【图形学手记】Inverse Transform Sampling 逆转换抽样
需求:
我们通过调查,得知大多数人在20岁左右初恋,以20岁为基准,以随机变量X表示早于或晚于该时间的年数,为了简单,假设X值域为[-5,5],并且PDF(X)是一个正态分布函数(当然可以为任意分布,这里具体化一个熟悉的,方便后面验证)
现在要求,做出一个计算机模拟程序,该程序能算出一系列X的值,并且这些值是符合观测所得的PDF(X)的
困难:
1.我们不可能有现成的函数,能够直接生成一系列值并且符合该分布。(虽然例子中指定了正态分布,但现实情况是任何分布都有可能,所以即使C++支持一系列分布函数,也不能解决本质问题)
2.难以求得一个函数的逆函数(至少我不知道怎么求。。至于为什么要求这个,下面会解释)
思路
1.得到一个均匀分布的,值域为[0,1]之间的随机函数并不困难,linux环境下有drand48()可用,windows下可借助于rand()实现;假设随机数为 r
2.可由PDF(X)得到CDF(X)
3.CDF(X)的值域是[0,1],CDF-1(X)的定义域是[0,1],如果我们可以得到CDF的逆函数,就可以直接通过该函数得到想要的结果
3.将CDF的定义域,也就是[-5,5],分成32段,定义为一个数组,假设数组名为cdfs,得到cdfs长度为33 ,其中cdfs[0] = 0,cdfs[32]=1
4.找到cdfs(i),使得cdfs(i)是升序排列后找到的,大于等于r的cdfs数组中的最小值,如果没有找到的话,就返回cdfs(32),也就是1
5.假设找到的i = 15,此时情况如下图
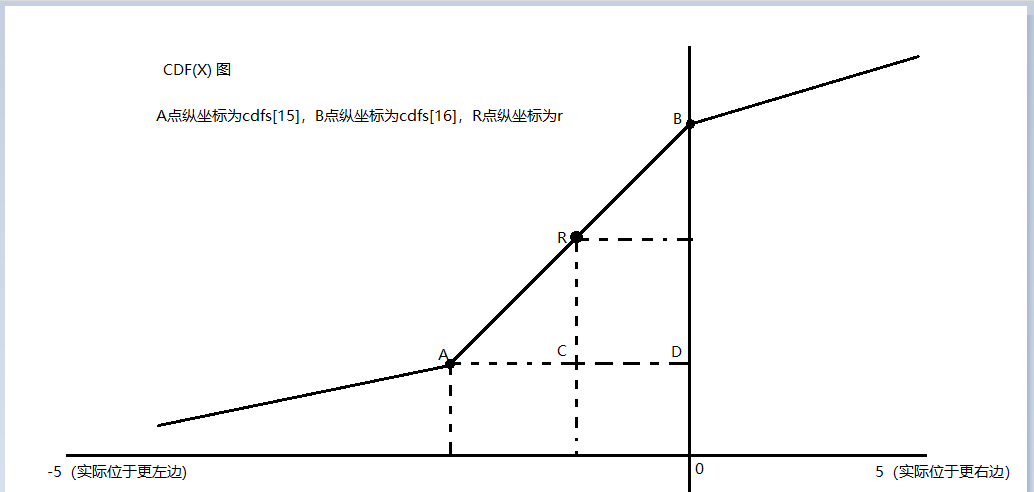
显然我们只需要知道AC的长度即可得到随机变量X的取值,假设该值为x,则 x = A点的横坐标 + AC的长度
由于A点是第15个点,所以 x = -5 + (10/32)*15 + AC
而由于 AC / AD = RC / BD,所以 AC = RC * AD / BD
其中,RC = r - cdfs[15] , AD = B点横坐标 - A点横坐标,也就是一个dx的长度,即 (10/32),BD = B点纵坐标 - A点纵坐标 = cdfs[16] - cdfs[15]
这样就得出x了
大体思路就是如此,以下是简陋的代码实现,C++基本属于不会用,后面会持续改进这个例子
#include <iostream>
#include <random>
#define M_PI 3.14159265358979323846 using namespace std; // 产生0~1之间的随机数
double randx() {
random_device rd;
default_random_engine gen{ rd() };
uniform_real_distribution<> distr;
return distr(gen);
} // standard normal distribution function
float pdf(const float& x)
{
return / sqrtf( * M_PI) * exp(-x * x * 0.5);
} // create CDF
// nbins 将cdf分成多少段
// minBound 下限
// maxBound 上限
float* cdfCreator(const int nbins, float minBound, float maxBound) { // cdf容量是要比nbin多1的;试想如果nbins=2,也就是说把[-5,5]分成2段,结果对CDF来说形成了3个节点,分别是-5,0,5
//float cdf[nbins + 1], dx = (maxBound - minBound) / nbins, sum = 0;
float* cdf = new float[nbins + ];
float dx = (maxBound - minBound) / nbins;
cdf[] = ;
cdf[nbins] = ;
for (int n = ; n < nbins; n++) {
float x = minBound + (maxBound - minBound) * (n / (float)(nbins));
// 计算dx这一小块对应的概率
float pdf_x = pdf(x) * dx;
cdf[n] = cdf[n - ] + pdf_x;
} // 调试信息
cout << "[DEBUG] cdf: ";
for (int i = ; i < ; i++) {
cout << "cdf[" << i << "]: " << cdf[i] << endl;
} return cdf;
} float sample(float* cdf, const uint32_t & nbins, const float& minBound, const float& maxBound)
{
float r = randx();
float dx = (maxBound - minBound) / nbins; // 从cdf开始,到cdf+nbins+1为止,找到第一个大于或等于r的值,在这个例子中,cdf+nbins=32,也就是cdf[32],即cdf数组的最后一个元素
// 得到的ptr指向从cdf[0]到cdf[32]中随机的一个元素的地址
// 由于后买计算bd时用到了off+1,为了不越界,所以off最大只能为31,所以ptr最大能取第cdf[31]的地址,所以下面要-1
float* ptr = std::lower_bound(cdf, cdf + nbins - , r); // 由于lower_bound的性质,cdf[ptr-cdf]永远是大于r的,为了符合我们上文的构思,这里就进行减一处理,对应于上图,off是15而不是16
int off = ptr - cdf - ; float rc = r - cdf[off];
