分段树(segment tree)的实现 —— 强化学习中 "优先级回放机制" 的重要组成部分
分段树(segment tree)是强化学习中 "优先级回放机制" 的重要组成部分。本文针对分段树(segment tree)的一个开源版本的实现来进行分析,代码地址:
https://gitee.com/devilmaycry812839668/Rainbow/blob/master/memory.py
Transition_dtype = np.dtype(
[('timestep', np.int32), ('state', np.uint8, (84, 84)), ('action', np.int32), ('reward', np.float32),
('nonterminal', np.bool_)])
blank_trans = (0, np.zeros((84, 84), dtype=np.uint8), 0, 0.0, False) # Segment tree data structure where parent node values are sum/max of children node values
class SegmentTree():
def __init__(self, size):
self.index = 0
self.size = size
self.full = False # Used to track actual capacity
self.tree_start = 2 ** (size - 1).bit_length() - 1 # Put all used node leaves on last tree level
self.sum_tree = np.zeros((self.tree_start + self.size,), dtype=np.float32)
self.data = np.array([blank_trans] * size, dtype=Transition_dtype) # Build structured array
self.max = 1 # Initial max value to return (1 = 1^ω) # Updates nodes values from current tree
def _update_nodes(self, indices):
children_indices = indices * 2 + np.expand_dims([1, 2], axis=1)
self.sum_tree[indices] = np.sum(self.sum_tree[children_indices], axis=0) # Propagates changes up tree given tree indices
def _propagate(self, indices):
parents = (indices - 1) // 2
unique_parents = np.unique(parents)
self._update_nodes(unique_parents)
if parents[0] != 0:
self._propagate(parents) # Updates values given tree indices
def update(self, indices, values):
self.sum_tree[indices] = values # Set new values
self._propagate(indices) # Propagate values
current_max_value = np.max(values)
self.max = max(current_max_value, self.max) # Propagates single value up tree given a tree index for efficiency
def _propagate_index(self, index):
parent = (index - 1) // 2
left, right = 2 * parent + 1, 2 * parent + 2
self.sum_tree[parent] = self.sum_tree[left] + self.sum_tree[right]
if parent != 0:
self._propagate_index(parent) # Updates single value given a tree index for efficiency
