Spring Cloud Eureka源码分析 --- client 注册流程
Eureka Client 是一个Java 客户端,用于简化与Eureka Server的交互,客户端同时也具备一个内置的、使用轮询负载算法的负载均衡器。
在应用启动后,将会向Eureka Server发送心跳(默认周期为30秒),如果Eureka Server在多个心跳周期没有收到某个节点的心跳,Eureka Server 将会从服务注册表中把这个服务节点移除(默认90秒)。
Eureka Client具有缓存的机制,即使所有的Eureka Server 都挂掉的话,客户端依然可以利用缓存中的信息消费其它服务的API。下面我们一起来看客户端相关操作。
1.从启动类入手
我们还是和分析 Eureka Server 源码一样,从启动类的@EnableDiscoveryClient注解入手看调用流程。
进入 EnableDiscoveryClient 之后,通过注释知道它的作用是为了激活 DiscoveryClient:
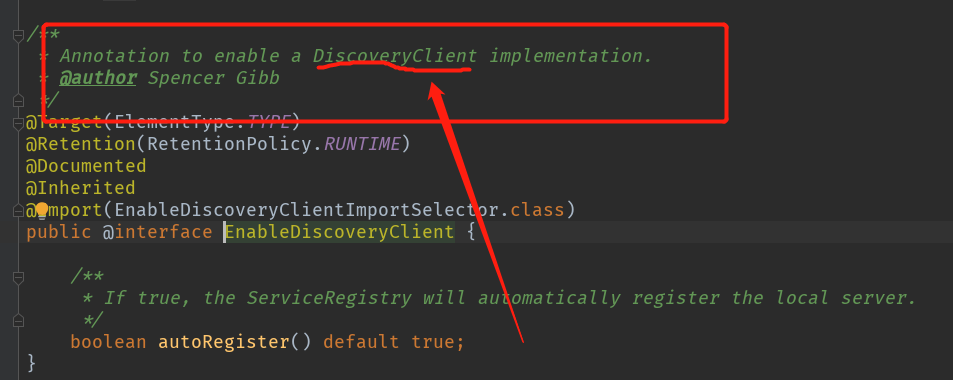
首先是在类头使用了 import 注解引入了:EnableDiscoveryClientImportSelector。该类的主要作用是实例化:AutoServiceRegistrationConfiguration。
@Order(Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 100)
public class EnableDiscoveryClientImportSelector
extends SpringFactoryImportSelector<EnableDiscoveryClient> {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
//调用父类的方法,拿到通过父类方法要注入的全路径类名数组
String[] imports = super.selectImports(metadata);
//获得该注解(@EnableDiscoveryClient)的所有属性参数
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationAttributes.fromMap(
metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(getAnnotationClass().getName(), true));
//获得属性autoRegister的值,该值默认是true的
boolean autoRegister = attributes.getBoolean("autoRegister");
//根据注解配置来判断是否要实例化下面的那个自动配置类
if (autoRegister) {
List<String> importsList = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(imports));
importsList.add("org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.AutoServiceRegistrationConfiguration");
imports = importsList.toArray(new String[0]);
} else {
Environment env = getEnvironment();
if(ConfigurableEnvironment.class.isInstance(env)) {
ConfigurableEnvironment configEnv = (ConfigurableEnvironment)env;
LinkedHashMap<String, Object> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
map.put("spring.cloud.service-registry.auto-registration.enabled", false);
MapPropertySource propertySource = new MapPropertySource(
"springCloudDiscoveryClient", map);
configEnv.getPropertySources().addLast(propertySource);
}
}
return imports;
}
@Override
protected boolean isEnabled() {
return getEnvironment().getProperty(
"spring.cloud.discovery.enabled", Boolean.class, Boolean.TRUE);
}
@Override
protected boolean hasDefaultFactory() {
return true;
}
}
这里最终的目的是想实例化:AutoServiceRegistrationConfiguration,我们来看他做了什么:
@Configuration
@Import(AutoServiceRegistrationConfiguration.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "spring.cloud.service-registry.auto-registration.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
public class AutoServiceRegistrationAutoConfiguration {
@Autowired(required = false)
private AutoServiceRegistration autoServiceRegistration;
@Autowired
private AutoServiceRegistrationProperties properties;
@PostConstruct
protected void init() {
if (autoServiceRegistration == null && this.properties.isFailFast()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Auto Service Registration has been requested, but there is no AutoServiceRegistration bean");
}
}
}
从这里看主要目的是为了实例化:AutoServiceRegistration,AutoServiceRegistrationProperties这两个类。那么初始化这两个bean的作用是什么呢,查看调用 的地方:
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties
@ConditionalOnClass(EurekaClientConfig.class)
@Import(DiscoveryClientOptionalArgsConfiguration.class)
@ConditionalOnBean(EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration.Marker.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "eureka.client.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
@AutoConfigureBefore({ NoopDiscoveryClientAutoConfiguration.class,
CommonsClientAutoConfiguration.class, ServiceRegistryAutoConfiguration.class })
@AutoConfigureAfter(name = {"org.springframework.cloud.autoconfigure.RefreshAutoConfiguration",
"org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration",
"org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.AutoServiceRegistrationAutoConfiguration"})
public class EurekaClientAutoConfiguration {
......
......
......
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(AutoServiceRegistrationProperties.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "spring.cloud.service-registry.auto-registration.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
public EurekaRegistration eurekaRegistration(EurekaClient eurekaClient, CloudEurekaInstanceConfig instanceConfig, ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, ObjectProvider<HealthCheckHandler> healthCheckHandler) {
return EurekaRegistration.builder(instanceConfig)
.with(applicationInfoManager)
.with(eurekaClient)
.with(healthCheckHandler)
.build();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(AutoServiceRegistrationProperties.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "spring.cloud.service-registry.auto-registration.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
public EurekaAutoServiceRegistration eurekaAutoServiceRegistration(ApplicationContext context, EurekaServiceRegistry registry, EurekaRegistration registration) {
return new EurekaAutoServiceRegistration(context, registry, registration);
}
......
