JAVA实现扫描线算法
首先说一下,教科书上的扫描线算法确实是用c++很好实现,而且网上有很多源码,而java实现的基本没有(可能是我没看到),所以还是打算自己码(实验作业写这个而自己又个是写java的猿0.0)。
对于扫描线的实现过程,我只在这里大概讲下书本上的内容(自己去看),主要还是讲一下自己实现时算法的改动和实现方法。
扫描线算法:顾名思义,就是从Ymin开始扫描,然后构建出NET,之后根据NET建立AET。
贴个图:
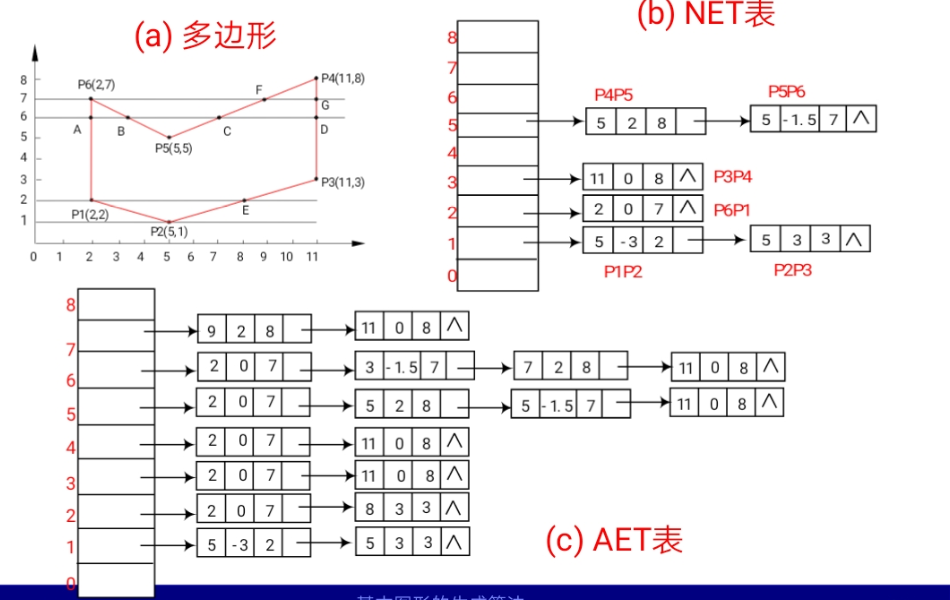

实现的时候首先是构造NET,因为对于java来说不能像c++一样直接用指针所以我用对象数组和Node类(如下代码)构造了类似数组+指针的数据结构。在实现了NET后开始通过NET实现AET,在这里我改变了一种实现方式,教科书上是一次次遍历扫描线,然后将NET插入AET后进行排序等一系列操作,而我因为是自己写的数据结构,如果说再建个表按书上的方式来最后还得自己实现链表排序等一系列操作。所以我这里直接用一个包含Arraylist的对象数组代替了。我的方法是:直接从NET开始遍历每个节点,得到节点后将它以及它自己之后会引申出的插入AET的节点(比如当前扫描线y=0 节点 X:1 dx:-1 Ymax:3 那之后会插入AET的就是 0 -1 1 和 -1 -1 2 )将这些节点不论顺序的先插入AET对应扫描线位置的对象数组的list中,将NET中节点全部遍历完之后再最后对AET中每个对象数组的list进行排序。最后得到了NET在进行打印。
贴个代码(仅供参考学习交流):
package PolygonScanningAndFilling;
public class Node { //新编表记录x,dx,yMax
public int x;
public float dx;
public int yMax;
public Node next;
public int ymin;
public Node(int x, int dx, int yMax){
this.x=x;
this.dx=dx;
this.yMax=yMax;
}
public void getYmin(int Ymin){
this.ymin=Ymin;
}
}
package PolygonScanningAndFilling; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List; public class classAndArray { public List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
public classAndArray(){ }
public void listSort() {
Collections.sort(list);
}
}
package PolygonScanningAndFilling; import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent;
import java.awt.event.KeyListener;
import java.awt.event.MouseAdapter;
import java.awt.event.MouseEvent;
import java.io.IOException; public class PolygonScanning extends JPanel { static int X0;
static int Y0;
static int X1;
static int Y1;
static int a[]=new int [10]; //保存点击的10个x坐标
static int b[]=new int [10]; //保存点击的10个y坐标
static int index=0;
static int time=0;
static int time2=0;
static boolean add;
@Override
protected void paintComponent(Graphics g) {
super.paintComponent(g);
this.addMouseListener(new MouseAdapter() {
public void mouseExited(MouseEvent e) {
time++;
repaint(); }
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e) { if(e.getButton() == e.BUTTON1) {
add=true;
if(index!=0)
{
for(int i=0;i<index;i++)
{
if(a[i]==e.getX()&&b[i]==e.getY())
add=false;
}
}
if(add)
{ a[index]=e.getX();
b[index]=e.getY(); System.out.println("坐标为("+a[index]+","+b[index]+")");
index++; //frame.setVisible(true);
repaint();
System.out.print(time2);
if(time2==0)
time2++;
}
} // if(e.getButton() == e.BUTTON3)
// {
//
// }
} }); Graphics2D g2d = (Graphics2D)g;
int Ymax=0;
for(int i=0;i<b.length;i++)
{
if(Ymax<b[i])
Ymax=b[i];
}
// System.out.println("Ymax"+Ymax); /*
* 画出多边形
*/
if(time2>0)
{
System.out.print("开始");
int Sum=0;
for(;Sum<=index;Sum++) {
if(Sum==index-1)
{
g2d.drawLine(a[Sum], b[Sum], a[0],b[0]); break;
}
else
{
