【数据结构】30、hashmap=》hash 计算方式
前提知识
写在前面,为什么num&(length - 1) 在length是2的n次幂的时候等价于num%length
n - 1意味着比n最高位小的位都为1,而高的位都为0,因此通过与可以剔除位数比n最高位更高的部分,只保留比n最高位小的部分,也就是取余了。
而且用位运算取代%,效率会比较高。
基于以上几点,我们再看看hashmap中如何计算hash值得
这里吧key的hashcode取出来,然后把它右移16位,然后取异或
这里从我Google得到的信息是,int是4个字节,也就是32位,我们右移16位也即是把高位的数据右移到低位的16位,然后做异或,那就是把高位和低位的数据进行重合
同时保留了低位和高位的信息
但是为什么是右移16位,这边保留疑问,我要是右移8位,4位,2位呢???
不做右移肯定不是,不做右移直接异或,那不就是0么
我们直接做个测试
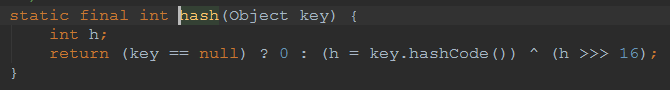
public static int hash(Object key) {
int h;
//也就将key的hashCode无符号右移16位然后与hashCode异或从而得到hash值在putVal方法中(n - 1)& hash计算得到桶的索引位置
//注意,这里h是int值,也就是32位,然后无符号又移16位,那么就是折半,折半之后和原来的数据做异或操作,正好整合了高位和低位的数据
//混合原始哈希码的高位和低位,以此来加大低位的随机性,而且混合后的低位掺杂了高位的部分特征,这样高位的信息也被变相保留下来。
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
//测试,如果我们不做高位低位的操作看看hash冲突是大还是小
public static int hash2(Object key) {
return (int) key;
}
public static int hash3(Object key) {
int h = key.hashCode();
//我们不做右移试试,那就自己跟自己异或。。。没意义,只能是0了
return (key == null) ? 0 : h ^ h;
}
public static int hash4(Object key) {
int h;
//我们不做右移试试,或者右移8位试试
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 8);
}
public static int hash5(Object key) {
int h;
//我们不做右移试试,或者右移8位试试
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
public static int hash6(Object key) {
int h;
//我们不做右移试试,或者右移8位试试
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 2);
}
hash3的测试可以去除不用考虑了
public void testHash() {
//产生随机数
int init = 64 * 64;
int size = 64 * 64;
for(int j = 0; j < 10; ++j) {
// int size = init * (j+1);
size *= 2;
int hash1[] = new int[size];
int hash2[] = new int[size];
int hash3[] = new int[size];
int hash4[] = new int[size];
int hash5[] = new int[size];
int hash6[] = new int[size];
int testCount = size;
int exist1 = 0;
int exist2 = 0;
int exist3 = 0;
int exist4 = 0;
int exist5 = 0;
int exist6 = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < testCount; ++i) {
int key = (int) ((Math.random() * (size - 1)) + 1);
if(hash1[MyHashMap.hash(key)&(size - 1)] != 0) {