......
......
}
原因是在这里实例化bean的时候被做为前置条件。
EurekaClientAutoConfiguration 算是到目前为止比较重要的一个类,主要做的事情包括:
- 注册 EurekaClientConfigBean ,初始化client端配置信息;
- 注册 EurekaInstanceConfigBean ,初始化客户端实例信息;
- 初始化 EurekaRegistration,EurekaServiceRegistry,EurekaAutoServiceRegistration实现Eureka服务自动注册;
- 初始化 EurekaClient ,ApplicationInfoManager。EurekaClient 的默认实现是 DiscoveryClient,是我们接下来要分析的重点;
- 初始化 EurekaHealthIndicator,为
/health端点提供Eureka相关信息,主要有Status当前实例状态和applications服务列表。
继续看 EurekaClientAutoConfiguration 又在哪里被使用:
@ConditionalOnClass(ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "spring.cloud.config.discovery.enabled", matchIfMissing = false)
@Configuration
@Import({ EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration.class, // this emulates @EnableDiscoveryClient, the import selector doesn't run before the bootstrap phase
EurekaClientAutoConfiguration.class })
public class EurekaDiscoveryClientConfigServiceBootstrapConfiguration {
}
在 EurekaDiscoveryClientConfigServiceBootstrapConfiguration 类中被作为注入的对象。
而 EurekaDiscoveryClientConfigServiceBootstrapConfiguration 被引用的分地方就比较特殊,被配置在配置文件中。
spring.factories
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapConfiguration=\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.config.EurekaDiscoveryClientConfigServiceBootstrapConfiguration
这个配置的Key部分对应着一个注解类 BootstrapConfiguration:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface BootstrapConfiguration {
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied.
*/
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
}
他被使用的地方是:BootstrapApplicationListener 的 164行,在这里拿到类的全路径之后,186行进行加载类。
public class BootstrapApplicationListener
implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent>, Ordered {
......
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = event.getEnvironment();
......
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
String configName = environment
.resolvePlaceholders("${spring.cloud.bootstrap.name:bootstrap}");
for (ApplicationContextInitializer<?> initializer : event.getSpringApplication()
.getInitializers()) {
if (initializer instanceof ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer) {
context = findBootstrapContext(
(ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer) initializer,
configName);
}
}
if (context == null) {
//在这里被调用
context = bootstrapServiceContext(environment, event.getSpringApplication(),
configName);
}
apply(context, event.getSpringApplication(), environment);
}
private ConfigurableApplicationContext bootstrapServiceContext(
ConfigurableEnvironment environment, final SpringApplication application,
String configName) {
StandardEnvironment bootstrapEnvironment = new StandardEnvironment();
MutablePropertySources bootstrapProperties = bootstrapEnvironment
.getPropertySources();
for (PropertySource<?> source : bootstrapProperties) {
bootstrapProperties.remove(source.getName());
}
String configLocation = environment
.resolvePlaceholders("${spring.cloud.bootstrap.location:}");
Map<String, Object> bootstrapMap = new HashMap<>();
bootstrapMap.put("spring.config.name", configName);
// if an app (or test) uses spring.main.web-application-type=reactive, bootstrap will fail
// force the environment to use none, because if though it is set below in the builder
// the environment overrides it
bootstrapMap.put("spring.main.web-application-type", "none");
if (StringUtils.hasText(configLocation)) {
bootstrapMap.put("spring.config.location", configLocation);
}
bootstrapProperties.addFirst(
new MapPropertySource(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, bootstrapMap));
for (PropertySource<?> source : environment.getPropertySources()) {
if (source instanceof StubPropertySource) {
continue;
}
bootstrapProperties.addLast(source);
}
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
// 在这里扫描BootstrapConfiguration注解
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>(SpringFactoriesLoader
.loadFactoryNames(BootstrapConfiguration.class, classLoader));
for (String name : StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(
environment.getProperty("spring.cloud.bootstrap.sources", ""))) {
names.add(name);
}
// TODO: is it possible or sensible to share a ResourceLoader?
SpringApplicationBuilder builder = new SpringApplicationBuilder()
.profiles(environment.getActiveProfiles()).bannerMode(Mode.OFF)
.environment(bootstrapEnvironment)
// Don't use the default properties in this builder
.registerShutdownHook(false).logStartupInfo(false)
.web(WebApplicationType.NONE);
if (environment.getPropertySources().contains("refreshArgs")) {
// If we are doing a context refresh, really we only want to refresh the
// Environment, and there are some toxic listeners (like the
// LoggingApplicationListener) that affect global static state, so we need a
// way to switch those off.
builder.application()
.setListeners(filterListeners(builder.application().getListeners()));
}
List<Class<?>> sources = new ArrayList<>();
for (String name : names) {
Class<?> cls = ClassUtils.resolveClassName(name, null);
try {
cls.getDeclaredAnnotations();
}
catch (Exception e) {
continue;
}
sources.add(cls);
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(sources);
builder.sources(sources.toArray(new Class[sources.size()]));
final ConfigurableApplicationContext context = builder.run();
// gh-214 using spring.application.name=bootstrap to set the context id via
// `ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer` prevents apps from getting the actual
// spring.application.name
// during the bootstrap phase.
context.setId("bootstrap");
// Make the bootstrap context a parent of the app context
addAncestorInitializer(application, context);
// It only has properties in it now that we don't want in the parent so remove
// it (and it will be added back later)
bootstrapProperties.remove(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
mergeDefaultProperties(environment.getPropertySources(), bootstrapProperties);
return context;
}
......
......
