Simple Addition Permits Voltage Control Of DC-DC Converter's Output
http://electronicdesign.com/power/simple-addition-permits-voltage-control-dc-dc-converters-output
In a standard dc-dc converter, a resistor divider typically defines a fixed output voltage. However, applications like programmable output voltage power supplies and motor control circuits require dynamic control of the dc-dc converter’s output voltage. The circuit described here allows control of the converter’s output voltage, VOut, with a control voltage, VC.
In a conventional dc-dc buck converter, VOut is:
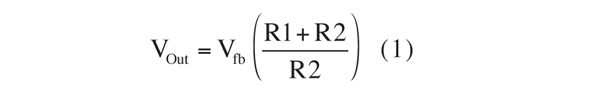
so VOut is fixed by the values of R1 and R2 (Fig. 1).
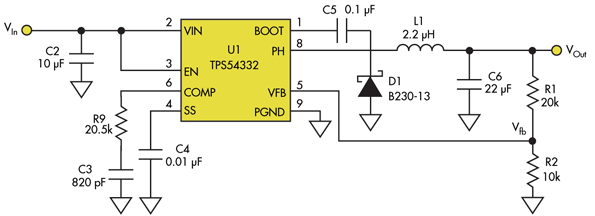
1. The output voltage in a conventional dc-dc buck converter is fixed and depends on the resistor divider, R1/R2.
The added circuitry in Figure 2 enables users to control the same dc-dc converter’s output voltage using VC.
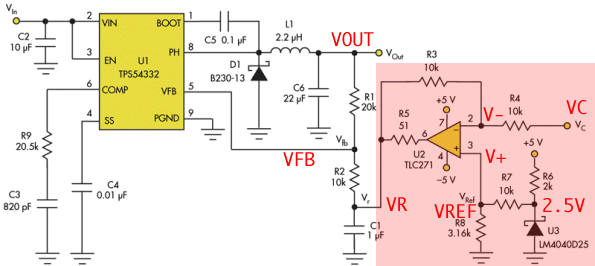
In this case, R2 is not connected to the ground but, rather, to Vr. Equation 1 then becomes:
VOUT = VFB + ( ( VFB - VR ) / R2 ) * R1
VOUT - VR = VFB - VR + ( ( VFB - VR ) / R2 ) * R1
VOUT - VR = ( VFB - VR ) * R2 / R2 + ( VFB - VR ) * R1 / R2
VOUT - VR = ( VFB - VR ) * ( R2 + R1 ) / R2
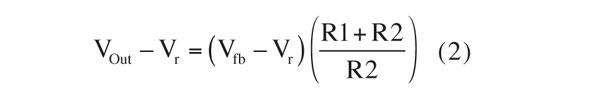
Since R1 = 20 kΩ and R2 = 10 kΩ, Equation 2 can be simplified to:
VOut – Vr = 3(Vfb – Vr)(3)
or:
VOut = 3 Vfb – 2 Vr(4)
( VC - V- ) / R4 = ( V- - VR ) / R3 ( I4 = I3 )
VC / R4 - V- / R4 = V- / R3 - VR / R3
V- / R4 + V- / R3 = VC / R4 + VR / R3
V- * ( R3 + R4 ) / ( R3 * R4 ) = ( VC * R3 + VR * R4 )/ ( R3 * R4 )
V- * ( R3 + R4 ) = ( VC * R3 + VR * R4 )
VR * R4 = V- * ( R3 + R4 ) - VC * R3
V- = V+ = VREF : VR * R4 = VREF * ( R3 + R4 ) - VC * R3
R3 = R4 : VR * R3 = VREF * ( R3 + R3 ) - VC * R3
VR = VREF * 2 - VC
R3 and R4 have the same value, 10 kΩ, so amplifier U2’s output voltage is:
Vr = 2 VRef – VC(5)
where VRef is the reference voltage generated by U3 after resistor divider R7/R8.
