is_callable Callbacks / Callables What is a “callable”? 可调用 回调函数
PHP: Callback / Callable 类型 - Manual https://www.php.net/manual/zh/language.types.callable.php
Callback / Callable 类型
自 PHP 5.4 起可用 callable 类型指定回调类型 callback。本文档基于同样理由使用 callback 类型信息。
一些函数如 call_user_func() 或 usort() 可以接受用户自定义的回调函数作为参数。回调函数不止可以是简单函数,还可以是对象的方法,包括静态类方法。
传递
PHP是将函数以string形式传递的。 可以使用任何内置或用户自定义函数,但除了语言结构例如:array(),echo,empty(),eval(),exit(),isset(),list(),print 或 unset()。
一个已实例化的 object 的方法被作为 array 传递,下标 0 包含该 object,下标 1 包含方法名。 在同一个类里可以访问 protected 和 private 方法。
静态类方法也可不经实例化该类的对象而传递,只要在下标 0 中包含类名而不是对象。自 PHP 5.2.3 起,也可以传递 'ClassName::methodName'。
除了普通的用户自定义函数外,也可传递 匿名函数 给回调参数。
Example #1 回调函数示例
<?php
// An example callback function
function my_callback_function() {
echo 'hello world!';
}
// An example callback method
class MyClass {
static function myCallbackMethod() {
echo 'Hello World!';
}
}
// Type 1: Simple callback
call_user_func('my_callback_function');
// Type 2: Static class method call
call_user_func(array('MyClass', 'myCallbackMethod'));
// Type 3: Object method call
$obj = new MyClass();
call_user_func(array($obj, 'myCallbackMethod'));
// Type 4: Static class method call (As of PHP 5.2.3)
call_user_func('MyClass::myCallbackMethod');
// Type 5: Relative static class method call (As of PHP 5.3.0)
class A {
public static function who() {
echo "A\n";
}
}
class B extends A {
public static function who() {
echo "B\n";
}
}
call_user_func(array('B', 'parent::who')); // A
// Type 6: Objects implementing __invoke can be used as callables (since PHP 5.3)
class C {
public function __invoke($name) {
echo 'Hello ', $name, "\n";
}
}
$c = new C();
call_user_func($c, 'PHP!');
?>Example #2 使用 Closure 的示例
<?php
// Our closure
$double = function($a) {
return $a * 2;
};
// This is our range of numbers
$numbers = range(1, 5);
// Use the closure as a callback here to
// double the size of each element in our
// range
$new_numbers = array_map($double, $numbers);
print implode(' ', $new_numbers);
?>以上例程会输出:
2 4 6 8 10
Note:
在函数中注册有多个回调内容时(如使用 call_user_func() 与 call_user_func_array()),如在前一个回调中有未捕获的异常,其后的将不再被调用。
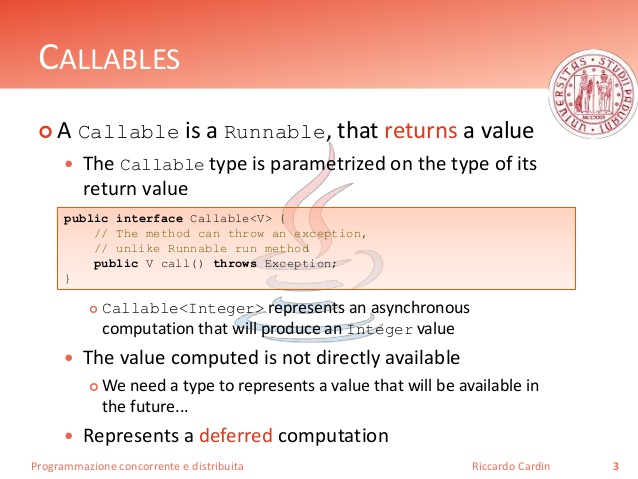
Callbacks / Callables
Callbacks can be denoted by callable type hint as of PHP 5.4. This documentation used callback type information for the same purpose.
Some functions like call_user_func() or usort() accept user-defined callback functions as a parameter. Callback functions can not only be simple functions, but also object methods, including static class methods.
