13.深入k8s:Pod 水平自动扩缩HPA及其源码分析

转载请声明出处哦~,本篇文章发布于luozhiyun的博客:https://www.luozhiyun.com
源码版本是1.19
Pod 水平自动扩缩
Pod 水平自动扩缩工作原理
Pod 水平自动扩缩全名是Horizontal Pod Autoscaler简称HPA。它可以基于 CPU 利用率或其他指标自动扩缩 ReplicationController、Deployment 和 ReplicaSet 中的 Pod 数量。
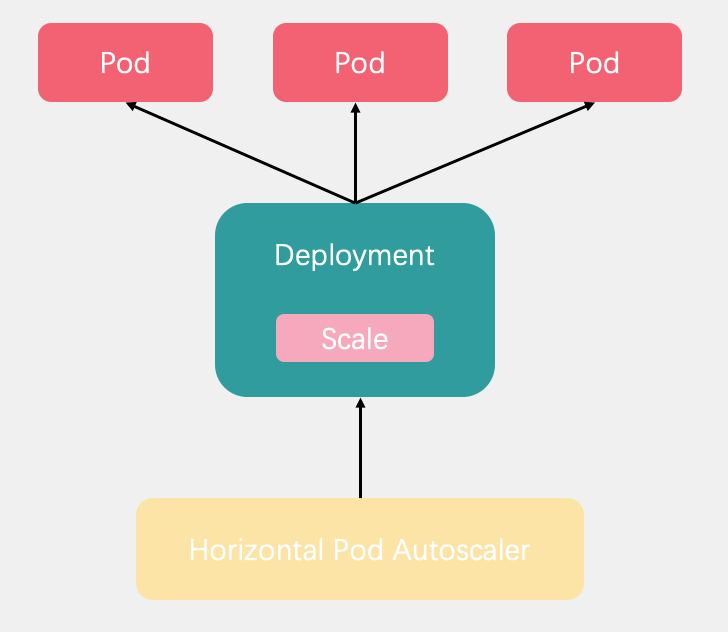
Pod 水平自动扩缩器由--horizontal-pod-autoscaler-sync-period 参数指定周期(默认值为 15 秒)。每个周期内,控制器管理器根据每个 HorizontalPodAutoscaler 定义中指定的指标查询资源利用率。
Pod 水平自动扩缩控制器跟据当前指标和期望指标来计算扩缩比例,公式为:
desiredReplicas = ceil[currentReplicas * ( currentMetricValue / desiredMetricValue )]
currentReplicas表示当前度量值,desiredMetricValue表示期望度量值,desiredReplicas表示期望副本数。例如,当前度量值为 200m,目标设定值为 100m,那么由于 200.0/100.0 == 2.0, 副本数量将会翻倍。 如果当前指标为 50m,副本数量将会减半,因为50.0/100.0 == 0.5。
我们可以通过使用kubectl来创建HPA。如通过 kubectl create 命令创建一个 HPA 对象, 通过 kubectl get hpa 命令来获取所有 HPA 对象, 通过 kubectl describe hpa 命令来查看 HPA 对象的详细信息。 最后,可以使用 kubectl delete hpa 命令删除对象。
也可以通过kubectl autoscale来创建 HPA 对象。 例如,命令 kubectl autoscale rs foo --min=2 --max=5 --cpu-percent=80 将会为名 为 foo 的 ReplicationSet 创建一个 HPA 对象, 目标 CPU 使用率为 80%,副本数量配置为 2 到 5 之间。
如果指标变化太频繁,我们也可以使用--horizontal-pod-autoscaler-downscale-stabilization指令设置扩缩容延迟时间,表示的是自从上次缩容执行结束后,多久可以再次执行缩容,默认是5m。
Pod 水平自动扩缩示例
编写用于测试的Deployment:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hpatest
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hpatest
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hpatest
spec:
containers:
- name: hpatest
image: nginx
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
command: ["/bin/sh"]
args: ["-c","/usr/sbin/nginx; while true;do echo `hostname -I` > /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html; sleep 120;done"]
ports:
- containerPort: 80
resources:
requests:
cpu: 1m
memory: 100Mi
limits:
cpu: 3m
memory: 400Mi
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: hpatest-svc
spec:
selector:
app: hpatest
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
protocol: TCP
编写HPA,用于水平扩展,当cpu达到50%的利用率的时候开始扩展:
apiVersion: autoscaling/v1
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: haptest-nginx
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: hpatest
minReplicas: 2
maxReplicas: 6
targetCPUUtilizationPercentage: 50
写一个简单的压测脚本:
[root@localhost HPA]# vim hpatest.sh
while true
do
wget -q -O- http://10.68.50.65
done
观察一下hpa的TARGETS情况:
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get hpa -w
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
hpatest Deployment/hpatest 0%/50% 1 5 1 5m47s
hpatest Deployment/hpatest 400%/50% 1 5 1 5m49s
hpatest Deployment/hpatest 400%/50% 1 5 4 6m4s
hpatest Deployment/hpatest 400%/50% 1 5 5 6m19s
hpatest Deployment/hpatest 500%/50% 1 5 5 6m49s
观察是否会自动扩容:
[root@localhost ~]# kubectl get pods -o wide -w
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
hpatest-bbb44c476-jv8zr 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s <none> 192.168.13.130 <none> <none>
hpatest-bbb44c476-sk6qb 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s <none> 192.168.13.130 <none> <none>
hpatest-bbb44c476-7s5qn 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s <none> 192.168.13.130 <none> <none>
hpatest-bbb44c476-7s5qn 1/1 Running 0 6s 172.20.0.23 192.168.13.130 <none> <none>
hpatest-bbb44c476-sk6qb 1/1 Running 0 6s 172.20.0.22 192.168.13.130 <none> <none>
hpatest-bbb44c476-jv8zr 1/1 Running 0 6s 172.20.0.21 192.168.13.130 <none> <none>
hpatest-bbb44c476-dstnf 0/1 Pending 0 0s <none> <none> <none> <none>
hpatest-bbb44c476-dstnf 0/1 Pending 0 0s <none> 192.168.13.130 <none> <none>
hpatest-bbb44c476-dstnf 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s <none> 192.168.13.130 <none> <none>
hpatest-bbb44c476-dstnf 1/1 Running 0 6s 172.20.0.24 192.168.13.130 <none> <none>
停止压测之后,HPA开始自动缩容:
[root@localhost HPA]# kubectl get pod -w
hpatest-bbb44c476-dstnf 0/1 Terminating 0 9m52s
hpatest-bbb44c476-jv8zr 0/1 Terminating 0 10m
hpatest-bbb44c476-7s5qn 0/1 Terminating 0 10m
hpatest-bbb44c476-sk6qb 0/1 Terminating 0 10m
hpatest-bbb44c476-sk6qb 0/1 Terminating 0 10m
hpatest-bbb44c476-dstnf 0/1 Terminating 0 10m
hpatest-bbb44c476-dstnf 0/1 Terminating 0 10m
hpatest-bbb44c476-7s5qn 0/1 Terminating 0 10m
hpatest-bbb44c476-7s5qn 0/1 Terminating 0 10m
hpatest-bbb44c476-jv8zr 0/1 Terminating 0 10m
hpatest-bbb44c476-jv8zr 0/1 Terminating 0 10m
源码分析
初始化
文件位置:cmd/kube-controller-manager/app/controllermanager.go
func NewControllerInitializers(loopMode ControllerLoopMode) map[string]InitFunc {
...
