达拉草201771010105《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十三周学习总结
达拉草201771010105《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十三周学习总结
第一部分:理论知识
事件处理基础:
事件源:能够产生事件的对象都可 以成为事件源,如文本框、按钮等。一个事件源是一个 能够注册监听器并向监听器发送事件对象的对象。
事件监听器:事件监听器对象接 收事件源发送的通告(事件对象),并对发生的事件作 出响应。一个监听器对象就是一个实现了专门监听器接 口的类实例,该类必须实现接口中的方法,这些方法当 事件发生时,被自动执行。
事件对象:Java将事件的相关信息 封装在一个事件对象中,所有的事件对象都最终派生于 java.util.EventObject类。不同的事件源可以产生不 同类别的事件。
监听器对象:是一个实现了特定监听器接口( listener interface)的类实例。
注册监听器方法 eventSourceObject.addEventListener(eventListenerObject)
动作事件(ActionEvent):当特定组件动作(点 击按钮)发生时,该组件生成此动作事件。
能够触发动作事件的动作,主要包括: (1) 点击按钮 (2) 双击一个列表中的选项; (3) 选择菜单项; (4) 在文本框中输入回车。
监听器接口的实现:
监听器类必须实现与事件源相对应的接口,即必 须提供接口中方法的实现。
监听器接口方法实现 class Mylistener implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed (ActionEvent event) { …… } }
命令按钮Jbutton主要API:
1.创建按钮对象 JButton类常用的一组构造方法: (1) JButton(String text):创建一个带文本的按钮。 (2) JButton(Icon icon) :创建一个带图标的按钮。 (3)JButton(String text, Icon icon) :创建一个带文本和图标 的按钮。
2.按钮对象的常用方法 ① getLabel( ):返回按钮的标签字符串; ② setLabel(String s):设置按钮的标签为字符串s。
实验十三 图形界面事件处理技术
实验时间 2018-11-22
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握事件处理的基本原理,理解其用途;
(2) 掌握AWT事件模型的工作机制;
(3) 掌握事件处理的基本编程模型;
(4) 了解GUI界面组件观感设置方法;
(5) 掌握WindowAdapter类、AbstractAction类的用法;
(6) 掌握GUI程序中鼠标事件处理技术。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第11章示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材443页-444页程序11-1,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 在事件处理相关代码处添加注释;
l 用lambda表达式简化程序;
l 掌握JButton组件的基本API;
l 掌握Java中事件处理的基本编程模型。
package button; import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* A frame with a button panel
*/
public class ButtonFrame extends JFrame
{
private JPanel buttonPanel;
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200; public ButtonFrame()
{
setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); // 创建按钮
JButton yellowButton = new JButton("Yellow");
JButton blueButton = new JButton("Blue");
JButton redButton = new JButton("Red"); buttonPanel = new JPanel(); // 向面板添加按钮
buttonPanel.add(yellowButton);
buttonPanel.add(blueButton);
buttonPanel.add(redButton); // 将面板添加到帧
add(buttonPanel); // 创建按钮动作
ColorAction yellowAction = new ColorAction(Color.YELLOW);
ColorAction blueAction = new ColorAction(Color.BLUE);
ColorAction redAction = new ColorAction(Color.RED); // 用按钮关联动作
yellowButton.addActionListener(yellowAction);
blueButton.addActionListener(blueAction);
redButton.addActionListener(redAction);
}//通过addActionListener关联监听器对象和组件 /**
* An action listener that sets the panel's background color.
*/
private class ColorAction implements ActionListener//implements实现了ActionListener监听器接口
{
private Color backgroundColor; public ColorAction(Color c)
{
backgroundColor = c;
} public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)//更改容器的背景色
{
buttonPanel.setBackground(backgroundColor);
}
}
}
package button; import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* @version 1.34 2015-06-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class ButtonTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new ButtonFrame();
frame.setTitle("ButtonTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
程序运行结果如下:
测试程序2:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材449页程序11-2,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 在组件观感设置代码处添加注释;
l 了解GUI程序中观感的设置方法。
package plaf; import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.SwingUtilities;
import javax.swing.UIManager; /**
* A frame with a button panel for changing look-and-feel
*/
public class PlafFrame extends JFrame
{
private JPanel buttonPanel; public PlafFrame()
{
buttonPanel = new JPanel(); UIManager.LookAndFeelInfo[] infos = UIManager.getInstalledLookAndFeels();//返回表示当前可用的 LookAndFeel 实现的 LookAndFeelInfo 数组
for (UIManager.LookAndFeelInfo info : infos)
makeButton(info.getName(), info.getClassName()); add(buttonPanel);//将指定组件追加到此容器的尾部
pack();//调整此窗口的大小,以适合其子组件的首选大小和布局
} /**
* Makes a button to change the pluggable look-and-feel.
