C5 标准IO库:APUE 笔记
C5 :标准IO库
在第三章中,所有IO函数都是围绕文件描述符展开,文件描述符用于后续IO操作。由于文件描述符相关的操作是不带缓冲的IO,需要操作者本人指定缓冲区分配、IO长度等,对设备环境要求一定的了解。
本章引入文件流概念,IO库将处理很多底层IO细节。
1 缓冲
提供缓冲的目的是尽量减少read和write的调用次数。标准IO提供了以下3种缓冲:
1.1 全缓冲
在填满标准IO缓冲区后再进行实际IO操作,标准IO函数通常使用malloc获取使用的缓冲区
1.2 行缓冲
在输入和输出中遇到换行符时,标准IO才执行IO操作。对于行缓冲有2个限制
- 标准IO库用来收集每一行的缓冲区长度固定,所以只要是填满了缓冲区,就会进行IO操作
- 只要是通过标准IO从一个不带缓冲的流或者一个行缓冲的流得到输入数据,那么就会flush行缓冲输出流
1.3 不带缓冲
标准库不对字符进行缓冲存储,标准错误流通常是不带缓冲的,这样就可以尽快将信息显示出来
可以使用setbuf函数打开或者关闭缓冲机制,为了带缓冲进行IO,参数buf必须指向一个长度为BUFSIZE的缓冲区,头文件stdio.h。成功返回-,出错返回-1。
/* If BUF is NULL, make STREAM unbuffered.
Else make it use buffer BUF, of size BUFSIZ. */
extern void setbuf (FILE *__restrict __stream, char *__restrict __buf) __THROW; /* Make STREAM use buffering mode MODE.
If BUF is not NULL, use N bytes of it for buffering;
else allocate an internal buffer N bytes long. */
extern int setvbuf (FILE *__restrict __stream, char *__restrict __buf, int __modes, size_t __n) __THROW;
setvbuf的mode参数可以精确说明缓冲类型,mode参数实现为:
_IOFBF 全缓冲,_IOLBF 行缓冲,_IONBF 不带缓冲。
- 如果指定一个不带缓冲的流,则忽略buf和size参数。
- 如果指定全缓冲和行缓冲,则buf和size可选择指定一个缓冲区及其长度。
- 如果流是带缓冲的,而buf是NULL,则标准IO库自动为流分配合适长度的缓冲区,长度由BUFSIZE指定。
2 流
2.1 打开、关闭流
可以使用fopen等函数打开一个IO流,头文件stdio.h。成功返回文件指针,出错返回NULL。
/* Open a file and create a new stream for it.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern FILE *fopen (const char *__restrict __filename,
const char *__restrict __modes) __wur;
/* Open a file, replacing an existing stream with it.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern FILE *freopen (const char *__restrict __filename,
const char *__restrict __modes,
FILE *__restrict __stream) __wur;
fopen函数打开路径为__filename的文件
freopen函数在一个指定的流上打开文件。如果该流已经打开,则先关闭该流。如果该流已经定向,则使用freopen清除该定向。
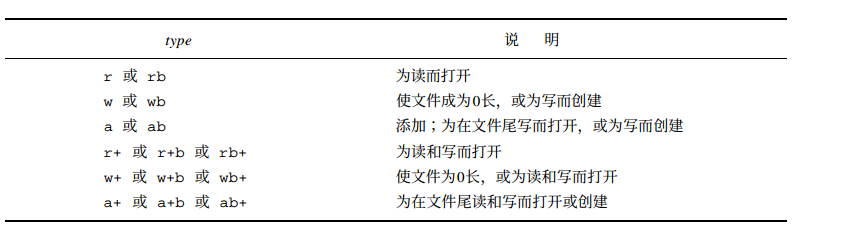
mode参数指定对该IO流的读写方式,ISO C规定mode参数可以右15种取值。
使用fclose可以关闭一个打开的流,头文件stdio.h。成功返回0,失败返回-1。
/* Close STREAM.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern int fclose (FILE *__stream);
/* Flush STREAM, or all streams if STREAM is NULL.
2.2 读、写流
2.2.1 每次一个字符的IO
下面函数用于一次读取一个字符,头文件stdio.h。成功返回下一个字符,达到文件尾或者出错,返回EOF(定义在libio.h)。
/* Read a character from STREAM.
These functions are possible cancellation points and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern int fgetc (FILE *__stream);
extern int getc (FILE *__stream);
/* Read a character from stdin.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern int getchar (void);
#ifndef EOF
# define EOF (-)
#endif
前两个函数的区别是,getc可以被实现为宏,而fgetc不能实现为宏?
getchar等价于geic (stdin)。
这三个函数达到文件尾或者出错,都返回EOF。为区别文件尾或者出错,需要调用以下函数进行判断,头文件stdio.h。成功返回非0,失败返回0。可以作为bool型判断。
/* Clear the error and EOF indicators for STREAM. */
extern void clearerr (FILE *__stream) __THROW;
/* Return the EOF indicator for STREAM. */
extern int feof (FILE *__stream) __THROW __wur;
/* Return the error indicator for STREAM. */
extern int ferror (FILE *__stream) __THROW __wur;
调用clearerr可以清除这两个标志。
也可以使用ubgetc将字符再写回流缓冲区,头文件stdio.h。成功返回c,失败返回EOF。
/* Push a character back onto the input buffer of STREAM.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern int ungetc (int __c, FILE *__stream);
对应的写缓冲区函数为:
/* Write a character to STREAM.
