DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.8


代码:
x = rand(1,11); n = 0:10;
k = 0:500; w = (pi/500)*k; % [0,pi] axis divided into 501 points.
X = x * (exp(-j*pi/500)) .^ (n'*k); % DTFT of x % signal shifted by two samples
y = x; m = n + 2;
Y = y * (exp(-j*pi/500)) .^ (m'*k); % DTFT of y = x(n-2) magX = abs(X); angX = angle(X); realX = real(X); imagX = imag(X);
magY = abs(Y); angY = angle(Y); realY = real(Y); imagY = imag(Y); %verification
Y_check = (exp(-j*2) .^ w) .* X; % multiplication by exp(-j2w)
error = max(abs(Y-Y_check)); % Difference figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'x & y sequence')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,1,1); stem(n,x); title('x sequence'); xlabel('n'); ylabel('x(n)'); grid on;
subplot(2,1,2); stem(m,y); title('y sequence'); xlabel('n'); ylabel('y(n)'); grid on; %% --------------------------------------------------------------
%% START X's mag ang real imag
%% --------------------------------------------------------------
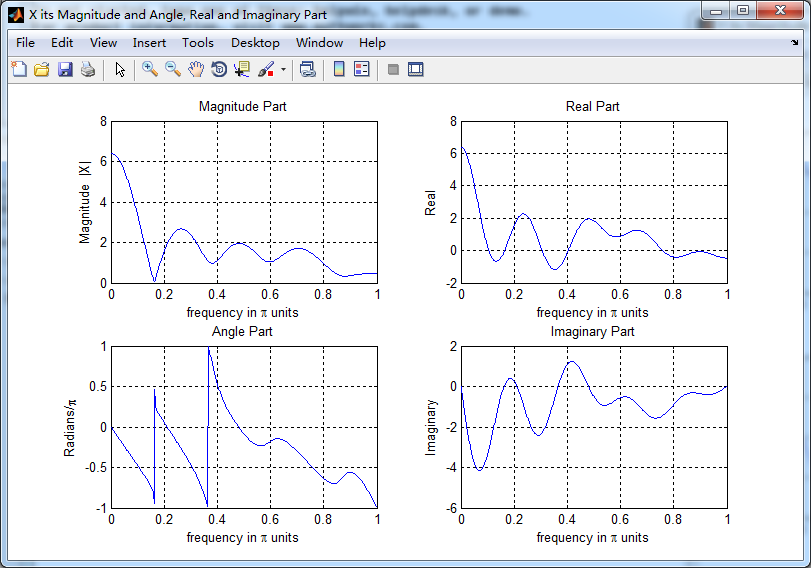
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'X its Magnitude and Angle, Real and Imaginary Part');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi,magX); grid on; % axis([-2,2,0,15]);
title('Magnitude Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |X|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, angX/pi); grid on; % axis([-2,2,-1,1]);
title('Angle Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot('2,2,2'); plot(w/pi, realX); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(w/pi, imagX); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary');
%% --------------------------------------------------------------
%% END X's mag ang real imag
%% -------------------------------------------------------------- %% --------------------------------------------------------------
%% START Y's mag ang real imag
%% --------------------------------------------------------------
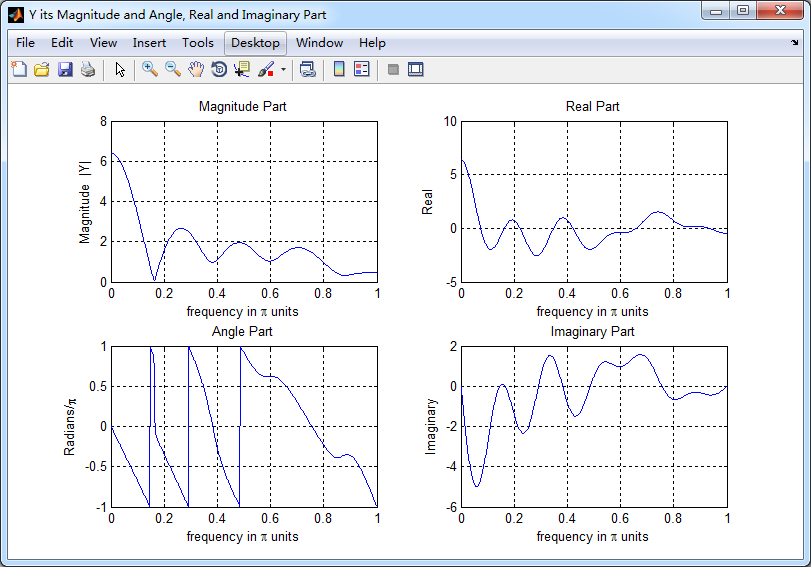
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Y its Magnitude and Angle, Real and Imaginary Part');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi,magY); grid on; % axis([-2,2,0,15]);
title('Magnitude Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |Y|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, angY/pi); grid on; % axis([-2,2,-1,1]);
title('Angle Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot('2,2,2'); plot(w/pi, realY); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(w/pi, imagY); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary'); %% --------------------------------------------------------------
%% END Y's mag ang real imag
%% --------------------------------------------------------------
运行结果:


DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.8的更多相关文章
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.21
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) % Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*a ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.19
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Discrete-time Signa ...