* @param name the button name
* @param className the name of the look-and-feel class
*/
private void makeButton(String name, String className)
{
// 向面板添加按钮 JButton button = new JButton(name);//创建一个带文本的按钮
buttonPanel.add(button); // 设置按钮动作 button.addActionListener(event -> {
// 按钮动作:切换到新的外观和感觉
try
{
UIManager.setLookAndFeel(className);
SwingUtilities.updateComponentTreeUI(this);
pack();//调整此窗口的大小,以适合其子组件的首选大小和布局。
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
package plaf; import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* @version 1.32 2015-06-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class PlafTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new PlafFrame();
frame.setTitle("PlafTest");//将此窗体的标题设置为指定的字符串。
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
程序运行结果如下:

测试程序3:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材457页-458页程序11-3,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握AbstractAction类及其动作对象;
l 掌握GUI程序中按钮、键盘动作映射到动作对象的方法。
package action; import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* A frame with a panel that demonstrates color change actions.
*/
public class ActionFrame extends JFrame
{
private JPanel buttonPanel;
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200; public ActionFrame()
{
setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); buttonPanel = new JPanel(); // 定义行为
//根据指定的文件创建一个 ImageIcon
Action yellowAction = new ColorAction("Yellow", new ImageIcon("yellow-ball.gif"),
Color.YELLOW);
Action blueAction = new ColorAction("Blue", new ImageIcon("blue-ball.gif"), Color.BLUE);
Action redAction = new ColorAction("Red", new ImageIcon("red-ball.gif"), Color.RED); // 为这些操作添加按钮
buttonPanel.add(new JButton(yellowAction));
buttonPanel.add(new JButton(blueAction));
buttonPanel.add(new JButton(redAction)); // 将面板添加到帧
add(buttonPanel); // 将Y、B和R键与名称关联
InputMap imap = buttonPanel.getInputMap(JComponent.WHEN_ANCESTOR_OF_FOCUSED_COMPONENT);
imap.put(KeyStroke.getKeyStroke("ctrl Y"), "panel.yellow");
imap.put(KeyStroke.getKeyStroke("ctrl B"), "panel.blue");
imap.put(KeyStroke.getKeyStroke("ctrl R"), "panel.red"); // 把名字和动作联系起来
ActionMap amap = buttonPanel.getActionMap();
amap.put("panel.yellow", yellowAction);
amap.put("panel.blue", blueAction);
amap.put("panel.red", redAction);
} public class ColorAction extends AbstractAction
{
/**
* Constructs a color action.
* @param name the name to show on the button
* @param icon the icon to display on the button
* @param c the background color
*/
public ColorAction(String name, Icon icon, Color c)
{
putValue(Action.NAME, name);
putValue(Action.SMALL_ICON, icon);
putValue(Action.SHORT_DESCRIPTION, "Set panel color to " + name.toLowerCase());
putValue("color", c);
} public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
Color c = (Color) getValue("color");
buttonPanel.setBackground(c);//设置此组件的背景色
}
}
}
package action; import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* @version 1.34 2015-06-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class ActionTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new ActionFrame();
frame.setTitle("ActionTest");//将此窗体的标题设置为指定的字符串
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
程序运行结果如下:
测试程序4:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材462页程序11-4、11-5,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握GUI程序中鼠标事件处理技术。
package mouse; import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* A component with mouse operations for adding and removing squares.
*/
public class MouseComponent extends JComponent
{
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200; private static final int SIDELENGTH = 10;
private ArrayList<Rectangle2D> squares;
private Rectangle2D current; // 包含鼠标光标的正方形 public MouseComponent()
{
squares = new ArrayList<>();
current = null; addMouseListener(new MouseHandler());
addMouseMotionListener(new MouseMotionHandler());
} public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); } public void paintComponent(Graphics g)
{
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g; // 绘制所有正方形
for (Rectangle2D r : squares)
g2.draw(r);
} /**
* Finds the first square containing a point.
