Python自学笔记——Matplotlib风羽自定义
【前言】对于气象专业的小学生来说,风场是预报重要的参考数据,我们所知的风羽有四种:短线代表风速2m/s,长线代表风速4m/s,空心三角代表风速20m/s,实心三角代表风速50m/s。而matplotlib的风羽只有短线、长线、三角三种,而这里的三角不分空心实心,但是可通过改变风羽颜色为白色使三角变为空心形状,虽然这三种可以自定义各自代表的风速,但是仍与我们的使用习惯不符,即使把三角设成20m/s,原本一个实心三角就能表示的50m/s的风在matplotlib中需要两个三角外加两条长线一条短线。为了迎合预报员的需求,我在研究了matplotlib的风场函数barbs()的源代码quiver.py文件后,对quiver.py做了适当的调整,使得matplotlib也有了空心三角和实心三角之分。
一、函数barbs的使用
barb(X, Y, U, V,, **kw)
X:风场数据X坐标
Y:风场数据Y坐标
U:风的水平方向分量
V:风的垂直方向分量
'''
Demonstration of wind barb plots
'''
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.linspace(-5, 5, 5)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, x)
U, V = 12*X, 12*Y
data = [(-1.5, .5, -6, -6),(1, -1, -46, 46),(-3, -1, 11, -11),(1, 1.5, 80, 80),(0.5, 0.25, 25, 15),(-1.5, -0.5, -5, 40)]
data = np.array(data, dtype=[('x', np.float32), ('y', np.float32), ('u', np.float32), ('v', np.float32)])
# Default parameters, uniform grid
ax = plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
ax.barbs(X, Y, U, V)
# Arbitrary set of vectors, make them longer and change the pivot point
#(point around which they're rotated) to be the middle
ax = plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
ax.barbs(data['x'], data['y'], data['u'], data['v'], length=8, pivot='middle')
# Showing colormapping with uniform grid. Fill the circle for an empty barb,
# don't round the values, and change some of the size parameters
ax = plt.subplot(2, 2, 3)
ax.barbs(X, Y, U, V, np.sqrt(U*U + V*V), fill_empty=True, rounding=False,sizes=dict(emptybarb=0.25, spacing=0.2, height=0.3))
# Change colors as well as the increments for parts of the barbs
ax = plt.subplot(2, 2, 4)
ax.barbs(data['x'], data['y'], data['u'], data['v'], flagcolor='r',barbcolor=['b', 'g'], barb_increments=dict(half=10, full=20, flag=100),flip_barb=True)
plt.show()

二、源代码解读
1.class Barbs()
class Barbs(mcollections.PolyCollection):
@docstring.interpd
def __init__(self, ax, *args, **kw):
'...'
def _find_tails(self, mag, rounding=True, half=5, full=10, flag=50):
'...'
def _make_barbs(self, u, v, nflags, nbarbs, half_barb, empty_flag, length,pivot, sizes, fill_empty, flip):
'...'
def set_UVC(self, U, V, C=None):
'...'
def set_offsets(self, xy):
'...'
