Spark RDDs vs DataFrames vs SparkSQL
简介
Spark的 RDD、DataFrame 和 SparkSQL的性能比较。
2方面的比较
单条记录的随机查找
aggregation聚合并且sorting后输出
使用以下Spark的三种方式来解决上面的2个问题,对比性能。
Using RDD’s
Using DataFrames
Using SparkSQL
数据源
在HDFS中3个文件中存储的9百万不同记录
- 每条记录11个字段
总大小 1.4 GB
实验环境
HDP 2.4
Hadoop version 2.7
Spark 1.6
HDP Sandbox
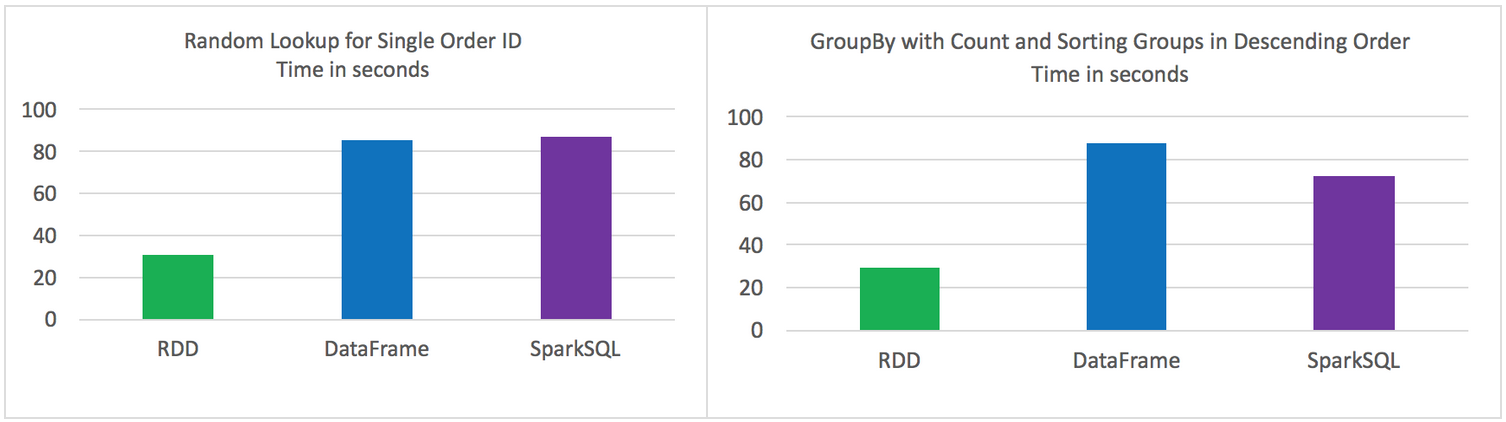
测试结果
原始的RDD 比 DataFrames 和 SparkSQL性能要好
DataFrames 和 SparkSQL 性能差不多
使用DataFrames 和 SparkSQL 比 RDD 操作更直观
Jobs都是独立运行,没有其他job的干扰
2个操作
Random lookup against 1 order ID from 9 Million unique order ID's
GROUP all the different products with their total COUNTS and SORT DESCENDING by product name
代码
RDD Random Lookup
#!/usr/bin/env python from time import time
from pyspark import SparkConf, SparkContext conf = (SparkConf()
.setAppName("rdd_random_lookup")
.set("spark.executor.instances", "")
.set("spark.executor.cores", 2)
.set("spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled", "false")
.set("spark.shuffle.service.enabled", "false")
.set("spark.executor.memory", "500MB"))
sc = SparkContext(conf = conf) t0 = time() path = "/data/customer_orders*"
lines = sc.textFile(path) ## filter where the order_id, the second field, is equal to 96922894
print lines.map(lambda line: line.split('|')).filter(lambda line: int(line[1]) == 96922894).collect() tt = str(time() - t0)
print "RDD lookup performed in " + tt + " seconds"
DataFrame Random Lookup
#!/usr/bin/env python from time import time
from pyspark.sql import *
from pyspark import SparkConf, SparkContext conf = (SparkConf()
.setAppName("data_frame_random_lookup")
.set("spark.executor.instances", "")
.set("spark.executor.cores", 2)
.set("spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled", "false")
.set("spark.shuffle.service.enabled", "false")
.set("spark.executor.memory", "500MB"))
sc = SparkContext(conf = conf) sqlContext = SQLContext(sc) t0 = time() path = "/data/customer_orders*"
lines = sc.textFile(path) ## create data frame
orders_df = sqlContext.createDataFrame( \
lines.map(lambda l: l.split("|")) \
.map(lambda p: Row(cust_id=int(p[0]), order_id=int(p[1]), email_hash=p[2], ssn_hash=p[3], product_id=int(p[4]), product_desc=p[5], \
country=p[6], state=p[7], shipping_carrier=p[8], shipping_type=p[9], shipping_class=p[10] ) ) ) ## filter where the order_id, the second field, is equal to 96922894
orders_df.where(orders_df['order_id'] == 96922894).show() tt = str(time() - t0)
print "DataFrame performed in " + tt + " seconds"
SparkSQL Random Lookup
#!/usr/bin/env python from time import time
from pyspark.sql import *
from pyspark import SparkConf, SparkContext conf = (SparkConf()
.setAppName("spark_sql_random_lookup")
.set("spark.executor.instances", "")
.set("spark.executor.cores", 2)
.set("spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled", "false")
.set("spark.shuffle.service.enabled", "false")
.set("spark.executor.memory", "500MB"))
sc = SparkContext(conf = conf) sqlContext = SQLContext(sc) t0 = time() path = "/data/customer_orders*"
lines = sc.textFile(path) ## create data frame
orders_df = sqlContext.createDataFrame( \
lines.map(lambda l: l.split("|")) \
.map(lambda p: Row(cust_id=int(p[0]), order_id=int(p[1]), email_hash=p[2], ssn_hash=p[3], product_id=int(p[4]), product_desc=p[5], \
country=p[6], state=p[7], shipping_carrier=p[8], shipping_type=p[9], shipping_class=p[10] ) ) ) ## register data frame as a temporary table
orders_df.registerTempTable("orders") ## filter where the customer_id, the first field, is equal to 96922894