}
BootstrapApplicationListener 实现了ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent,作为监听器在项目启动的时候被加载。Spring根据应用启动的过程,提供了四种事件供我们使用:
- ApplicationStartedEvent :Spring Boot启动开始时执行的事件;
- ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent:Spring Boot 对应Enviroment已经准备完毕,但此时上下文context还没有创建;
- ApplicationPreparedEvent:Spring Boot 上下文context创建完成,但此时spring中的bean是没有完全加载完成的;
- ApplicationFailedEvent:Spring Boot 启动异常时执行事件。
即这里的BootstrapApplicationListener 是在项目启动加载环境变量完成,还没有创建bean的时候去加载的。
分析到这里,我们把整个的EnableDiscoveryClient注解的初始化链路都走了一遍。大致流程如下:
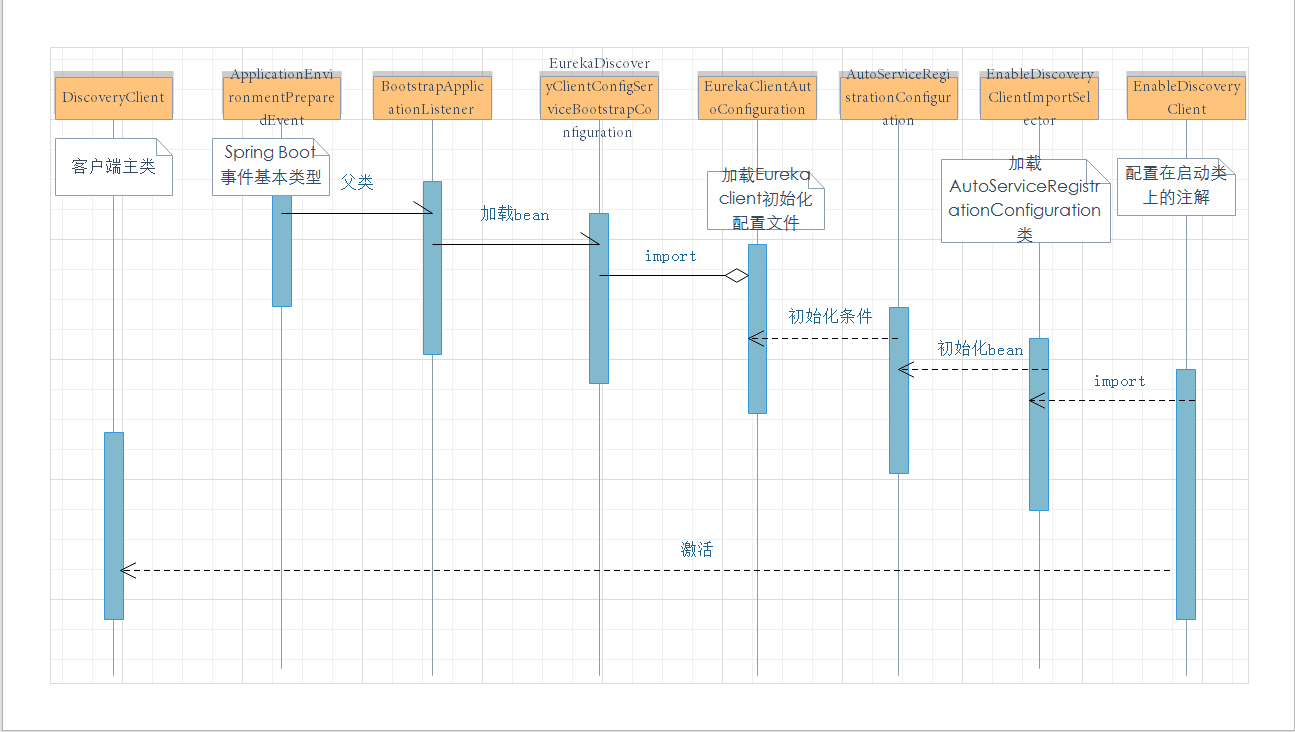
总结上面分析的部分主要两个作用:
- 初始化配置文件;
- 激活 DiscoveryClient。
下面就开始分析DiscoveryClient的作用。
2. DiscoveryClient
启动客户端的时候查看启动日志你会看到服务注册也是从 DiscoveryClient 类中发出的:
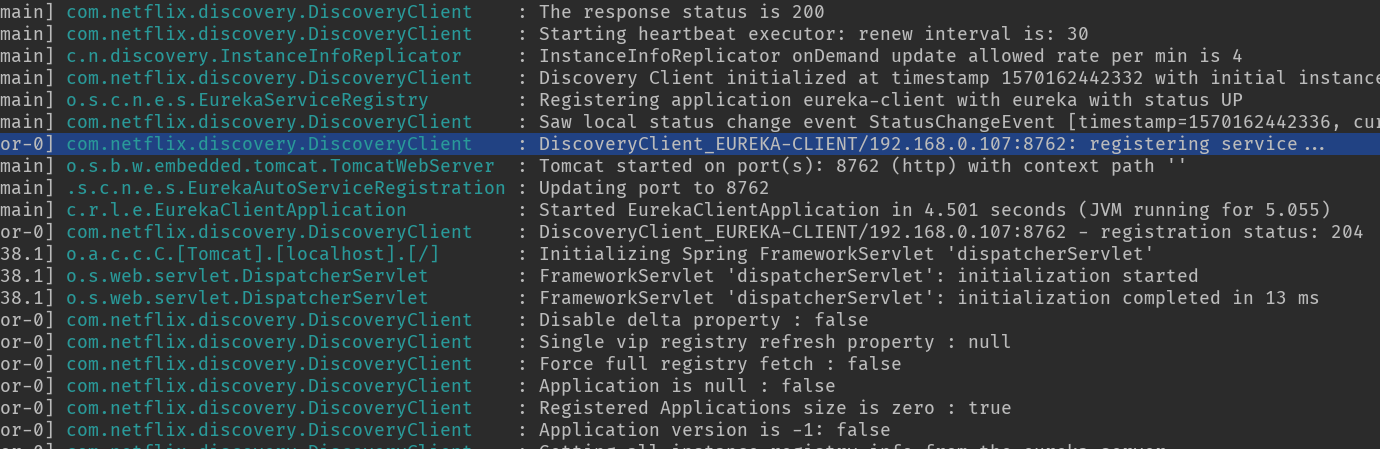
足以见得这个类在服务注册过程中应该做了一些重要的事情。下面一起来分析一下具体实现。
2.1 服务注册
DiscoveryClient 是一个接口,继续观看它的实现类,可以看到每个实现类中都有一个:DESCRIPTION字段,这个字段明确描述了当前类的作用。
- EurekaDiscoveryClient:client 的主要实现逻辑类;
- CompositeDiscoveryClient:会装载别的服务注册客户端,顺序查找;
- NoopDiscoveryClient:已经被废弃;
- SimpleDiscoveryClient:具体的服务实例从 SimpleDiscoveryProperties 配置中获取。
从描述上看 EurekaDiscoveryClient 是 client 的主要实现类。而在 EurekaDiscoveryClient 中,获取client实例主要是从 EurekaClient 中查找的:
@Override
public List<ServiceInstance> getInstances(String serviceId) {
List<InstanceInfo> infos = this.eurekaClient.getInstancesByVipAddress(serviceId,false);
List<ServiceInstance> instances = new ArrayList<>();
for (InstanceInfo info : infos) {
instances.add(new EurekaServiceInstance(info));
}
return instances;
}
DiscoveryClient 是 EurekaClient 的唯一实现类,他有一个很重要的构造方法:
@Inject
DiscoveryClient(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, EurekaClientConfig config, AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs args,Provider<BackupRegistry> backupRegistryProvider) {
if (args != null) {
this.healthCheckHandlerProvider = args.healthCheckHandlerProvider;
this.healthCheckCallbackProvider = args.healthCheckCallbackProvider;
this.eventListeners.addAll(args.getEventListeners());
this.preRegistrationHandler = args.preRegistrationHandler;
} else {
this.healthCheckCallbackProvider = null;
this.healthCheckHandlerProvider = null;
this.preRegistrationHandler = null;
}
this.applicationInfoManager = applicationInfoManager;
InstanceInfo myInfo = applicationInfoManager.getInfo();
clientConfig = config;
staticClientConfig = clientConfig;
transportConfig = config.getTransportConfig();
instanceInfo = myInfo;
if (myInfo != null) {
appPathIdentifier = instanceInfo.getAppName() + "/" + instanceInfo.getId();
} else {
logger.warn("Setting instanceInfo to a passed in null value");
}
this.backupRegistryProvider = backupRegistryProvider;
this.urlRandomizer = new EndpointUtils.InstanceInfoBasedUrlRandomizer(instanceInfo);
localRegionApps.set(new Applications());
fetchRegistryGeneration = new AtomicLong(0);
remoteRegionsToFetch = new AtomicReference<String>(clientConfig.fetchRegistryForRemoteRegions());
