Qt开发技术:QCharts(四)QChart面积图介绍、Demo以及代码详解
若该文为原创文章,未经允许不得转载
原博主博客地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq21497936
原博主博客导航:https://blog.csdn.net/qq21497936/article/details/102478062
本文章博客地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq21497936/article/details/108240696
各位读者,知识无穷而人力有穷,要么改需求,要么找专业人士,要么自己研究
红胖子(红模仿)的博文大全:开发技术集合(包含Qt实用技术、树莓派、三维、OpenCV、OpenGL、ffmpeg、OSG、单片机、软硬结合等等)持续更新中…(点击传送门)
上一篇:《Qt开发技术:QCharts(三)QCharts样条曲线图介绍、Demo以及代码详解》
下一篇: 敬请期待…
前言
红胖子,来也!
按照顺序,本章为面积图。
补充
QCharts所有的图表都依赖《Qt开发技术:QCharts(一)QCharts基本介绍以及图表框架详解》中的QChart、QChartView、QLegend、QValueAxis。
Demo


Demo下载地址
当前为v1.1.0版本
CSDN:https://download.csdn.net/download/qq21497936/12753524
QQ群:1047134658(点击“文件”搜索“qChartsTools”,群内与博文同步更新)
面积图
概述
面积图是使用QAreaSeries类或AreaSeries QML类型实现的。默认情况下,X轴被用作一个边界和QLineSeries或线列作为另一个。但是,可以使用QLineSeries或LineSeries作为两个边界。
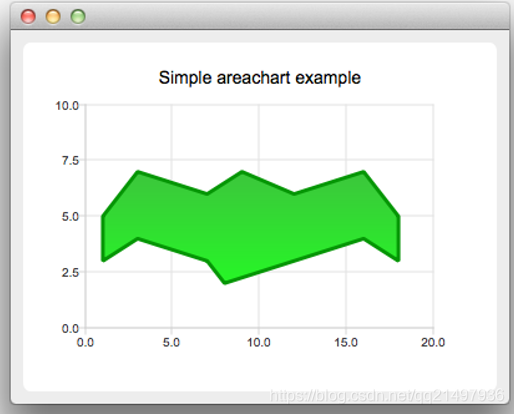
QAreaSeries(面积图类)
概述
QAreaSeries类在面积图中显示数据。
面积序列用于显示定量数据。它是基于一系列线,用颜色强调边界线之间的区域。由于区域序列基于行序列,QAreaSeries构造函数需要一个QLineSeries实例,该实例定义区域的上边界。默认情况下,使用绘图区域底部作为下边界绘制面积图。下边界可以由另一条线指定,而不是绘图区域的底部。在这种情况下,QAReaSeries应该用两个QLineSeries实例初始化。
注意:当下边界值大于上边界值时,术语上下边界可能会产生误导。重点是这两条边界线之间的区域将被填充。
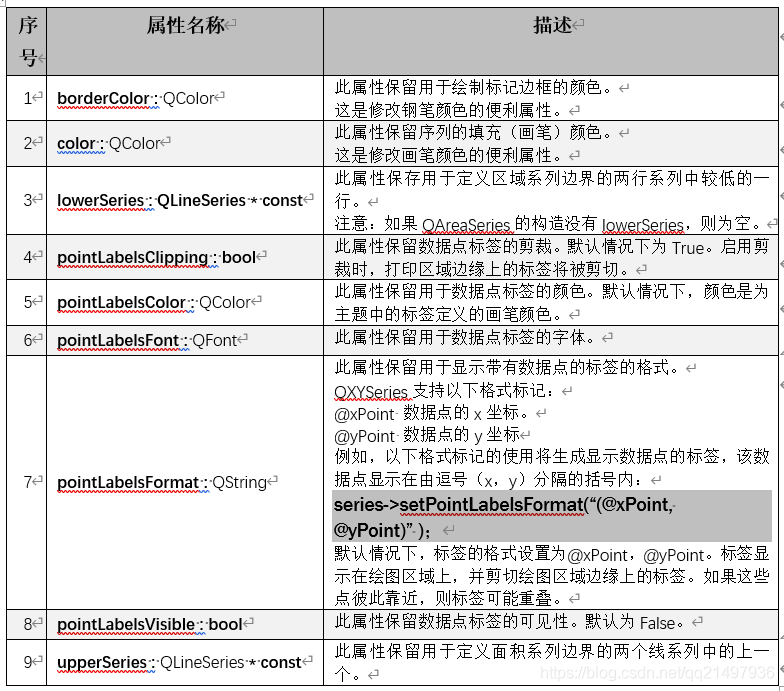
下面的代码片段说明了如何创建基本面积图:
_pLineSeries = new QLineSeries;
_pLineSeries2 = new QLineSeries;
_pLineSeries3 = new QLineSeries;
_pLineSeries4 = new QLineSeries;
// 方式一:逐一添加,大批量数据较慢
_pLineSeries->append(0, qrand()%11);
_pLineSeries->append(1, qrand()%11);
_pLineSeries->append(2, qrand()%11);
_pLineSeries->append(3, qrand()%11);
_pLineSeries->append(4, qrand()%11);
_pLineSeries->append(5, qrand()%11);
_pLineSeries->append(6, qrand()%11);
_pLineSeries->append(7, qrand()%11);
_pLineSeries->append(8, qrand()%11);
_pLineSeries->append(9, qrand()%11);
_pLineSeries->append(10, qrand()%11);
_pLineSeries->setName("通道1");
_pLineSeries->setPen(QPen(QColor(qrand()%256, qrand()%256, qrand()%256), 2));
// 通用:将数据插入到图表中
_pAreaSeries = new QAreaSeries();
_pAreaSeries->setName("面积1");
_pLineSeries->setPointsVisible(true);
_pLineSeries->setPointLabelsFormat("(@xPoint,@yPoint)");
_pAreaSeries->setUpperSeries(_pLineSeries);
_pChart->addSeries(_pAreaSeries);
效率更高的方式为:
// 方式二:逐一添加,大批量数据插入
QList<QLineSeries *> list;
list.append(_pLineSeries);
list.append(_pLineSeries2);
list.append(_pLineSeries3);
list.append(_pLineSeries4);
for(int index = 0; index < 4; index++)