def _update_index(self, index, value):
self.sum_tree[index] = value # Set new value
self._propagate_index(index) # Propagate value
self.max = max(value, self.max) def append(self, data, value):
self.data[self.index] = data # Store data in underlying data structure
self._update_index(self.index + self.tree_start, value) # Update tree
self.index = (self.index + 1) % self.size # Update index
self.full = self.full or self.index == 0 # Save when capacity reached
self.max = max(value, self.max) # Searches for the location of values in sum tree
def _retrieve(self, indices, values):
children_indices = (indices * 2 + np.expand_dims([1, 2], axis=1)) # Make matrix of children indices
# If indices correspond to leaf nodes, return them
if children_indices[0, 0] >= self.sum_tree.shape[0]:
return indices
# If children indices correspond to leaf nodes, bound rare outliers in case total slightly overshoots
elif children_indices[0, 0] >= self.tree_start:
children_indices = np.minimum(children_indices, self.sum_tree.shape[0] - 1)
left_children_values = self.sum_tree[children_indices[0]]
successor_choices = np.greater(values, left_children_values).astype(
np.int32) # Classify which values are in left or right branches
successor_indices = children_indices[
successor_choices, np.arange(indices.size)] # Use classification to index into the indices matrix
successor_values = values - successor_choices * left_children_values # Subtract the left branch values when searching in the right branch
return self._retrieve(successor_indices, successor_values) # Searches for values in sum tree and returns values, data indices and tree indices
def find(self, values):
indices = self._retrieve(np.zeros(values.shape, dtype=np.int32), values)
data_index = indices - self.tree_start
return (self.sum_tree[indices], data_index, indices) # Return values, data indices, tree indices # Returns data given a data index
def get(self, data_index):
return self.data[data_index % self.size] def total(self):
return self.sum_tree[0]
