leetcode排列组合相关
78/90子集
输入: [1,2,2]
78输出:
[[], [1], [2], [1 2], [2], [1 2], [2 2], [1 2 2]]
90输出:
[[], [1], [2], [1 2], [2 2], [1 2 2]]
// 递归版简单很多,且与下面的39/40组合总和很相似
public static List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
// subset2用
// Arrays.sort(nums);
dfs(res, temp, nums, 0);
return res;
}
private static void dfs(List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> temp, int[] nums, int j) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
for (int i = j; i < nums.length; i++) {
// subset2用
// if (i != j && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) continue;
temp.add(nums[i]);
dfs(res, temp, nums, i + 1);
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
}
}
// 非递归版
// 结果变量
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
// 方便判断是否出现重复
Arrays.sort(nums);
// 先加上空子集
res.add(new ArrayList<>());
// 用于90
// int last = nums[0], size = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < nums.length; j++) {
// 用于90,如果出现不同值,就更新size,让下面i从0开始。如果相同,那么size就不需要更新,让i从tempSize - size开始,即去掉了上一轮中已经存在的,从上一轮才更新的数组进行添加。
// if (last != nums[j]) {
// last = nums[j];
// size = res.size();
// }
int tempSize = res.size();
// 遍历,把目前所拥有的所有子集都作为新子集,并在每个新子集中添加新元素
for (int i = 0; i < tempSize; i++) {
// 用于90
// for (int i = tempSize - size; i < tempSize; i++) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(res.get(i)));
res.get(res.size() - 1).add(nums[j]);
}
}
return res;
39/40组合总和
40(39是无重复元素的数组,所以省去排序。另外允许重复选取元素,所以递归调用函数时index不需要+1)
给定一个数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。
- 所有数字(包括目标数)都是正整数。
- 解集不能包含重复的组合。
思路:
- 排序,防止后面得出重复组合
- 新建midRes和res数组
- 调用递归函数,记录index表示遍历的起始位置(并不是选了多少个candidates)
- 从index开始遍历candidates
- 如果i不等于index,且当前遍历与上一个数相同,就continue。(防止得出重复组合)
- 如果target >= candidates[i]那么可以加入到midRes,然后递归调用函数,在i+1和target-candidates[i]的基础上。然后删除刚刚加入的元素(其实本轮遍历已经结束了),要找新的组合。
if (target == 0) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(midRes));
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < candidates.length; i++) {
// 由于上面进行了排序,所以相同的数都排在了一起
// i > index表示i在剩下的组合里已经不是第一个,那如果它和之前的相同,就会重复取值,所以这里continue。当然,如果在无重复元素数组中便不需要这一步和之前的sort
if (i > index && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]) continue;
if (target >= candidates[i]) { // 所以没有target < 0的情况
midRes.add(candidates[i]);
// 由于不能有重复地选取数字,所以i+1,表示上一个已经被取了。
