吴裕雄--天生自然 python数据分析:基于Keras使用CNN神经网络处理手写数据集
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.image as mpimg
import seaborn as sns
%matplotlib inline np.random.seed(2) from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
import itertools from keras.utils.np_utils import to_categorical # convert to one-hot-encoding
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense, Dropout, Flatten, Conv2D, MaxPool2D
from keras.optimizers import RMSprop
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
from keras.callbacks import ReduceLROnPlateau sns.set(style='white', context='notebook', palette='deep')
# Load the data
train = pd.read_csv("F:\\kaggleDataSet\MNSI\\train.csv")
test = pd.read_csv("F:\\kaggleDataSet\MNSI\\test.csv")
Y_train = train["label"] # Drop 'label' column
X_train = train.drop(labels = ["label"],axis = 1) # free some space
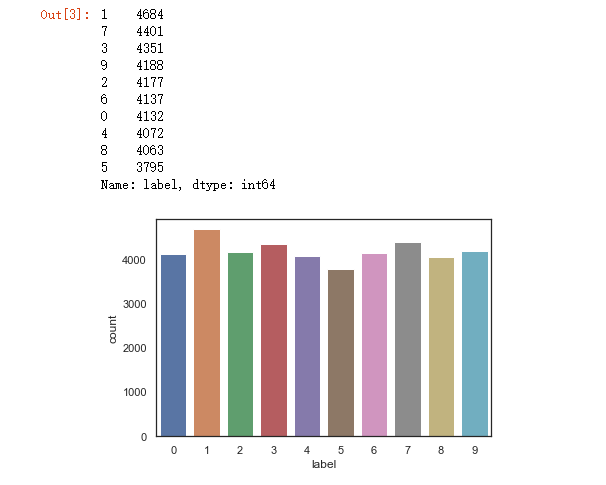
del train g = sns.countplot(Y_train) Y_train.value_counts()
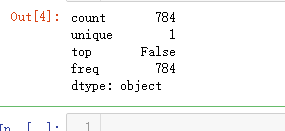
# Check the data
X_train.isnull().any().describe()
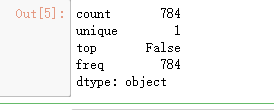
test.isnull().any().describe()
# Normalize the data
X_train = X_train / 255.0
test = test / 255.0
# Reshape image in 3 dimensions (height = 28px, width = 28px , canal = 1)
X_train = X_train.values.reshape(-1,28,28,1)
test = test.values.reshape(-1,28,28,1)
# Encode labels to one hot vectors (ex : 2 -> [0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0])
Y_train = to_categorical(Y_train, num_classes = 10)
# Set the random seed
random_seed = 2
# Split the train and the validation set for the fitting
X_train, X_val, Y_train, Y_val = train_test_split(X_train, Y_train, test_size = 0.1, random_state=random_seed)
# Some examples
g = plt.imshow(X_train[0][:,:,0])
# Set the CNN model
# my CNN architechture is In -> [[Conv2D->relu]*2 -> MaxPool2D -> Dropout]*2 -> Flatten -> Dense -> Dropout -> Out model = Sequential() model.add(Conv2D(filters = 32, kernel_size = (5,5),padding = 'Same',
activation ='relu', input_shape = (28,28,1)))
model.add(Conv2D(filters = 32, kernel_size = (5,5),padding = 'Same',
activation ='relu'))
model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2)))
model.add(Dropout(0.25)) model.add(Conv2D(filters = 64, kernel_size = (3,3),padding = 'Same',
activation ='relu'))
model.add(Conv2D(filters = 64, kernel_size = (3,3),padding = 'Same',
activation ='relu'))
model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(2,2)))
model.add(Dropout(0.25)) model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(256, activation = "relu"))
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
model.add(Dense(10, activation = "softmax"))
# Define the optimizer
optimizer = RMSprop(lr=0.001, rho=0.9, epsilon=1e-08, decay=0.0)
# Compile the model
model.compile(optimizer = optimizer , loss = "categorical_crossentropy", metrics=["accuracy"])
# Set a learning rate annealer
learning_rate_reduction = ReduceLROnPlateau(monitor='val_acc',
patience=3,
verbose=1,
factor=0.5,
min_lr=0.00001)
epochs = 1 # Turn epochs to 30 to get 0.9967 accuracy
batch_size = 86
# Without data augmentation i obtained an accuracy of 0.98114
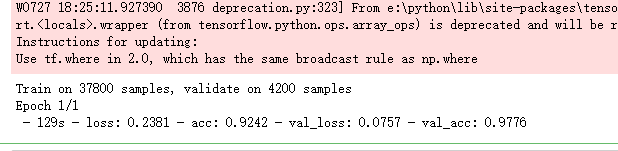
history = model.fit(X_train, Y_train, batch_size = batch_size, epochs = epochs,
validation_data = (X_val, Y_val), verbose = 2)
# With data augmentation to prevent overfitting (accuracy 0.99286) datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
featurewise_center=False, # set input mean to 0 over the dataset
samplewise_center=False, # set each sample mean to 0
featurewise_std_normalization=False, # divide inputs by std of the dataset
samplewise_std_normalization=False, # divide each input by its std