分段树的具体逻辑结构如下:(原图地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/pinard/p/9797695.html)
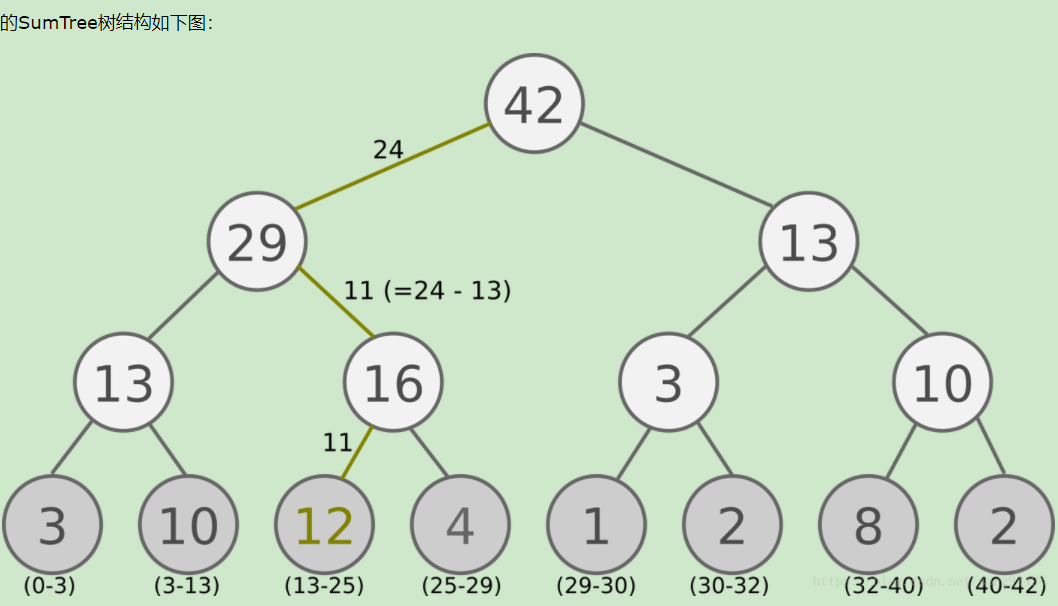
这个segment tree可以分为两个部分,一个部分是权重(待检索数据的权重)的索引部分,另一部分是数据(待检索数据)的存储部分。
上图中的数据部分(待检索的数据)就是下图的表示:

权重(待检索数据的权重)的索引部分为:
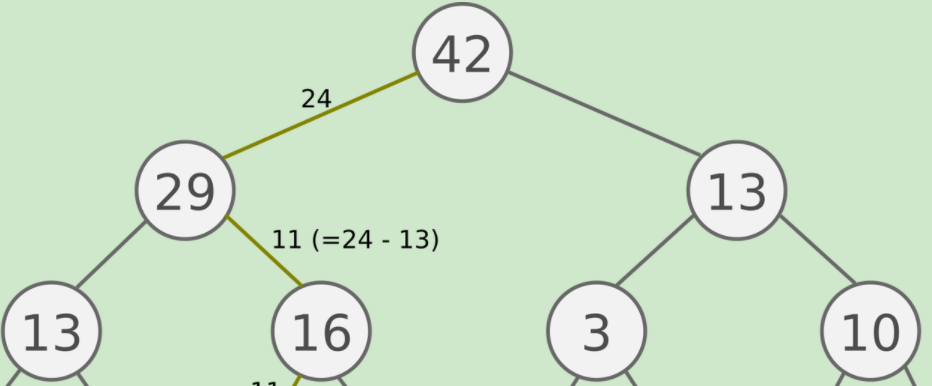
===================================================
代码分析:
在__init__ 函数部分:

self.size = size #指的是需要存储的数据(待检索的数据)的最多个数。
self.full #是记录存储的数据个数有没有达到最多个数的要求,即是否存储满。
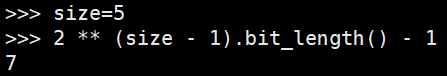
self.tree_start = 2 ** (size - 1).bit_length() - 1
#比较不好理解的部分,如果存储size个数据,那么需要编号的话就是0 到 size-1 ,
#最大的编号size-1的二进制表示的长度为 (size - 1).bit_length(),
# (size - 1).bit_length() 长的二进制位所能表示的最多个数编号为 0 到 2 ** (size - 1).bit_length() - 1
形象的说,看下图:
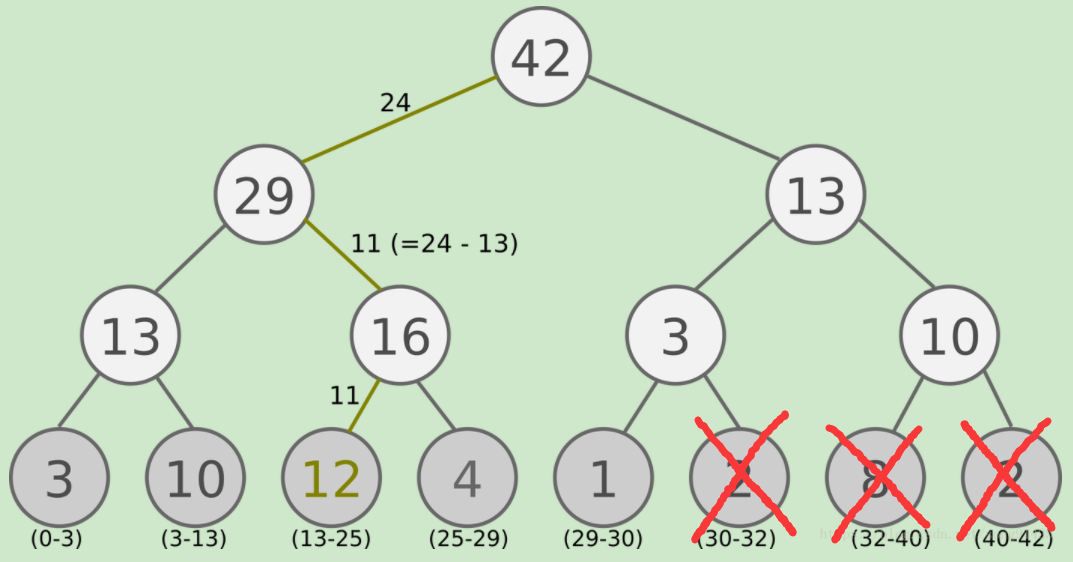
如果我们有5个数据,而这5个数据全部为同一层的叶子节点,那么构建一个二叉树后如果非叶子节点的部分为满二叉树,那么非叶子节点的部分为 7。
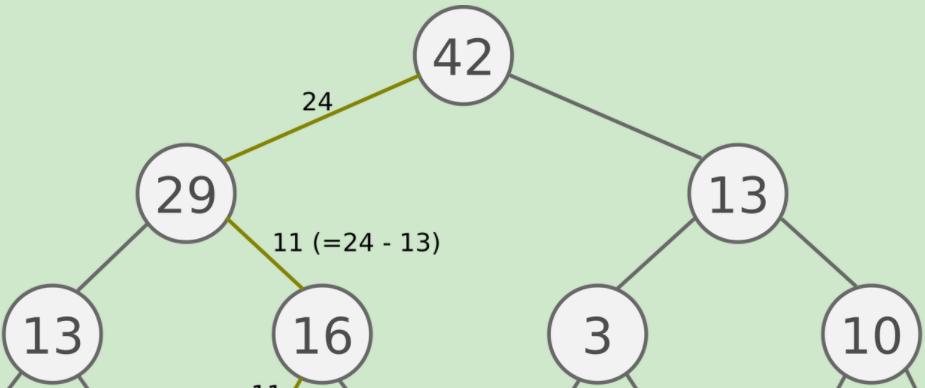
非叶子节点,也是分段树中索引节点的个数,在size=5时,个数为7 。
self.sum_tree = np.zeros((self.tree_start + self.size,), dtype=np.float32)
生成一个float数组矩阵,大小为索引节点个数 self.tree_start 与 数据节点个数 self.size 的和。其中,索引节点和数据节点存储的都是权重值。
segment tree中存储的是待检索数据的权重,其中叶节点是直接存储的待检索数据的权重,非叶节点则存储的是子节点权重之和。而self.data 则是存储的待检索数据,数据的数据类型为自定义的 Transition_dtype
self.data = np.array([blank_trans] * size, dtype=Transition_dtype)
self.max = 1 #初始化segment tree时新存入节点的默认权重值,初始化为 1
=====================================================
单个数据的插入,并更新segment tree中对应的权重值,并对与其相关的上层节点的权重值进行更新。
# Propagates single value up tree given a tree index for efficiency
def _propagate_index(self, index):
parent = (index - 1) // 2
left, right = 2 * parent + 1, 2 * parent + 2
self.sum_tree[parent] = self.sum_tree[left] + self.sum_tree[right]
if parent != 0:
self._propagate_index(parent) # Updates single value given a tree index for efficiency
def _update_index(self, index, value):
self.sum_tree[index] = value # Set new value
self._propagate_index(index) # Propagate value
self.max = max(value, self.max) def append(self, data, value):
self.data[self.index] = data # Store data in underlying data structure