VOut = 3 Vfb – 2 Vr(4)
Combining Equation 4 and Equation 5:
VOut = 3 Vfb – 4 VRef + 2 VC (6)
To simplify Equation 6, choose components that make:
3 Vfb = 4 VRef(7)
Then Equation 6 becomes:
VOut = 2 VC (8)
The internal voltage reference of U1 is 0.8 V. ( TPS54332 )
VREF = 3VFB / 4 = 3 *0.8 / 4 = 0.6V
LM4040D25 : 2.5V : By choosing R7 = 10 kΩ and R8 = 3.16 kΩ, VRef = 0.6 V, satisfying Equation 7.
Finally, C1 lowers U2’s output impedance at high frequencies,
maintaining the stability of U1’s feedback loop.
The added circuitry allows users to control the buck converter’s output voltage,
VOut, in the range of 0 to 5 V with a control voltage, VC, in the range of 0 to 2.5 V.
Similar circuitry can be designed for use with a boost converter,
or any other dc-dc converter, as long as its feedback voltage pin is accessible.
Using an operational amplifier in the feedback path
A very flexible way of influencing the feedback pin while not being so restricted
in terms of the control signal is to use an operational amplifier.
It can be used to inject some current into the feedback divider which then
forces the control loop of the power supply to change the output voltage.
This way the output voltage can be varied continuously as a function
of the current injected into the feedback node.
Often, the information controlling the output voltage change on a power supply in sensor applications
as well as motor drive applications is an analog signal.
Depending on the nature of this control signal, the circuit around the operational amplifier
can be defined to set the lowest voltage output independent of what the control signal range is.
Also there is great flexibility in the ratio of control signal change to change in the output voltage.
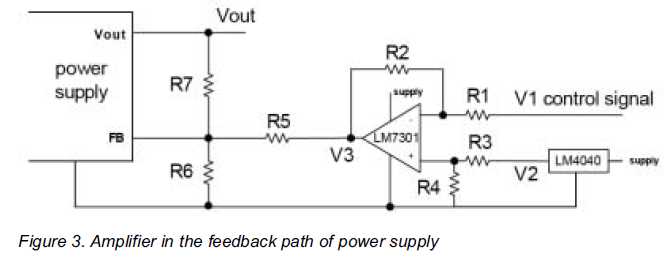
Figure 3 shows an amplifier circuit in the feedback path of a switching power supply.
The difference amplifier uses an operational amplifier and four additional resistors R1 through R4.
The output of the operational amplifier acts like a voltage source.
In order to inject a current into the feedback node this voltage is converted into a current by resistor R5.
It equals the internal impedance of the current source which the operational amplifier and R5 constitute.
Together with the feedback resistors R6 and R7 any output voltage changes
can be set based on almost any given control signal.
The signal voltage V1 is the control signal.
The voltage V2 is a reference voltage for the operational amplifier.
It should be a fairly constant voltage since variations on it will
change the output voltage of the power supply as well.
If a fairly precise rail in the system is available it can generally be used.
A good solution is a low voltage reference IC such as National Semiconductors LM4040.
Simple Addition Permits Voltage Control Of DC-DC Converter's Output的更多相关文章
- Simple dc/dc converter increases available power in dual-voltage system
The schematic in Figure 1 shows a way to increase the power available from a current-limited 5V supp ...
- PID DC/DC Converter Controller Using a PICmicro Microcontroller
http://www.microchip.com/stellent/idcplg?IdcService=SS_GET_PAGE&nodeId=1824&appnote=en011794 ...
- LT1946A-- Transformerless dc/dc converter produces bipolar outputs
Dual-polarity supply provides ±12V from one IC VC (Pin 1): Error Amplifier Output Pin. Tie external ...
- Practice safe dc/dc converter
Short-circuit protection is an obvious requirement for a power supply, especially when its load conn ...