controllers["horizontalpodautoscaling"] = startHPAController
...
}
HPA Controller和其他的Controller一样,都在NewControllerInitializers方法中进行注册,然后通过startHPAController来启动。
startHPAController
文件位置:cmd/kube-controller-manager/app/autoscaling.go
func startHPAController(ctx ControllerContext) (http.Handler, bool, error) {
...
return startHPAControllerWithLegacyClient(ctx)
}
func startHPAControllerWithLegacyClient(ctx ControllerContext) (http.Handler, bool, error) {
hpaClient := ctx.ClientBuilder.ClientOrDie("horizontal-pod-autoscaler")
metricsClient := metrics.NewHeapsterMetricsClient(
hpaClient,
metrics.DefaultHeapsterNamespace,
metrics.DefaultHeapsterScheme,
metrics.DefaultHeapsterService,
metrics.DefaultHeapsterPort,
)
return startHPAControllerWithMetricsClient(ctx, metricsClient)
}
func startHPAControllerWithMetricsClient(ctx ControllerContext, metricsClient metrics.MetricsClient) (http.Handler, bool, error) {
hpaClient := ctx.ClientBuilder.ClientOrDie("horizontal-pod-autoscaler")
hpaClientConfig := ctx.ClientBuilder.ConfigOrDie("horizontal-pod-autoscaler")
scaleKindResolver := scale.NewDiscoveryScaleKindResolver(hpaClient.Discovery())
scaleClient, err := scale.NewForConfig(hpaClientConfig, ctx.RESTMapper, dynamic.LegacyAPIPathResolverFunc, scaleKindResolver)
if err != nil {
return nil, false, err
}
// 初始化
go podautoscaler.NewHorizontalController(
hpaClient.CoreV1(),
scaleClient,
hpaClient.AutoscalingV1(),
ctx.RESTMapper,
metricsClient,
ctx.InformerFactory.Autoscaling().V1().HorizontalPodAutoscalers(),
ctx.InformerFactory.Core().V1().Pods(),
ctx.ComponentConfig.HPAController.HorizontalPodAutoscalerSyncPeriod.Duration,
ctx.ComponentConfig.HPAController.HorizontalPodAutoscalerDownscaleStabilizationWindow.Duration,
ctx.ComponentConfig.HPAController.HorizontalPodAutoscalerTolerance,
ctx.ComponentConfig.HPAController.HorizontalPodAutoscalerCPUInitializationPeriod.Duration,
ctx.ComponentConfig.HPAController.HorizontalPodAutoscalerInitialReadinessDelay.Duration,
).Run(ctx.Stop)
return nil, true, nil
}
最后会调用到startHPAControllerWithMetricsClient方法,启动一个线程来调用NewHorizontalController方法初始化一个HPA Controller,然后执行Run方法。
Run
文件位置:pkg/controller/podautoscaler/horizontal.go
func (a *HorizontalController) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()
defer a.queue.ShutDown()
klog.Infof("Starting HPA controller")
defer klog.Infof("Shutting down HPA controller")
if !cache.WaitForNamedCacheSync("HPA", stopCh, a.hpaListerSynced, a.podListerSynced) {
return
}
// 启动异步线程,每秒执行一次
go wait.Until(a.worker, time.Second, stopCh)
<-stopCh
}
这里会调用worker执行具体的扩缩容的逻辑。
核心代码分析
worker里面一路执行下来会走到reconcileAutoscaler方法里面,这里是HPA的核心。下面我们专注看看这部分。
reconcileAutoscaler:计算副本数
func (a *HorizontalController) reconcileAutoscaler(hpav1Shared *autoscalingv1.HorizontalPodAutoscaler, key string) error {
...
//副本数为0,不启动自动扩缩容
if scale.Spec.Replicas == 0 && minReplicas != 0 {
// Autoscaling is disabled for this resource
desiredReplicas = 0
rescale = false
setCondition(hpa, autoscalingv2.ScalingActive, v1.ConditionFalse, "ScalingDisabled", "scaling is disabled since the replica count of the target is zero")
// 如果当前副本数大于最大期望副本数,那么设置期望副本数为最大副本数
} else if currentReplicas > hpa.Spec.MaxReplicas {
rescaleReason = "Current number of replicas above Spec.MaxReplicas"
desiredReplicas = hpa.Spec.MaxReplicas
// 同上
} else if currentReplicas < minReplicas {
rescaleReason = "Current number of replicas below Spec.MinReplicas"
desiredReplicas = minReplicas
} else {
var metricTimestamp time.Time
//计算需要扩缩容的数量
metricDesiredReplicas, metricName, metricStatuses, metricTimestamp, err = a.computeReplicasForMetrics(hpa, scale, hpa.Spec.Metrics)
if err != nil {
...