remoteRegionsRef = new AtomicReference<>(remoteRegionsToFetch.get() == null ? null : remoteRegionsToFetch.get().split(","));
//上面主要是初始化一些参数
//如果 shouldFetchRegistry= true,注册监控
if (config.shouldFetchRegistry()) {
this.registryStalenessMonitor = new ThresholdLevelsMetric(this, METRIC_REGISTRY_PREFIX + "lastUpdateSec_", new long[]{15L, 30L, 60L, 120L, 240L, 480L});
} else {
this.registryStalenessMonitor = ThresholdLevelsMetric.NO_OP_METRIC;
}
//如果shouldRegisterWithEureka=true,注册监控
if (config.shouldRegisterWithEureka()) {
this.heartbeatStalenessMonitor = new ThresholdLevelsMetric(this, METRIC_REGISTRATION_PREFIX + "lastHeartbeatSec_", new long[]{15L, 30L, 60L, 120L, 240L, 480L});
} else {
this.heartbeatStalenessMonitor = ThresholdLevelsMetric.NO_OP_METRIC;
}
logger.info("Initializing Eureka in region {}", clientConfig.getRegion());
//如果shouldRegisterWithEureka = false && shouldFetchRegistry=false
//就不做初始化的工作,直接返回
if (!config.shouldRegisterWithEureka() && !config.shouldFetchRegistry()) {
logger.info("Client configured to neither register nor query for data.");
scheduler = null;
heartbeatExecutor = null;
cacheRefreshExecutor = null;
eurekaTransport = null;
instanceRegionChecker = new InstanceRegionChecker(new PropertyBasedAzToRegionMapper(config), clientConfig.getRegion());
// This is a bit of hack to allow for existing code using DiscoveryManager.getInstance()
// to work with DI'd DiscoveryClient
DiscoveryManager.getInstance().setDiscoveryClient(this);
DiscoveryManager.getInstance().setEurekaClientConfig(config);
initTimestampMs = System.currentTimeMillis();
logger.info("Discovery Client initialized at timestamp {} with initial instances count: {}",
initTimestampMs, this.getApplications().size());
return; // no need to setup up an network tasks and we are done
}
//从这里开始创建各种任务的线程池
try {
// default size of 2 - 1 each for heartbeat and cacheRefresh
//创建定时线程池,线程数量为2个,分别用来维持心跳连接和刷新其他eureka client实例缓存
scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2,
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build());
//创建一个线程池,线程池大小默认为2个,用来维持心跳连接
heartbeatExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1, clientConfig.getHeartbeatExecutorThreadPoolSize(), 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-HeartbeatExecutor-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build()
); // use direct handoff
//创建一个线程池,线程池大小默认为2个,用来刷新其他eureka client实例缓存
cacheRefreshExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1, clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorThreadPoolSize(), 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-CacheRefreshExecutor-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build()
); // use direct handoff
eurekaTransport = new EurekaTransport();
scheduleServerEndpointTask(eurekaTransport, args);
......
......
......