self._update_index(self.index + self.tree_start, value) # Update tree
self.index = (self.index + 1) % self.size # Update index
self.full = self.full or self.index == 0 # Save when capacity reached
self.max = max(value, self.max)
由于我们的数据是存储在 self.data 中, 而数据对应的权重值是存储在segment tree中。
self.index 是 self.data 中当前可以写入的位置的索引号。同时,self.index+self.tree_start 也是对应权重在 self.sum_tree 中的索引位置。
def append: 中的输入参数value则是数据data对应的权重值。也就是说self.sum_tree中索引号self.index+self.tree_start中所存储的权重值为value。
def _propagate_index(self, index) 函数:
更新segment tree中子节点的父节点权重值,segment tree中索引为index的节点的父节点的索引为 parent = (index - 1) // 2
而index节点的父节点的子节点中的左右节点分别为: left, right = 2 * parent + 1, 2 * parent + 2
当然,index节点的左右子节点中也必然包括index节点。
self.sum_tree[parent] = self.sum_tree[left] + self.sum_tree[right]
根据左右子节点的权重更新父节点的权重值。
if parent != 0:
self._propagate_index(parent)
迭代修改父节点的权重值,直到修改到根节点,即索引号为0的节点。
def _update_nodes(self, indices):
def _update_nodes(self, indices):
def update(self, indices, values):
一次性为多个节点修改权重值,具体类似于插入单个节点。
===========================================================
检索操作,在segment_tree中检索多个值(values)的索引号,并将其存入 indices 中。
检索操作应该是segment_tree的精髓部分,segment_tree 最重要的一个功能就是按照self.data中元素所对应的self.sum_tree中的权重值进行随机采样。
indices = self._retrieve(np.zeros(values.shape, dtype=np.int32), values)
def _retrieve(self, indices, values):
children_indices = (indices * 2 + np.expand_dims([1, 2], axis=1)) # Make matrix of children indices
# If indices correspond to leaf nodes, return them
if children_indices[0, 0] >= self.sum_tree.shape[0]:
return indices
# If children indices correspond to leaf nodes, bound rare outliers in case total slightly overshoots
elif children_indices[0, 0] >= self.tree_start:
children_indices = np.minimum(children_indices, self.sum_tree.shape[0] - 1)
left_children_values = self.sum_tree[children_indices[0]]
successor_choices = np.greater(values, left_children_values).astype(
np.int32) # Classify which values are in left or right branches
successor_indices = children_indices[