}
klog.V(4).Infof("proposing %v desired replicas (based on %s from %s) for %s", metricDesiredReplicas, metricName, metricTimestamp, reference)
rescaleMetric := ""
if metricDesiredReplicas > desiredReplicas {
desiredReplicas = metricDesiredReplicas
rescaleMetric = metricName
}
if desiredReplicas > currentReplicas {
rescaleReason = fmt.Sprintf("%s above target", rescaleMetric)
}
if desiredReplicas < currentReplicas {
rescaleReason = "All metrics below target"
}
//从1.18开始支持behavior字段
//可以在扩缩容的时候指定一个稳定窗口,以防止缩放目标中的副本数量出现波动
//doc:https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/run-application/horizontal-pod-autoscale/#support-for-configurable-scaling-behavior
if hpa.Spec.Behavior == nil {
desiredReplicas = a.normalizeDesiredReplicas(hpa, key, currentReplicas, desiredReplicas, minReplicas)
} else {
desiredReplicas = a.normalizeDesiredReplicasWithBehaviors(hpa, key, currentReplicas, desiredReplicas, minReplicas)
}
rescale = desiredReplicas != currentReplicas
}
...
}
这一段代码是reconcileAutoscaler里面的核心代码,在这里会确定一个区间,首先根据当前的scale对象和当前hpa里面配置的对应的参数的值,决策当前的副本数量,其中针对于超过设定的maxReplicas和小于minReplicas两种情况,只需要简单的修正为对应的值,直接更新对应的scale对象即可,而scale副本为0的对象,则hpa不会在进行任何操作。
对于当前副本数在maxReplicas和minReplicas之间的时候,则需要计算是否需要扩缩容,计算则是调用computeReplicasForMetrics方法来实现。
最后如果设置了Behavior则调用normalizeDesiredReplicasWithBehaviors函数来修正最后的结果,Behavior相关可以看文档:https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/run-application/horizontal-pod-autoscale/#support-for-configurable-scaling-behavior。
下面我们一步步分析。
computeReplicasForMetrics:遍历度量目标
func (a *HorizontalController) computeReplicasForMetrics(hpa *autoscalingv2.HorizontalPodAutoscaler, scale *autoscalingv1.Scale,
metricSpecs []autoscalingv2.MetricSpec) (replicas int32, metric string, statuses []autoscalingv2.MetricStatus, timestamp time.Time, err error) {
...
//这里的度量目标可以是一个列表,所以遍历之后取最大的需要扩缩容的数量
for i, metricSpec := range metricSpecs {
//根据type类型计算需要扩缩容的数量
replicaCountProposal, metricNameProposal, timestampProposal, condition, err := a.computeReplicasForMetric(hpa, metricSpec, specReplicas, statusReplicas, selector, &statuses[i])
if err != nil {
if invalidMetricsCount <= 0 {
invalidMetricCondition = condition
invalidMetricError = err
}
invalidMetricsCount++
}
//记录最大的需要扩缩容的数量
if err == nil && (replicas == 0 || replicaCountProposal > replicas) {
timestamp = timestampProposal
replicas = replicaCountProposal
metric = metricNameProposal
}
}
...
return replicas, metric, statuses, timestamp, nil
}
因为我们在设置metrics的时候实际上是一个数组,如下:
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2beta2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: php-apache
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: php-apache
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 50
- type: Pods
pods:
metric:
name: packets-per-second
target:
type: AverageValue
averageValue: 1k
- type: Object
object:
metric:
name: requests-per-second
describedObject:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
name: main-route
target:
type: Value
value: 10k
例如这个官方的例子中,设置了三个metric,所以我们在上面的代码中遍历所有的metrics,然后选取返回副本数最大的那个。主要计算逻辑都在computeReplicasForMetric中,下面我们看看这个方法。
computeReplicasForMetric:根据type计算副本数
func (a *HorizontalController) computeReplicasForMetric(hpa *autoscalingv2.HorizontalPodAutoscaler, spec autoscalingv2.MetricSpec,
specReplicas, statusReplicas int32, selector labels.Selector, status *autoscalingv2.MetricStatus) (replicaCountProposal int32, metricNameProposal string,
timestampProposal time.Time, condition autoscalingv2.HorizontalPodAutoscalerCondition, err error) {
//根据不同的类型来进行计量
switch spec.Type {
//表示如果是一个k8s对象,如Ingress对象
case autoscalingv2.ObjectMetricSourceType:
...
// 表示pod度量类型
case autoscalingv2.PodsMetricSourceType:
metricSelector, err := metav1.LabelSelectorAsSelector(spec.Pods.Metric.Selector)
if err != nil {
condition := a.getUnableComputeReplicaCountCondition(hpa, "FailedGetPodsMetric", err)
return 0, "", time.Time{}, condition, fmt.Errorf("failed to get pods metric value: %v", err)
}
//仅支持AverageValue度量目标,计算需要扩缩容的数量
replicaCountProposal, timestampProposal, metricNameProposal, condition, err = a.computeStatusForPodsMetric(specReplicas, spec, hpa, selector, status, metricSelector)
if err != nil {
return 0, "", time.Time{}, condition, fmt.Errorf("failed to get pods metric value: %v", err)
}
// 表示Resource度量类型
case autoscalingv2.ResourceMetricSourceType:
...
case autoscalingv2.ExternalMetricSourceType:
...
default:
errMsg := fmt.Sprintf("unknown metric source type %q", string(spec.Type))
err = fmt.Errorf(errMsg)
condition := a.getUnableComputeReplicaCountCondition(hpa, "InvalidMetricSourceType", err)
return 0, "", time.Time{}, condition, err
}
return replicaCountProposal, metricNameProposal, timestampProposal, autoscalingv2.HorizontalPodAutoscalerCondition{}, nil
}
这里会根据不同的度量类型来进行统计,目前度量类型有四种,分别是Pods、Object、Resource、External,解释如下:
const (
// ObjectMetricSourceType is a metric describing a kubernetes object
// (for example, hits-per-second on an Ingress object).
// 这种度量专门用来描述k8s的内置对象
ObjectMetricSourceType MetricSourceType = "Object"
// PodsMetricSourceType is a metric describing each pod in the current scale
// target (for example, transactions-processed-per-second). The values
// will be averaged together before being compared to the target value.
// 这种度量描述在目前被统计的每个pod平均期望值
PodsMetricSourceType MetricSourceType = "Pods"
// ResourceMetricSourceType is a resource metric known to Kubernetes, as
// specified in requests and limits, describing each pod in the current
// scale target (e.g. CPU or memory). Such metrics are built in to
// Kubernetes, and have special scaling options on top of those available
// to normal per-pod metrics (the "pods" source).