{
QList<QPointF> listPointF;
for(int index = 0; index < 11; index++)
{
listPointF << QPointF(index, qrand()%11);
}
list.at(index)->append(listPointF);
list.at(index)->setName(QString("通道%1").arg(index+1));
list.at(index)->setPen(QPen(QColor(qrand()%256, qrand()%256, qrand()%256), 2));
}
// 通用:将数据插入到图表中
_pAreaSeries = new QAreaSeries();
_pAreaSeries->setName("面积1");
_pLineSeries->setPointsVisible(true);
_pLineSeries->setPointLabelsFormat("(@xPoint,@yPoint)");
_pAreaSeries->setUpperSeries(_pLineSeries);
_pChart->addSeries(_pAreaSeries);
_pAreaSeries2 = new QAreaSeries();
_pAreaSeries2->setName("面积2");
_pAreaSeries2->setUpperSeries(_pLineSeries2);
_pChart->addSeries(_pAreaSeries2);
_pAreaSeries3 = new QAreaSeries();
_pAreaSeries3->setName("面积3");
_pAreaSeries3->setUpperSeries(_pLineSeries3);
_pAreaSeries3->setLowerSeries(_pLineSeries2);
_pChart->addSeries(_pAreaSeries3);
_pAreaSeries4 = new QAreaSeries();
_pAreaSeries4->setName("面积4");
_pAreaSeries4->setUpperSeries(_pLineSeries4);
_pAreaSeries4->setLowerSeries(_pLineSeries3);
_pChart->addSeries(_pAreaSeries4);
Demo核心代码解析
建立QChart显示框架
AreaChartWidget::AreaChartWidget(QWidget *parent) :
QWidget(parent),
_pChartView(0),
_pChart(0),
_pXValueAxis(0),
_pYValueAxis(0),
_pLegend(0),
_pLineSeries(0),
_pLineSeries2(0),
_pLineSeries3(0),
_pLineSeries4(0),
_pAreaSeries(0),
_pAreaSeries2(0),
_pAreaSeries3(0),
_pAreaSeries4(0)
{
_pChartView = new QChartView(this);
_pChart = new QChart();
initData();
}
初始化数据
void AreaChartWidget::initData()
{
_pLineSeries = new QLineSeries;
_pLineSeries2 = new QLineSeries;
_pLineSeries3 = new QLineSeries;
_pLineSeries4 = new QLineSeries;
// 方式一:逐一添加,大批量数据较慢
_pLineSeries->append(0, qrand()%11);
_pLineSeries->append(1, qrand()%11);
_pLineSeries->append(2, qrand()%11);
_pLineSeries->append(3, qrand()%11);
_pLineSeries->append(4, qrand()%11);
_pLineSeries->append(5, qrand()%11);
_pLineSeries->append(6, qrand()%11);
_pLineSeries->append(7, qrand()%11);
_pLineSeries->append(8, qrand()%11);
_pLineSeries->append(9, qrand()%11);
_pLineSeries->append(10, qrand()%11);
_pLineSeries->setName("通道1");
_pLineSeries->setPen(QPen(QColor(qrand()%256, qrand()%256, qrand()%256), 2));
// 通用:将数据插入到图表中
_pAreaSeries = new QAreaSeries();
_pAreaSeries->setName("面积1");
_pLineSeries->setPointsVisible(true);
_pLineSeries->setPointLabelsFormat("(@xPoint,@yPoint)");