exist1++;
} else {
hash1[MyHashMap.hash(key)&(size - 1)] = 1;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < testCount; ++i) {
int key = (int) ((Math.random() * (size - 1)) + 1);
if(hash2[MyHashMap.hash2(key)&(size - 1)] != 0) {
exist2++;
} else {
hash2[MyHashMap.hash2(key)&(size - 1)] = 1;
}
}
// for(int i = 0; i < testCount; ++i) {
//
// int key = (int) ((Math.random() * (size - 1)) + 1);
//
// if(hash3[MyHashMap.hash3(key)&(size - 1)] != 0) {
// exist3++;
// } else {
// hash3[MyHashMap.hash3(key)&(size - 1)] = 1;
// }
// }
for(int i = 0; i < testCount; ++i) {
int key = (int) ((Math.random() * (size - 1)) + 1);
if(hash4[MyHashMap.hash4(key)&(size - 1)] != 0) {
exist4++;
} else {
hash4[MyHashMap.hash4(key)&(size - 1)] = 1;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < testCount; ++i) {
int key = (int) ((Math.random() * (size - 1)) + 1);
if(hash5[MyHashMap.hash5(key)&(size - 1)] != 0) {
exist5++;
} else {
hash5[MyHashMap.hash5(key)&(size - 1)] = 1;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < testCount; ++i) {
int key = (int) ((Math.random() * (size - 1)) + 1);
if(hash6[MyHashMap.hash6(key)&(size - 1)] != 0) {
exist6++;
} else {
hash6[MyHashMap.hash6(key)&(size - 1)] = 1;
}
}
System.out.println("冲突比较:\t1:" + exist1 + "\t2:" + exist2 + "\t4:" + exist4 + "\t5:" + exist5 + "\t6:" + exist6);
}
}
开始测试:
上面是size会递增的,现在我们先测size不变的情况看看效果
size=64 * 64
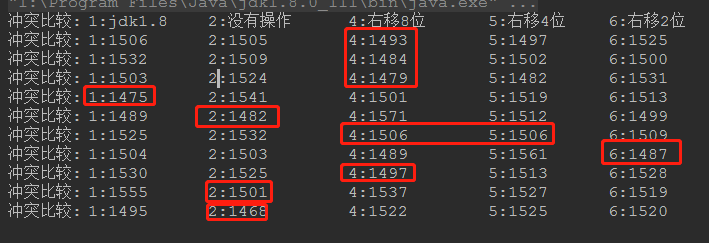
从结果上看明显是右移8位冲突比较少!!!
我们把size扩大一倍

再扩大一倍
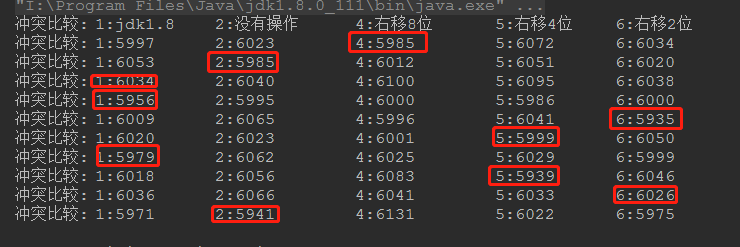
这次还比较平价
有人会说这是因为每次随机的数不一样的,每次都是产生新的随机数,没有可比性
那么我们每次用一个固定的数去进行hash碰撞
还是64*64开始,依次乘以2,4
@org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
public void testHash2() throws InterruptedException {
//产生随机数
int init = 64 * 64;
int size = 8; System.out.println("冲突比较:\t1:jdk1.8\t2:没有操作\t\t4:右移8位\t\t5:右移4位\t\t6:右移2位"); for(int j = 0; j < 10; ++j) {
// int size = init * (j+1);
size = 8 * j + size;
int hash1[] = new int[size];