successor_choices, np.arange(indices.size)] # Use classification to index into the indices matrix
successor_values = values - successor_choices * left_children_values # Subtract the left branch values when searching in the right branch
return self._retrieve(successor_indices, successor_values)
children_indices = (indices * 2 + np.expand_dims([1, 2], axis=1))
indices ,多个值的索引,children_indices 为indices所对应的父节点下的左右子节点的索引矩阵,0行(matrix的0行)为所有左子节点的索引值,1行(matrix的1行)为所有右子节点的索引值。这里初始化时多个值的初始索引均设置为根节点,即0号节点。
children_indices[0, 0] >= self.sum_tree.shape[0] 子节点索引号最小的,即children_indices[0, 0] (因为indices中索引值为从小到大顺序排列),如果最小索引值大于self.sum_tree的长度则表示当前节点(即indices节点)为叶子节点。

该部分代码对应的情形如下:

children_indices[0, 0] >= self.tree_start 如果索引号最小的节点小于segment tree的非叶子节点个数,那么子节点children_indices必然是叶子节点。
但是在该种情况下,会出现indices子节点不为叶子节点,该种情况下会有部分子节点不属于segment tree,如上图中的红叉部分节点(这里特指第一个红叉的点)。
第一个红叉的点需要被排除掉,因为第一个红叉点的索引号已经超出了segment tree中所能表示的叶节点的范围。其实,该种情况极难发生,因为不对次情况做处理的话也是会在下一步中只考虑对应的左子节点,因为待检索的权重值必然小于左子节点所对应的权重值,因此不对后续结果有影响。但是由于极小概率下浮点数表示的精度问题会导致将第一个红叉点也加入到考虑范围内,因此对该种情况进行特殊处理。

如果查找的权重值value大于左子节点的权重值则下一个查找的节点为右子节点。如果下次迭代从右子节点开始查找对应的权重值,则需要将待查找的权重value减去左子节点的权重。
self._retrieve(successor_indices, successor_values)
反复迭代查找权重值,直到达到叶子节点。
参考文献:
https://www.cnblogs.com/pinard/p/9797695.html
分段树(segment tree)的实现 —— 强化学习中 "优先级回放机制" 的重要组成部分的更多相关文章
- 『线段树 Segment Tree』
更新了基础部分 更新了\(lazytag\)标记的讲解 线段树 Segment Tree 今天来讲一下经典的线段树. 线段树是一种二叉搜索树,与区间树相似,它将一个区间划分成一些单元区间,每个单元区间 ...
- 线段树(Segment Tree)(转)
原文链接:线段树(Segment Tree) 1.概述 线段树,也叫区间树,是一个完全二叉树,它在各个节点保存一条线段(即“子数组”),因而常用于解决数列维护问题,基本能保证每个操作的复杂度为O(lg ...
- 强化学习中的无模型 基于值函数的 Q-Learning 和 Sarsa 学习
强化学习基础: 注: 在强化学习中 奖励函数和状态转移函数都是未知的,之所以有已知模型的强化学习解法是指使用采样估计的方式估计出奖励函数和状态转移函数,然后将强化学习问题转换为可以使用动态规划求解的 ...
- 深度强化学习中稀疏奖励问题Sparse Reward
Sparse Reward 推荐资料 <深度强化学习中稀疏奖励问题研究综述>1 李宏毅深度强化学习Sparse Reward4 强化学习算法在被引入深度神经网络后,对大量样本的需求更加 ...
- 强化学习中REIINFORCE算法和AC算法在算法理论和实际代码设计中的区别
背景就不介绍了,REINFORCE算法和AC算法是强化学习中基于策略这类的基础算法,这两个算法的算法描述(伪代码)参见Sutton的reinforcement introduction(2nd). A ...