* @param p a point
* @return the first square that contains p
*/
public Rectangle2D find(Point2D p)
{
for (Rectangle2D r : squares)
{
if (r.contains(p)) return r;
}
return null;
} /**
* Adds a square to the collection.
* @param p the center of the square
*/
public void add(Point2D p)
{
double x = p.getX();
double y = p.getY(); current = new Rectangle2D.Double(x - SIDELENGTH / 2, y - SIDELENGTH / 2, SIDELENGTH,
SIDELENGTH);
squares.add(current);
repaint();
} /**
* Removes a square from the collection.
* @param s the square to remove
*/
public void remove(Rectangle2D s)
{
if (s == null) return;
if (s == current) current = null;
squares.remove(s);
repaint();
} private class MouseHandler extends MouseAdapter
{
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent event)
{
// 如果光标不在正方形中,则添加一个新的正方形
current = find(event.getPoint());
if (current == null) add(event.getPoint());
} public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent event)
{
// 如果双击,删除当前方块
current = find(event.getPoint());
if (current != null && event.getClickCount() >= 2) remove(current);
}
} private class MouseMotionHandler implements MouseMotionListener
{
public void mouseMoved(MouseEvent event)
{
// 设置鼠标光标,如果里面是交叉
// 一个矩形 if (find(event.getPoint()) == null) setCursor(Cursor.getDefaultCursor());
else setCursor(Cursor.getPredefinedCursor(Cursor.CROSSHAIR_CURSOR));
} public void mouseDragged(MouseEvent event)
{
if (current != null)
{
int x = event.getX();
int y = event.getY(); // 拖动当前矩形将其置于(x,y)中心
current.setFrame(x - SIDELENGTH / 2, y - SIDELENGTH / 2, SIDELENGTH, SIDELENGTH);
repaint();
}
}
}
}
package mouse; import javax.swing.*; /**
* A frame containing a panel for testing mouse operations
*/
public class MouseFrame extends JFrame
{
public MouseFrame()
{
add(new MouseComponent());//将指定组件追加到此容器的尾部
pack();//调整此窗口的大小,以适合其子组件的首选大小和布局
}
}
package mouse; import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* @version 1.34 2015-06-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class MouseTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new MouseFrame();
frame.setTitle("MouseTest");//将此窗体的标题设置为指定的字符串
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
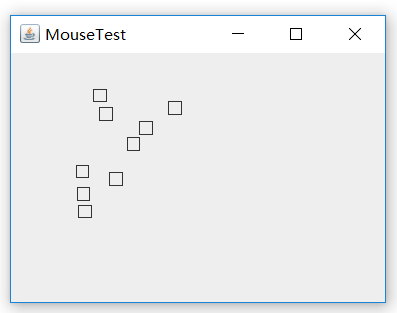
程序运行结果如下:
实验2:结对编程练习
利用班级名单文件、文本框和按钮组件,设计一个有如下界面(图1)的点名器,要求用户点击开始按钮后在文本输入框随机显示2017级网络与信息安全班同学姓名,如图2所示,点击停止按钮后,文本输入框不再变换同学姓名,此同学则是被点到的同学姓名。
结对同学:韩腊梅
package 点名器; import java.util.*;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import javax.swing.event.*;
public class NameFrame extends JFrame implements ActionListener{ private JButton A;
private JButton B;
private static boolean flag = true;
public NameFrame(){
this.setLayout(null);//布局管理器必须先初始化为空才能赋值
A = new JButton("准备中");
B = new JButton("开始");
this.add(A);
A.setOpaque(true);//如果为 true,则该组件绘制其边界内的所有像素。
A.setBackground(Color.CYAN);
A.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,22));
A.setHorizontalAlignment(JButton.CENTER);
A.setVerticalAlignment(JButton.CENTER);
A.setBounds(100,80,200,60); this.add(B);
B.setBounds(160,160,80,26);
B.addActionListener(this); this.setTitle("随机点名器");
this.setBounds(400,400,400,300);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
int i=0;
String names[]=new String[50];
try {
Scanner in=new Scanner(new File("D:\\studentnamelist.txt"));
while(in.hasNextLine())
{
names[i]=in.nextLine();
i++;
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
if(B.getText()=="开始"){
A.setBackground(Color.ORANGE);
flag = true;
new Thread(){
public void run(){
while(NameFrame.flag){
Random r = new Random();
int i= r.nextInt(47);
A.setText(names[i]);
}
}
}.start();
B.setText("停止");
B.setBackground(Color.YELLOW);
}
else if(B.getText()=="停止"){
flag = false;
B.setText("开始");
B.setBackground(Color.BLUE);
A.setBackground(Color.WHITE);
}
}
public static void main(String arguments []){
new NameFrame();
}
}
运行结果如下:

实验总结:
在这周的学习中我们学习了图形界面事件处理技术的知识,首先掌握了事件处理的基本原理,并学会了事件处理的基本编程模型。通过这次的实验基本上掌握了事件处理的基本原理,但对用lambda表达式简化程序不是很理解。
达拉草201771010105《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十三周学习总结的更多相关文章
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第九周学习总结
第九周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 异常.断言和调试.日志 1.捕获 ...