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to initialize DiscoveryClient!", e);
}
//抓取远程实例注册信息,fetchRegistry()方法里的参数,这里为false,意思是要不要强制抓取所有实例注册信息
//这里获取注册信息,分两种方式,一种是全量获取,另一种是增量获取,默认是增量获取
if (clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry() && !fetchRegistry(false)) {
//如果配置的是要获取实例注册信息,但是从远程获取失败,从备份获取实例注册信息
fetchRegistryFromBackup();
}
// call and execute the pre registration handler before all background tasks (inc registration) is started
if (this.preRegistrationHandler != null) {
this.preRegistrationHandler.beforeRegistration();
}
//如果client配置注册到eureka server 且 强制 初始化就注册到eureka 那么就注册到eureka server,默认是不初始化就注册到eureka
if (clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka() && clientConfig.shouldEnforceRegistrationAtInit()) {
try {
if (!register() ) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Registration error at startup. Invalid server response.");
}
} catch (Throwable th) {
logger.error("Registration error at startup: {}", th.getMessage());
throw new IllegalStateException(th);
}
}
// finally, init the schedule tasks (e.g. cluster resolvers, heartbeat, instanceInfo replicator, fetch
//初始化维持心跳连接、更新注册信息缓存的定时任务
initScheduledTasks();
try {
Monitors.registerObject(this);
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.warn("Cannot register timers", e);
}
// This is a bit of hack to allow for existing code using DiscoveryManager.getInstance()
// to work with DI'd DiscoveryClient
DiscoveryManager.getInstance().setDiscoveryClient(this);
DiscoveryManager.getInstance().setEurekaClientConfig(config);
initTimestampMs = System.currentTimeMillis();
logger.info("Discovery Client initialized at timestamp {} with initial instances count: {}",
initTimestampMs, this.getApplications().size());
}
初始化的过程主要做了两件事:
- 创建了 scheduler 定时任务的线程池,heartbeatExecutor 心跳检查线程池(服务续约),cacheRefreshExecutor 服务获取线程池 ;
- 调用
initScheduledTasks()方法开启线程池,往上面3个线程池分别添加相应任务。然后创建了一个instanceInfoReplicator(Runnable任务),然后调用InstanceInfoReplicator.start方法,把这个任务放进上面scheduler定时任务线程池(服务注册并更新)。
接着看 initScheduledTasks做了哪些事情 :
private void initScheduledTasks() {
//获取服务列表信息
if (clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry()) {
// registry cache refresh timer
//获取默认的注册频率信息,默认30S
int registryFetchIntervalSeconds = clientConfig.getRegistryFetchIntervalSeconds();
//如果缓存刷新超时,下一次执行的delay最大是registryFetchIntervalSeconds的几倍(默认10),默认每次执行是上一次的2倍
int expBackOffBound = clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorExponentialBackOffBound();
//执行CacheRefreshThread,服务列表缓存刷新任务
scheduler.schedule(
new TimedSupervisorTask(
"cacheRefresh",
scheduler,
cacheRefreshExecutor,
registryFetchIntervalSeconds,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
expBackOffBound,
new CacheRefreshThread()
),
registryFetchIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
//注册到eureka server
if (clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka()) {
//续租时间间隔,默认30s
int renewalIntervalInSecs = instanceInfo.getLeaseInfo().getRenewalIntervalInSecs();
// 如果心跳任务超时,下一次执行的delay最大是renewalIntervalInSecs的几倍(默认10),默认每次执行是上一次的2倍
int expBackOffBound = clientConfig.getHeartbeatExecutorExponentialBackOffBound();
logger.info("Starting heartbeat executor: " + "renew interval is: {}", renewalIntervalInSecs);
// Heartbeat timer
//执行HeartbeatThread,发送心跳数据
scheduler.schedule(
new TimedSupervisorTask(
"heartbeat",
scheduler,
heartbeatExecutor,
renewalIntervalInSecs,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
expBackOffBound,
new HeartbeatThread()
),
renewalIntervalInSecs, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 客户端实例信息复制
instanceInfoReplicator = new InstanceInfoReplicator(
this,
instanceInfo,
clientConfig.getInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds(),
2); // burstSize
//注册监听器
statusChangeListener = new ApplicationInfoManager.StatusChangeListener() {
@Override
public String getId() {
return "statusChangeListener";
}
@Override
public void notify(StatusChangeEvent statusChangeEvent) {
if (InstanceStatus.DOWN == statusChangeEvent.getStatus() ||
InstanceStatus.DOWN == statusChangeEvent.getPreviousStatus()) {
// log at warn level if DOWN was involved
logger.warn("Saw local status change event {}", statusChangeEvent);
} else {
logger.info("Saw local status change event {}", statusChangeEvent);
}
instanceInfoReplicator.onDemandUpdate();
}
};
if (clientConfig.shouldOnDemandUpdateStatusChange()) {
applicationInfoManager.registerStatusChangeListener(statusChangeListener);
}
//进行服务刷新
instanceInfoReplicator.start(clientConfig.getInitialInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds());
} else {
logger.info("Not registering with Eureka server per configuration");
}
}
总的来说initScheduledTasks()做了以下几件事:
如果shouldFetchRegistry=true,即要从Eureka Server获取服务列表:
启动刷新服务列表定时线程(DiscoveryClient-CacheRefreshExecutor-%d),默认registryFetchIntervalSeconds=30s执行一次,任务为
CacheRefreshThread,即从Eureka Server获取服务列表,也刷新客户端缓存。如果shouldRegisterWithEureka=true,即要注册到Eureka Server。
启动heartbeat心跳定时线程(DiscoveryClient-HeartbeatExecutor-%d),默认renewalIntervalInSecs=30s续约一次,任务为
HeartbeatThread,即客户端向Eureka Server发送心跳;启动InstanceInfo复制器定时线程(DiscoveryClient-InstanceInfoReplicator-%d),开启定时线程检查当前Instance的DataCenterInfo、LeaseInfo、InstanceStatus,如果发现变更就执行
discoveryClient.register(),将实例信息同步到Server端。
上面有一个需要关注的点是:InstanceInfoReplicator。它会去定时刷新客户端实例的最新信息:当前实例最新数据,租约信息,实例状态。InstanceInfoReplicator 是一个线程类,关注 run()方法:
public void run() {
try {
/**
* 刷新 InstanceInfo
* 1、刷新 DataCenterInfo
* 2、刷新 LeaseInfo 租约信息
* 3、根据HealthCheckHandler获取InstanceStatus,并更新,如果状态发生变化会触发所有StatusChangeListener
*/
discoveryClient.refreshInstanceInfo();
//刷新完之后,当前服务有变更,还未同步给server,发起注册
Long dirtyTimestamp = instanceInfo.isDirtyWithTime();
if (dirtyTimestamp != null) {
//发起注册
discoveryClient.register();
instanceInfo.unsetIsDirty(dirtyTimestamp);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("There was a problem with the instance info replicator", t);
} finally {
Future next = scheduler.schedule(this, replicationIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
scheduledPeriodicRef.set(next);
}
}
看一下register()的实现:
/**
* Register with the eureka service by making the appropriate REST call.
