Floyd(弗洛伊德)算法(C语言)
转载:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35644234/article/details/60875818
Floyd算法的介绍
算法的特点
弗洛伊德算法是解决任意两点间的最短路径的一种算法,可以正确处理有向图或有向图或负权(但不可存在负权回路)的最短路径问题,同时也被用于计算有向图的传递闭包。
算法的思路
通过Floyd计算图G=(V,E)中各个顶点的最短路径时,需要引入两个矩阵,矩阵S中的元素a[i][j]表示顶点i(第i个顶点)到顶点j(第j个顶点)的距离。矩阵P中的元素b[i][j],表示顶点i到顶点j经过了b[i][j]记录的值所表示的顶点。
假设图G中顶点个数为N,则需要对矩阵D和矩阵P进行N次更新。初始时,矩阵D中顶点a[i][j]的距离为顶点i到顶点j的权值;如果i和j不相邻,则a[i][j]=∞,矩阵P的值为顶点b[i][j]的j的值。 接下来开始,对矩阵D进行N次更新。第1次更新时,如果”a[i][j]的距离” > “a[i][0]+a[0][j]”(a[i][0]+a[0][j]表示”i与j之间经过第1个顶点的距离”),则更新a[i][j]为”a[i][0]+a[0][j]”,更新b[i][j]=b[i][0]。 同理,第k次更新时,如果”a[i][j]的距离” > “a[i][k-1]+a[k-1][j]”,则更新a[i][j]为”a[i][k-1]+a[k-1][j]”,b[i][j]=b[i][k-1]。更新N次之后,操作完成!
补充:以下面图为例子,b[i][j]中存储的是Vi~Vj之间的中介点,b[i][j]初始值为j,比如V0~V3最短路径是V0-->V2-->V1-->v3,在计算最短路径时转换为V0-->V2的距离加上V2-->V3的最短距离,接下来类似于递归,V2-->V3的最短路径就是以V1为中介点,V2-->V1的距离加上V1-->V3的距离。因此,b[0][3]=2
实例说明
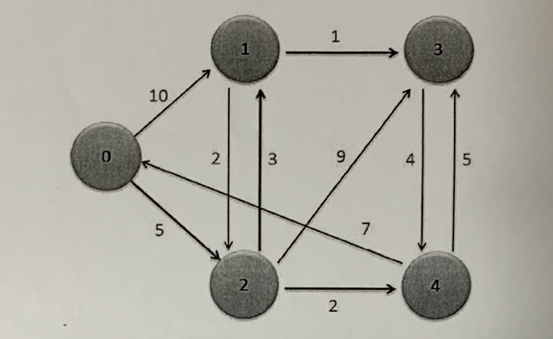
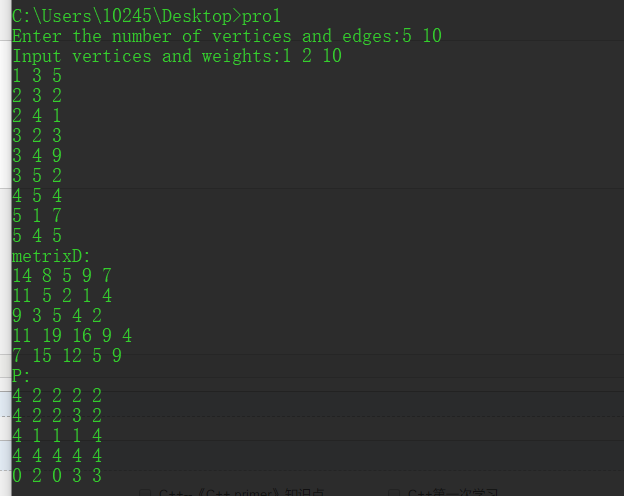
将整体分为两个步骤
1.计算metrixD矩阵(两顶点之间的最短距离)和P矩阵(两顶点的中介点)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h> void Create_metrixD_P(int** metrixD, int **P ,int VerNum, int EdgNum)
{
int x, y, Weight, edg_count = ;
int i, j, k; for (i = ; i < VerNum; ++i) {
for (j = ; j < VerNum; ++j) {
metrixD[i][j] = INT_MAX;
P[i][j] = j;
}
} while (edg_count < EdgNum) {
scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &y, &Weight);
metrixD[x - ][y - ] = Weight;
edg_count++;
}
} //Floyd algorithm
void Floyd(int **metirxD, int **P, int VerNum) {
int n, x, y, temp = ;
//The triple loop looks for shortest paths and weights
for (n = ; n < VerNum; ++n) {
for (x = ; x < VerNum; ++x) {
for (y = ; y < VerNum; ++y) {
//The distance between two vertices is compared to the distance through a vertex
temp = (metirxD[x][n] == INT_MAX || metirxD[n][y] == INT_MAX) ? INT_MAX : (metirxD[x][n] + metirxD[n][y]);
if (temp < metirxD[x][y]) {
//Update matrix information
metirxD[x][y] = temp;
P[x][y] = n;
}
}
}
}
} void Show_metrixD_P(int** metrixD, int **P, int VerNum)
{
int x, y;
printf("metrixD:\n");
for (x = ; x < VerNum; ++x) {
for (y = ; y < VerNum; ++y) {
if (metrixD[x][y] == INT_MAX) {
printf("∞ ");
}
else {
printf("%d ", metrixD[x][y]);
}
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("P:\n");
for (x = ; x < VerNum; ++x) {
for (y = ; y < VerNum; ++y) {
printf("%d ", P[x][y]);
}
printf("\n");