_pAreaSeries->setUpperSeries(_pLineSeries);
_pChart->addSeries(_pAreaSeries);
// 方式二:逐一添加,大批量数据插入
QList<QLineSeries *> list;
list.append(_pLineSeries);
list.append(_pLineSeries2);
list.append(_pLineSeries3);
list.append(_pLineSeries4);
for(int index = 1; index < 4; index++)
{
QList<QPointF> listPointF;
for(int index = 0; index < 11; index++)
{
listPointF << QPointF(index, qrand()%11);
}
list.at(index)->append(listPointF);
list.at(index)->setName(QString("通道%1").arg(index+1));
list.at(index)->setPen(QPen(QColor(qrand()%256, qrand()%256, qrand()%256), 2));
}
// 通用:将数据插入到图表中
_pAreaSeries2 = new QAreaSeries();
_pAreaSeries2->setName("面积2");
_pAreaSeries2->setUpperSeries(_pLineSeries2);
_pChart->addSeries(_pAreaSeries2);
_pAreaSeries3 = new QAreaSeries();
_pAreaSeries3->setName("面积3");
_pAreaSeries3->setUpperSeries(_pLineSeries3);
_pAreaSeries3->setLowerSeries(_pLineSeries2);
_pChart->addSeries(_pAreaSeries3);
_pAreaSeries4 = new QAreaSeries();
_pAreaSeries4->setName("面积4");
_pAreaSeries4->setUpperSeries(_pLineSeries4);
_pAreaSeries4->setLowerSeries(_pLineSeries3);
_pChart->addSeries(_pAreaSeries4);
// 通用:X轴和Y轴的处理(先插入数据再处理轴,否则不会有轴)
_pChart->createDefaultAxes();
_pYValueAxis = dynamic_cast<QValueAxis *>(_pChart->axisY());
// _pYValueAxis = new QValueAxis(_pChart);
_pYValueAxis->setRange(0, 10);
_pYValueAxis->setLinePen(QPen(Qt::black, 1));
// tick
_pYValueAxis->setTickCount(5);
_pYValueAxis->setGridLinePen(QPen(Qt::gray, 1));
_pYValueAxis->setGridLineVisible(true);
// subTick
_pYValueAxis->setMinorTickCount(4);
_pYValueAxis->setMinorGridLineVisible(true);
_pYValueAxis->setLabelFormat("%d");
// _pChart->addAxis(_pYValueAxis, Qt::AlignLeft);
_pXValueAxis = dynamic_cast<QValueAxis *>(_pChart->axisX());
// _pXValueAxis = new QValueAxis(_pChart);
_pXValueAxis->setRange(0, 10);
_pXValueAxis->setLinePen(QPen(Qt::black, 1));
// tick
_pXValueAxis->setTickCount(5);
_pXValueAxis->setGridLinePen(QPen(Qt::gray, 1));
_pXValueAxis->setGridLineVisible(true);
// subTick
_pXValueAxis->setMinorTickCount(4); // 相反
_pXValueAxis->setMinorGridLineVisible(true);
_pXValueAxis->setLabelFormat("%d s");
// _pChart->addAxis(_pXValueAxis, Qt::AlignBottom);
// 通用:视图显示设置为图表
_pChartView->setRubberBand(QChartView::NoRubberBand); // 不缩放
_pChartView->setDragMode(QChartView::NoDrag); // 拽拖:需要自己重写QCharView
_pChartView->setChart(_pChart);
// 标识