solve(candidates, i+1, target - candidates[i], midRes, res);
midRes.remove(midRes.size() - 1);
}
}
77组合
从n取k个,列出所有不重复组合。
下面代码还有i <= n - k + size +1优化,其思想是,通过观察(5,3)可知,第一层只需遍历到3,第二层才到4,第三层才到5。将这规律扩展开来就能得到这个优化。
// 仿照上面的格式,但index从1开始
dfs(res, temp, n, k, 1);
// dfs
if (temp.size()==k) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
return;
}
int size = temp.size();
for (int i = j; i <= n - k + size + 1; i++) {
temp.add(i);
dfs(res, temp, n, k, i + 1);
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
}
46/47全排序,同颜色球不相邻的排序方法
思路与上面的类似,不同在于这里没有midRes数组,一切操作在原数组中进行。详细解析如下:
利用递归方法,先固定第一个位置的数,即下面的start,然后后面的数就相当于组成了新数组,所以又固定总体的第二个,即新数组的第一个,所以innerPermute的递归调用中,start+1。可以把innerPermute(nums, start + 1)理解为新数组的全排组合。而如此递归下去后,总会固定到总体的最后一位,即start == nums.length - 1,此时就直接输出当前nums,因为前面的都固定了,就相当于一个排列就已经组成了。另外,在每次求innerPermute(nums, start + 1)前,固定位置的数是可以是当前数字start以及start+1到最后的任意一个数,所以要循环的交换,即下图第一步中,1-1、1-2、1-3、1-4交换,相当于代码中for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++)和swap(nums, start, i);部分,而交换并求start+1到end这个新数组的全排列后,要再次交换回来。因为在上面循环交换中,1-2交换后,如果不换回来,就变成2-3交换而不是1-3了。这就是代码又多了一个swap(nums, start, i);的原因。
更进一步的permutation就要去重的,即1,1,2只有3个输出([1,1,2], [1,2,1], [2,1,1])而不是6个。而去重的方法就是现在交换前,做判断,详细看代码中containsDuplicate的注解。
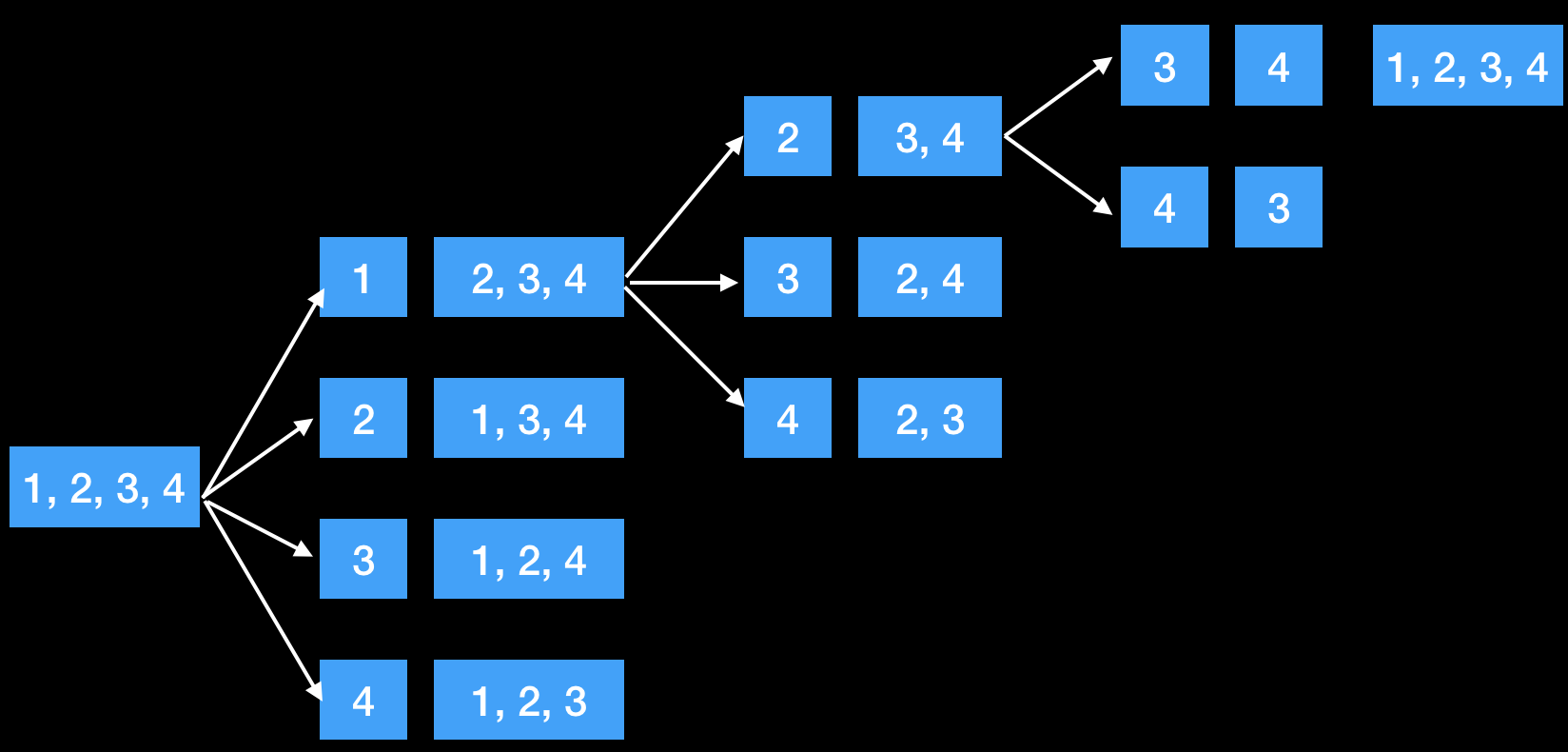
// 递归函数
if (start == nums.length - 1) { // 如果是“同颜色球不相邻”,不能-1
List<Integer> tempres = new ArrayList<>();
for (int num : nums) {
tempres.add(num);
}
res.add(tempres);
}
// start表示固定哪一个,固定后就相当于一个新数组,所以i从start开始
for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (containsDuplicate(nums, start, i)) { // 用于47去重
if (start == 0 || (nums[i] != nums[start - 1])) { // 用于“同颜色球不相邻”
swap(nums, start, i);
innerPermute(nums, start + 1);
swap(nums, start, i);
}
}
}
// containsDuplicate
// 检查新数组一部分,即start到当前要交换的数之间[start, end-1],将要交换到start位置的数,外层i,本层的end,是否已经在新数组中出现过,出现过就返回false,跳过这个数的交换。遍历完确定没有出现过才交换。比如[1,2,3,1]中,最后的1-1是不需要交换和取全排的,而判断就是(arr[0] == arr[3]) 返回false。再如比如[1,2,3,2]中,最后的1-2也是不需要交换和取全排的,因为之前已经进行了1-2交换,而判断就是(arr[1] == arr[3]) 返回false。
for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
if (arr[i] == arr[end]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
leetcode排列组合相关的更多相关文章
- 排列组合相关算法 python
获取指定长度得全部序列 通过事件来表述这个序列,即n重伯努利实验(二项分布)的全部可能结果.比如时间a表示为: a = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9], 假设每次实验为从 ...