int hash2[] = new int[size];
int hash4[] = new int[size];
int hash5[] = new int[size];
int hash6[] = new int[size]; int testCount = size / 3;
int exist1 = 0;
int exist2 = 0;
int exist4 = 0;
int exist5 = 0;
int exist6 = 0; for(int i = 0; i < testCount; ++i) {
Thread.sleep(i + 1);
int key = (int) ((Math.random() * (size - 1)) + 1) * j * (i + 1); if(hash1[MyHashMap.hash(key)&(size - 1)] != 0) {
exist1++;
} else {
hash1[MyHashMap.hash(key)&(size - 1)] = 1;
} if(hash2[MyHashMap.hash2(key)&(size - 1)] != 0) {
exist2++;
} else {
hash2[MyHashMap.hash2(key)&(size - 1)] = 1;
} if(hash4[MyHashMap.hash4(key)&(size - 1)] != 0) {
exist4++;
} else {
hash4[MyHashMap.hash4(key)&(size - 1)] = 1;
} if(hash5[MyHashMap.hash5(key)&(size - 1)] != 0) {
exist5++;
} else {
hash5[MyHashMap.hash5(key)&(size - 1)] = 1;
} if(hash6[MyHashMap.hash6(key)&(size - 1)] != 0) {
exist6++;
} else {
hash6[MyHashMap.hash6(key)&(size - 1)] = 1;
}
} System.out.println("冲突比较:\t1:" + exist1 + "\t\t2:" + exist2 + "\t\t4:" + exist4 + "\t\t\t5:" + exist5 + "\t\t6:" + exist6);
} }
我们还是执行三次比较:

从第一次看结果好像jdk自带的方式冲突还比较多。。。
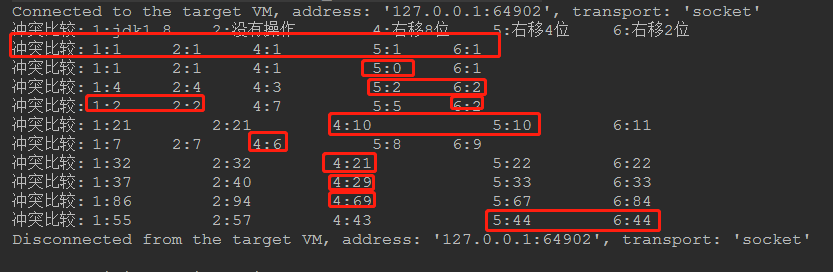
我最后再来一次,怎么感觉越来越不对劲。。。
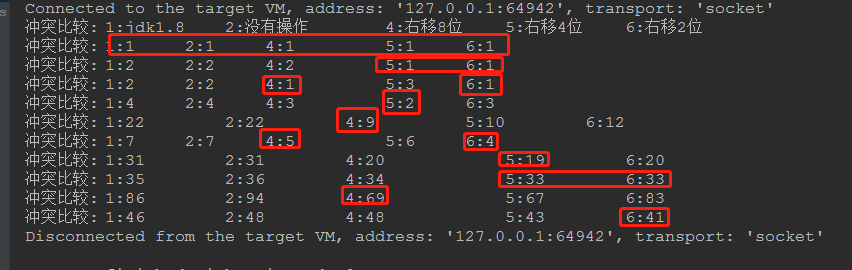
总结:我懵逼了啊!!!为什么啊,我测试出来感觉jdk自带的右移16位的方式,并不能有效减少冲突,反而右移4或者8位测试效果比较好!!!
求大神解答!!!
【数据结构】30、hashmap=》hash 计算方式的更多相关文章
- 数据结构之HashMap
前言 在我们开发中,HashMap是我们非常常用的数据结构,接下来我将进一步去了解HashMap的原理.结构. 1.HashMap的实现原理 HashMap底层是基于Hash表(也称“散列”)的数据结 ...
- Java基础-时间复杂度计算方式
Java基础-时间复杂度计算方式 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 时间复杂度通常是衡量算法的优劣的,衡量算法的时间严格来讲是很难衡量的,由于不同的机器性能不用环境 ...
- HashMap循环遍历方式及其性能对比(zhuan)
http://www.trinea.cn/android/hashmap-loop-performance/ ********************************************* ...
- HashMap循环遍历方式及其性能对比
主要介绍HashMap的四种循环遍历方式,各种方式的性能测试对比,根据HashMap的源码实现分析性能结果,总结结论. 1. Map的四种遍历方式 下面只是简单介绍各种遍历示例(以HashMap为 ...
- flex布局中flex-grow与flex-shrink的计算方式
CSS 中的 Flex(弹性布局) 可以很灵活的控制网页的布局,其中决定 Flex 布局内项目宽度/高度的是三个属性: flex-basis, flex-grow, flex-shrink. flex ...