// Resource描述的是每个pod中资源,如CPU或内存
ResourceMetricSourceType MetricSourceType = "Resource"
// ExternalMetricSourceType is a global metric that is not associated
// with any Kubernetes object. It allows autoscaling based on information
// coming from components running outside of cluster
// (for example length of queue in cloud messaging service, or
// QPS from loadbalancer running outside of cluster).
// External类型表示的是一种全局的度量,和k8s对象无关,主要依赖外部集群提供信息
ExternalMetricSourceType MetricSourceType = "External"
)
我们这里不会全部都介绍,挑选pod度量类型作为例子。pod这个分支会调用computeStatusForPodsMetric方法来计算需要扩缩容的数量。
computeStatusForPodsMetric&GetMetricReplicas:计算需要扩缩容的数量
文件位置:pkg/controller/podautoscaler/replica_calculator.go
func (a *HorizontalController) computeStatusForPodsMetric(currentReplicas int32, metricSpec autoscalingv2.MetricSpec, hpa *autoscalingv2.HorizontalPodAutoscaler, selector labels.Selector, status *autoscalingv2.MetricStatus, metricSelector labels.Selector) (replicaCountProposal int32, timestampProposal time.Time, metricNameProposal string, condition autoscalingv2.HorizontalPodAutoscalerCondition, err error) {
//计算需要扩缩容的数量
replicaCountProposal, utilizationProposal, timestampProposal, err := a.replicaCalc.GetMetricReplicas(currentReplicas, metricSpec.Pods.Target.AverageValue.MilliValue(), metricSpec.Pods.Metric.Name, hpa.Namespace, selector, metricSelector)
if err != nil {
condition = a.getUnableComputeReplicaCountCondition(hpa, "FailedGetPodsMetric", err)
return 0, timestampProposal, "", condition, err
}
...
return replicaCountProposal, timestampProposal, fmt.Sprintf("pods metric %s", metricSpec.Pods.Metric.Name), autoscalingv2.HorizontalPodAutoscalerCondition{}, nil
}
func (c *ReplicaCalculator) GetMetricReplicas(currentReplicas int32, targetUtilization int64, metricName string, namespace string, selector labels.Selector, metricSelector labels.Selector) (replicaCount int32, utilization int64, timestamp time.Time, err error) {
//获取pod中度量数据
metrics, timestamp, err := c.metricsClient.GetRawMetric(metricName, namespace, selector, metricSelector)
if err != nil {
return 0, 0, time.Time{}, fmt.Errorf("unable to get metric %s: %v", metricName, err)
}
//通过结合度量数据来计算希望扩缩容的数量是多少
replicaCount, utilization, err = c.calcPlainMetricReplicas(metrics, currentReplicas, targetUtilization, namespace, selector, v1.ResourceName(""))
return replicaCount, utilization, timestamp, err
}
这里会调用GetRawMetric方法来获取pod对应的度量数据,然后再调用calcPlainMetricReplicas方法结合度量数据与目标期望来计算希望扩缩容的数量是多少。
calcPlainMetricReplicas:计算副本数具体实现
calcPlainMetricReplicas方法逻辑比较多,下面分开来讲解。
func (c *ReplicaCalculator) calcPlainMetricReplicas(metrics metricsclient.PodMetricsInfo, currentReplicas int32, targetUtilization int64, namespace string, selector labels.Selector, resource v1.ResourceName) (replicaCount int32, utilization int64, err error) {
podList, err := c.podLister.Pods(namespace).List(selector)
...
//将pod分成三类进行统计,得到ready的pod数量、ignored Pod集合、missing Pod集合
readyPodCount, ignoredPods, missingPods := groupPods(podList, metrics, resource, c.cpuInitializationPeriod, c.delayOfInitialReadinessStatus)
//在度量的数据里移除ignored Pods集合的数据
removeMetricsForPods(metrics, ignoredPods)
//计算pod中container request 设置的资源之和
requests, err := calculatePodRequests(podList, resource)
...
}
这里会调用groupPods将pod列表的进行一个分类统计。ignoredPods集合里面包含了pod状态为PodPending的数据;missingPods列表里面包含了在度量数据里面根据pod名找不到的数据。
因为missingPods的度量数据已经在metrics里是找不到的,然后只需要剔除掉ignored Pods集合中度量的资源就好了。
接下来调用calculatePodRequests方法统计pod中container request 设置的资源之和。
我们继续往下看:
func (c *ReplicaCalculator) calcPlainMetricReplicas(metrics metricsclient.PodMetricsInfo, currentReplicas int32, targetUtilization int64, namespace string, selector labels.Selector, resource v1.ResourceName) (replicaCount int32, utilization int64, err error) {
...
//获取资源使用率
usageRatio, utilization := metricsclient.GetMetricUtilizationRatio(metrics, targetUtilization)
...
}
到这里会调用GetMetricUtilizationRatio方法计算资源使用率。 这个方法比较简单:
usageRatio=currentUtilization/targetUtilization;
currentUtilization = metrics值之和metricsTotal/metrics的长度;
继续往下:
func (c *ReplicaCalculator) calcPlainMetricReplicas(metrics metricsclient.PodMetricsInfo, currentReplicas int32, targetUtilization int64, namespace string, selector labels.Selector, resource v1.ResourceName) (replicaCount int32, utilization int64, err error) {
...
rebalanceIgnored := len(ignoredPods) > 0 && usageRatio > 1.0
if !rebalanceIgnored && len(missingPods) == 0 {
if math.Abs(1.0-usageRatio) <= c.tolerance {
// return the current replicas if the change would be too small
return currentReplicas, utilization, nil
}
//如果没有unready 或 missing 的pod,那么使用 usageRatio*readyPodCount计算需要扩缩容数量
return int32(math.Ceil(usageRatio * float64(readyPodCount))), utilization, nil
}
if len(missingPods) > 0 {
if usageRatio < 1.0 {
//如果是缩容,那么将missing pod使用率设置为目标资源使用率
for podName := range missingPods {
metrics[podName] = metricsclient.PodMetric{Value: targetUtilization}
}
} else {
//如果是扩容,那么将missing pod使用率设置为0
for podName := range missingPods {
metrics[podName] = metricsclient.PodMetric{Value: 0}
}
}
}
if rebalanceIgnored {
// 将unready pods使用率设置为0
for podName := range ignoredPods {
metrics[podName] = metricsclient.PodMetric{Value: 0}
}
}
...