}
} int main(void)
{
int VerNum, EdgNum, i;
int** metrixD, ** P; printf("Enter the number of vertices and edges:");
scanf("%d%d", &VerNum, &EdgNum); metrixD = (int**)malloc(VerNum * sizeof(int));
P = (int**)malloc(VerNum * sizeof(int)); for (i = ; i < VerNum; ++i) {
metrixD[i] = (int*)malloc(VerNum * sizeof(int));
P[i] = (int*)malloc(VerNum * sizeof(int));
} printf("Input vertices and weights:");
Create_metrixD_P(metrixD, P, VerNum, EdgNum);
Floyd(metrixD, P, VerNum);
Show_metrixD_P(metrixD, P, VerNum); for (i = ; i < VerNum; ++i) {
free(metrixD[i]);
free(P[i]);
}
free(metrixD);
free(P); return ;
}
2.输出顶点之间的最短距离与路径
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h> #define VEXNUM 5 //Adjacency matrix: shows the distance between vertices
int metirxD[VEXNUM][VEXNUM] = {
INT_MAX,, , INT_MAX,INT_MAX,
INT_MAX,INT_MAX,, , INT_MAX,
INT_MAX,, INT_MAX,, ,
INT_MAX,INT_MAX,INT_MAX,INT_MAX,,
, INT_MAX,INT_MAX,, INT_MAX
}; //Path: passing vertex between two vertices
int P[VEXNUM][VEXNUM] = {
,,,,,
,,,,,
,,,,,
,,,,,
,,,,
}; //Floyd algorithm
void Floyd() {
int n, x, y, temp = ;
//The triple loop looks for shortest paths and weights
for (n = ; n < VEXNUM; ++n) {
for (x = ; x < VEXNUM; ++x) {
for (y = ; y < VEXNUM; ++y) {
//The distance between two vertices is compared to the distance through a vertex
temp = (metirxD[x][n] == INT_MAX || metirxD[n][y] == INT_MAX) ? INT_MAX : (metirxD[x][n] + metirxD[n][y]);
if (temp < metirxD[x][y]) {
//Update matrix information
metirxD[x][y] = temp;
P[x][y] = n;
}
}
}
}
} void Show_Path() {
int x, y, temp = ;
//Output the shortest path between two vertices
for (x = ; x < VEXNUM - ; ++x) {
for (y = x + ; y < VEXNUM; ++y) {
printf("V%d-->V%d weight:%d path:V%d", x, y, metirxD[x][y], x);
temp = P[x][y];
while (temp != y) {
printf("-->V%d", temp);
temp = P[temp][y];
}
printf("-->V%d", y);
printf("\n");
}
}
} int main(void)
{
Floyd();
Show_Path(); return ;
}

完整代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h> void Create_metrixD_P(int** metrixD, int **P ,int VerNum, int EdgNum)
{
int x, y, Weight, edg_count = ;
int i, j, k; for (i = ; i < VerNum; ++i) {
for (j = ; j < VerNum; ++j) {
metrixD[i][j] = INT_MAX;
P[i][j] = j;
}
} while (edg_count < EdgNum) {
scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &y, &Weight);
metrixD[x - ][y - ] = Weight;
edg_count++;
}
} //Floyd algorithm
