shell脚本中的逻辑判断、文件目录属性判断、if特殊用法、case判断
7月12日任务
20.5 shell脚本中的逻辑判断
20.6 文件目录属性判断
20.7 if特殊用法
20.8/20.9 case判断
20.5 shell脚本中的逻辑判断
逻辑判断在shell中随处可见,如果没有逻辑判断,就相当于单纯敲命令了,没有任何的意义,所以可见逻辑判断在shell中的重要性。
下面介绍下shell常用的3种格式,if和fi是对应的,第一种是最常用的,一般第三种使用很少。
格式1-->if 条件 ; then 语句; fi
[root@jimmylinux- ~]# a=
[root@jimmylinux- ~]# if [ $a -gt ] 条件语句之间要有空格分开,方括号2边也需要空格。
> then
> echo ok
> fi
ok 以上是分开执行的效果 [root@jimmylinux- ~]# if [ $a -gt ]; then echo ok; fi
ok 这种是直接以一条命令方式执行的效果
编写shell脚本方式
[root@jimmylinux- shell]# vi if1.sh #!/bin/bash
a=
if [ $a -gt ]
then
echo ok
fi
[root@jimmylinux-001 shell]# sh if1.sh 执行脚本
ok 输出脚本结果
格式2-->if 条件; then 语句; else 语句; fi
[root@jimmylinux- shell]# vi if2.sh #!/bin/bash
a=
if [ $a -gt ]
then
echo ok
else
echo nook
fi [root@jimmylinux-001 shell]# sh if2.sh nook
[root@jimmylinux-001 shell]# sh -x if2.sh
+ a=1
+ '[' 1 -gt 3 ']'
+ echo nook
nook
格式3-->if …; then … ;elif …; then …; else …; fi
[root@jimmylinux- shell]# vi if3.sh #!/bin/bash
a=
if [ $a -gt ]
then
echo ">1"
elif [ $a -gt ]
then
echo "<6 && >1"
else
echo nook
fi [root@jimmylinux- shell]# sh if3.sh
nook [root@jimmylinux- shell]# sh -x if3.sh
+ a=
+ '[' -gt ']'
+ '[' -gt ']'
+ echo nook
nook
逻辑判断表达式
if [ $a -gt $b ]; if [ $a -lt ]; if [ $b -eq ]等等 -gt 表示>
-lt 表示<
-ge 表示>=
-le 表示<=
-eq 表示=
-ne 表示≠
也可以使用 && || 结合多个条件 if [ $a –gt ] && [ $a -lt ]; then
if [ $b –gt ] || [ $b -lt ]; then && 表示并且
|| 表示或者
20.6 文件目录属性判断
在shell中经常会和文件和目录打交道,例如判断文件或目录大小、判断是否为空等属性。
首先创建一个测试脚本,根据不同的条件进行判断。
1、[ -f file ]判断是否是普通文件,并且存在。
[root@jimmylinux- shell]# vi file1.sh #!/bin/bash
f="/tmp/test666" 定义一个f变量值
if [ -f $f ] 判断f这个值是否存在
then
echo $f exist 存在则退出
else
touch $f 反之touch创建f变量值
fi
[root@jimmylinux- shell]# sh -x file1.sh 如果文件不存在自动创建
+ f=/tmp/test666
+ '[' -f /tmp/test666 ']'
+ touch /tmp/test666 [root@jimmylinux- shell]# sh -x file1.sh 如果文件存在则退出
+ f=/tmp/test666
+ '[' -f /tmp/test666 ']'
+ echo /tmp/test666 exist
/tmp/test666 exist
2、[ -d file ] 判断是否是目录,并且存在。
[root@jimmylinux- shell]# vi file2.sh #!/bin/bash
f="/tmp/test666"
if [ -d $f ]
then
echo $f exist
else
touch $f
fi [root@jimmylinux- shell]# sh -x file2.sh
+ f=/tmp/test666
+ '[' -d /tmp/test666 ']'
+ touch /tmp/test666
3、[ -e file ] 判断文件或目录是否存在
[root@jimmylinux- shell]# vi file2.sh #!/bin/bash
f="/tmp/test666"
if [ -e $f ]
then
echo $f exist
else
touch $f
fi [root@jimmylinux- shell]# sh -x file2.sh
+ f=/tmp/test666
+ '[' -e /tmp/test666 ']'
+ echo /tmp/test666 exist
/tmp/test666 exist
4、[ -r file ] 判断文件是否可读
[root@jimmylinux- shell]# vi file2.sh #!/bin/bash
f="/tmp/test666"
if [ -r $f ]
then
echo $f readable
fi [root@jimmylinux- shell]# sh -x file2.sh