float ad = dx;
float bd = cdf[off + ] - cdf[off];
float ac = rc * ad / bd;
float x = minBound + dx * off + ac;
return x;
} int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
// create CDF
const int nbins = ;
float minBound = -, maxBound = ;
float* cdf = cdfCreator(nbins, minBound, maxBound); // our simulation
int numSims = ; //样本容量10万
const int numBins = ; // to collect data on our sim
int bins[numBins]; // to collect data on our sim
memset(bins, 0x0, sizeof(int) * numBins); // set all the bins to 0 ,将bins的前sizeof(int)*numBins个字节全部设置值为0x0 for (int i = ; i < numSims; i++) { // 抽样十万
float x = sample(cdf, nbins, minBound, maxBound); // random var between -5 and 5 //计算x落在了我们自己定义的哪个分段里
int whichBin = (int)((numBins - ) * (x - minBound) / (maxBound - minBound));
bins[whichBin]++;
} // 输出bins看看对不对
for (int i = ; i < numBins; i++) {
/*float r = bins[i] / (float)numSims;
printf("%f %f\n", 5 * (2 * (i / (float)(numBins)) - 1), r);
cout << "[debug]i: " << i << endl;*/
cout << "bins[" << i << "]: " << bins[i] << endl;
} delete cdf;
return ;
}
运行结果:像是那么回事
bins[0]: 0
bins[1]: 0
bins[2]: 1
bins[3]: 0
bins[4]: 0
bins[5]: 0
bins[6]: 2
bins[7]: 0
bins[8]: 1
bins[9]: 2
bins[10]: 5
bins[11]: 7
bins[12]: 6
bins[13]: 7
bins[14]: 13
bins[15]: 28
bins[16]: 34
bins[17]: 34
bins[18]: 52
bins[19]: 95
bins[20]: 92
bins[21]: 92
bins[22]: 166
bins[23]: 163
bins[24]: 239
bins[25]: 391
bins[26]: 366
bins[27]: 426
bins[28]: 705
bins[29]: 724
bins[30]: 719
bins[31]: 1200
bins[32]: 1150
bins[33]: 1191
bins[34]: 1793
bins[35]: 1861
bins[36]: 1916
bins[37]: 2504
bins[38]: 2557
bins[39]: 2630
bins[40]: 3243
bins[41]: 3278
bins[42]: 3316
bins[43]: 3811
bins[44]: 3896
bins[45]: 3857
bins[46]: 3811
bins[47]: 4013
bins[48]: 4150
bins[49]: 3827
bins[50]: 3830
bins[51]: 3803
bins[52]: 3542
bins[53]: 3287
bins[54]: 3315
bins[55]: 3029
bins[56]: 2618
bins[57]: 2590
bins[58]: 2474
bins[59]: 1882
bins[60]: 1832
bins[61]: 1735
bins[62]: 1171
bins[63]: 1176
bins[64]: 1191
bins[65]: 722
bins[66]: 705
bins[67]: 665
bins[68]: 379
bins[69]: 321
bins[70]: 382
bins[71]: 213
bins[72]: 185
bins[73]: 164
bins[74]: 97
bins[75]: 88
bins[76]: 75
bins[77]: 39
bins[78]: 30
bins[79]: 33
bins[80]: 21
bins[81]: 7
bins[82]: 6
bins[83]: 7
bins[84]: 3
bins[85]: 3
bins[86]: 3
bins[87]: 1
bins[88]: 0
bins[89]: 2
bins[90]: 0
bins[91]: 0
bins[92]: 0
bins[93]: 0
bins[94]: 0
bins[95]: 0
bins[96]: 0
bins[97]: 0
bins[98]: 0
bins[99]: 0
【图形学手记】Inverse Transform Sampling 逆转换抽样的更多相关文章
- 【图形学手记】law of the unconscious statistician
以扔色子为例,结果集为{1,2,3,4,5,6},每个数字出现的概率为1/6 以色子结果为随机变量X,如果我们定义函数F(X) = (X-3)2,我们来计算F(X)的概率分布: X=1,F(1)=(1 ...