_pLegend = _pChart->legend();
_pLegend->setAlignment(Qt::AlignRight);
// 平滑
_pChartView->setRenderHint(QPainter::Antialiasing, true);
// 阴影
_pChart->setDropShadowEnabled(true);
}
设置数据线是否显示(标签显示会同步)
void AreaChartWidget::setDataVisible(int index, bool visible)
{
if(index < 0 || index > 3)
{
return;
}
QList<QAreaSeries *> list;
list.append(_pAreaSeries);
list.append(_pAreaSeries2);
list.append(_pAreaSeries3);
list.append(_pAreaSeries4);
list.at(index)->setVisible(visible);
}
设置主题样式
void AreaChartWidget::setTheme(QChart::ChartTheme theme)
{
_pChart->setTheme(theme);
}
设置动画模式
void AreaChartWidget::setAnimationOptions(QChart::AnimationOption option)
{
_pChart->setAnimationOptions(option);
}
设置标签显示位置
void AreaChartWidget::setAlignment(Qt::Alignment align)
{
_pLegend->setAlignment(align);
}
设置标签是否可见
void AreaChartWidget::setLegendVisible(bool visible)
{
_pLegend->setVisible(visible);
_pChartView->setRenderHint(QPainter::Antialiasing);
}
设置是否绘制平滑
void AreaChartWidget::setAntialiasing(bool antialiasing)
{
_pChartView->setRenderHint(QPainter::Antialiasing, antialiasing);
}
设置是否有阴影
void AreaChartWidget::setShadow(bool shadow)
{
_pChart->setDropShadowEnabled(shadow);
}
是否显示数据点(新增)
void AreaChartWidget::setPointVisible(bool visible)
{
_pAreaSeries->setPointsVisible(visible);
_pAreaSeries2->setPointsVisible(visible);
_pAreaSeries3->setPointsVisible(visible);
_pAreaSeries4->setPointsVisible(visible);
}
是否显示数据点坐标(新增)
void AreaChartWidget::setPointLabelVisible(bool visible)
{
_pAreaSeries->setPointLabelsFormat("(@xPoint,@yPoint)");
_pAreaSeries->setPointLabelsVisible(visible);
_pAreaSeries2->setPointLabelsFormat("(@xPoint,@yPoint)");
_pAreaSeries2->setPointLabelsVisible(visible);
_pAreaSeries3->setPointLabelsFormat("(@xPoint,@yPoint)");
_pAreaSeries3->setPointLabelsVisible(visible);
_pAreaSeries4->setPointLabelsFormat("(@xPoint,@yPoint)");
_pAreaSeries4->setPointLabelsVisible(visible);
}
重置随机数据
void AreaChartWidget::resetData()
{
_pChart->removeAllSeries();
_pLineSeries = new QLineSeries;
_pLineSeries2 = new QLineSeries;
_pLineSeries3 = new QLineSeries;
_pLineSeries4 = new QLineSeries;
QList<QLineSeries *> list;
list.append(_pLineSeries);
list.append(_pLineSeries2);
list.append(_pLineSeries3);
list.append(_pLineSeries4);
for(int index = 0; index < 4; index++)
{
QList<QPointF> listPointF;
for(int index = 0; index < 11; index++)
{