- 通过读源代码可知类Barbs有五个方法分别为
__init__、_find_tails、_make_barbs、set_UVC、set_offsets。
2.__init__
@docstring.interpd
def __init__(self, ax, *args, **kw):
"""
The constructor takes one required argument, an Axes
instance, followed by the args and kwargs described
by the following pylab interface documentation:
%(barbs_doc)s
"""
self._pivot = kw.pop('pivot', 'tip')
self._length = kw.pop('length', 7)
barbcolor = kw.pop('barbcolor', None)
flagcolor = kw.pop('flagcolor', None)
self.sizes = kw.pop('sizes', dict())
self.fill_empty = kw.pop('fill_empty', False)
self.barb_increments = kw.pop('barb_increments', dict())
self.rounding = kw.pop('rounding', True)
self.flip = kw.pop('flip_barb', False)
transform = kw.pop('transform', ax.transData)
# Flagcolor and and barbcolor provide convenience parameters for
# setting the facecolor and edgecolor, respectively, of the barb
# polygon. We also work here to make the flag the same color as the
# rest of the barb by default
if None in (barbcolor, flagcolor):
kw['edgecolors'] = 'face'
if flagcolor:
kw['facecolors'] = flagcolor
elif barbcolor:
kw['facecolors'] = barbcolor
else:
# Set to facecolor passed in or default to black
kw.setdefault('facecolors', 'k')
else:
kw['edgecolors'] = barbcolor
kw['facecolors'] = flagcolor
# Parse out the data arrays from the various configurations supported
x, y, u, v, c = _parse_args(*args)
self.x = x
self.y = y
xy = np.hstack((x[:, np.newaxis], y[:, np.newaxis]))
# Make a collection
barb_size = self._length ** 2 / 4 # Empirically determined
mcollections.PolyCollection.__init__(self, [], (barb_size,),
offsets=xy,
transOffset=transform, **kw)
self.set_transform(transforms.IdentityTransform())
self.set_UVC(u, v, c)
__init__()方法为初始化方法,此方法中flagcolor、barbcolor为设置风羽颜色的关键字,中间的说明文字提示颜色设置是针对所有的风羽的,所以通过颜色设置达不到风羽中既有空心白色三角又有实心黑色三角。初始化方法中在对一些参数进行了初始化赋值后执行了set_UVC()方法,所以我们顺着这个set_UVC()方法往下继续读。
3.set_UVC()
def set_UVC(self, U, V, C=None):
self.u = ma.masked_invalid(U, copy=False).ravel()
self.v = ma.masked_invalid(V, copy=False).ravel()
if C is not None:
c = ma.masked_invalid(C, copy=False).ravel()
x, y, u, v, c = delete_masked_points(self.x.ravel(),
self.y.ravel(),
self.u, self.v, c)
else:
x, y, u, v = delete_masked_points(self.x.ravel(), self.y.ravel(),
self.u, self.v)
magnitude = np.hypot(u, v)
flags, emptyflags,barbs, halves, empty = self._find_tails(magnitude,
self.rounding,
**self.barb_increments)
# Get the vertices for each of the barbs
plot_barbs = self._make_barbs(u, v, flags, emptyflags,barbs, halves, empty,
self._length, self._pivot, self.sizes,
self.fill_empty, self.flip)
self.set_verts(plot_barbs)
# Set the color array
if C is not None:
self.set_array(c)
# Update the offsets in case the masked data changed
xy = np.hstack((x[:, np.newaxis], y[:, np.newaxis]))
self._offsets = xy
self.stale = True
- 在此方法中,首先进行了变量的命名赋值,然后依次执行了方法
_find_tails和_make_barbs。_make_barbs的输入为_find_tails的输出,_find_tails的输入中有一个为magnitude = np.hypot(u, v),np.hypot()为勾股定理方法,因此可知magnitude为风速。
4._find_tails
def _find_tails(self, mag, rounding=True, half=5, full=10, flag=50):
'''
Find how many of each of the tail pieces is necessary. Flag
specifies the increment for a flag, barb for a full barb, and half for
half a barb. Mag should be the magnitude of a vector (i.e., >= 0).
This returns a tuple of:
(*number of flags*, *number of barbs*, *half_flag*, *empty_flag*)
*half_flag* is a boolean whether half of a barb is needed,
since there should only ever be one half on a given
barb. *empty_flag* flag is an array of flags to easily tell if
a barb is empty (too low to plot any barbs/flags.
'''
# If rounding, round to the nearest multiple of half, the smallest
# increment
if rounding:
mag = half * (mag / half + 0.5).astype(np.int)
num_flags = np.floor(mag / flag).astype(np.int)
mag = np.mod(mag, flag)
num_barb = np.floor(mag / full).astype(np.int)
mag = np.mod(mag, full)
half_flag = mag >= half
empty_flag = ~(half_flag | (num_flags > 0) | (num_emptyflags > 0) |(num_barb > 0))
return num_flags,num_barb, half_flag, empty_flag
- 通过读此方法的说明文档可知,此方法作用为根据输入的风速、设置的短线长线三角的数值计算并返回三角、长线、短线的个数以及有没有无风的情况。
5._make_barbs
def _make_barbs(self, u, v, nflags, nbarbs, half_barb, empty_flag, length,
pivot, sizes, fill_empty, flip):
'''
This function actually creates the wind barbs. *u* and *v*
are components of the vector in the *x* and *y* directions,
respectively.