void Floyd(int **metirxD, int **P, int VerNum) {
int n, x, y, temp = ;
//The triple loop looks for shortest paths and weights
for (n = ; n < VerNum; ++n) {
for (x = ; x < VerNum; ++x) {
for (y = ; y < VerNum; ++y) {
//The distance between two vertices is compared to the distance through a vertex
temp = (metirxD[x][n] == INT_MAX || metirxD[n][y] == INT_MAX) ? INT_MAX : (metirxD[x][n] + metirxD[n][y]);
if (temp < metirxD[x][y]) {
//Update matrix information
metirxD[x][y] = temp;
P[x][y] = n;
}
}
}
}
} void Show_metrixD_P(int** metrixD, int **P, int VerNum)
{
int x, y;
printf("metrixD:\n");
for (x = ; x < VerNum; ++x) {
for (y = ; y < VerNum; ++y) {
if (metrixD[x][y] == INT_MAX) {
printf("∞ ");
}
else {
printf("%d ", metrixD[x][y]);
}
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("P:\n");
for (x = ; x < VerNum; ++x) {
for (y = ; y < VerNum; ++y) {
printf("%d ", P[x][y]);
}
printf("\n");
}
} void Show_Path(int **metirxD, int **P, int VerNum) {
int x, y, temp = ;
//Output the shortest path between two vertices
for (x = ; x < VerNum - ; ++x) {
for (y = x + ; y < VerNum; ++y) {
printf("V%d-->V%d weight:%d path:V%d", x, y, metirxD[x][y], x);
temp = P[x][y];
while (temp != y) {
printf("-->V%d", temp);
temp = P[temp][y];
}
printf("-->V%d", y);
printf("\n");
}
}
} int main(void)
{
int VerNum, EdgNum, i;
int** metrixD, ** P; printf("Enter the number of vertices and edges:");
scanf("%d%d", &VerNum, &EdgNum); metrixD = (int**)malloc(VerNum * sizeof(int));
P = (int**)malloc(VerNum * sizeof(int)); for (i = ; i < VerNum; ++i) {
metrixD[i] = (int*)malloc(VerNum * sizeof(int));
P[i] = (int*)malloc(VerNum * sizeof(int));
} printf("Input vertices and weights:");
Create_metrixD_P(metrixD, P, VerNum, EdgNum);
Floyd(metrixD, P, VerNum);
Show_metrixD_P(metrixD, P, VerNum);
Show_Path(metrixD, P, VerNum); for (i = ; i < VerNum; ++i) {
free(metrixD[i]);
free(P[i]);
}
free(metrixD);
free(P); return ;
}
Floyd(弗洛伊德)算法(C语言)的更多相关文章
- 经典问题----最短路径(Floyd弗洛伊德算法)(HDU2066)
问题简介: 给定T条路,S个起点,D个终点,求最短的起点到终点的距离. 思路简介: 弗洛伊德算法即先以a作为中转点,再以a.b作为中转点,直到所有的点都做过中转点,求得所有点到其他点的最短路径,Flo ...
- Floyd弗洛伊德算法
先看懂如何使用 用Java实现一个地铁票价计算程序 String station = "A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8 A9 T1 A10 A11 A12 A13 T2 A1 ...
- 数据结构C语言版 弗洛伊德算法实现
/* 数据结构C语言版 弗洛伊德算法 P191 编译环境:Dev-C++ 4.9.9.2 */ #include <stdio.h>#include <limits.h> # ...