* 使用http的方式注册eureka服务
*/
boolean register() throws Throwable {
logger.info(PREFIX + "{}: registering service...", appPathIdentifier);
EurekaHttpResponse<Void> httpResponse;
try {
httpResponse = eurekaTransport.registrationClient.register(instanceInfo);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn(PREFIX + "{} - registration failed {}", appPathIdentifier, e.getMessage(), e);
throw e;
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info(PREFIX + "{} - registration status: {}", appPathIdentifier, httpResponse.getStatusCode());
}
return httpResponse.getStatusCode() == 204;
}
往下跟踪到 RestTemplateEurekaHttpClient类:
public class RestTemplateEurekaHttpClient implements EurekaHttpClient {
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
private String serviceUrl;
public RestTemplateEurekaHttpClient(RestTemplate restTemplate, String serviceUrl) {
this.restTemplate = restTemplate;
this.serviceUrl = serviceUrl;
if (!serviceUrl.endsWith("/")) {
this.serviceUrl = this.serviceUrl+"/";
}
}
@Override
public EurekaHttpResponse<Void> register(InstanceInfo info) {
String urlPath = serviceUrl + "apps/" + info.getAppName();
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.add(HttpHeaders.ACCEPT_ENCODING, "gzip");
headers.add(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_TYPE, MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE);
ResponseEntity<Void> response = restTemplate.exchange(urlPath, HttpMethod.POST,
new HttpEntity<>(info, headers), Void.class);
return anEurekaHttpResponse(response.getStatusCodeValue())
.headers(headersOf(response)).build();
}
......
......
......
}
封装了RestTemplate http client 模板方法,给 server 端发送一个post 请求。所以启动 client 的时候,向服务端发送注册请求的地方就在这里。
2.2 服务续约
服务续约的入口在DiscoveryClient 类initScheduledTasks()方法的heartBeat timer定时器任务中:
// Heartbeat timer
//开启定时任务每隔30s发送一次 心跳请求
scheduler.schedule(
new TimedSupervisorTask(
"heartbeat",
scheduler,
heartbeatExecutor,
renewalIntervalInSecs,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
expBackOffBound,
new HeartbeatThread()
),
renewalIntervalInSecs, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
/**
* The heartbeat task that renews the lease in the given intervals.
*/
private class HeartbeatThread implements Runnable {
public void run() {
if (renew()) {
lastSuccessfulHeartbeatTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}
}
/**
* Renew with the eureka service by making the appropriate REST call
*/
boolean renew() {
EurekaHttpResponse<InstanceInfo> httpResponse;
try {
httpResponse = eurekaTransport.registrationClient.sendHeartBeat(instanceInfo.getAppName(), instanceInfo.getId(), instanceInfo, null);
logger.debug(PREFIX + "{} - Heartbeat status: {}", appPathIdentifier, httpResponse.getStatusCode());
if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == 404) {
REREGISTER_COUNTER.increment();
logger.info(PREFIX + "{} - Re-registering apps/{}", appPathIdentifier, instanceInfo.getAppName());
long timestamp = instanceInfo.setIsDirtyWithTime();
boolean success = register();
if (success) {
instanceInfo.unsetIsDirty(timestamp);
}
return success;
}
return httpResponse.getStatusCode() == 200;
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error(PREFIX + "{} - was unable to send heartbeat!", appPathIdentifier, e);
return false;
}
}
@Override
public EurekaHttpResponse<InstanceInfo> sendHeartBeat(String appName, String id,
InstanceInfo info, InstanceStatus overriddenStatus) {
String urlPath = serviceUrl + "apps/" + appName + '/' + id + "?status="
+ info.getStatus().toString() + "&lastDirtyTimestamp="
+ info.getLastDirtyTimestamp().toString() + (overriddenStatus != null
? "&overriddenstatus=" + overriddenStatus.name() : "");
ResponseEntity<InstanceInfo> response = restTemplate.exchange(urlPath,
HttpMethod.PUT, null, InstanceInfo.class);
EurekaHttpResponseBuilder<InstanceInfo> eurekaResponseBuilder = anEurekaHttpResponse(
response.getStatusCodeValue(), InstanceInfo.class)
.headers(headersOf(response));
if (response.hasBody())
eurekaResponseBuilder.entity(response.getBody());
return eurekaResponseBuilder.build();
}
上面贴出来了客户端发送心跳请求的完整调用过程,每隔30s客户端向服务端发送一次请求,向服务端重新注册自己。
2.3 服务下线
服务下线比较好理解,在服务关闭的时候取消本机的各种定时任务,给服务端发送请求告知自己下线。
/**
* Shuts down Eureka Client. Also sends a deregistration request to the
* eureka server.