listPointF << QPointF(index, qrand()%11);
}
list.at(index)->append(listPointF);
list.at(index)->setName(QString("通道%1").arg(index+1));
list.at(index)->setPen(QPen(QColor(qrand()%256, qrand()%256, qrand()%256), 2));
}
_pAreaSeries = new QAreaSeries();
_pAreaSeries->setName("面积1");
_pAreaSeries->setUpperSeries(_pLineSeries);
_pAreaSeries2 = new QAreaSeries();
_pAreaSeries->setName("面积2");
_pAreaSeries2->setUpperSeries(_pLineSeries2);
_pChart->addSeries(_pAreaSeries2);
_pAreaSeries3 = new QAreaSeries();
_pAreaSeries3->setName("面积3");
_pAreaSeries3->setUpperSeries(_pLineSeries3);
_pAreaSeries3->setLowerSeries(_pLineSeries2);
_pChart->addSeries(_pAreaSeries3);
_pAreaSeries4 = new QAreaSeries();
_pAreaSeries4->setName("面积4");
_pAreaSeries4->setUpperSeries(_pLineSeries3);
_pAreaSeries4->setLowerSeries(_pLineSeries4);
_pChart->addSeries(_pAreaSeries4);
_pChart->addSeries(_pAreaSeries);
resetColor();
}
初始化颜色
void AreaChartWidget::resetColor()
{
QList<QLineSeries *> list;
list.append(_pLineSeries);
list.append(_pLineSeries2);
list.append(_pLineSeries3);
list.append(_pLineSeries4);
for(int index = 0; index < list.size(); index++)
{
list.at(index)->setColor(QColor(qrand()%256, qrand()%256, qrand()%256));
}
}
工程模板:对应版本号v1.1.0
对应版本号v1.1.0
增加面积图
对折线图、曲线图和面积图增加数据点显示、数据点标签显示
上一篇:《Qt开发技术:QCharts(三)QCharts样条曲线图介绍、Demo以及代码详解》
下一篇: 敬请期待…
Qt开发技术:QCharts(四)QChart面积图介绍、Demo以及代码详解的更多相关文章
- Qt开发技术:QCharts(三)QCharts样条曲线图介绍、Demo以及代码详解
若该文为原创文章,未经允许不得转载原博主博客地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq21497936原博主博客导航:https://blog.csdn.net/qq21497936/ar ...
- Qt开发技术:Q3D图表开发笔记(三):Q3DSurface三维曲面图介绍、Demo以及代码详解
前言 qt提供了q3d进行三维开发,虽然这个框架没有得到大量运用也不是那么成功,性能上也有很大的欠缺,但是普通的点到为止的应用展示还是可以的. 其中就包括华丽绚烂的三维图表,数据量不大的时候是可 ...
- FFmpeg开发笔记(四):ffmpeg解码的基本流程详解
若该文为原创文章,未经允许不得转载原博主博客地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq21497936原博主博客导航:https://blog.csdn.net/qq21497936/ar ...
- Qt开发技术:Q3D图表开发笔记(一):Q3DScatter三维散点图介绍、Demo以及代码详解
前言 qt提供了q3d进行三维开发,虽然这个框架没有得到大量运用也不是那么成功,性能上也有很大的欠缺,但是普通的点到为止的应用展示还是可以的. 其中就包括华丽绚烂的三维图表,数据量不大的时候是可 ...
- Qwt开发笔记(二):Qwt基础框架介绍、折线图介绍、折线图Demo以及代码详解
前言 QWT开发笔记系列整理集合,这是目前使用最为广泛的Qt图表类(Qt的QWidget代码方向只有QtCharts,Qwt,QCustomPlot),使用多年,系统性的整理,本系列旨在系统解说并 ...
- FFmpeg开发笔记(五):ffmpeg解码的基本流程详解(ffmpeg3新解码api)
若该文为原创文章,未经允许不得转载原博主博客地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq21497936原博主博客导航:https://blog.csdn.net/qq21497936/ar ...