zca_whitening=False, # apply ZCA whitening
rotation_range=10, # randomly rotate images in the range (degrees, 0 to 180)
zoom_range = 0.1, # Randomly zoom image
width_shift_range=0.1, # randomly shift images horizontally (fraction of total width)
height_shift_range=0.1, # randomly shift images vertically (fraction of total height)
horizontal_flip=False, # randomly flip images
vertical_flip=False) # randomly flip images datagen.fit(X_train)
# Fit the model
history = model.fit_generator(datagen.flow(X_train,Y_train, batch_size=batch_size),
epochs = epochs, validation_data = (X_val,Y_val),
verbose = 2, steps_per_epoch=X_train.shape[0] // batch_size
, callbacks=[learning_rate_reduction])

# Plot the loss and accuracy curves for training and validation
fig, ax = plt.subplots(2,1)
ax[0].plot(history.history['loss'], color='b', label="Training loss")
ax[0].plot(history.history['val_loss'], color='r', label="validation loss",axes =ax[0])
legend = ax[0].legend(loc='best', shadow=True) ax[1].plot(history.history['acc'], color='b', label="Training accuracy")
ax[1].plot(history.history['val_acc'], color='r',label="Validation accuracy")
legend = ax[1].legend(loc='best', shadow=True)
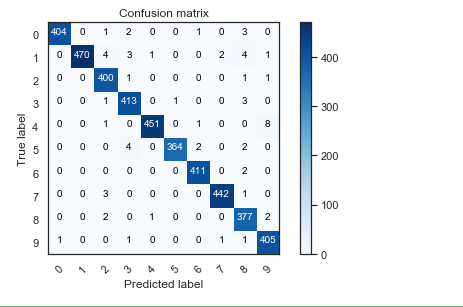
# Look at confusion matrix def plot_confusion_matrix(cm, classes,
normalize=False,
title='Confusion matrix',
cmap=plt.cm.Blues):
"""
This function prints and plots the confusion matrix.
Normalization can be applied by setting `normalize=True`.
"""
plt.imshow(cm, interpolation='nearest', cmap=cmap)
plt.title(title)
plt.colorbar()
tick_marks = np.arange(len(classes))
plt.xticks(tick_marks, classes, rotation=45)
plt.yticks(tick_marks, classes) if normalize:
cm = cm.astype('float') / cm.sum(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis] thresh = cm.max() / 2.
for i, j in itertools.product(range(cm.shape[0]), range(cm.shape[1])):
plt.text(j, i, cm[i, j],
horizontalalignment="center",
color="white" if cm[i, j] > thresh else "black") plt.tight_layout()
plt.ylabel('True label')
plt.xlabel('Predicted label') # Predict the values from the validation dataset
Y_pred = model.predict(X_val)
# Convert predictions classes to one hot vectors
Y_pred_classes = np.argmax(Y_pred,axis = 1)
# Convert validation observations to one hot vectors
Y_true = np.argmax(Y_val,axis = 1)
# compute the confusion matrix
confusion_mtx = confusion_matrix(Y_true, Y_pred_classes)
# plot the confusion matrix
plot_confusion_matrix(confusion_mtx, classes = range(10))
# Display some error results # Errors are difference between predicted labels and true labels
errors = (Y_pred_classes - Y_true != 0) Y_pred_classes_errors = Y_pred_classes[errors]
Y_pred_errors = Y_pred[errors]
Y_true_errors = Y_true[errors]
X_val_errors = X_val[errors] def display_errors(errors_index,img_errors,pred_errors, obs_errors):
""" This function shows 6 images with their predicted and real labels"""
n = 0
nrows = 2
ncols = 3
fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows,ncols,sharex=True,sharey=True)
for row in range(nrows):
for col in range(ncols):
error = errors_index[n]
ax[row,col].imshow((img_errors[error]).reshape((28,28)))
ax[row,col].set_title("Predicted label :{}\nTrue label :{}".format(pred_errors[error],obs_errors[error]))
n += 1 # Probabilities of the wrong predicted numbers
Y_pred_errors_prob = np.max(Y_pred_errors,axis = 1) # Predicted probabilities of the true values in the error set
true_prob_errors = np.diagonal(np.take(Y_pred_errors, Y_true_errors, axis=1)) # Difference between the probability of the predicted label and the true label
delta_pred_true_errors = Y_pred_errors_prob - true_prob_errors # Sorted list of the delta prob errors