These functions are possible cancellation points and therefore not
marked with __THROW.
These functions is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern int fputc (int __c, FILE *__stream);
extern int putc (int __c, FILE *__stream);
/* Write a character to stdout.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern int putchar (int __c);
2.2.2 每次一行IO
下面两个函数每次读写输出一行,头文件stdio.h。成功返回buf,到达文件尾或者出错,返回NULL。
/* Get a newline-terminated string of finite length from STREAM.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern char *fgets (char *__restrict __s, int __n, FILE *__restrict __stream)
__wur;
/* Get a newline-terminated string from stdin, removing the newline.
This function is impossible to use safely. It has been officially
removed from ISO C11 and ISO C++14, and we have also removed it
from the _GNU_SOURCE feature list. It remains available when
explicitly using an old ISO C, Unix, or POSIX standard.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern char *gets (char *__s) __wur __attribute_deprecated__;
/* Write a string to STREAM.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern int fputs (const char *__restrict __s, FILE *__restrict __stream);
/* Write a string, followed by a newline, to stdout.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern int puts (const char *__s);
注意以下两点:
- 应当屏蔽使用puts或者gets。这两个函数都是从标准输入或输出读写,但由于无法指定缓冲区长度,将会导致缓冲区溢出错误
- 程序退出处,显示调用exit(0),将会冲洗任何未写的数据,然后关闭所有打开的流
- 读写一行都是以NULL为终止,但是缓冲区的NULL不会写入文件
3 二进制IO
上一节的流IO无法解决以下问题:当读取的数据是结构化数据(非字符串,可能读取到NULL,0),流IO将会截断。
为解决该问题,需要引入二进制IO函数fread和fwrite,头文件stdio.h。函数返回读或写的对象数。
/* Read chunks of generic data from STREAM.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern size_t fread (void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __stream) __wur;
/* Write chunks of generic data to STREAM.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern size_t fwrite (const void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __s);
4 定位流(访问偏移)
可使用ftell获取当前文件访问偏移量、fseek对文件访问进行偏移、rewind将流设置到起始位置。
/* Seek to a certain position on STREAM.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern int fseek (FILE *__stream, long int __off, int __whence);
/* Return the current position of STREAM.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern long int ftell (FILE *__stream) __wur;
/* Rewind to the beginning of STREAM.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern void rewind (FILE *__stream);
fseek的第三个参数whence与fseek的参数相同:
SEEK_SET指定从文件起始位置开始,SEEK_CUR指定从当前位置开始,SEEK_END指定从文件末尾
5 格式化IO
5.1 格式化输出
格式化输出由5个printf函数处理,头文件stdio.h。成功返回字符数,失败返回负值。
/* Write formatted output to stdout.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern int printf (const char *__restrict __format, ...);
/* Write formatted output to STREAM.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern int fprintf (FILE *__restrict __stream,
const char *__restrict __format, ...);
extern int dprintf (int __fd, const char *__restrict __fmt, ...)
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, , )));
/* Write formatted output to S. */
extern int sprintf (char *__restrict __s,
const char *__restrict __format, ...) __THROWNL;
/* Maximum chars of output to write in MAXLEN. */
extern int snprintf (char *__restrict __s, size_t __maxlen,
const char *__restrict __format, ...)
__THROWNL __attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, , )));
printf将格式化数据写到标准输出
fprintf将格式化数据写到指定的流
dprintf写到指定的文件描述符
sprintf写到数组S
snprintf是sprintf的安全版本,指定了缓冲区的长度,防止缓冲区溢出
5.2 格式化输入
格式化输入由3个scanf函数处理,头文件stdio.h。成功返回输入的参数,失败或者到达文件末尾,返回EOF。
/* Read formatted input from STREAM.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern int fscanf (FILE *__restrict __stream,
const char *__restrict __format, ...) __wur;
/* Read formatted input from stdin.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern int scanf (const char *__restrict __format, ...) __wur;
/* Read formatted input from S. */
extern int sscanf (const char *__restrict __s,
const char *__restrict __format, ...) __THROW;
6 临时文件
可以使用tmpnam或者tmpfile创建临时二进制文件。头文件stdio.h。
/* Generate a temporary filename. */
extern char *tmpnam (char *__s) __THROW __wur; /* Create a temporary file and open it read/write. This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern FILE *tmpfile (void) __wur;
tmpnam生成一个和现有文件名不同的有效路径字符串,最多调用TMP_MAX次,定义在stdio.h。返回指向唯一路径名的指针。如果输入为NULL,则路径名存放在静态区;如果不是NULL,则应该指向长度为L_tmpnam个字符的数组。
tmpfile创建一个临时二进制文件,在关闭该文件或者程序结束时将自动删除该文件。可以使用tmpfile创建一个临时文件,然后立即unlink。
7 内存流
/* Create a new stream that refers to a memory buffer. */
extern FILE *fmemopen (void *__s, size_t __len, const char *__modes)
__THROW __wur; /* Open a stream that writes into a malloc'd buffer that is expanded as
necessary. *BUFLOC and *SIZELOC are updated with the buffer's location
and the number of characters written on fflush or fclose. */
extern FILE *open_memstream (char **__bufloc, size_t *__sizeloc) __THROW __wur;
C5 标准IO库:APUE 笔记的更多相关文章
- [APUE]标准IO库(下)
一.标准IO的效率 对比以下四个程序的用户CPU.系统CPU与时钟时间对比 程序1:系统IO 程序2:标准IO getc版本 程序3:标准IO fgets版本 结果: [注:该表截取自APUE,上表中 ...