- [专业名词·硬件] 2、DC\DC、LDO电源稳压基本常识(包含基本原理、高效率模块设计、常见问题、基于nRF51822电源管理模块分析等)·长文
综述先看这里 第一节的1.1简单介绍了DC/DC是什么: 第二节是关于DC/DC的常见的疑问答疑,非常实用: 第三节是针对nRF51822这款芯片电源管理部分的DC/DC.LDO.1.8的详细分析,对 ...
- DC/DC与LDO的差别
转自:http://bbs.eetop.cn/thread-459121-1-1.html 在平时的学习中,我们都有接触LDO和DC/DC这一类的电源产品,但作为学生的我们队这些东西可能了解不够深刻, ...
- Add margining capability to a dc/dc converter
You can easily add margining capability—that is, the ability to digitally adjust the output voltage— ...
- DC DC降壓變換器ic 工作原理
目前DC/DC轉化器大致可分為:升壓型dc dc變化器.降壓型dc dc變化器及可升壓又可降壓dc dc變換器.我們今天主要提一下降壓型dc dc變換器的原理: 見下圖降壓變換器原理圖如圖1所示, 當 ...
- DC DC電路電感的選擇
注:只有充分理解電感在DC/DC電路中發揮的作用,才能更優的設計DC/DC電路.本文還包括對同步DC/DC及異步DC/DC概念的解釋. DCDC電路電感的選擇 簡介 在開關電源的設計中電感的設計為 ...
随机推荐
- 4.rabbitmq 路由
1. 生产者 #coding:utf8 import pika import json import sys severity = sys.argv[1] if len(sys.argv) > ...
- python基础(8)--迭代器、生成器、装饰器
1.迭代器 迭代器是访问集合元素的一种方式.迭代器对象从集合的第一个元素开始访问,直到所有的元素被访问完结束.迭代器只能往前不会后退,不过这也没什么,因为人们很少在迭代途中往后退.另外,迭代器的一大优 ...
- 我所遇到的C++连接问题汇总
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_7caa399301017k1e.html 1:无法打开kernel32.lib 针对不同版本的VS,lib库所在的地方都不一样,所以首先 ...
- appium---【Mac】Appium-Doctor提示WARN:“ ios_webkit_debug_proxy cannot be found”解决方案
“ ios_webkit_debug_proxy cannot be found”报错截图如下: 解决方案: 打开terminal终端,分别输入执行结束,再次运行appium-doctor即可看到运行 ...
- JavaScript: The Evil Parts - 1
最近在看JavaScript框架设计,在讲解类型判定的时候提到了一些“匪夷所思的情况”,不过没有明说都是什么时候会出现这些情况.自己玩儿了一下,写写随笔吧.不过可能除了我找到的,还有会其他时候会出现这 ...
- linux中忘记root密码解决方案
方法一: 如果用户具有sudo权限,那么直接可以运行如下命令: #sudo su root #passwd #更改密码 或者直接运行sudo passwd root命令就可以直接更改root密码. 有 ...
- python开发学习-day07(面向对象之多态、类的方法、反射、新式类and旧式类、socket编程)
s12-20160227-day07 *:first-child { margin-top: 0 !important; } body>*:last-child { margin-bottom: ...
- Window 下一台机器配置三个Tomcat实例
下面我们把配置的详细过程写在下面,以供参考:(此例以配置三个Tomcat为例) 1. 下载apache-tomcat-8.0.63,下载下来的文件为apache-tomcat-8.0.63.zip. ...
- phpstorm使用和配置技巧
1. 使用phpstorm的过程中,有时光标不小心变成了方块状,怎么修复回来呢? 见下图,去掉“Use block caret” 前面的对勾即可. 2.多项目并存的问题 PhpStorm或 WebSt ...
- ref:一种新的攻击方法——Java Web表达式注入
ref:https://blog.csdn.net/kk_gods/article/details/51840683 一种新的攻击方法——Java Web表达式注入 2016年07月06日 17:01 ...