- Floyd算法(弗洛伊德算法)
算法描述: Floyd算法又称为弗洛伊德算法,插点法,是一种用于寻找给定的加权图中顶点间最短路径的算法.从图的带权邻接矩阵A=[a(i,j)] n×n开始,递归地进行n次更新,即由矩阵D(0)=A,按 ...
- 弗洛伊德算法(Floyd算法)
原博来自http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/ 弗洛伊德算法介绍 和Dijkstra算法一样,弗洛伊德(Floyd)算法也是一种用于寻找给定的加权图中顶点间最短路径的 ...
- 弗洛伊德算法(Floyd )
package com.rao.graph; /** * @author Srao * @className Floyd * @date 2019/12/11 18:43 * @package com ...
- [从今天开始修炼数据结构]图的最短路径 —— 迪杰斯特拉算法和弗洛伊德算法的详解与Java实现
在网图和非网图中,最短路径的含义不同.非网图中边上没有权值,所谓的最短路径,其实就是两顶点之间经过的边数最少的路径:而对于网图来说,最短路径,是指两顶点之间经过的边上权值之和最少的路径,我们称路径上第 ...
- Floyd最短路径算法
看完这篇文章写的小程序,Floyd最短路径算法,求从一个点到另一个点的最短距离,中间可以经过其他任意个点.三个for循环,从i到j依次经过k的最短距离,最外层for循环是经过点K,内部两个循环是从i( ...
- 【转】位置式、增量式PID算法C语言实现
位置式.增量式PID算法C语言实现 芯片:STM32F107VC 编译器:KEIL4 作者:SY 日期:2017-9-21 15:29:19 概述 PID 算法是一种工控领域常见的控制算法,用于闭环反 ...
随机推荐
- 移动端300ms兼容问题(移动端经典问题)
移动端300ms延迟原因 2007 年初.苹果公司在发布首款 iPhone 前夕,遇到一个问题:当时的网站都是为大屏幕设备所设计的.于是苹果的工程师们做了一些约定,应对 iPhone 这种小屏幕浏览桌 ...
- jquery 父,子,兄弟节点获取
jquery 父,子,兄弟节点获取 jQuery.parent(expr) //找父元素 jQuery.parents(expr) //找到所有祖先元素,不限于父 ...
- 面试题常考&必考之--js中的难点!!!原型链,原型(__proto__),原型对象(prototype)结合例子更易懂
1>首先,我们先将函数对象认识清楚: 补充snow的另一种写法: var snow =function(){}; 2>其次:就是原型对象 每当我们定义一个函数对象的时候,这个对象中就会包含 ...
- 【转】Django框架请求生命周期
https://www.cnblogs.com/gaoya666/p/9100626.html 先看一张图吧! 1.请求生命周期 - wsgi, 他就是socket服务端,用于接收用户请求并将请求进行 ...
- HTML5和CSS3兼容清单
1.CSS3 2.CSS3选择器 3.HTML5 4.HTML5 From
- Django学习之模板
一.常用语法 1.变量 2.Filters 3.自定义filter 4.Tags 5.csrf_token 6.注释 7.注意事项 二.母板 2.继承母板 3.块(block) 4.组件 5.静态文件 ...
- django中自定义404错误页面
自定义404页面,如下5个步骤:1)使用自定义的404页面,必须在setting文件修改DEBUG = False(即关闭debug调试模式)2)必须在setting文件修改ALLOWED_HOSTS ...
- 《JavaScript 高级程序设计》
第 3 章 基本概念 3.5.2 位操作符 ECMAScript 中所有数值都是以 IEEE-754 64 位格式存储,但位操作符并不直接操作 64 位的值.而是先将 64 位的值转换成 32 位的整 ...
- Vue实战:音乐播放器(一) 页面效果
先看一下效果图 首页 歌单详情页 歌手列表 歌手详情页 排行页面 榜单的详情页(排序样式) 搜索页面 搜索结果 播放器内核 歌词自动滚动 播放列表 用户中心
- flex 数字上标
以A的3次方为例,我们输入以下代码: /** * 部分代码参考Adobe文档: * http://help.adobe.com/zh_CN/AS3LCR/Flash_10.0/flash/text/e ...