*/
@PreDestroy
@Override
public synchronized void shutdown() {
if (isShutdown.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
logger.info("Shutting down DiscoveryClient ...");
if (statusChangeListener != null && applicationInfoManager != null) {
applicationInfoManager.unregisterStatusChangeListener(statusChangeListener.getId());
}
//取消各种定时任务
cancelScheduledTasks();
// If APPINFO was registered
if (applicationInfoManager != null
&& clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka()
&& clientConfig.shouldUnregisterOnShutdown()) {
applicationInfoManager.setInstanceStatus(InstanceStatus.DOWN);
//向服务端发送请求告知自己下线
unregister();
}
if (eurekaTransport != null) {
eurekaTransport.shutdown();
}
//关闭监控
heartbeatStalenessMonitor.shutdown();
registryStalenessMonitor.shutdown();
logger.info("Completed shut down of DiscoveryClient");
}
}
/**
* unregister w/ the eureka service.
*/
void unregister() {
// It can be null if shouldRegisterWithEureka == false
if(eurekaTransport != null && eurekaTransport.registrationClient != null) {
try {
logger.info("Unregistering ...");
EurekaHttpResponse<Void> httpResponse = eurekaTransport.registrationClient.cancel(instanceInfo.getAppName(), instanceInfo.getId());
logger.info(PREFIX + "{} - deregister status: {}", appPathIdentifier, httpResponse.getStatusCode());
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(PREFIX + "{} - de-registration failed{}", appPathIdentifier, e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
@Override
public EurekaHttpResponse<Void> cancel(String appName, String id) {
String urlPath = serviceUrl + "apps/" + appName + '/' + id;
ResponseEntity<Void> response = restTemplate.exchange(urlPath, HttpMethod.DELETE,
null, Void.class);
return anEurekaHttpResponse(response.getStatusCodeValue())
.headers(headersOf(response)).build();
}
2.4 服务获取 和 服务刷新
服务启动的时候会去服务端全量拉取所有已经注册过的其余client实例信息,增量的时候就是在initScheduledTasks() 方法中每30s增量跑一次。
private void initScheduledTasks() {
if (clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry()) {
// registry cache refresh timer
int registryFetchIntervalSeconds = clientConfig.getRegistryFetchIntervalSeconds();
int expBackOffBound = clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorExponentialBackOffBound();
scheduler.schedule(
new TimedSupervisorTask(
"cacheRefresh",
scheduler,
cacheRefreshExecutor,
registryFetchIntervalSeconds,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
expBackOffBound,
new CacheRefreshThread()
),
registryFetchIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
......
......
......
}
/**
* The task that fetches the registry information at specified intervals.
*
*/
class CacheRefreshThread implements Runnable {
public void run() {
refreshRegistry();
}
}
@VisibleForTesting
void refreshRegistry() {
try {
boolean isFetchingRemoteRegionRegistries = isFetchingRemoteRegionRegistries();
boolean remoteRegionsModified = false;
// This makes sure that a dynamic change to remote regions to fetch is honored.
String latestRemoteRegions = clientConfig.fetchRegistryForRemoteRegions();
......
......
......
boolean success = fetchRegistry(remoteRegionsModified);
if (success) {
registrySize = localRegionApps.get().size();
lastSuccessfulRegistryFetchTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
......
......
......
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error("Cannot fetch registry from server", e);
}
}
/**
* Fetches the registry information.
*
* <p>
* This method tries to get only deltas after the first fetch unless there
* is an issue in reconciling eureka server and client registry information.
* </p>
*
* @param forceFullRegistryFetch Forces a full registry fetch.
*
* @return true if the registry was fetched
*/
private boolean fetchRegistry(boolean forceFullRegistryFetch) {
Stopwatch tracer = FETCH_REGISTRY_TIMER.start();
try {
// 如果现在增量服务获取不可用,或者是第一次获取服务的时候,拉去所有的应用
Applications applications = getApplications();
if (clientConfig.shouldDisableDelta()
|| (!Strings.isNullOrEmpty(clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress()))
|| forceFullRegistryFetch
|| (applications == null)
|| (applications.getRegisteredApplications().size() == 0)
|| (applications.getVersion() == -1)) //Client application does not have latest library supporting delta
{
logger.info("Disable delta property : {}", clientConfig.shouldDisableDelta());
logger.info("Single vip registry refresh property : {}", clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress());
logger.info("Force full registry fetch : {}", forceFullRegistryFetch);
logger.info("Application is null : {}", (applications == null));
logger.info("Registered Applications size is zero : {}",
(applications.getRegisteredApplications().size() == 0));
logger.info("Application version is -1: {}", (applications.getVersion() == -1));
getAndStoreFullRegistry();
} else {
getAndUpdateDelta(applications);
}
applications.setAppsHashCode(applications.getReconcileHashCode());
logTotalInstances();
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error(PREFIX + "{} - was unable to refresh its cache! status = {}", appPathIdentifier, e.getMessage(), e);
return false;
} finally {
if (tracer != null) {
tracer.stop();
}
}
// Notify about cache refresh before updating the instance remote status
onCacheRefreshed();
// Update remote status based on refreshed data held in the cache
updateInstanceRemoteStatus();
// registry was fetched successfully, so return true
return true;
}
客户端拉取服务端保存的所有客户端节点信息保存时间为3分钟,Eureka client取得的数据虽然是增量更新,仍然可能和30秒前取的数据一样,所以Eureka client要自己来处理重复信息。
另外,注意到在fetchRegistry()方法中:
applications.setAppsHashCode(applications.getReconcileHashCode());
每次增量更新,服务端都会带过来一个一致性hash码。Eureka client的增量更新,其实获取的是Eureka server最近三分钟内的变更,如果Eureka client有超过三分钟没有做增量更新的话(例如网络问题),这就造成了Eureka server和Eureka client之间的数据不一致。正常情况下,Eureka client多次增量更新后,最终的服务列表数据应该Eureka server保持一致,但如果期间发生异常,可能导致和Eureka server的数据不一致,为了暴露这个问题,Eureka server每次返回的增量更新数据中,会带有一致性哈希码,Eureka client用本地服务列表数据算出的一致性哈希码应该和Eureka server返回的一致,若不一致就证明增量更新出了问题导致Eureka client和Eureka server上的服务列表信息不一致了,此时需要全量更新。
关于客户端的代码分析就到这里,本篇主要从两个角度去分析:
- 从启动类入手,查看初始化了什么;
- 从启动日志入手,查看启动类做了什么。
如果大家有更好的分析角度,可以一起探讨,让我们踩着巨人的肩膀越走越远。
Spring Cloud Eureka源码分析 --- client 注册流程的更多相关文章
- Spring Cloud Eureka源码分析---服务注册
本篇我们着重分析Eureka服务端的逻辑实现,主要涉及到服务的注册流程分析. 在Eureka的服务治理中,会涉及到下面一些概念: 服务注册:Eureka Client会通过发送REST请求的方式向Eu ...