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.18
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Continuous-time Fou ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.23
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) : Ts = 0.0002 Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; x1 = exp(-1000 ...
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.16
代码: b = [0.0181, 0.0543, 0.0543, 0.0181]; % filter coefficient array b a = [1.0000, -1.7600, 1.1829, ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.22
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x2(n) Ts = 0.001; n = -5:1:5; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*abs(nT ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.17
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.15
上代码: subplot(1,1,1); b = 1; a = [1, -0.8]; n = [0:100]; x = cos(0.05*pi*n); y = filter(b,a,x); figur ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.13
上代码: w = [0:1:500]*pi/500; % freqency between 0 and +pi, [0,pi] axis divided into 501 points. H = ex ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.12
用到的性质 代码: n = -5:10; x = sin(pi*n/2); k = -100:100; w = (pi/100)*k; % freqency between -pi and +pi , ...
随机推荐
- 【STL】 set集合容器常用用法
set集合容器:实现了红黑树的平衡二叉检索树的数据结构,插入元素时,它会自动调整二叉树的排列,把元素放到适当的位置,以保证每个子树根节点键值大于左子树所有节点的键值,小于右子树所有节点的键值:另外,还 ...
- js验证手机号
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding= ...
- 获取指定文件下的所有file文件
/** * 描述:获取所有的文件列表 * @param file * @param list * @return */ private List<File> getAllFiles(Fil ...
- 【编程题目】题目:定义 Fibonacci 数列 输入 n,用最快的方法求该数列的第 n 项。
第 19 题(数组.递归):题目:定义 Fibonacci 数列如下:/ 0 n=0f(n)= 1 n=1/ f(n-1)+f(n-2) n=2输入 n,用最快的方法求该数列的第 n 项. 思路:递归 ...
- ios企业应用发布流程
转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/justinjing0612/article/details/8758692留作备忘 企业发布app的 过程比app store 发布的简单多了,没那 ...
- NodeVisitor的使用-遍历Geode节点并在它与父节点之间添加一个LOD节点
#include <osg\NodeVisitor>#include <osg\MatrixTransform>#include <osg\PagedLOD>#in ...
- CLR via C#(08)-操作符
对于操作符,我们并不陌生,例如+,-,*,%等二元操作符,以及++,!等一元操作符.但是对于非基元类型,我们需要通过一些自定义方法才能使用这些操作符.今天主要和大家分享关于操作符重载和转换操作符的知识 ...
- Delphi面向对象的可见性表示符
Delphi能通过在声明域和方法的时候用protected.private.public.published和automated指示符来对对象提供进一步的控制.使用这些关键字的语法如下 TSomeOb ...
- supervisor使用
supervisor是一个C/S系统,它可以在类unix操作系统让用户来监视和控制后台服务进程的数量,一个很重要的功能就是监控服务器的主要后台进程,并在出现问题是自动重启. 根据服务器上的python ...
- NBU expired Media,Media ID not found in EMM database
Subject:When attempting to expire a media in Veritas NetBackup (tm) 6.0 with the bpexpdate command, ...
