《图解设计模式》读书笔记4-2 STRATEGY模式
Strategy模式即策略模式,在编程中,策略指的就是算法。利用此模式可以整体替换算法,即使用不同方式解决同一个问题。比如设计一个围棋程序,通过切换算法可以方便地切换AI的难度。
示例程序
要实现:模拟两个人用不同的策略玩猜拳游戏。
UML
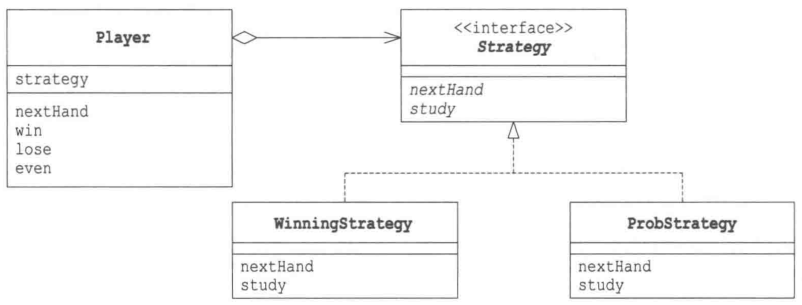
Hand类(手势类)
public class Hand {
public static final int HANDVALUE_ST = 0; // 表示石头的值
public static final int HANDVALUE_JD = 1; // 表示剪刀的值
public static final int HANDVALUE_BU = 2; // 表示布的值
public static final Hand[] hand = { // 表示猜拳中3种手势的实例
new Hand(HANDVALUE_ST),
new Hand(HANDVALUE_JD),
new Hand(HANDVALUE_BU),
};
private static final String[] name = { // 表示猜拳中手势所对应的字符串
"石头", "剪刀", "布",
};
private int handvalue; // 表示猜拳中出的手势的值
private Hand(int handvalue) {
this.handvalue = handvalue;
}
public static Hand getHand(int handvalue) { // 根据手势的值获取其对应的实例
return hand[handvalue];
}
public boolean isStrongerThan(Hand h) { // 如果this胜了h则返回true
return fight(h) == 1;
}
public boolean isWeakerThan(Hand h) { // 如果this输给了h则返回true
return fight(h) == -1;
}
private int fight(Hand h) { // 计分:平0, 胜1, 负-1
if (this == h) {
return 0;
} else if ((this.handvalue + 1) % 3 == h.handvalue) {
return 1;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
public String toString() { // 转换为手势值所对应的字符串
return name[handvalue];
}
}
Strategy接口
public interface Strategy {
//获取下一局要出的手势
public abstract Hand nextHand();
//如果win为true,表示上一局赢了,否则表示上一局输了
public abstract void study(boolean win);
}
WinningStrategy类
如果赢了就继续出同样的手势,否则换一个手势
public class WinningStrategy implements Strategy {
private Random random;
private boolean won = false;
private Hand prevHand;
public WinningStrategy(int seed) {
random = new Random(seed);
}
public Hand nextHand() {
if (!won) {
prevHand = Hand.getHand(random.nextInt(3));
}
return prevHand;
}
public void study(boolean win) {
won = win;
}
}
ProbStrategy类
根据以前的结果计算概率,确定这一次要出什么手势。
算法的具体内容不是关键,我们只需要知道这是一种算法就行了。
public class ProbStrategy implements Strategy {
private Random random;
private int prevHandValue = 0;
private int currentHandValue = 0;
private int[][] history = {
{1, 1, 1,},
{1, 1, 1,},
{1, 1, 1,},
};
public ProbStrategy(int seed) {
random = new Random(seed);
}
public Hand nextHand() {
int bet = random.nextInt(getSum(currentHandValue));
int handvalue = 0;
if (bet < history[currentHandValue][0]) {
handvalue = 0;
} else if (bet < history[currentHandValue][0] + history[currentHandValue][1]) {
handvalue = 1;
} else {
handvalue = 2;
}
prevHandValue = currentHandValue;
currentHandValue = handvalue;
return Hand.getHand(handvalue);
}
private int getSum(int hv) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