Passing
A PHP function is passed by its name as a string. Any built-in or user-defined function can be used, except language constructs such as:array(), echo, empty(), eval(), exit(), isset(), list(), print or unset().
A method of an instantiated object is passed as an array containing an object at index 0 and the method name at index 1. Accessing protected and private methods from within a class is allowed.
Static class methods can also be passed without instantiating an object of that class by passing the class name instead of an object at index 0. As of PHP 5.2.3, it is also possible to pass 'ClassName::methodName'.
Apart from common user-defined function, anonymous functions can also be passed to a callback parameter.
Example #1 Callback function examples
<?php
// An example callback function
function my_callback_function() {
echo 'hello world!';
}
// An example callback method
class MyClass {
static function myCallbackMethod() {
echo 'Hello World!';
}
}
// Type 1: Simple callback
call_user_func('my_callback_function');
// Type 2: Static class method call
call_user_func(array('MyClass', 'myCallbackMethod'));
// Type 3: Object method call
$obj = new MyClass();
call_user_func(array($obj, 'myCallbackMethod'));
// Type 4: Static class method call (As of PHP 5.2.3)
call_user_func('MyClass::myCallbackMethod');
// Type 5: Relative static class method call (As of PHP 5.3.0)
class A {
public static function who() {
echo "A\n";
}
}
class B extends A {
public static function who() {
echo "B\n";
}
}
call_user_func(array('B', 'parent::who')); // A
// Type 6: Objects implementing __invoke can be used as callables (since PHP 5.3)
class C {
public function __invoke($name) {
echo 'Hello ', $name, "\n";
}
}
$c = new C();
call_user_func($c, 'PHP!');
?>Example #2 Callback example using a Closure
<?php
// Our closure
$double = function($a) {
return $a * 2;
};
// This is our range of numbers
$numbers = range(1, 5);
// Use the closure as a callback here to
// double the size of each element in our
// range
$new_numbers = array_map($double, $numbers);
print implode(' ', $new_numbers);
?>The above example will output:
2 4 6 8 10
Note:
Callbacks registered with functions such as call_user_func() and call_user_func_array() will not be called if there is an uncaught exception thrown in a previous callback.
PHP: Callbacks / Callables - Manual https://www.php.net/manual/en/language.types.callable.php
python - What is a "callable"? - Stack Overflow https://stackoverflow.com/questions/111234/what-is-a-callable
A callable is anything that can be called.
The built-in callable (PyCallable_Check in objects.c) checks if the argument is either:
- an instance of a class with a
__call__method or - is of a type that has a non null tp_call (c struct) member which indicates callability otherwise (such as in functions, methods etc.)
The method named __call__ is (according to the documentation)
Called when the instance is ''called'' as a function
Example
class Foo:
def __call__(self):
print 'called'
foo_instance = Foo()
foo_instance() #this is calling the __call__ methodFrom Python's sources object.c:
/* Test whether an object can be called */
int
PyCallable_Check(PyObject *x)
{
if (x == NULL)
return 0;
if (PyInstance_Check(x)) {
PyObject *call = PyObject_GetAttrString(x, "__call__");
if (call == NULL) {
PyErr_Clear();
return 0;
}
/* Could test recursively but don't, for fear of endless
recursion if some joker sets self.__call__ = self */
Py_DECREF(call);
return 1;
}
else {
return x->ob_type->tp_call != NULL;
}
}
It says:
- If an object is an instance of some class then it is callable iff it has
__call__attribute. - Else the object
xis callable iffx->ob_type->tp_call != NULL
Desciption of tp_call field:
ternaryfunc tp_callAn optional pointer to a function that implements calling the object. This should be NULL if the object is not callable. The signature is the same as for PyObject_Call(). This field is inherited by subtypes.
You can always use built-in callable function to determine whether given object is callable or not; or better yet just call it and catch TypeError later. callable is removed in Python 3.0 and 3.1, use callable = lambda o: hasattr(o, '__call__') or isinstance(o, collections.Callable).