+ f=/tmp/test666
+ '[' -r /tmp/test666 ']'
+ echo /tmp/test666 readable
/tmp/test666 readable [root@jimmylinux- shell]# sh file2.sh
/tmp/test666 readable
5、[ -w file ] 判断文件是否可写
[root@jimmylinux- shell]# vi file2.sh #!/bin/bash
f="/tmp/test666"
if [ -w $f ]
then
echo $f writeable
fi [root@jimmylinux- shell]# sh file2.sh
/tmp/test666 writeable
6、[ -x file ] 判断文件是否可执行
[root@jimmylinux- shell]# vi file2.sh #!/bin/bash
f="/tmp/test666"
if [ -x $f ]
then
echo $f exeable
fi [root@jimmylinux- shell]# sh file2.sh 因为不可以执行,所以没有任何输出内容。
[root@jimmylinux- shell]# cat !$ 因为脚本文件并没有定义else内容
cat file2.sh
#!/bin/bash
f="/tmp/test666"
if [ -x $f ]
then
echo $f exeable
fi
例子:


20.7 if特殊用法
下面再介绍几个if的特殊用法
1、if [ -z "$n" ] 表示当变量n的值是否为空,具体操作示例如下:
[root@jimmylinux- shell]# vi if4.sh #!/bin/bash
n=`wc -l /tmp/lakala`
if [ $n -gt ]
then
echo abcdefg
fi [root@jimmylinux- shell]# sh -x if4.sh
++ wc -l /tmp/lakala
wc: /tmp/lakala: 没有那个文件或目录
+ n=
+ '[' -gt ']'
if4.sh: 第 行:[: -gt: 期待一元表达式
#!/bin/bash
n=`wc -l /tmp/lakala`
if [ -z "$n" ]
then
echo error
exit
elif [ $n -gt ]
then
echo abcdefg
fi [root@jimmylinux- shell]# sh -x if4.sh
++ wc -l /tmp/lakala
wc: /tmp/lakala: 没有那个文件或目录
+ n=
+ '[' -z '' ']'
+ echo error
error
+ exit
#!/bin/bash
if [ ! -f /tmp/lakala ]
then
echo "/tmp/lakala not exist."
exit
fi
n=`wc -l /tmp/lakala`
if [ -z "$n" ]
then
echo error
exit
elif [ $n -gt ]
then
echo abcdefg
fi [root@jimmylinux- shell]# sh if4.sh
/tmp/lakala not exist.
2、if [ -n "$a" ] 表示当变量a的值不为空
[root@jimmylinux- shell]# ls
.sh file1.sh file2.sh if1.sh if2.sh if3.sh if4.sh
[root@jimmylinux- shell]# if [ -n .sh ]; then echo ok; fi
ok [root@jimmylinux- shell]# echo $b [root@jimmylinux- shell]# if [ -n "$b" ]; then echo $b; else echo "b is null"; fi
b is null
文件不需要加双引号引起来
变量需要使用双引号引起来
if grep -q '' .txt;then...;fi -q为不显示过滤行:如果1.txt中含有123字符串的行,则执行then语句 if [ ! -e file ];then....;fi 文件不存在,则执行then语句 [ ] 中不能使用<,>,==,!=,>=,<=这样的符号
20.8/20.9 case判断

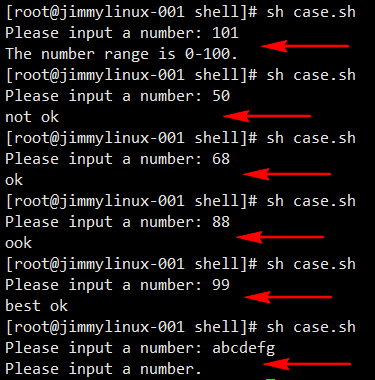
编写一个示例脚本
想实现脚本与用户的交互,你问用户做什么,用户输入什么,赋予什么值,输出的结果就是赋予的值。
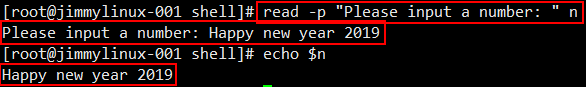
[root@jimmylinux- shell]# vi case.sh 编写示例脚本 添加以下内容 #!/bin/bash
read -p "Please input a number: " n
if [ -z "$n" ]
then
echo "Please input a number."
exit
fi n1=`echo $n|sed 's/[0-9]//g'`
if [ -n "$n1" ]
then
echo "Please input a number."
exit
fi if [ $n -lt ] && [ $n -ge ]
then
tag=
elif [ $n -ge ] && [ $n -lt ]
then
tag=
elif [ $n -ge ] && [ $n -lt ]
then
tag=
elif [ $n -ge ] && [ $n -le ]
then
tag=
else
tag=
fi case $tag in
)
echo "not ok"
;;
)
echo "ok"
;;
)
echo "ook"
;;
)
echo "best ok"
;;
*)
echo "The number range is 0-100."