sorted_dela_errors = np.argsort(delta_pred_true_errors) # Top 6 errors
most_important_errors = sorted_dela_errors[-6:] # Show the top 6 errors
display_errors(most_important_errors, X_val_errors, Y_pred_classes_errors, Y_true_errors)
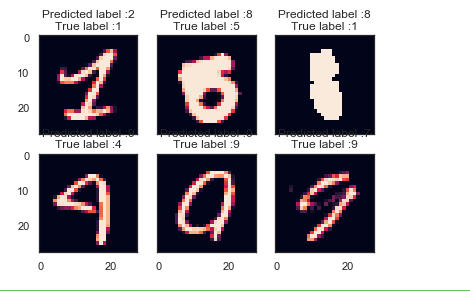
# predict results
results = model.predict(test) # select the indix with the maximum probability
results = np.argmax(results,axis = 1) results = pd.Series(results,name="Label")
submission = pd.concat([pd.Series(range(1,28001),name = "ImageId"),results],axis = 1)
submission.to_csv("cnn_mnist_datagen.csv",index=False)
吴裕雄--天生自然 python数据分析:基于Keras使用CNN神经网络处理手写数据集的更多相关文章
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:基于Keras的CNN分析太空深处寻找系外行星数据
#We import libraries for linear algebra, graphs, and evaluation of results import numpy as np import ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:糖尿病视网膜病变数据分析(完整版)
# This Python 3 environment comes with many helpful analytics libraries installed # It is defined by ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:所有美国股票和etf的历史日价格和成交量分析
# This Python 3 environment comes with many helpful analytics libraries installed # It is defined by ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 python数据分析:健康指标聚集分析(健康分析)
# This Python 3 environment comes with many helpful analytics libraries installed # It is defined by ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 python数据分析:葡萄酒分析
# import pandas import pandas as pd # creating a DataFrame pd.DataFrame({'Yes': [50, 31], 'No': [101 ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:人类发展报告——HDI, GDI,健康,全球人口数据数据分析
import pandas as pd # Data analysis import numpy as np #Data analysis import seaborn as sns # Data v ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 python数据分析:医疗费数据分析
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import os import matplotlib.pyplot as pl import seaborn as sn ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:钦奈水资源管理分析
df = pd.read_csv("F:\\kaggleDataSet\\chennai-water\\chennai_reservoir_levels.csv") df[&quo ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 PYTHON数据分析:医疗数据分析
import numpy as np # linear algebra import pandas as pd # data processing, CSV file I/O (e.g. pd.rea ...
随机推荐
- IOC与AOP的理解
转自 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38006047/article/details/80797386 1,理解“控制反转” 控制反转,也叫依赖注入,是面向对象编程中的一种设计理念 ...
- C++常用库函数 C函数库 cstdio
常用的C/C++函数库, cstdio(stdio.h) 标准输入输出库.C Standard Input and Output Library 1. 实例 #include <cstdio&g ...
- Error:Execution failed for task ':app:preDebugAndroidTestBuild'. > Conflict with dependency
Error : Execution failed for task ’ :app: preDebugAndroidTestBuild’.Conflict with dependency ‘com.an ...
- Linux下切换用户出现su: Authentication failure的解决办法
在切换用户时,密码没有输错,但始终无法成功地切换,还报出身份验证失败的错误,下面是具体解决方案: 在终端上输入指令sudo passwd root 此时输入你的密码 重复再次输入你的密码 再次用su指 ...
- python-day7爬虫基础之Ajax数据爬取
前几天一直在忙老师的项目,就没有继续学python,也没有写什么收获,今天晚上有空看看书,边看边理解着写吧: 首先说一下,我对Ajax的理解,就是有时候我们在浏览某个网页的时候,只要我们鼠标一直往下滑 ...
- 20199324《Linux内核原理与分析》第十二周作业
格式化字符串漏洞实验 一. 实验描述 格式化字符串漏洞是由像 printf(user_input) 这样的代码引起的,其中 user_input 是用户输入的数据,具有 Set-UID root 权限 ...
- android 获得存储设备状态
1.获取存储器总大小,可用大小 File path= Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory();StatFs fs = new StatFs(path.get ...
- Hardy-Weinberg laws
I.3 Diploids with two alleles: Hardy-Weinberg laws 假设子代是Aa,AA,aa的概率分别是PAa,PAA,Paa,A的基因概率是P1,a的基因概率是P ...
- MFC的程序,不想显示窗口,任务栏里也不显示
在dialog的oninitdialog里设置如下属性,很简单,网上一些乱七八糟的做法,一行代码就能搞定啊 SetWindowPos(&CWnd::wndNoTopMost,0,0,0,0,S ...
- Nginx的下载与安装
.创建文件输入网页中需要复制的 cat >/etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo<<EOF [nginx-stable] name=nginx stable repo ...