*nflags*, *nbarbs*, and *half_barb*, empty_flag* are,
*respectively, the number of flags, number of barbs, flag for
*half a barb, and flag for empty barb, ostensibly obtained
*from :meth:`_find_tails`.
*length* is the length of the barb staff in points.
*pivot* specifies the point on the barb around which the
entire barb should be rotated. Right now, valid options are
'head' and 'middle'.
*sizes* is a dictionary of coefficients specifying the ratio
of a given feature to the length of the barb. These features
include:
- *spacing*: space between features (flags, full/half
barbs)
- *height*: distance from shaft of top of a flag or full
barb
- *width* - width of a flag, twice the width of a full barb
- *emptybarb* - radius of the circle used for low
magnitudes
*fill_empty* specifies whether the circle representing an
empty barb should be filled or not (this changes the drawing
of the polygon).
*flip* is a flag indicating whether the features should be flipped to
the other side of the barb (useful for winds in the southern
hemisphere.
This function returns list of arrays of vertices, defining a polygon
for each of the wind barbs. These polygons have been rotated to
properly align with the vector direction.
'''
# These control the spacing and size of barb elements relative to the
# length of the shaft
spacing = length * sizes.get('spacing', 0.125)
full_height = length * sizes.get('height', 0.4)
full_width = length * sizes.get('width', 0.25)
empty_rad = length * sizes.get('emptybarb', 0.15)
# Controls y point where to pivot the barb.
pivot_points = dict(tip=0.0, middle=-length / 2.)
# Check for flip
if flip:
full_height = -full_height
endx = 0.0
endy = pivot_points[pivot.lower()]
# Get the appropriate angle for the vector components. The offset is
# due to the way the barb is initially drawn, going down the y-axis.
# This makes sense in a meteorological mode of thinking since there 0
# degrees corresponds to north (the y-axis traditionally)
angles = -(ma.arctan2(v, u) + np.pi / 2)
# Used for low magnitude. We just get the vertices, so if we make it
# out here, it can be reused. The center set here should put the
# center of the circle at the location(offset), rather than at the
# same point as the barb pivot; this seems more sensible.
circ = CirclePolygon((0, 0), radius=empty_rad).get_verts()
if fill_empty:
empty_barb = circ
else:
# If we don't want the empty one filled, we make a degenerate
# polygon that wraps back over itself
empty_barb = np.concatenate((circ, circ[::-1]))
barb_list = []
for index, angle in np.ndenumerate(angles):
# If the vector magnitude is too weak to draw anything, plot an
# empty circle instead
if empty_flag[index]:
# We can skip the transform since the circle has no preferred
# orientation
barb_list.append(empty_barb)
continue
poly_verts = [(endx, endy)]
offset = length
# Add vertices for each flag
for i in range(nflags[index]):
# The spacing that works for the barbs is a little to much for
# the flags, but this only occurs when we have more than 1
# flag.
if offset != length:
offset += spacing / 2.
poly_verts.extend(
[[endx, endy + offset],
[endx + full_height, endy - full_width / 2 + offset],
[endx, endy - full_width + offset]])
offset -= full_width + spacing
# Add vertices for each barb. These really are lines, but works
# great adding 3 vertices that basically pull the polygon out and
# back down the line
for i in range(nbarbs[index]):
poly_verts.extend(
[(endx, endy + offset),
(endx + full_height, endy + offset + full_width / 2),
(endx, endy + offset)])
offset -= spacing
# Add the vertices for half a barb, if needed
if half_barb[index]:
# If the half barb is the first on the staff, traditionally it
# is offset from the end to make it easy to distinguish from a
# barb with a full one
if offset == length:
poly_verts.append((endx, endy + offset))
offset -= 1.5 * spacing
poly_verts.extend(
[(endx, endy + offset),
(endx + full_height / 2, endy + offset + full_width / 4),
(endx, endy + offset)])