}
这里逻辑比较清晰,首先是判断如果missingPods和ignoredPods集合为空,那么检查一下是否在tolerance容忍度之内默认是0.1,如果在的话直接返回不进行扩缩容,否则返回usageRatio*readyPodCount表示需要扩缩容的容量;
如果missingPods集合不为空,那么需要判断一下是扩容还是缩容,相应调整metrics里面的值;
最后如果是扩容,还需要将ignoredPods集合的pod在metrics集合里设置为空。
接着看最后一部分:
func (c *ReplicaCalculator) calcPlainMetricReplicas(metrics metricsclient.PodMetricsInfo, currentReplicas int32, targetUtilization int64, namespace string, selector labels.Selector, resource v1.ResourceName) (replicaCount int32, utilization int64, err error) {
...
//重新计算资源利用率
newUsageRatio, _ := metricsclient.GetMetricUtilizationRatio(metrics, targetUtilization)
if math.Abs(1.0-newUsageRatio) <= c.tolerance || (usageRatio < 1.0 && newUsageRatio > 1.0) || (usageRatio > 1.0 && newUsageRatio < 1.0) {
return currentReplicas, utilization, nil
}
return int32(math.Ceil(newUsageRatio * float64(len(metrics)))), utilization, nil
}
因为上面重新对missingPods列表和ignoredPods列表中的metrics值进行了重新设置,所以这里需要重新计算资源利用率。
如果变化在容忍度之内,或者usageRatio与newUsageRatio一个大于一个小于零表示两者伸缩方向不一致,那么直接返回。否则返回newUsageRatio* metrics的长度作为扩缩容的具体值。
介绍完了这一块我们再来看看整个逻辑流程图:
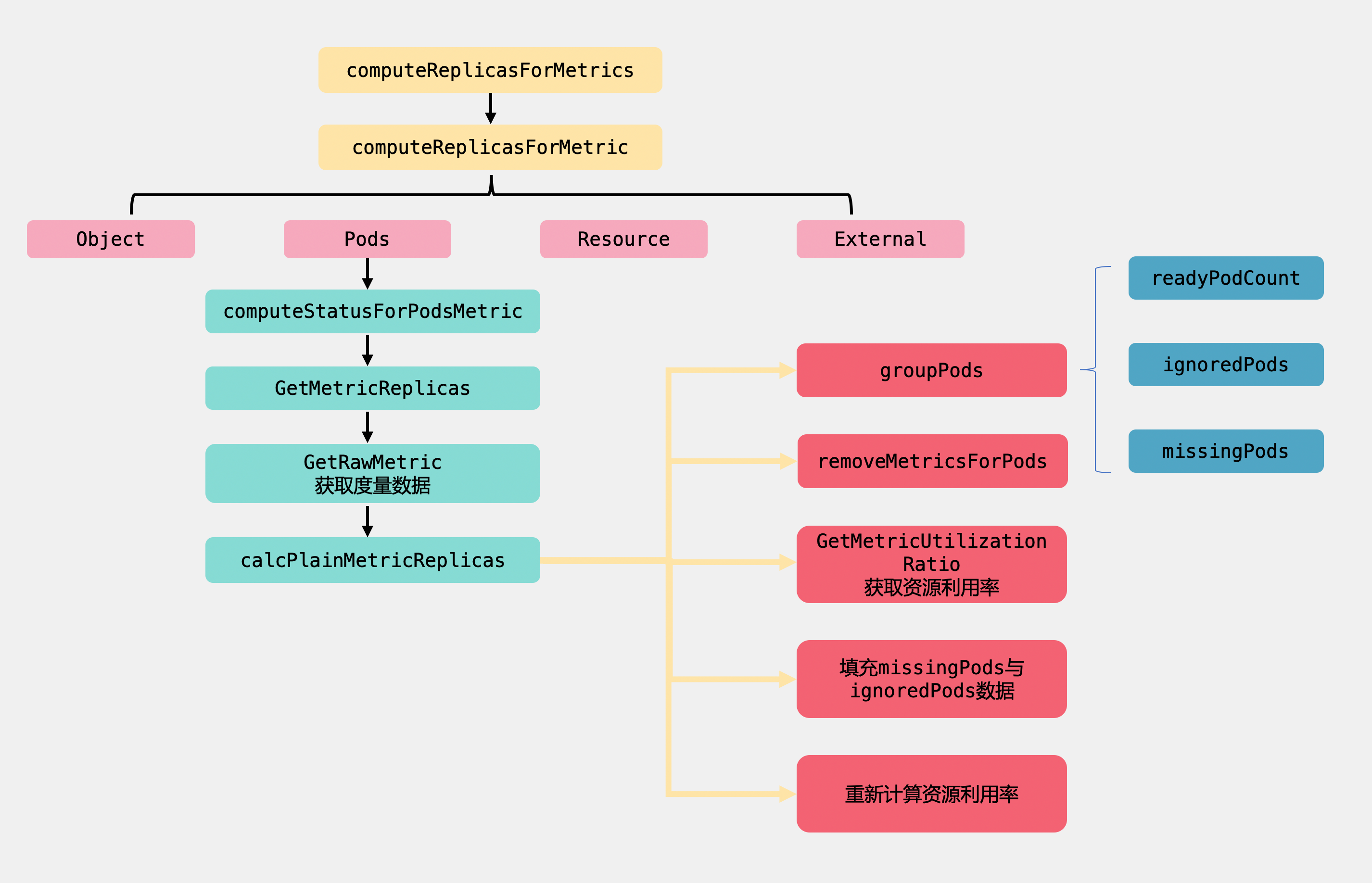
讲完了computeReplicasForMetrics方法,下面我们继续回到reconcileAutoscaler方法中往下看。
继续往下就到了检查是否设置了Behavior,如果没有设置那么走的是normalizeDesiredReplicas方法,这个方法较为简单,我们直接看看normalizeDesiredReplicasWithBehaviors方法做了什么,以及是怎么实现的。
normalizeDesiredReplicasWithBehaviors:Behavior限制
关于Behavior具体的例子可以到这里看:https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/run-application/horizontal-pod-autoscale/#default-behavior。
func (a *HorizontalController) normalizeDesiredReplicasWithBehaviors(hpa *autoscalingv2.HorizontalPodAutoscaler, key string, currentReplicas, prenormalizedDesiredReplicas, minReplicas int32) int32 {
//如果StabilizationWindowSeconds设置为空,那么给一个默认的值,默认300s
a.maybeInitScaleDownStabilizationWindow(hpa)
normalizationArg := NormalizationArg{
Key: key,
ScaleUpBehavior: hpa.Spec.Behavior.ScaleUp,
ScaleDownBehavior: hpa.Spec.Behavior.ScaleDown,
MinReplicas: minReplicas,
MaxReplicas: hpa.Spec.MaxReplicas,
CurrentReplicas: currentReplicas,
DesiredReplicas: prenormalizedDesiredReplicas}
//根据参数获取建议副本数
stabilizedRecommendation, reason, message := a.stabilizeRecommendationWithBehaviors(normalizationArg)
normalizationArg.DesiredReplicas = stabilizedRecommendation
...