;;
esac
shell脚本中的逻辑判断、文件目录属性判断、if特殊用法、case判断的更多相关文章
- shell脚本中的逻辑判断 文件目录属性判断 if特殊用法 case判断
case判断 • 格式 case 变量名 in value1) command ...
- Shell脚本中的逻辑判断、文件目录属性判断、if的特殊用法、case判断
1.Shell脚本中的逻辑判断 格式1:if 条件 ; then 语句; fi格式2:if 条件; then 语句; else 语句; fi格式3:if …; then … ;elif …; then ...
- Linux centosVMware shell脚本中的逻辑判断、文件目录属性判断、if特殊用法、case判断
一.shell脚本中的逻辑判断 格式1:if 条件 ; then 语句; fi 格式2:if 条件; then 语句; else 语句; fi 格式3:if …; then … ;elif …; th ...
- Shell脚本中让进程休眠的方法(sleep用法)
有时候写Shell的脚本,用于顺序执行一系列的程序. 有些程序在停止之后并没能立即退出,就例如有一个 tomcat 挂了,就算是用 kill -9 命令也还没瞬间就结束掉. 这么如果 shell 还没 ...
- shell脚本中 /dev/null 的用途
/dev/null 是一个特殊的设备文件,它丢弃一切写入其中的数据 可以将它 视为一个黑洞, 它等效于只写文件, 写入其中的所有内容都会消失, 尝试从中读取或输出不会有任何结果,同样,/dev/nul ...
- Shell脚本中判断输入参数个数的方法投稿:junjie 字体:[增加 减小] 类型:转载
Shell脚本中判断输入参数个数的方法 投稿:junjie 字体:[增加 减小] 类型:转载 这篇文章主要介绍了Shell脚本中判断输入参数个数的方法,使用内置变量$#即可实现判断输入了多少个参数 ...
- shell脚本中判断上一个命令是否执行成功
shell脚本中判断上一个命令是否执行成功 shell中使用符号“$?”来显示上一条命令执行的返回值,如果为0则代表执行成功,其他表示失败.结合if-else语句实现判断上一个命令是否执行成功. 示例 ...
- centos shell脚本编程2 if 判断 case判断 shell脚本中的循环 for while shell中的函数 break continue test 命令 第三十六节课
centos shell脚本编程2 if 判断 case判断 shell脚本中的循环 for while shell中的函数 break continue test 命令 ...
- [shell]上一个命令执行完成,才执行下一个操作 | shell脚本中判断上一个命令是否执行成功
shell脚本中判断上一个命令是否执行成功 shell中使用符号“$?”来显示上一条命令执行的返回值,如果为0则代表执行成功,其他表示失败.结合if-else语句实现判断上一个命令是否执行成功. 场 ...
随机推荐
- C语言I博客作业04
这个作业属于那个课程 C语言程序设计II 这个作业要求在哪里 https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/zswxy/SE2019-1/homework/9773 我在这个课程的目标 ...
- ctf pwn ida 分析技巧
几年前的笔记,搬运过来 --- 1 先根据运行程序得到的信息命名外围函数,主要函数大写开头 2 /添加注释 3 直接vim程序,修改alarm为isnan可以patch掉alarm函数 4 y 可 ...
- nginx篇最初级用法之地址重写
nginx服务器的地址重写,主要用到的配置参数是rewrite rewrite regex replacement flag rewrite 旧地址 新地址 [选项] 支持的选项有: last 不再读 ...
- linux 系统移植uboot
这里使用的版本为:u-boot-2014.04 查看并修改位置如下:u-boot-2014.04/include/configs/at91sam9x5ek.h(1)查看一下Linux内核在NandFl ...
- HTMLTestRunner加入logging输出
使用HTMLTestRunner生成html的测试报告的时候,报告中只有console输出,logging的输出无法保存, 如果要在报告中加入每一个测试用例执行的logging信息,则需要改HTMLT ...
- mysql group by使用方法注意
mysql group by使用方法注意 group by 后面只用能用having 不能加 where等域名
- Zabbix日志监控插件
#!/usr/bin/env python # coding:utf-8 import re import os import sys import logging logging.basicConf ...
- AI的真实感
目录 1.让AI"不完美"--估算和假设 2 AI感知 全能感知 特定感觉无知 3 AI的个性 4 AI的预判 5 AI的智能等级 AI的真实感一直是游戏AI程序员追求的目标, ...
- 关于设备与canvas画不出来的解决办法
连续四天解决一个在三星手机上面画canvas的倒计时饼图不出来的问题,困惑了很久,用了很多办法,甚至重写了那个方法,还是没有解决,大神给的思路是给父级加 "overflow: visible ...
- python学习-练习题
1.使用while循环输入 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 10 # cat lx.py #!/usr/local/bin/python3.6 #邹姣姣 #使用while循环输入 1 2 3 ...