# Rotate the barb according the angle. Making the barb first and
# then rotating it made the math for drawing the barb really easy.
# Also, the transform framework makes doing the rotation simple.
poly_verts = transforms.Affine2D().rotate(-angle).transform(
poly_verts)
barb_list.append(poly_verts)
return barb_list
- 通过读此方法的说明文档可知,此方法作用为根据输入的风数据以及短线长线三角的个数绘制风羽风向杆。
- 绘制过程为:判断地图坐标点是不是无风,如果无风就绘制一个空心圆圈代表。如果有风就开始按照三角、长线、短线的顺序绘制。
- 绘制方法为:
- 创建一个用于存储关键点坐标的列表
poly_verts - 计算关键点坐标
- 通过
transform方法将关键点坐标列表中的各个关键点依次用黑线连接起来,最终将风羽风向杆绘制出来
- 此方法的几个关键变量:
spacing:风羽上短线长线以及三角间的距离full_height:三角的高度full_width:三角的宽度endx:风羽绘制的起始点x坐标endy:风羽绘制的起始点y坐标angles:风向杆角度poly_verts:绘制风羽风向杆的关键点列表offset:绘制完一个三角或线后下一个三角或线的关键起始坐标
poly_verts = [(endx, endy)]
offset = length
# Add vertices for each flag
for i in range(nflags[index]):
# The spacing that works for the barbs is a little to much for
# the flags, but this only occurs when we have more than 1
# flag.
if offset != length:
offset += spacing / 2.
poly_verts.extend(
[[endx, endy + offset],
[endx + full_height, endy - full_width / 2 + offset],
[endx, endy - full_width + offset]])
offset -= full_width + spacing
- 这一段是绘制风羽的主要代码,利用图片的形式说明
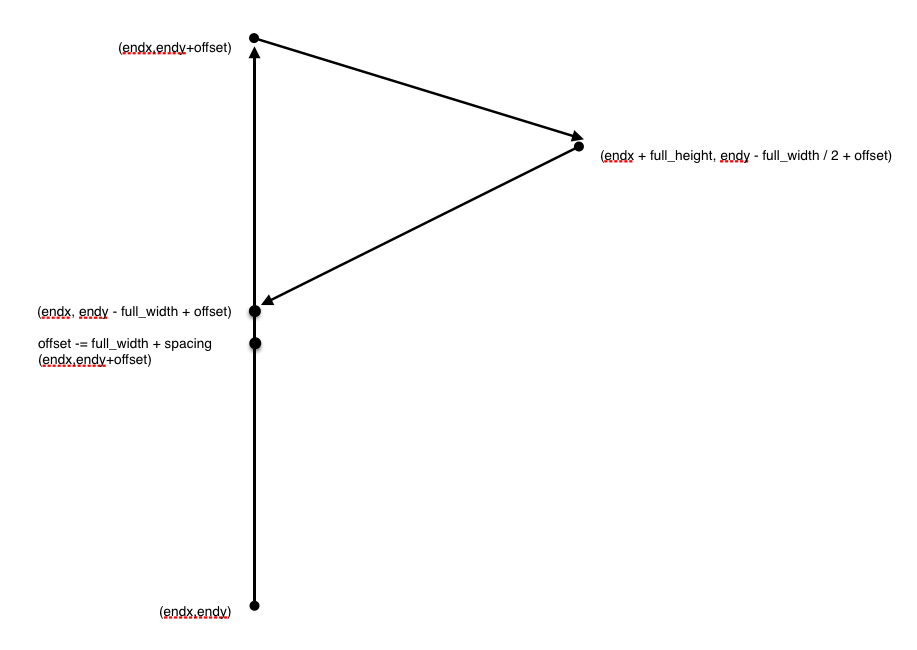
三、绘制空心实心三角
在了解了风羽的绘制过程后,发现可以通过增加关键点直接绘制实心三角,通过原绘制方法绘制空心三角。
1.实心三角绘制
- 实心三角绘制代码
# Add vertices for each flag
for i in range(nflags[index]):
# The spacing that works for the barbs is a little to much for
# the flags, but this only occurs when we have more than 1
# flag.
if offset != length:
offset += spacing / 2.