- .NET平台开源项目速览(11)KwCombinatorics排列组合使用案例(1)
今年上半年,我在KwCombinatorics系列文章中,重点介绍了KwCombinatorics组件的使用情况,其实这个组件我5年前就开始用了,非常方便,麻雀虽小五脏俱全.所以一直非常喜欢,才写了几 ...
- 【CodeForces】889 C. Maximum Element 排列组合+动态规划
[题目]C. Maximum Element [题意]给定n和k,定义一个排列是好的当且仅当存在一个位置i,满足对于所有的j=[1,i-1]&&[i+1,i+k]有a[i]>a[ ...
- python自带的排列组合函数
需求: 在你的面前有一个n阶的台阶,你一步只能上1级或者2级,请计算出你可以采用多少种不同的方法爬完这个楼梯?输入一个正整数表示这个台阶的级数,输出一个正整数表示有多少种方法爬完这个楼梯. 分析:提炼 ...
- [leetcode] 题型整理之排列组合
一般用dfs来做 最简单的一种: 17. Letter Combinations of a Phone Number Given a digit string, return all possible ...
- LeetCode 77 Combinations(排列组合)
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/combinations/#/description Problem:给两个正数分别为n和k,求出从1,2.......n这 ...
- 【LeetCode每天一题】Permutations(排列组合)
Given a collection of distinct integers, return all possible permutations. Example: Input: [1,2,3] O ...
- LeetCode OJ:Combinations (排列组合)
Given two integers n and k, return all possible combinations of k numbers out of 1 ... n. For exampl ...
- [LeetCode] Combinations 组合项
Given two integers n and k, return all possible combinations of k numbers out of 1 ... n. For exampl ...
随机推荐
- (转)Hibernate框架基础——cascade属性
http://blog.csdn.net/yerenyuan_pku/article/details/52760010 我们以部门和员工的关系为例讲解一对多关联关系映射时,删除部门时,如果部门有关联的 ...
- (转)Struts2的标签库
http://blog.csdn.net/yerenyuan_pku/article/details/68638679 Struts2的标签库 对于一个MVC框架而言,重点是实现两部分:业务逻辑控制器 ...
- ats 与 https
一些证书相关的描述: https://developer.apple.com/library/content/documentation/General/Reference/InfoPlistKe ...
- js输出非字符串,非null值
console.log(!"");//非空(true) console.log(!);//非0(true) console.log(!" ");//非空格(fa ...
- CAD类型转换
AcDbEntity *pEnt; AcDbCircle *pcir = AcDbCircle::cast(pEnt); static_cast<AcDbCircle*>(pEnt); p ...
- java 异常报错总结
1.java.lang.ArithmeticException:这是算数异常 比如分母位0 2. java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException:数组下标越界异常 3 ...
- c++ list双向链表管理对象
#cat list.cc #include <cstdlib> #include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> using names ...
- Win32 线程同步
Win32 线程同步 ## Win32线程同步 ### 1. 原子锁 ### 2. 临界区 {全局变量} CRITICAL_SECTION CS = {0}; // 定义并初始化临界区结构体变量 {线 ...
- Django REST framework - 视图
目录 Django REST framework 视图GenericAPIView GenericAPIView 例子 属性 混入 具体视图类 自定义基类 Django REST framework ...
- BZOJ 1641 USACO 2007 Nov. Cow Hurdles 奶牛跨栏
[题解] 弗洛伊德.更新距离的时候把$f[i][j]=min(f[i][j],f[i][k]+f[k][j])$改为$f[i][j]=min(f[i][j],max(f[i][k],f[k][j])) ...