- [APUE]标准IO库(上)
一.流和FILE对象 系统IO都是针对文件描述符,当打开一个文件时,即返回一个文件描述符,然后用该文件描述符来进行下面的操作,而对于标准IO库,它们的操作则是围绕流(stream)进行的. 当打开一个 ...
- C++ Primer 读书笔记: 第8章 标准IO库
第8章 标准IO库 8.1 面向对象的标准库 1. IO类型在三个独立的头文件中定义:iostream定义读写控制窗口的类型,fstream定义读写已命名文件的类型,而sstream所定义的类型则用于 ...
- 文件IO函数和标准IO库的区别
摘自 http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-26565142-id-3051729.html 1,文件IO函数,在Unix中,有如下5个:open,read,write,lsee ...
- 高级UNIX环境编程5 标准IO库
标准IO库都围绕流进进行的 <stdio.h><wchar.h> memccpy 一般用汇编写的 ftell/fseek/ftello/fseeko/fgetpos/fsetp ...
- c++ primer 学习杂记3【标准IO库】
第8章 标准IO库 发现书中一个错误,中文版p248 流状态的查询和控制,举了一个代码例子: int ival; // read cin and test only for EOF; loop is ...
- 18、标准IO库详解及实例
标准IO库是由Dennis Ritchie于1975年左右编写的,它是Mike Lestbain写的可移植IO库的主要修改版本,2010年以后, 标准IO库几乎没有进行什么修改.标准IO库处理了很多细 ...
- 第十三篇:带缓冲的IO( 标准IO库 )
前言 在之前,学习了 read write 这样的不带缓冲IO函数. 而本文将讲解标准IO库中,带缓冲的IO函数. 为什么要有带缓冲IO函数 标准库提供的带缓冲IO函数是为了减少 read 和 wri ...
- 带缓冲的IO( 标准IO库 )
前言 在之前,学习了 read write 这样的不带缓冲IO函数.而本文将讲解标准IO库中,带缓冲的IO函数. 为什么要有带缓冲IO函数 标准库提供的带缓冲IO函数是为了减少 read 和 writ ...
随机推荐
- javascript 之 valueOf
var m = { i:10, toString:function () { console.log('toString'); return this.i; }, valueOf:function ( ...
- 15.遇到window leaked的解决方法
遇到这个可能是android:configChanges没有配置好 可以试试配置为这个 mcc|mnc|locale|touchscreen|keyboard|keyboardHidden|navig ...
- Java中的反射[转载]
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_38259539/article/details/71799078#commentBox 1.什么是反射? 反射是通过一个类可以知道其中所 ...
- k8s-离线安装k8s
1.开始 目标 coreos的igniton.json有很强的可配置性,通过安装时指定集群配置的ignition.json, 安装完成后打开https://{{Master_IP}}:6443/ui直 ...
- ViewFlipper
main.xml <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xml ...
- VUE 2.0在IE中打开页面空白的原因及解决方法
前言 因为工作的需要,学习Vue2.0也有一段时间,最近在用Vue2.0的官方脚手架工具构建的项目,chrome中跑一直没有问题,但ie打开出现了bug: 问题 ie打开vue2.0项目空白,控制台报 ...
- sift算法特征点如何匹配?
https://www.zhihu.com/question/23371175 我需要把一张照片和训练集中的图片进行匹配.我把一张照片提取特征值并建立kd树,然后把训练集的图片依次读进来,然后把图片的 ...
- CSS Text(文本)
CSS Text(文本) 一.文本颜色 color 颜色属性被用来设置文字的颜色. 颜色是通过CSS最经常的指定: 十六进制值 - 如: #FF0000 一个RGB值 - 如: RGB(255,0,0 ...
- Elasticsearch、MongoDB、Hadoop适用场景
如果你仅仅想要通过关键字和简单的分析,那么Elasticsearch可以完成任务: 如果你需要查询文档,并且包含更加复杂的分析过程,那么MongoDB相当适合: 如果你有一个海量的数据,需要大量不同的 ...
- 20145303刘俊谦 《Java程序设计》第4周学习总结
20145303刘俊谦 <Java程序设计>第4周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 1.继承:继承是面向对象的第二大特征,避免多个类间重复定义共同行为.把单独抽取出来的那个类称为父类,其他的多个 ...