//根据scaleDown或scaleUp指定的参数做限制
desiredReplicas, reason, message := a.convertDesiredReplicasWithBehaviorRate(normalizationArg)
...
return desiredReplicas
}
这个方法主要分为两部分,一部分是调用stabilizeRecommendationWithBehaviors方法来根据时间窗口来获取一个建议副本数;另一部分convertDesiredReplicasWithBehaviorRate方法是根据scaleDown或scaleUp指定的参数做限制。
stabilizeRecommendationWithBehaviors
func (a *HorizontalController) stabilizeRecommendationWithBehaviors(args NormalizationArg) (int32, string, string) {
recommendation := args.DesiredReplicas
foundOldSample := false
oldSampleIndex := 0
var scaleDelaySeconds int32
var reason, message string
var betterRecommendation func(int32, int32) int32
// 如果期望的副本数大于等于当前的副本数,则延迟时间=scaleUpBehaviro的稳定窗口时间
if args.DesiredReplicas >= args.CurrentReplicas {
scaleDelaySeconds = *args.ScaleUpBehavior.StabilizationWindowSeconds
betterRecommendation = min
reason = "ScaleUpStabilized"
message = "recent recommendations were lower than current one, applying the lowest recent recommendation"
} else {
// 期望副本数<当前的副本数
scaleDelaySeconds = *args.ScaleDownBehavior.StabilizationWindowSeconds
betterRecommendation = max
reason = "ScaleDownStabilized"
message = "recent recommendations were higher than current one, applying the highest recent recommendation"
}
//获取一个最大的时间窗口
maxDelaySeconds := max(*args.ScaleUpBehavior.StabilizationWindowSeconds, *args.ScaleDownBehavior.StabilizationWindowSeconds)
obsoleteCutoff := time.Now().Add(-time.Second * time.Duration(maxDelaySeconds))
cutoff := time.Now().Add(-time.Second * time.Duration(scaleDelaySeconds))
for i, rec := range a.recommendations[args.Key] {
if rec.timestamp.After(cutoff) {
// 在截止时间之后,则当前建议有效, 则根据之前的比较函数来决策最终的建议副本数
recommendation = betterRecommendation(rec.recommendation, recommendation)
}
//如果被遍历到的建议时间是在obsoleteCutoff之前,那么需要重新设置建议
if rec.timestamp.Before(obsoleteCutoff) {
foundOldSample = true
oldSampleIndex = i
}
}
//如果被遍历到的建议时间是在obsoleteCutoff之前,那么需要重新设置建议
if foundOldSample {
a.recommendations[args.Key][oldSampleIndex] = timestampedRecommendation{args.DesiredReplicas, time.Now()}
} else {
a.recommendations[args.Key] = append(a.recommendations[args.Key], timestampedRecommendation{args.DesiredReplicas, time.Now()})
}
return recommendation, reason, message
}
这个方法首先会去校验当前是扩容还是缩容,如果是扩容,那么将scaleDelaySeconds设置为ScaleUpBehavior的时间,并将betterRecommendation方法设置为min;如果是缩容那么则相反。
然后会遍历建议,如果建议时间在窗口时间cutoff之后,那么需要调用betterRecommendation方法来获取建议值,然后将获取到的最终结果返回。
convertDesiredReplicasWithBehaviorRate
func (a *HorizontalController) convertDesiredReplicasWithBehaviorRate(args NormalizationArg) (int32, string, string) {
var possibleLimitingReason, possibleLimitingMessage string
//如果期望副本数大于当前副本数
if args.DesiredReplicas > args.CurrentReplicas {
//获取预期扩容的pod数量
scaleUpLimit := calculateScaleUpLimitWithScalingRules(args.CurrentReplicas, a.scaleUpEvents[args.Key], args.ScaleUpBehavior)
if scaleUpLimit < args.CurrentReplicas {
// We shouldn't scale up further until the scaleUpEvents will be cleaned up
scaleUpLimit = args.CurrentReplicas
}
maximumAllowedReplicas := args.MaxReplicas
if maximumAllowedReplicas > scaleUpLimit {
maximumAllowedReplicas = scaleUpLimit
possibleLimitingReason = "ScaleUpLimit"
possibleLimitingMessage = "the desired replica count is increasing faster than the maximum scale rate"
} else {
possibleLimitingReason = "TooManyReplicas"
possibleLimitingMessage = "the desired replica count is more than the maximum replica count"
}
if args.DesiredReplicas > maximumAllowedReplicas {
return maximumAllowedReplicas, possibleLimitingReason, possibleLimitingMessage