Example, a simplistic cache implementation:
class Cached:
def __init__(self, function):
self.function = function
self.cache = {}
def __call__(self, *args):
try: return self.cache[args]
except KeyError:
ret = self.cache[args] = self.function(*args)
return ret
Usage:
@Cached
def ack(x, y):
return ack(x-1, ack(x, y-1)) if x*y else (x + y + 1)
Example from standard library, file site.py, definition of built-in exit() and quit() functions:
class Quitter(object):
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
def __repr__(self):
return 'Use %s() or %s to exit' % (self.name, eof)
def __call__(self, code=None):
# Shells like IDLE catch the SystemExit, but listen when their
# stdin wrapper is closed.
try:
sys.stdin.close()
except:
pass
raise SystemExit(code)
__builtin__.quit = Quitter('quit')
__builtin__.exit = Quitter('exit')3.3.6. 模拟可调用对象
object.__call__(self[, args...])-
此方法会在实例作为一个函数被“调用”时被调用;如果定义了此方法,则
x(arg1, arg2, ...)就相当于x.__call__(arg1, arg2, ...)的快捷方式。
3.3.6. Emulating callable objects
object.__call__(self[, args...])-
Called when the instance is “called” as a function; if this method is defined,
x(arg1, arg2, ...)is a shorthand forx.__call__(arg1, arg2, ...).
3. Data model — Python 3.8.3 documentation https://docs.python.org/3/reference/datamodel.html#object.__call__

https://www.php.net/manual/zh/function.array-map.php
array_map
(PHP 4 >= 4.0.6, PHP 5, PHP 7)
array_map — 为数组的每个元素应用回调函数
说明
array_map():返回数组,是为 array1 每个元素应用 callback函数之后的数组。 callback 函数形参的数量和传给 array_map() 数组数量,两者必须一样。
参数
callback-
回调函数,应用到每个数组里的每个元素。
array1-
数组,遍历运行
callback函数。 ...-
数组列表,每个都遍历运行
callback函数。
返回值
返回数组,包含 callback 函数处理之后 array1 的所有元素。
范例
Example #1 array_map() 例子
<?php
function cube($n)
{
return($n * $n * $n);
}
$a = array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
$b = array_map("cube", $a);
print_r($b);
?>这使得 $b 成为:
Array
(
[0] => 1
[1] => 8
[2] => 27
[3] => 64
[4] => 125
)
Example #2 array_map() 使用匿名函数 (PHP 5.3.0 起)
<?php
$func = function($value) {
return $value * 2;
};
print_r(array_map($func, range(1, 5)));
?>https://www.php.net/manual/en/function.array-map.php
array_map
(PHP 4 >= 4.0.6, PHP 5, PHP 7)
array_map — Applies the callback to the elements of the given arrays
Description
array_map() returns an array containing the results of applying the callback function to the corresponding index of array1 (and ... if more arrays are provided) used as arguments for the callback. The number of parameters that the callback function accepts should match the number of arrays passed to array_map().
Parameters
callback-
Callback function to run for each element in each array.
NULLcan be passed as a value tocallbackto perform a zip operation on multiple arrays. If onlyarray1is provided, array_map() will return the input array. array1-
An array to run through the
callbackfunction. ...-
Supplementary variable list of array arguments to run through the
callbackfunction.
Return Values
Returns an array containing the results of applying the callback function to the corresponding index of array1 (and ... if more arrays are provided) used as arguments for the callback.
The returned array will preserve the keys of the array argument if and only if exactly one array is passed. If more than one array is passed, the returned array will have sequential integer keys.
is_callable Callbacks / Callables What is a “callable”? 可调用 回调函数的更多相关文章
- jQuery使用():Callbacks回调函数列表之异步编程(含源码分析)
Callbacks的基本功能回调函数缓存与调用 特定需求模式的Callbacks Callbacks的模拟源码 一.Callbacks的基本功能回调函数缓存与调用 Callbacks即回调函数集合,在 ...
- jQuery 源码解析(八) 异步队列模块 Callbacks 回调函数详解
异步队列用于实现异步任务和回调函数的解耦,为ajax模块.队列模块.ready事件提供基础功能,包含三个部分:Query.Callbacks(flags).jQuery.Deferred(funct) ...
- php--->使用callable强制指定回调类型
php 使用callable强制指定回调类型 如果一个方法需要接受一个回调方法作为参数,我们可以这样写 <?php function dosth($callback){ call_user_fu ...