print sqlContext.sql("SELECT * FROM orders where order_id = 96922894").collect() tt = str(time() - t0)
print "SparkSQL performed in " + tt + " seconds"
RDD with GroupBy, Count, and Sort Descending
#!/usr/bin/env python from time import time
from pyspark import SparkConf, SparkContext conf = (SparkConf()
.setAppName("rdd_aggregation_and_sort")
.set("spark.executor.instances", "")
.set("spark.executor.cores", 2)
.set("spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled", "false")
.set("spark.shuffle.service.enabled", "false")
.set("spark.executor.memory", "500MB"))
sc = SparkContext(conf = conf) t0 = time() path = "/data/customer_orders*"
lines = sc.textFile(path) counts = lines.map(lambda line: line.split('|')) \
.map(lambda x: (x[5], 1)) \
.reduceByKey(lambda a, b: a + b) \
.map(lambda x:(x[1],x[0])) \
.sortByKey(ascending=False) for x in counts.collect():
print x[1] + '\t' + str(x[0]) tt = str(time() - t0)
print "RDD GroupBy performed in " + tt + " seconds"
DataFrame with GroupBy, Count, and Sort Descending
#!/usr/bin/env python from time import time
from pyspark.sql import *
from pyspark import SparkConf, SparkContext conf = (SparkConf()
.setAppName("data_frame_aggregation_and_sort")
.set("spark.executor.instances", "")
.set("spark.executor.cores", 2)
.set("spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled", "false")
.set("spark.shuffle.service.enabled", "false")
.set("spark.executor.memory", "500MB"))
sc = SparkContext(conf = conf) sqlContext = SQLContext(sc) t0 = time() path = "/data/customer_orders*"
lines = sc.textFile(path) ## create data frame
orders_df = sqlContext.createDataFrame( \
lines.map(lambda l: l.split("|")) \
.map(lambda p: Row(cust_id=int(p[0]), order_id=int(p[1]), email_hash=p[2], ssn_hash=p[3], product_id=int(p[4]), product_desc=p[5], \
country=p[6], state=p[7], shipping_carrier=p[8], shipping_type=p[9], shipping_class=p[10] ) ) ) results = orders_df.groupBy(orders_df['product_desc']).count().sort("count",ascending=False) for x in results.collect():
print x tt = str(time() - t0)
print "DataFrame performed in " + tt + " seconds"
SparkSQL with GroupBy, Count, and Sort Descending
#!/usr/bin/env python from time import time
from pyspark.sql import *
from pyspark import SparkConf, SparkContext conf = (SparkConf()
.setAppName("spark_sql_aggregation_and_sort")
.set("spark.executor.instances", "")
.set("spark.executor.cores", 2)
.set("spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled", "false")
.set("spark.shuffle.service.enabled", "false")
.set("spark.executor.memory", "500MB"))
sc = SparkContext(conf = conf) sqlContext = SQLContext(sc) t0 = time() path = "/data/customer_orders*"
lines = sc.textFile(path) ## create data frame
orders_df = sqlContext.createDataFrame(lines.map(lambda l: l.split("|")) \
.map(lambda r: Row(product=r[5]))) ## register data frame as a temporary table
orders_df.registerTempTable("orders") results = sqlContext.sql("SELECT product, count(*) AS total_count FROM orders GROUP BY product ORDER BY total_count DESC") for x in results.collect():
print x tt = str(time() - t0)
print "SparkSQL performed in " + tt + " seconds"
原文:https://community.hortonworks.com/articles/42027/rdd-vs-dataframe-vs-sparksql.html
Spark RDDs vs DataFrames vs SparkSQL的更多相关文章
- Spark 官方文档(5)——Spark SQL,DataFrames和Datasets 指南
Spark版本:1.6.2 概览 Spark SQL用于处理结构化数据,与Spark RDD API不同,它提供更多关于数据结构信息和计算任务运行信息的接口,Spark SQL内部使用这些额外的信息完 ...