sum += history[hv][i];
}
return sum;
}
public void study(boolean win) {
if (win) {
history[prevHandValue][currentHandValue]++;
} else {
history[prevHandValue][(currentHandValue + 1) % 3]++;
history[prevHandValue][(currentHandValue + 2) % 3]++;
}
}
}
Player类(玩家类)
public class Player {
private String name;
private Strategy strategy;
private int wincount;
private int losecount;
private int gamecount;
public Player(String name, Strategy strategy) { // 赋予姓名和策略
this.name = name;
this.strategy = strategy;
}
public Hand nextHand() { // 策略决定下一局要出的手势
return strategy.nextHand();
}
public void win() { // 胜
strategy.study(true);
wincount++;
gamecount++;
}
public void lose() { // 负
strategy.study(false);
losecount++;
gamecount++;
}
public void even() { // 平
gamecount++;
}
public String toString() {
return "[" + name + ":" + gamecount + " games, " +
wincount + " win, " + losecount + " lose" + "]";
}
}
测试类
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int seed1 = Integer.parseInt("888");
int seed2 = Integer.parseInt("999");
Player player1 = new Player("小明", new WinningStrategy(seed1));
Player player2 = new Player("小紅", new ProbStrategy(seed2));
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
Hand nextHand1 = player1.nextHand();
Hand nextHand2 = player2.nextHand();
if (nextHand1.isStrongerThan(nextHand2)) {
System.out.println("胜利:" + player1);
player1.win();
player2.lose();
} else if (nextHand2.isStrongerThan(nextHand1)) {
System.out.println("失败:" + player2);
player1.lose();
player2.win();
} else {
System.out.println("平局...");
player1.even();
player2.even();
}
}
System.out.println("结果:");
System.out.println(player1.toString());
System.out.println(player2.toString());
}
}
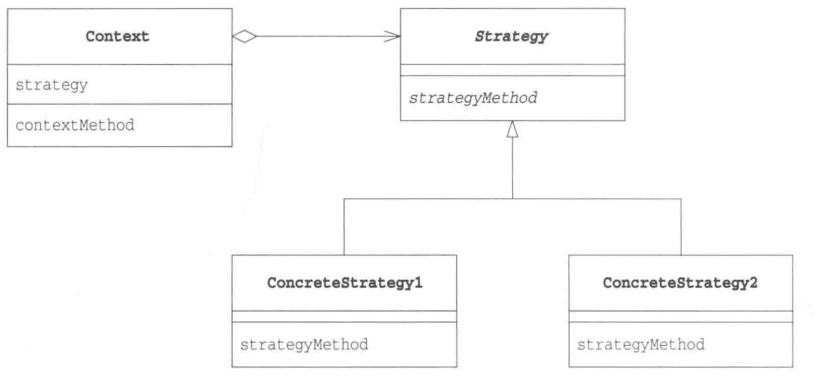
角色
Strategy(策略):抽象类或接口,负责定义策略用到的方法。
ConcreteStrategy(具体的策略):具体的策略类,继承Strategy接口,实现其中的方法。
Context(上下文):使用策略类的角色。注意:Context类和Strategy类是聚合关系,或者说是委托关系。
模式的类图:
想法
这个模式的实现非常简单:Context使用委托这种弱关联关系,方便地实现算法的整体替换。
《图解设计模式》读书笔记4-2 STRATEGY模式的更多相关文章
- HeadFirst设计模式读书笔记(3)-装饰者模式(Decorator Pattern)
装饰者模式:动态地将责任附件到对象上.若要扩展功能,装饰者提东了比继承更有弹性的替代方案. 装饰者和被装饰对象有相同的超类型 你可以用一个或者多个装饰者包装一个对象. 既然装饰者和被装饰对象有相同的超 ...
- HeadFirst设计模式读书笔记--目录
HeadFirst设计模式读书笔记(1)-策略模式(Strategy Pattern) HeadFirst设计模式读书笔记(2)-观察者模式(Observer Pattern) HeadFirst设计 ...
- Head First 设计模式读书笔记(1)-策略模式
一.策略模式的定义 策略模式定义了算法族,分别封装起来,让它们之间可以互换替换,此模式让算法的变化独立使用算法的客户. 二.使用策略模式的一个例子 2.1引出问题 某公司做了一套模拟鸭子的游戏:该游戏 ...
- C#设计模式学习笔记:(19)策略模式
本笔记摘抄自:https://www.cnblogs.com/PatrickLiu/p/8057654.html,记录一下学习过程以备后续查用. 一.引言 今天我们要讲行为型设计模式的第七个模式--策 ...