- Qt开发技术:图形视图框架(二)场景QGraphicsScene、QGraphicsItem与QGraphicsView详解
前话 Qt的图形视图框架,最核心的三个类为:QGraphicsScene.QGraphicsItem与QGraphicsView. 基于图形框架的高级白板软件Demo QGraphicsSce ...
- “全栈2019”Java第一百零四章:匿名内部类与外部成员互访详解
难度 初级 学习时间 10分钟 适合人群 零基础 开发语言 Java 开发环境 JDK v11 IntelliJ IDEA v2018.3 文章原文链接 "全栈2019"Java第 ...
- ARM Cortex-M底层技术(2)—启动代码详解
杂谈 工作了一天,脑袋比较乱.一直想把底层的知识写成一个系列,希望可以坚持下去.为什么要写底层的东西呢?首先,工作用到了这部分内容,最近和内部Flash打交道比较多,自然而然会接触到一些底层的东西:第 ...
- 【转】UML类图与类的关系详解
UML类图与类的关系详解 2011-04-21 来源:网络 在画类图的时候,理清类和类之间的关系是重点.类的关系有泛化(Generalization).实现(Realization).依赖(D ...
随机推荐
- Jmeter学习之三_知识梳理
Jmeter学习之三_知识梳理 背景 简单学习了Jmeter的两个用例 感觉可以继续深入学习一下Jmeter了. 所以想着趁体检入职之前继续学习完善一下. 希望能够继续提高 Jmeter的相关知识 1 ...
- redis 设置密码之后,通过命令行一键刷新的办法
之前以为很麻烦 发现还是自己太low了. redis-cli -a Test1127 flushall
- 基于华为fusionstorage的块存储CSI
承接上文,块存储的CSI要比对象存储复杂一些,但总的处理逻辑还是一致的.下面以华为fusionstorage的CSI为例进行介绍,该插件支持了多个后端存储,如fusionstorage和oceanst ...
- 【团队效率提升】Python-PyWebIO介绍
作者:京东零售 关键 Q&A快速了解PyWebIO Q:首先,什么是PyWebIO? A:PyWebIO提供了一系列命令式的交互函数,能够让咱们用只用Python就可以编写 Web 应用, 不 ...
- Java单元测试浅析(JUnit+Mockito)
作者:京东物流 秦彪 1. 什么是单元测试 (1)单元测试环节: 测试过程按照阶段划分分为:单元测试.集成测试.系统测试.验收测试等.相关含义如下: 1) 单元测试: 针对计算机程序模块进 ...
- 如何处理开发环境没有问题,线上环境有问题这个bug
解决思路 首先确认开发环境有没有这个问题: 如果没有这个问题: 将你的地址切换为线上的环境,看看线上环境有没有这个问题: 如果切换为线上环境有这个问题,就可以调试了: 如果切换为线上环境没有这个问题, ...
- Go-操作redis/redigo
目录 Go-操作redis 安装 连接 使用 设置key过期时间 批量获取mget.批量设置mset 列表操作 hash操作 Pipelining(管道) redis发布会订阅模式 事务操作 万能操作 ...
- Gin 应用多实例部署session问题、session参数与刷新
目录 一.Gin Session 存储的实现方案 二.memstore:基于内存的实现 2.1 基本使用 2.2 关键参数 三.使用redis:多实例部署 3.1 使用redis优势 3.2 基本使用 ...
- 设计模式学习-使用go实现备忘录模式
备忘录模式 定义 优点 缺点 适用范围 代码实现 参考 备忘录模式 定义 备忘录( Memento ):在不破坏封装性的前提下,获取一个对象的内部状态,并在该对象之处保存该状态.这样以后就可将该对象恢 ...
- P9816 少项式复合幂 题解
题目链接:少项式复合幂 注意到题目的模并不是很大,我们考虑两个核心的性质. \(f(f(x)) \bmod p=f(f(x) \bmod p) \bmod p\),证明直接代入 \(f(x)\) 进去 ...