- System.currentTimeMillis()计算方式与时间的单位转换
目录[-] 一.时间的单位转换 二.System.currentTimeMillis()计算方式 一.时间的单位转换 1秒=1000毫秒(ms) 1毫秒=1/1,000秒(s)1秒=1,000,000 ...
- NTC(负温度)热敏电阻.阻值的计算方式
来源 :http://blog.csdn.net/blue0432/article/details/8690190 现在低成本测温方案中NTC热敏电阻用的比较多,一般采用查表的方法获取温度值,这就牵涉 ...
- mysql中TPS, QPS 的计算方式
今天突然有个同事问题一个问题, mysqlTPS和QPS的计算公式是什么? 以前确实也没有关注过这个计算公式,所以查了下学习了下: 下面是参考内容. 在做db基准测试的时候,qps,tps 是衡量数 ...
- 自学Aruba1.3-WLAN一些基本常识802.11n速率计算方式、802.11n及802.11AC速率表
点击返回:自学Aruba之路 自学Aruba1.3-WLAN一些基本常识802.11n速率计算 1. 802.11n速率计算方式1.1 802.11n使用的主要技术 802.11n采用MIMO多天线技 ...
随机推荐
- jquery 源码学习(二)
在网上找到一篇广为流传的文章<常用正则表达式>,逐一分析,不足地方进行补充和纠正 作者:nuysoft/JS攻城师/高云 QQ:47214707 EMail:nuysoft@gmail ...
- linux下安装sqlite3
1.介绍:sqlite3是linux上的小巧的数据库,一个文件就是一个数据库.2.安装: 要安装sqlite3,可以在终端提示符后运行下列命令: sudo apt-get install sqli ...
- Web 存储之localStorage
1.localStorage的浏览器支持情况 localStorage属于永久性存储,不移除永久存在:sessionStorage属于会话结束就消失. localStorage存储的大小在5M左右,不 ...
- CUDA—使用GPU暴力破解密码
GPU支持大规模的并行加速运算,胜在量上,CPU处理大量的并行运算显得力不从心,它是胜在逻辑上.利用显卡加速的应用越来越多,但如果说GPU即将或最终将替代CPU还有点言过其实,二者最终将优势互补,各尽 ...
- Python中 如何将一个字符串分成一个个字符
其实 一个字符串 实质也是 一个列表 就很简单了: a = ' for item in a: print(item) 打印结果: 121512 如果进而要统计字符出现的次数 , 那就很简单了.
- 从入门机器学习的零单排:OctaveMatlab经常使用绘图知识
OctaveMatlab经常使用绘图知识 之前一段时间在coursera看了Andrew ng的机器学习的课程,感觉还不错,算是入门了.这次打算以该课程的作业为主线,对机器学习基本知识做一下总结.小弟 ...
- 【C语言学习】C语言功能
代码,功能为了更好地实现模块化编程.那么,什么是函数的性质?在函数中定义的变量(全局变量.局部变量.静态变量)如何存储?为什么范围和全局变量和局部变量的寿命是不一样的?只是有一个更深入的了解的功能.能 ...
- WPF异常捕获,并使程序不崩溃!
原文:WPF异常捕获,并使程序不崩溃! 在.NET中,我们使用try-catch-finally来处理异常.但,当一个Exception抛出,抛出Exception的代码又没有被try包围时,程序就崩 ...
- POJ1185:火炮(减少国家)
Description 命令将军打算N*M该网络格他们的炮兵部队部署在地图上.一个N*M该地图由N行M列,每个地图格它可以是山(使用"H" 表示),也可能是平原(用"P& ...
- 【转载】MySQL和Keepalived高可用双主复制
服务器主机IP和虚拟浮动IP配置 RealServer A 192.168.75.133 RealServer B 192.168.75.134 VIP A 192.168.75.110 VIP B ...