poly_verts.extend(
[[endx, endy + offset],
[endx + full_height/4, endy - full_width / 8 + offset],
[endx, endy - full_width / 8 + offset],
[endx + full_height/4, endy - full_width / 8 + offset],
[endx + full_height/2, endy - full_width / 4 + offset],
[endx, endy - full_width / 4 + offset],
[endx + full_height/2, endy - full_width / 4 + offset],
[endx + 3*full_height/4, endy - 3*full_width / 8 + offset],
[endx, endy - 3*full_width / 8 + offset],
[endx + 3*full_height/4, endy - 3*full_width / 8 + offset],
[endx + full_height, endy - full_width / 2 + offset],
[endx,endy-full_width/2+offset],
[endx + full_height, endy - full_width / 2 + offset],
[endx + 3*full_height/4, endy - 5*full_width / 8 + offset],
[endx, endy - 5*full_width / 8 + offset],
[endx + 3*full_height/4, endy - 5*full_width / 8 + offset],
[endx + full_height/2, endy - 3*full_width / 4 + offset],
[endx, endy - 3*full_width / 4 + offset],
[endx + full_height/2, endy - 3*full_width / 4 + offset],
[endx + full_height/4, endy - 7*full_width / 8 + offset],
[endx, endy - 7*full_width / 8 + offset],
[endx + full_height/4, endy - 7*full_width / 8 + offset],
[endx, endy - full_width + offset]])
offset -= full_width + spacing
实心三角绘制示意图
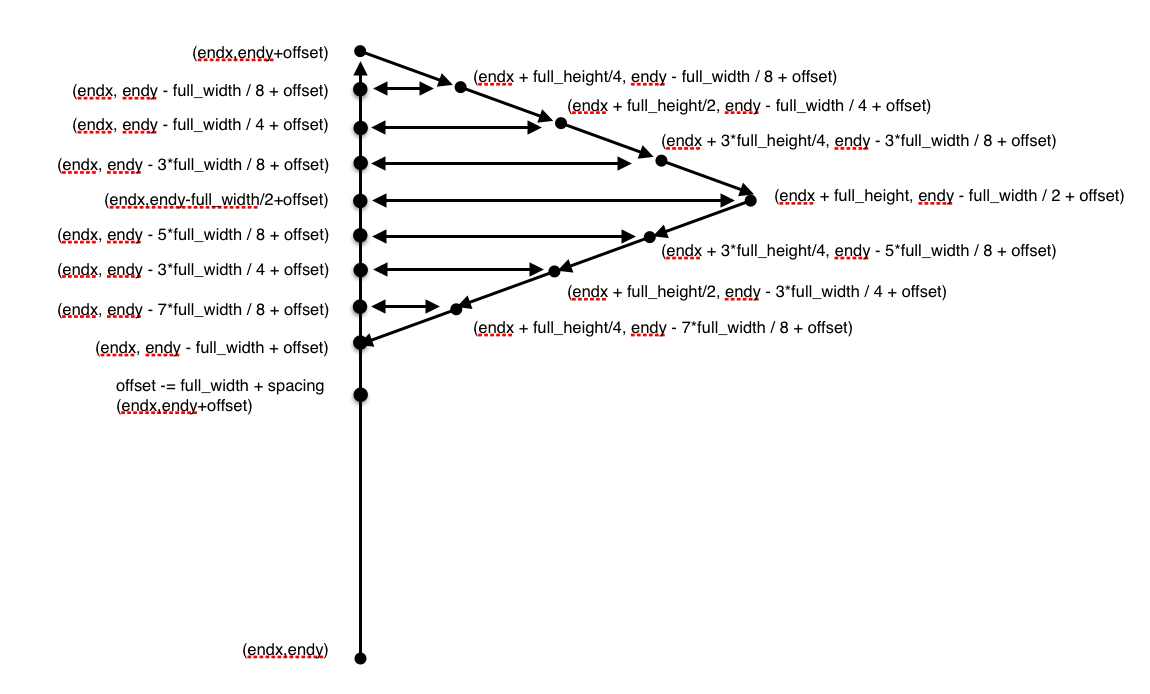
方法参数中加入nfullflags
def _make_barbs(self, u, v, nfullflags, nflags,nbarbs, half_barb, empty_flag, length,pivot, sizes, fill_empty, flip):
'...'
2.实心三角个数计算
def _find_tails(self, mag, rounding=True, half=2, full=4, flag=20,fullflag=50):
'''
Find how many of each of the tail pieces is necessary. Flag
specifies the increment for a flag, barb for a full barb, and half for
half a barb. Mag should be the magnitude of a vector (i.e., >= 0).
