记得上次用markdown写博客,尽管我有markdown使用经验,但第一篇markdown博客还是不得已的"回滚"了. 传送门:记录一下第一次用markdown写博客 ...
- Objectarx 相交矩形求并集 面域转多段线
测试结果: 主要思路:拾取一个点作为矩形的插入点,分别以该点进行两次jig操作,就能得到白色的两个相交的polyline,之后需要变成红色的封闭多段线.做法就是:求出两个白色矩形的面域,然后通过boo ...
- .NET Core 3 WPF MVVM框架 Prism系列之事件聚合器
本文将介绍如何在.NET Core3环境下使用MVVM框架Prism的使用事件聚合器实现模块间的通信 一.事件聚合器 在上一篇 .NET Core 3 WPF MVVM框架 Prism系列之模块化 ...
- C++类中的重载
函数重载回顾 函数重载的本质为相互独立的不同函数 C++中通过函数名和函数参数确定函数调用 无法直接通过函数名得到重载函数的入口地址 函数重载必然发生在同一个作用域 类中的成员函数可以进行重载 构造函 ...