- Effective Spark RDDs with Alluxio【转】
转自:http://kaimingwan.com/post/alluxio/effective-spark-rdds-with-alluxio 1. 介绍 2. 引言 3. Alluxio and S ...
- Spark(十二)SparkSQL简单使用
一.SparkSQL的进化之路 1.0以前: Shark 1.1.x开始:SparkSQL(只是测试性的) SQL 1.3.x: SparkSQL(正式版本)+Datafram ...
- Spark入门实战系列--6.SparkSQL(上)--SparkSQL简介
[注]该系列文章以及使用到安装包/测试数据 可以在<倾情大奉送--Spark入门实战系列>获取 .SparkSQL的发展历程 1.1 Hive and Shark SparkSQL的前身是 ...
- Spark入门实战系列--6.SparkSQL(中)--深入了解SparkSQL运行计划及调优
[注]该系列文章以及使用到安装包/测试数据 可以在<倾情大奉送--Spark入门实战系列>获取 1.1 运行环境说明 1.1.1 硬软件环境 线程,主频2.2G,10G内存 l 虚拟软 ...
- Spark入门实战系列--6.SparkSQL(下)--Spark实战应用
[注]该系列文章以及使用到安装包/测试数据 可以在<倾情大奉送--Spark入门实战系列>获取 .运行环境说明 1.1 硬软件环境 线程,主频2.2G,10G内存 l 虚拟软件:VMwa ...
- 一个spark SQL和DataFrames的故事
package com.lin.spark import org.apache.spark.sql.{Row, SparkSession} import org.apache.spark.sql.ty ...
- Apache Spark 2.2.0 中文文档 - Spark SQL, DataFrames and Datasets Guide | ApacheCN
Spark SQL, DataFrames and Datasets Guide Overview SQL Datasets and DataFrames 开始入门 起始点: SparkSession ...
- Spark记录-SparkSql官方文档中文翻译(部分转载)
1 概述(Overview) Spark SQL是Spark的一个组件,用于结构化数据的计算.Spark SQL提供了一个称为DataFrames的编程抽象,DataFrames可以充当分布式SQL查 ...
随机推荐
- 关于css选择器中有小数点的标签获取
需求说明 因为项目中章节配置的时候有小数点,1,1.1,1.2,1.11的标题,这个时候每一行标题的id,class设置成标题号是独一无二的标记.但是,直接用js获取是获取不到的,例如$('#3.22 ...
- Scala中 object 和 class的区别
object 在scala中没有静态方法和静态字段,所以在scala中可以用object来实现这些功能,直接用对象名调用的方法都是采用这种实现方式,例如Array.toString.对象的构造器在第一 ...
- STL --> string类字符串
基本使用方法 一.输入 string s: cin >> s; getline(cin, s) ; //使用默认的'\n'作为终止符 getline(cin, s, '!') ; //以' ...
- java基础笔记(6)----面向对象的三大特性
简介:面向对象的三大特性就是封装,继承,多态,是面向对象的核心. 封装 简介:封装是类的边界,可以对数据起到保护作用 特性:属性私有,提供公开的get/set方法 属性私有:private 数据类型 ...
- (译文)JavaScript基础——JavaScript中的深拷贝
在JavaScript中如何拷贝一个对象? 通过引用调用 function mutate(obj) { obj.a = true; } const obj = {a: false}; mutate(o ...
- 201621123057 《Java程序设计》第1周学习总结
1.本周学习总结 .java - - 源程序 .class - - 字节码文件 JVM - - 虚拟机 JRE - - 执行环境 JDK - - 开发工具包 其中,运行的是.class,而非.java ...
- Flask 扩展 HTTP认证
Restful API不保存状态,无法依赖Cookie及Session来保存用户信息,自然也无法使用Flask-Login扩展来实现用户认证.所以这里,我们就要介绍另一个扩展,Flask-HTTPAu ...
- HNOI 2012 永无乡
codevs 1477 永无乡 http://codevs.cn/problem/1477/ 2012年湖南湖北省队选拔赛 时间限制: 1 s 空间限制: 128000 KB 题目描述 Des ...
- requestAnimationFrame Web中写动画的另一种选择
HTML5和CSS3盛行的今天 动画变得很简单实现 我们可以用transition . animation + keyframe .也可以用canvas等 我在上一篇 点击回到顶部的文章中发现的这个 ...
- kali rolling更新源之gpg和dirmngr问题
1.编辑 /etc/apt/source.list gedit /etc/apt/sources.list 输入更新源,可以选任何可用更新源,这里设置官方源 deb http://http.kali. ...