- JavaScript设计模式:读书笔记(未完)
该篇随我读书的进度持续更新阅读书目:<JavaScript设计模式> 2016/3/30 2016/3/31 2016/4/8 2016/3/30: 模式是一种可复用的解决方案,可用于解决 ...
- Head First设计模式读书笔记
阅读指南: 精读一章内容,手工输入一章代码(注1),与书中描述的思想进行印证,实在搞不懂就放过吧.设计模式绝对不会一次就看懂的. 这本书对于理解设计模式很有帮助,就是例子不太符合中国人的思维模式,但是 ...
- 图解http读书笔记
以前对HTTP协议一知半解,一直不清楚前端需要对于HTTP了解到什么程度,知道接触的东西多了,对于性能优化.服务端的配合和学习中也渐渐了解到了HTTP基础的重要性,看了一些大神对HTTP书籍的推荐,也 ...
- Java设计模式学习笔记(二) 简单工厂模式
前言 本篇是设计模式学习笔记的其中一篇文章,如对其他模式有兴趣,可从该地址查找设计模式学习笔记汇总地址 正文开始... 1. 简介 简单工厂模式不属于GoF23中设计模式之一,但在软件开发中应用也较为 ...
- Java设计模式学习笔记(三) 工厂方法模式
前言 本篇是设计模式学习笔记的其中一篇文章,如对其他模式有兴趣,可从该地址查找设计模式学习笔记汇总地址 1. 简介 上一篇博客介绍了简单工厂模式,简单工厂模式存在一个很严重的问题: 就是当系统需要引入 ...
- Java设计模式学习笔记(四) 抽象工厂模式
前言 本篇是设计模式学习笔记的其中一篇文章,如对其他模式有兴趣,可从该地址查找设计模式学习笔记汇总地址 1. 抽象工厂模式概述 工厂方法模式通过引入工厂等级结构,解决了简单工厂模式中工厂类职责太重的问 ...
随机推荐
- [Python3] 015 冰冻集合的内置方法
目录 0. 前言 英文名 元素要求 使用限制 返回 方法数量 1. 如何查看 frozenset() 的内置方法 2. 少废话,上例子 2.1 copy() 2.2 difference() 2.3 ...
- 洛谷 P3182 [HAOI2016]放棋子(高精度,错排问题)
传送门 解题思路 不会错排问题的请移步——错排问题 && 洛谷 P1595 信封问题 这一道题其实就是求对于每一行的每一个棋子都放在没有障碍的地方的方案数. 因为障碍是每行.每列只有一 ...
- 洛谷 - P4008 - 文本编辑器 - 无旋Treap
https://www.luogu.org/problem/P4008 无旋Treap也可以维护序列. 千万要注意要先判断p节点存在才进行Show操作,不然输出一个'\0'(或者RecBin里面的东西 ...
- 将地址转成blob格式(服务器下运行)
<div id="forAppend" class="demo"></div> <script> var eleAppend ...
- WinForm的RadioButton使用小技巧
http://www.cnblogs.com/sjrhero/articles/1883155.html 当多个RadioButton同在一个容器里面的时候,多半的操作都是要得到其中一个的值这个时候我 ...
- jquery的点击事件
一.任务需求:两个按钮,一个DIV,点击显示按钮显示DIV,点击隐藏按钮,隐藏DIV. 二.任务分析:监听按钮的点击,操作DIV的显示隐藏效果. 三.代码实现: <body> <bu ...
- Solr的学习使用之(六)获取数据列表-SolrDocumentList
以下是我项目中获取新闻数据列表的写法,包括数据总量.数据列表,接下来会贴出分片查询(facet)等高级查询 基本的注释都有了: private ListPage<News> queryFr ...
- C# WinForm定时触发事件
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; usin ...
- json和dict 在requests中请求
上面的问题,在这么晚的夜里解决了 data 接受的是json格式数据, json 接受dict格式点的数据, 这个文章中也讲到了https://www.cnblogs.com/beile/p/1086 ...
- python tkinter画圆
x0=150 #圆心横坐标 y0=100 #圆心纵坐标 canvas.create_oval(x0-10,y0-10,x0+10,y0+10) #圆外矩形左上角与右下角坐标 canv ...