- Pseudo Random Nubmer Sampling
Pseudo Random Nubmer Sampling https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inverse\_transform\_sampling given a dis ...
- 从随机过程到马尔科夫链蒙特卡洛方法(MCMC)
从随机过程到马尔科夫链蒙特卡洛方法 1. Introduction 第一次接触到 Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) 是在 theano 的 deep learning t ...
- MCMC and Bayesian Data Analysis(PPT在文件模块)
How to generate a sample from $p(x)$? Let's first see how Matlab samples from a $p(x)$. In Matlab, t ...
- Direct2D教程VI——转换(Transform)
目前博客园中成系列的Direct2D的教程有 1.万一的 Direct2D 系列,用的是Delphi 2009 2.zdd的 Direct2D 系列,用的是VS中的C++ 3.本文所在的 Direct ...
- 随机抽样问题(蓄水池问题Reservoir Sampling)
转自:孤影醉残阳 http://hi.baidu.com/siyupy/item/e4bb218fedf4a0864414cfad 随机抽样问题(蓄水池问题Reservoir Sampling) 随即 ...
- 其实 Gradle Transform 就是个纸老虎 —— Gradle 系列(4)
前言 目前,使用 AGP Transform API 进行字节码插桩已经非常普遍了,例如 Booster.神策等框架中都有 Transform 的影子.Transform 听起来很高大上,其本质就是一 ...
- 集显也能硬件编码:Intel SDK && 各种音视频编解码学习详解
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_4155bb1d0100soq9.html INTEL MEDIA SDK是INTEL推出的基于其内建显示核心的编解码技术,我们在播放高清 ...
- 我的Android进阶之旅------>Android中编解码学习笔记
编解码学习笔记(一):基本概念 媒体业务是网络的主要业务之间.尤其移动互联网业务的兴起,在运营商和应用开发商中,媒体业务份量极重,其中媒体的编解码服务涉及需求分析.应用开发.释放license收费等等 ...
随机推荐
- context容器上下文件
在web项目中想要获取哪个bean,得先得到容器上下文context public class MyLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements Se ...
- 线段树(SegmentTree)基础模板
线段树模板题来源:https://www.lintcode.com/problem/segment-tree-build/description 201. 线段树的构造 /** * Definitio ...
- 什么是Redis缓存穿透、缓存雪崩和缓存击穿
https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1619572269435584821&wfr=spider&for=pc 缓存穿透 缓存穿透,是指查询一个数据库一定 ...
- docker compose无法解析正确的版本
docker compose无法解析正确的版本.如果你使用了一个左双引号,而不是正常的双引号,docker compose将解析版本为“2”,而不是2.应该改为: version: "2&q ...
- 程序流程图、N-S图、PAD图
在需求分阶段经常使用3种方法去剖析我们所面对的业务. 程序流程图 任何复杂的程序图都应由5种基本控制结构组成或嵌套而成. 盒图(N-S图) Nassi和Scheiderman提出了一种符合结构化程序设 ...
- 【leetcode】1249. Minimum Remove to Make Valid Parentheses
题目如下: Given a string s of '(' , ')' and lowercase English characters. Your task is to remove the min ...
- Mybatis中通过父类/接口来限定类的别名(TypeAlias)配置
- 【杂题】[AGC034D] Manhattan Max Matching【费用流】
Description 有一个无限大的平面,有2N个位置上面有若干个球(可能重复),其中N个位置是红球,N个位置是蓝球,红球与蓝球的总数均为S. 给出2N个位置和上面的球数,现要将红球与蓝球完美匹配, ...
- Cqoi2017试题泛做
Day1 4813: [Cqoi2017]小Q的棋盘 树形背包DP. #include <cstdio> #define maxn 110 #define R register #defi ...
- (Java多线程系列四)停止线程
停止线程 停止线程的思路 ①使用退出标志,使线程正常退出,也就是当run()方法结束后线程终止. class Thread01 extends Thread { // volatile关键字解决线程的 ...