This returns a tuple of:
(*number of flags*, *number of barbs*, *half_flag*, *empty_flag*)
*half_flag* is a boolean whether half of a barb is needed,
since there should only ever be one half on a given
barb. *empty_flag* flag is an array of flags to easily tell if
a barb is empty (too low to plot any barbs/flags.
'''
# If rounding, round to the nearest multiple of half, the smallest
# increment
if rounding:
mag = half * (mag / half + 0.5).astype(np.int)
num_fullflags = np.floor(mag / fullflag).astype(np.int)
mag = np.mod(mag, fullflag)
num_flags = np.floor(mag / flag).astype(np.int)
mag = np.mod(mag, flag)
num_barb = np.floor(mag / full).astype(np.int)
mag = np.mod(mag, full)
half_flag = mag >= half
empty_flag = ~(half_flag | (num_flags > 0) | (num_fullflags > 0) |(num_barb > 0))
return num_fullflags,num_flags,num_barb, half_flag, empty_flag
3. 调整set_UVC中相关方法使用
fullflags, flags,barbs, halves, empty = self._find_tails(magnitude,
self.rounding,
**self.barb_increments)
# Get the vertices for each of the barbs
plot_barbs = self._make_barbs(u, v, fullflags, flags,barbs, halves, empty,
self._length, self._pivot, self.sizes,
self.fill_empty, self.flip)
四、测试
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_subplot(111);
ax.axis([-1,1,-1,1])
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_yticks([])
ax.barbs(0,0,30*1.5,40*1.5,length=8,linewidth=0.5)
plt.show()
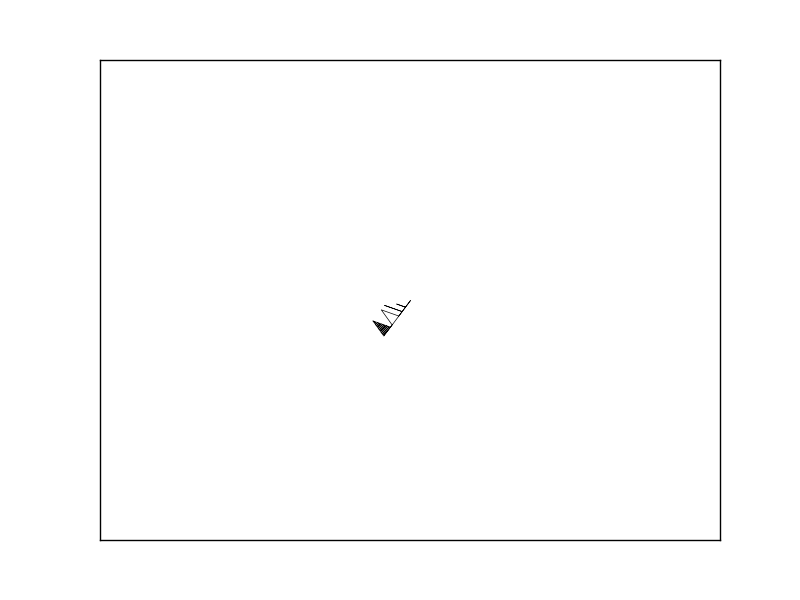
五、总结
通过本次实践一方面解决了自己实际问题,另一方面锻炼了自己阅读代码的能力,是一次很重要的学习过程,为我的Python之路打下坚实基础。
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。
想观看Matplotlib教学视频,了解更多Matplotlib实用技巧可关注
微信公众账号: MatplotlibClass

今日头条号:Matplotlib小讲堂

Python自学笔记——Matplotlib风羽自定义的更多相关文章
- Python自学笔记——matplotlib极坐标.md
一.极坐标 在平面内取一个定点O,叫极点,引一条射线Ox,叫做极轴,再选定一个长度单位和角度的正方向(通常取逆时针方向).对于平面内任何一点M,用ρ表示线段OM的长度(有时也用r表示),θ表示从Ox到 ...
- python自学笔记
python自学笔记 python自学笔记 1.输出 2.输入 3.零碎 4.数据结构 4.1 list 类比于java中的数组 4.2 tuple 元祖 5.条件判断和循环 5.1 条件判断 5.2 ...
- python自学笔记(一)
我没学过python,通过网上和一些图书资料,自学并且记下笔记. 很多细节留作以后自己做项目时再研究,这样能更高效一些. python基础自学笔记 一.基本输入和输出 pthon3.0用input提示 ...