}
} else if args.DesiredReplicas < args.CurrentReplicas {
//获取预期缩容的pod数量
scaleDownLimit := calculateScaleDownLimitWithBehaviors(args.CurrentReplicas, a.scaleDownEvents[args.Key], args.ScaleDownBehavior)
if scaleDownLimit > args.CurrentReplicas {
// We shouldn't scale down further until the scaleDownEvents will be cleaned up
scaleDownLimit = args.CurrentReplicas
}
minimumAllowedReplicas := args.MinReplicas
if minimumAllowedReplicas < scaleDownLimit {
minimumAllowedReplicas = scaleDownLimit
possibleLimitingReason = "ScaleDownLimit"
possibleLimitingMessage = "the desired replica count is decreasing faster than the maximum scale rate"
} else {
possibleLimitingMessage = "the desired replica count is less than the minimum replica count"
possibleLimitingReason = "TooFewReplicas"
}
if args.DesiredReplicas < minimumAllowedReplicas {
return minimumAllowedReplicas, possibleLimitingReason, possibleLimitingMessage
}
}
return args.DesiredReplicas, "DesiredWithinRange", "the desired count is within the acceptable range"
}
这个方法和上面的方法有些类似,不过是根据behavior具体行为来做一个约束。如果是scaleUp,那么需要调用calculateScaleUpLimitWithScalingRules来获取预期扩容的pod数量,calculateScaleUpLimitWithScalingRules方法里面会根据behavior设置的selectPolicy以及scaleUp.type参数来做一个计算,如下:
func calculateScaleUpLimitWithScalingRules(currentReplicas int32, scaleEvents []timestampedScaleEvent, scalingRules *autoscalingv2.HPAScalingRules) int32 {
var result int32
var proposed int32
var selectPolicyFn func(int32, int32) int32
if *scalingRules.SelectPolicy == autoscalingv2.DisabledPolicySelect {
return currentReplicas // Scaling is disabled
} else if *scalingRules.SelectPolicy == autoscalingv2.MinPolicySelect {
selectPolicyFn = min // For scaling up, the lowest change ('min' policy) produces a minimum value
} else {
selectPolicyFn = max // Use the default policy otherwise to produce a highest possible change
}
for _, policy := range scalingRules.Policies {
//获取最近变更的副本数
replicasAddedInCurrentPeriod := getReplicasChangePerPeriod(policy.PeriodSeconds, scaleEvents)
periodStartReplicas := currentReplicas - replicasAddedInCurrentPeriod
//根据不同的policy类型,决定不同的预期值
if policy.Type == autoscalingv2.PodsScalingPolicy {
proposed = int32(periodStartReplicas + policy.Value)
} else if policy.Type == autoscalingv2.PercentScalingPolicy {
proposed = int32(math.Ceil(float64(periodStartReplicas) * (1 + float64(policy.Value)/100)))
}
result = selectPolicyFn(result, proposed)
}
return result
}
func getReplicasChangePerPeriod(periodSeconds int32, scaleEvents []timestampedScaleEvent) int32 {
period := time.Second * time.Duration(periodSeconds)
cutoff := time.Now().Add(-period)
var replicas int32
//遍历最近变更
for _, rec := range scaleEvents {
if rec.timestamp.After(cutoff) {
// 更新副本修改的数量, 会有正负,最终replicas就是最近变更的数量
replicas += rec.replicaChange
}
}
return replicas
}
如果没有设置selectPolicy那么selectPolicyFn默认就是max方法,然后在遍历Policies的时候,如果type是pod,那么就加上一个具体值,如果是Percent,那么就加上一个百分比。
如果当前的副本数已经大于scaleUpLimit,那么则设置scaleUpLimit为当前副本数,如果期望副本数超过了最大允许副本数,那么直接返回,否则返回期望副本数就好了。
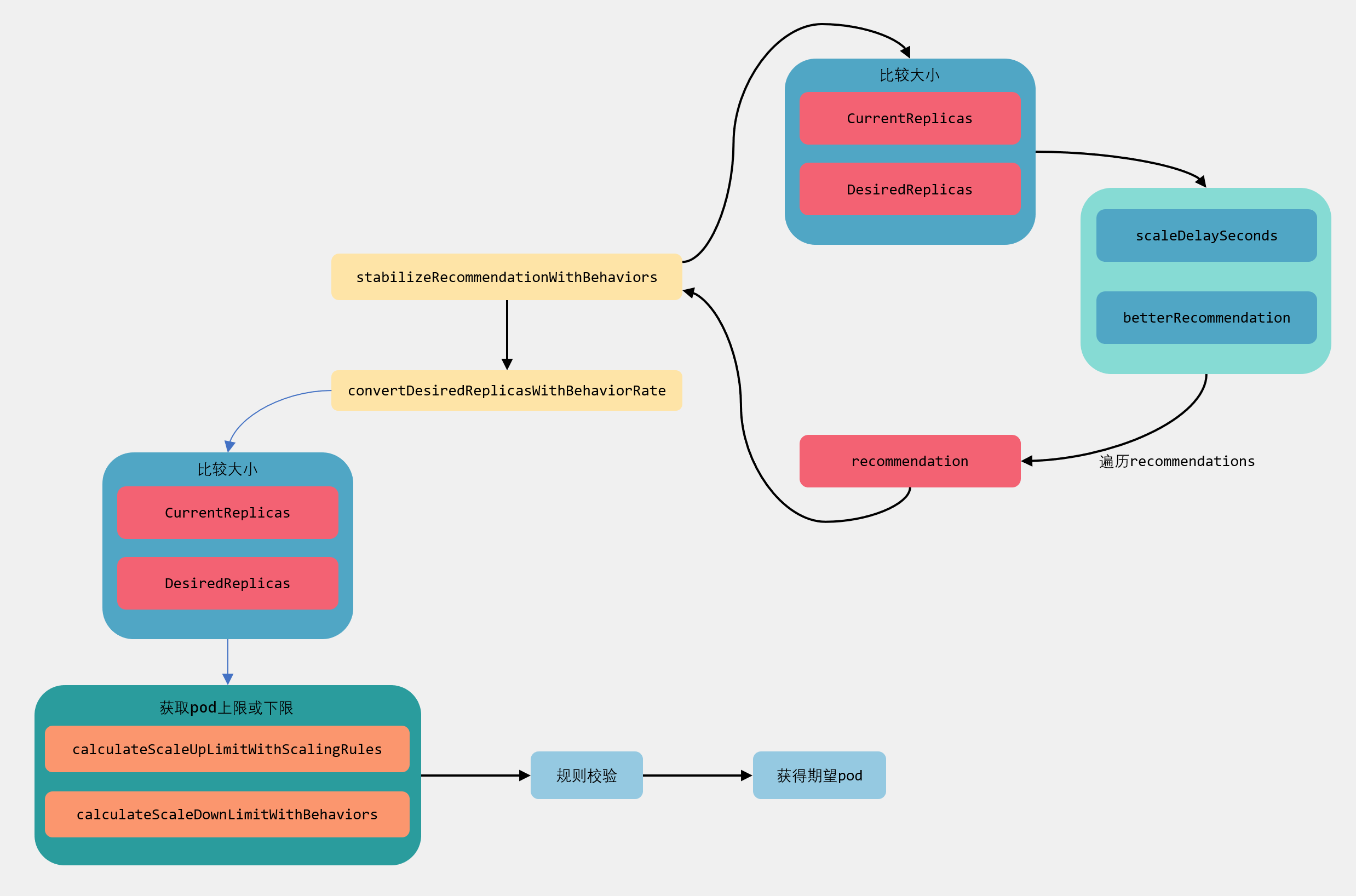
下面来一张图理一下逻辑:
总结
水平扩展大体逻辑可以用下面这两张图来进行一个概括,如果感兴趣的话,其中有很多细微的逻辑还是需要参照文档和代码一起理解起来才会更加的好。


Reference
https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/run-application/horizontal-pod-autoscale/
https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/run-application/horizontal-pod-autoscale-walkthrough/
13.深入k8s:Pod 水平自动扩缩HPA及其源码分析的更多相关文章
- 【六】K8s-Pod 水平自动扩缩实践(简称HPA)
一.概述 Pod 水平自动扩缩(Horizontal Pod Autoscaler)简称 HPA,HPA 可以根据 CPU 利用率进行自动伸缩 Pod 副本数量,除了 CPU 利用率,也可以基于其他应 ...