- 201871010132-张潇潇《面向对象程序设计(java)》第一周学习总结
面向对象程序设计(Java) 博文正文开头 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cn ...
- 扎西平措 201571030332《面向对象程序设计 Java 》第一周学习总结
<面向对象程序设计(java)>第一周学习总结 正文开头: 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 ...
- 杨其菊201771010134《面向对象程序设计Java》第二周学习总结
第三章 Java基本程序设计结构 第一部分:(理论知识部分) 本章主要学习:基本内容:数据类型:变量:运算符:类型转换,字符串,输入输出,控制流程,大数值以及数组. 1.基本概念: 1)标识符:由字母 ...
- 201871010124 王生涛《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第一周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/xbsf/ ...
- 201871010115——马北《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201777010217-金云馨《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201871010132——张潇潇《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201771010123汪慧和《面向对象程序设计Java》第二周学习总结
一.理论知识部分 1.标识符由字母.下划线.美元符号和数字组成, 且第一个符号不能为数字.标识符可用作: 类名.变量名.方法名.数组名.文件名等.第二部分:理论知识学习部分 2.关键字就是Java语言 ...
- 达拉草201771010105《面向对象程序设计(java)》第三周学习总结
达拉草201771010105«面向对象程序设计(java)»第三周学习总结 第一部分:实验部分 1.实验目的与要求 (1)进一步掌握Eclipse集成开发环境下java程序开发基本步骤: (2)熟 ...
随机推荐
- SoapUI+excel接口自动化测试简述
1.自动化测试工具介绍 由于系统前后端分离,所以接口测试势在必行,在接触了几天接口测试框架,包括postman.httpclient.loadrunner.soapUI等,下面具体讲讲最终决定使用so ...
- CentOS7离线安装MySQL8.0
CentOS7离线安装MySQL8.0 卸载软件 rpm -e --nodeps 要卸载的软件包 root@jacky zookeeper]# rpm -e --nodeps java-1.6.0-o ...
- Matlab高级教程_第二篇:MATLAB和C#对应数据类型的讲解(多讲一点儿C#的矩阵运算)
1. MATLAB对应C#的数据类型主要在引入的父类库MWArray当中.有如下对应规则 .NET TYPE MWArrayTYPE MATLAB Type System.Double MWNumer ...
- 八、linux-mysql的mysql主从复制原理和实战
1.mysql主从复制介绍 mysql支持单向.双向.链式级联.实时.异步复制,在复制过程中,一台服务器充当主服务器(Master),而一个或多个其它服务器充当从服务器(Slave). 复制:单向同步 ...
- springboot 整合thymeleaf 书笔记
pom.xml依赖添加 <!--引入thymeleaf--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</ ...
- mui 左侧选项卡-div模式 的选项卡切换监听
使用$('#segmentedControls').on('change', '.mui-control-item', function () { })和 document.getElementByI ...
- 网络流dinic板子
bool bfs(){ memset(deep,0,sizeof(deep)); queue<int>que; que.push(s); deep[s]=1; while(!que.emp ...
- 5-6 学生CPP成绩计算
给出下面的人员基类框架: class Person { protected: string name; int age; public: Person(); Person (string p_name ...
- TCP与UDP 笔记
本文整理自:<图解TCP/IP 第5版>作者:[日] 竹下隆史,[日] 村山公保,[日] 荒井透,[日] 苅田幸雄 著译者:乌尼日其其格出版时间:2013-07 TCP提供可靠的通信传输, ...
- Redis为什么会比MySQL快?
1.Redis是基于内存存储的,MySQL是基于磁盘存储的 2.Redis存储的是k-v格式的数据.时间复杂度是O(1),常数阶,而MySQL引擎的底层实现是B+Tree,时间复杂度是O(logn), ...