- Matplotlib风羽自定义
[前言]对于气象专业的小学生来说,风场是预报重要的参考数据,我们所知的风羽有四种:短线代表风速2m/s,长线代表风速4m/s,空心三角代表风速20m/s,实心三角代表风速50m/s.而matplotl ...
- python自学笔记一
之前看过一段时间的小甲鱼零基础自学python,b站上有高清免费资源[av4050443],但是作为零基础实在学得艰难,下载了python核心编程pdf,在这里做一些笔记. 虽然使用的是第二版的教材, ...
- Python 自学笔记(一)环境搭建
一,关于Python的介绍 关于Python的介绍,我不想多说了,网上随便一搜,很多介绍,这里我主要写下我的自学Python的 过程,也是为了促进我能继续学习下去. 二,环境搭建 1,这里我只讲解Wi ...
- python 自学笔记(四) 列表
有几天没有更新博客了,毕竟是自学,最近事情确实比较多,有时候想学的时候反而没时间,到有时间的时候反而不想学.以后得想办法改掉这个缺点,只要有时间就要学习自己想学的东西,希望自学的同学能和我共同交流,其 ...
- Python自学笔记-sorted()函数(来自廖雪峰的官网Python3)
感觉廖雪峰的官网http://www.liaoxuefeng.com/里面的教程不错,所以学习一下,把需要复习的摘抄一下. 以下内容主要为了自己复习用,详细内容请登录廖雪峰的官网查看. 排序算法 排序 ...
- 如何深入系统的学习一门编程语言——python自学笔记
前言 最早接触python的时候,他并没有现在这么火,我也没把他太当回事,那时候我对python的印象就是给运维人员使用的一门很古老的语言,显然随着tensorflow(以下简称tf)的兴起,pyth ...
随机推荐
- VC++.Net CAD编程架构
1.每个对应的菜单项的图形抽象的, 图形抽象基类, 取决于改变来自子(如矩形.椭圆形) 2.在Doc对象管理列表管理,图形对象,当图形需要重绘或序列存储,通过遍历该列表的对象可以是 3. 每个类的职责 ...
- 大批量烧写openwrt系统
http://wiki.openwrt.org/toh/tp-link/tl-wr1043nd OEM mass flashing Flashing hundreds of devices using ...
- TODOList项目
[ 爱上Swift]十二期:TODOList项目 好久没有写Swift甚是想念,Swift,Xcode都比较稳定了写个程序熟悉一下,当然时间原因都是小Demo,废话不多说先上图. 下面是跑起来之后 ...
- MVC5模板部署到mono
VS2013中的MVC5模板部署到mono上的艰辛历程 2014-10-27 09:30 by FuzhePan, 3954 阅读, 46 评论, 收藏, 编辑 部署环境:CentOS7 + Mono ...
- .Net下简单地实现MD5加密
在.Net中为我们提供了一个方法HashPasswordForStoringInConfigFile,可以简单方便地实现MD5加密.该方法位于System.Web命名空间下,所以需要在引用中添加Sys ...
- SDUTOJ 2054 双向链表
#include<iostream> #include<stdlib.h> using namespace std; typedef int ElemType; typedef ...
- NET实现仓库看板的一些感想
NET实现仓库看板的一些感想 从一名技术开发人员到实施人员的蜕变,从不同的角度看待同一个问题,或许会有不一样的结果.这里记录一下最近一个项目实施的案例,非常有感触! 一. 项目情况简介 本次项目是给一 ...
- hadoop大数据处理之表与表的连接
hadoop大数据处理之表与表的连接 前言: hadoop中表连接其实类似于我们用sqlserver对数据进行跨表查询时运用的inner join一样,两个连接的数据要有关系连接起来,中间必须有一个 ...
- Nginx+phpfastcgi下flush输出问题
最近由于业务需要,需要使用php的flush输出缓存刷新,处理浏览器超时问题. 最初的测试代码如下: ob_start();//打开缓冲区 for ($i=10; $i>0; $i--) { e ...
- linux 之 snprintf函数用法
int snprintf(char *restrict buf, size_t n, const char * restrict format, ...); 函数说明:最多从源串中拷贝n-1个字符到 ...