- Kubernetes Pod水平自动伸缩(HPA)
HPA简介 HAP,全称 Horizontal Pod Autoscaler, 可以基于 CPU 利用率自动扩缩 ReplicationController.Deployment 和 ReplicaS ...
- 8.深入k8s:资源控制Qos和eviction及其源码分析
转载请声明出处哦~,本篇文章发布于luozhiyun的博客:https://www.luozhiyun.com,源码版本是1.19 又是一个周末,可以愉快的坐下来静静的品味一段源码,这一篇涉及到资源的 ...
- 通过Dapr实现一个简单的基于.net的微服务电商系统(十一)——一步一步教你如何撸Dapr之自动扩/缩容
上一篇我们讲到了dapr提供的bindings,通过绑定可以让我们的程序轻装上阵,在极端情况下几乎不需要集成任何sdk,仅需要通过httpclient+text.json即可完成对外部组件的调用,这样 ...
- 三十三、HPA实现自动扩缩容
通过HPA实现业务应用的动态扩缩容 HPA控制器介绍 当系统资源过高的时候,我们可以使用如下命令来实现 Pod 的扩缩容功能 $ kubectl -n luffy scale deployment m ...
- Knative 基本功能深入剖析:Knative Serving 自动扩缩容 Autoscaler
Knative Serving 默认情况下,提供了开箱即用的快速.基于请求的自动扩缩容功能 - Knative Pod Autoscaler(KPA).下面带你体验如何在 Knative 中玩转 Au ...
- k8s Pod的自动水平伸缩(HPA)
我们知道,当访问量或资源需求过高时,使用:kubectl scale命令可以实现对pod的快速伸缩功能 但是我们平时工作中我们并不能提前预知访问量有多少,资源需求多少. 这就很麻烦了,总不能为了需求总 ...
- 7.深入k8s:任务调用Job与CronJob及源码分析
转载请声明出处哦~,本篇文章发布于luozhiyun的博客:https://www.luozhiyun.com 在使用job中,我会结合源码进行一定的讲解,我们也可以从源码中一窥究竟,一些细节k8s是 ...
- 15.深入k8s:Event事件处理及其源码分析
转载请声明出处哦~,本篇文章发布于luozhiyun的博客:https://www.luozhiyun.com 源码版本是1.19 概述 k8s的Event事件是一种资源对象,用于展示集群内发生的情况 ...
随机推荐
- luogu_P3373 solution
luogu_P3373 solution Problme Description Now, you have a known series, there are three operations: ...
- Appium + Python App自动化第一个脚本
今天跟大家讲解一个Appium和Python App自动化的脚本.[1]打开你的夜神模拟器(或者连接你的手机) [2]打开桌面的Appium [3]下载你要测的App的apk文件,放到桌面[4]拖动你 ...
- codeblocks显示:不支持的16位应用程序 解决办法
我是win10 64位系统,写c++运行就会显示不兼容16位应用程序.以前编出来的exe还能用,今天编出的就炸了. 试了用vs编译.vs能用. 试了网上找的各种解决方案, 360修复, 注册表, 重构 ...
- 【亲测】手把手教你如何破解pycharm(附安装包和破解文件)
此教程支持最新的2019.3版本的Pycharm,并兼容之前的版本. 一.准备工作: 1.下载Pycharm 有条件的可以自行去官网下载,这里我提供了我下载的版本,已上传到百度网盘,链接在下方. 2. ...
- 序列号,IMEI,IMSI,ICCID的含义
什么是序列号? 序列号是一串标识你手机出生证明以及身材特征的信息,甚至还可用来识别是否为官方翻新机.你可以简单的将这一串数字分割为:aabccdddeef 的形式.拿iPhone 4为例 aa = 工 ...
- android 数据绑定(4)实用特性及疑惑:使用控件、格式化@string/xxx、对象传递、双向数据绑定
1.在布局内使用其它控件 1.1 效果 箭头所指3个控件的内容随输入框内容而变化. 1.2 示例代码 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="u ...
- Codeforces1247D Power Products 暴力+优化
题意 给定数组\(a(\left| a \right|\leq 10^5)\)和整数\(k(2\leq k \leq 100)\),问满足一下条件的二元组\(<i,j>\)的数目: \(1 ...
- pyqt 设置QTabWidget标签页不可选
pyqt 设置QTabWidget标签页不可选 for i in range(1,7): self.tabWidget.setTabEnabled(i,False)i-对应标签页的位数
- 搭建一个低配版的Mock Server
mock翻译过来是模仿的意思,Server是服务器.粗暴点直译就是模仿服务器. 写在前面 通过阅读本文,你将对Mock的使用有一定的了解,对前后端分离的概念有了更深一步的认识,对Koa的使用有一定的了 ...
- ASP.NET Core 3.x控制IHostedService启动顺序浅探
想写好中间件,这是基础. 一.前言 今天这个内容,基于于ASP.NET Core 3.x. 从3.x开始,ASP.NET Core使用了通用主机模式.它将WebHostBuilder放到了通用的I ...