- Spring Cloud Eureka源码分析之服务注册的流程与数据存储设计!
Spring Cloud是一个生态,它提供了一套标准,这套标准可以通过不同的组件来实现,其中就包含服务注册/发现.熔断.负载均衡等,在spring-cloud-common这个包中,org.sprin ...
- Spring Cloud Eureka源码分析之三级缓存的设计原理及源码分析
Eureka Server 为了提供响应效率,提供了两层的缓存结构,将 Eureka Client 所需要的注册信息,直接存储在缓存结构中,实现原理如下图所示. 第一层缓存:readOnlyCache ...
- Spring Cloud Eureka源码分析之心跳续约及自我保护机制
Eureka-Server是如何判断一个服务不可用的? Eureka是通过心跳续约的方式来检查各个服务提供者的健康状态. 实际上,在判断服务不可用这个部分,会分为两块逻辑. Eureka-Server ...
- 【spring cloud】源码分析(一)
概述 从服务发现注解 @EnableDiscoveryClient入手,剖析整个服务发现与注册过程 一,spring-cloud-common包 针对服务发现,本jar包定义了 DiscoveryCl ...
- Spring Cloud Ribbon 源码分析---负载均衡算法
上一篇分析了Ribbon如何发送出去一个自带负载均衡效果的HTTP请求,本节就重点分析各个算法都是如何实现. 负载均衡整体是从IRule进去的: public interface IRule{ /* ...
- Spring Cloud Ribbon源码分析---负载均衡实现
上一篇结合 Eureka 和 Ribbon 搭建了服务注册中心,利用Ribbon实现了可配置负载均衡的服务调用.这一篇我们来分析Ribbon实现负载均衡的过程. 从 @LoadBalanced入手 还 ...
- Feign 系列(05)Spring Cloud OpenFeign 源码解析
Feign 系列(05)Spring Cloud OpenFeign 源码解析 [TOC] Spring Cloud 系列目录(https://www.cnblogs.com/binarylei/p/ ...
- Eureka 源码分析之 Eureka Server
文章首发于公众号<程序员果果> 地址 : https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/FfJrAGQuHyVrsedtbr0Ihw 简介 上一篇文章<Eureka 源码分析 ...
随机推荐
- Celery:Next Steps
参考文档:http://docs.celeryproject.org/en/latest/getting-started/next-steps.html#next-steps
- Java读书笔记
一.背景 工作中越来越发现对基础理解的重要性,所谓基础不牢,地动山摇.所以抽了点时间看看几本Java体系的电子书,并做笔记,如下: 二.近期要看的电子书 1.Spring实战(第4版) 2.Sprin ...
- oracle 如何预估将要创建的索引的大小
一.1 oracle 如何预估将要创建的索引的大小 oracle 提供了2种可以预估将要创建的索引大小的办法: ① 利用包 Dbms_space.create_index_cost 直接得到 ② ...
- vue v-show无法动态更新的问题
本人之前学过angularJS,记得v-for绑定的数组,只要切换v-if = ''item.show'' 只要改变相关的值,就可以对应的值,视图就会重新渲染,但是在vue中却不灵了,找到答案了,需要 ...
- JavaScript获得URL地址栏参数防乱码
JavaScript获得URL地址栏参数防乱码 JavaScript中经常需要解析地址栏中拼接的参数.下面的代码基本是固定的代码,这里摘录下备用. //获得地址栏参数值 function getUrl ...
- Java开发环境之Eclipse
查看更多Java开发环境配置,请点击<Java开发环境配置大全> 拾壹章:Eclipse安装教程 1)去官网下载安装包 http://www.eclipse.org/downloads/ ...
- C++中string的实现原理
C++中string的实现原理 背景 当我刚开始学习C++,对C还是有一部分的了解,所以以C的思维去学C++,导致我很长一段时间的学习都处于一个懵逼的状态,C++的各种特性,标准库,模板还有版本的迭代 ...
- 小白式Git使用教程,从0到1
Git是什么? Git是目前世界上最先进的分布式版本控制系统.工作原理 / 流程: Workspace:工作区 Index / Stage:暂存区 Repository:仓库区(或本地仓库) Remo ...
- dijkstra,belllman-ford,spfa最短路算法
参考博客 时间复杂度对比: Dijkstra: O(n2) Dijkstra + 优先队列(堆优化): O(E+V∗logV) SPFA: O(k∗E) ,k为每个节点进入队列的次数,一般小于等 ...
- 微信小程序~项目步骤和流程
从运营的角度讲制作,不是从程序的角度讲开发,所以简单明晰,通俗易懂,小白也能按照流程完成制作. 微信小程序制作步骤及流程 1.确定好微信小程序的的定位和目的 如行业,功能,内容,目标用户,目标市场,意 ...