- PHP Callable强制指定回调类型的方法
如果一个方法需要接受一个回调方法作为参数,我们可以这样写 <?php function dosth($callback){ call_user_func($callback); } functi ...
- jQuery 2.0.3 源码分析 回调对象 - Callbacks
源码API:http://api.jquery.com/jQuery.Callbacks/ jQuery.Callbacks()是在版本1.7中新加入的.它是一个多用途的回调函数列表对象,提供了一种强 ...
- jQuery.Callbacks之源码解读
在上一篇jQuery.Callbacks之demo主要说了Callbacks对象初始化常见的选项,这一篇主要分析下Callbacks对象的源代码,对给出两个较为繁琐的demo // String to ...
- jQuery 第十章 工具方法-高级方法 $.ajax() $.Callbacks() .....
$.ajax() $.Callbacks() $.Deferred() .then() $.when() ---------------------------------------------- ...
- PHP7函数大全(4553个函数)
转载来自: http://www.infocool.net/kb/PHP/201607/168683.html a 函数 说明 abs 绝对值 acos 反余弦 acosh 反双曲余弦 addcsla ...
- Yii源码阅读笔记(三十五)
Container,用于动态地创建.注入依赖单元,映射依赖关系等功能,减少了许多代码量,降低代码耦合程度,提高项目的可维护性. namespace yii\di; use ReflectionClas ...
随机推荐
- python的if和else语句
1.单分支选择结构: if表达式: 语句块 2.双分支结构 if表达式: 语句块1 else: 语句块2 3.多分支结构 if 表达式1: 语句块1 elif 表达式2: 语句块2 elif 表达式3 ...
- SpringBoot 与 SpringSecurity
一.环境搭建 (1)IDEA创建SpringBoot工程 (2)导入依赖 (3)如果是thymeleaf项目 需导入thymeleaf整合security的依赖 (4)编写配置类(采用AOP横切入程序 ...
- Apache Calcite 论文学习笔记
特别声明:本文来源于掘金,"预留"发表的[Apache Calcite 论文学习笔记](https://juejin.im/post/5d2ed6a96fb9a07eea32a6f ...
- java中定时器设置时间
<!-- 0 0 10,14,16 * * ? 每天上午10点,下午2点,4点 0 0/30 9-17 * * ? 朝九晚五工作时间内每半小时 0 0 12 ? * WED 表示每个星期三中午1 ...
- TodoMVC Example知识点总结
案例来自于vue.js的官方示例:https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/examples/todomvc.html,我在案例学习过程中,试着对其中的一些知识点进行记录: 一.浏览器数据存储, ...
- 第六章节 BJROBOT 动态导航壁障
导航前说明:一定要确保你小车在构建好地图的基础上进行! 1.把小车平放在你想要构建地图区域的地板上,打开资料里的虚拟机,打开一个终端, ssh 过去主控端启动 roslaunch znjrobot b ...
- layer做阻塞式弹出层的方法
今天遇到一个问题: layer弹出一个confirm提示窗,然后confirm还没有点击对应的按钮的时候,就已经执行了后续代码,我这里做出的判断是,是否需要进行后续操作,但是因为layer.confi ...
- 一言不合就开始搞JDK源码
Java是一门面向对象的编程语言,那什么是面向对象呢,下面将是历史上最通俗易懂的解释了,请看下图: 哈哈,解释的够清楚的了吧.闪. 从源码学编程的好处 学Java编程时,最好同时看一些Java的源码 ...
- Github美化 添加徽章
Github美化 添加徽章 0. 前言 1. 准备 2. 开始 a. 打开shields.io b.制作静态徽章 c.制作动态徽章 d. 结果 3.额外 0. 前言 之前看见很多大项目都有很多勋章,比 ...
- 借助Docker搭建JMeter+Grafana+Influxdb监控平台
我们都知道Jmeter提供了原生的结果查看,既然有原生的查看结果,为什么还要多此一举使用其他工具进行查看呢,除了查看内容丰富外还有最主要的原因:Jmeter提供的查看结果插件本身是比较消耗性能的,所以 ...