- BZOJ.4695.最假女选手(线段树 Segment tree Beats!)
题目链接 区间取\(\max,\ \min\)并维护区间和是普通线段树无法处理的. 对于操作二,维护区间最小值\(mn\).最小值个数\(t\).严格次小值\(se\). 当\(mn\geq x\)时 ...
- SpiningUP 强化学习 中文文档
2020 OpenAI 全面拥抱PyTorch, 全新版强化学习教程已发布. 全网第一个中文译本新鲜出炉:http://studyai.com/course/detail/ba8e572a 个人认为 ...
- 强化学习中的经验回放(The Experience Replay in Reinforcement Learning)
一.Play it again: reactivation of waking experience and memory(Trends in Neurosciences 2010) SWR发放模式不 ...
- 【数据结构系列】线段树(Segment Tree)
一.线段树的定义 线段树,又名区间树,是一种二叉搜索树. 那么问题来了,啥是二叉搜索树呢? 对于一棵二叉树,若满足: ①它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值 ②若它的右子树不空, ...
- 线段树(segment tree)
线段树在一些acm题目中经常见到,这种数据结构主要应用在计算几何和地理信息系统中.下图就为一个线段树: (PS:可能你见过线段树的不同表示方式,但是都大同小异,根据自己的需要来建就行.) 1.线段树基 ...
随机推荐
- 华为云短信服务教你用C++实现Smgp协议
本文分享自华为云社区<华为云短信服务教你用C++实现Smgp协议>,作者:张俭. 引言&协议概述 中国联合网络通信有限公司短消息网关系统接口协议(SGIP)是中国网通为实现短信业务 ...
- C++面向对象语言自制多级菜单
因为要做一个小应用,需要一个菜单类,在网上找了许久,也没有找到一款心仪的菜单类,索性用C++语言,自制一个命令行级别的菜单类,并制作成库,现记录下来,供以后借鉴. 一.特性 无限制条目 无限制层级 用 ...
- Idea克隆检出git项目
1.我这里假设你已经安装好了Idea和Git环境 2. .
- FinalReference 如何使 GC 过程变得拖拖拉拉
本文基于 OpenJDK17 进行讨论,垃圾回收器为 ZGC. 提示: 为了方便大家索引,特将在上篇文章 <以 ZGC 为例,谈一谈 JVM 是如何实现 Reference 语义的> 中讨 ...
- springboot+security自定义登录-1-基础-自定义用户和登录界面
为何学习spring security? 理由如下: 1)虽然可以不用,但难免部分客户又要求 2)某种程度上,security还是不错的,譬如csrf,oauth等等,省了一些功夫. 3)虽然spri ...
- 美团携手HarmonyOS SDK,开启便捷生活新篇章
华为开发者大会(HDC 2024)于6月21日在东莞松山湖拉开序幕,通过一系列精彩纷呈的主题演讲.峰会.专题论坛和互动体验,为开发者们带来了一场知识与技术的盛宴.6月23日,<HarmonyOS ...
- Linux 内核:设备树 学习总结
背景 之前写过设备树DTS 学习:学习总结(应用篇)的学习,但是是偏向于应用:这次针对了设备树的架构以及在驱动中的使用流程做了补充. 基于 Linux 内核 v4.14. 目录 标题 说明 设备树:d ...
- Linux 中 uid、gid、euid、egid、groups 之间的关系
导航 1 权限匹配流程 2 五种身份变化 3 有效用户/组 4 特权对 Shell 脚本无效 5 Sudo 与 SUID/SGID 的优先级 6 SUID.SGID.Sticky 各自的功能 Linu ...
- 3.8折钜惠,瑞芯微RK3568J国产工业评估板“限时折扣”!
- Spring的@Configuration和@Bean注解定义第三方bean
@Configuration和@Bean注解的使用 @Configuration标注在类上,相当于把该类作为spring的xml配置文件中<beans>,作用为:配置spring容器(应用 ...