g2d.drawLine(a[Sum], b[Sum], a[Sum+1],b[Sum+1]); } }
} if(time!=0) { Node [] head =new Node [Ymax]; //建立对应扫描边数的链表长度
for(int i=0;i<index-1;i++)
{ if(b[i]<b[i+1]) //从第一个点开始若前一个点小于后一个点
{
if(head[b[i]]==null)
head[b[i]]=new Node(0,0,0);
head[b[i]].ymin=b[i]; if(head[b[i]].next==null) //该点是第一个插入的节点
{
head[b[i]].next=new Node(0,0,0);
head[b[i]].next.x=a[i];
head[b[i]].next.dx=(float)(a[i]-a[i+1])/(b[i]-b[i+1]);
head[b[i]].next.yMax=b[i+1]; //ymax为后一点的y
}
else { //该点不是第一个插入的节点
if(head[b[i]].next.next==null)
head[b[i]].next.next=new Node(0,0,0);
if((float)(a[i]-a[i+1])/(b[i]-b[i+1])<head[b[i]].next.dx) //当前插入x比之前存在的节点x小
{
head[b[i]].next.next.x=head[b[i]].next.x;
head[b[i]].next.next.dx=head[b[i]].next.dx;
head[b[i]].next.next.yMax=head[b[i]].next.yMax;
head[b[i]].next.x=a[i];
head[b[i]].next.dx=(float)(a[i]-a[i+1])/(b[i]-b[i+1]);
head[b[i]].next.yMax=b[i+1];
}
else
{
head[b[i]].next.next.x=a[i];
head[b[i]].next.next.dx=(float)(a[i]-a[i+1])/(b[i]-b[i+1]);
head[b[i]].next.next.yMax=b[i+1];
}
}
}
else
{
if(head[b[i+1]]==null)
head[b[i+1]]=new Node(0,0,0);
head[b[i+1]].ymin=b[i+1];
if(head[b[i+1]].next==null) //该点是第一个插入的节点
{
head[b[i+1]].next=new Node(0,0,0);
head[b[i+1]].next.x=a[i+1];
head[b[i+1]].next.dx=(float)(a[i]-a[i+1])/(b[i]-b[i+1]);
head[b[i+1]].next.yMax=b[i]; //ymax为后一点的y
}
else { //该点不是第一个插入的节点
if(head[b[i+1]].next.next==null)
head[b[i+1]].next.next=new Node(0,0,0);
if((float)(a[i]-a[i+1])/(b[i]-b[i+1])<head[b[i+1]].next.dx) //当前插入x比之前存在的节点x小
{
head[b[i+1]].next.next.x=head[b[i+1]].next.x;
head[b[i+1]].next.next.dx=(float)head[b[i+1]].next.dx;
head[b[i+1]].next.next.yMax=head[b[i+1]].next.yMax;
head[b[i+1]].next.x=a[i+1];
head[b[i+1]].next.dx=(float)(a[i]-a[i+1])/(b[i]-b[i+1]);
head[b[i+1]].next.yMax=b[i];
}
else
{
head[b[i+1]].next.next.x=a[i+1];
head[b[i+1]].next.next.dx=(float)(a[i]-a[i+1])/(b[i]-b[i+1]);
head[b[i+1]].next.next.yMax=b[i];
}
}
} }
if(index>0)
{ if(b[0]<b[index-1]) //从第一个点到最后一个点
{
if(head[b[0]]==null)
head[b[0]]=new Node(0,0,0);
head[b[0]].ymin=b[0]; if(head[b[0]].next==null) //该点是第一个插入的节点
{
head[b[0]].next=new Node(0,0,0);
head[b[0]].next.x=a[0];
head[b[0]].next.dx=(float)(a[0]-a[index-1])/(b[0]-b[index-1]);
head[b[0]].next.yMax=b[index-1]; //ymax为后一点的y
}
else { //该点不是第一个插入的节点
if(head[b[0]].next.next==null)
head[b[0]].next.next=new Node(0,0,0);
if((float)(a[0]-a[index-1])/(b[0]-b[index-1])<head[b[0]].next.dx) //当前插入x比之前存在的节点x小
{
head[b[0]].next.next.x=head[b[0]].next.x;
head[b[0]].next.next.dx=head[b[0]].next.dx;
head[b[0]].next.next.yMax=head[b[0]].next.yMax;
head[b[0]].next.x=a[0];
head[b[0]].next.dx=(float)(a[0]-a[index-1])/(b[0]-b[index-1]);
head[b[0]].next.yMax=b[index-1];
}
else
{
head[b[0]].next.next.x=a[0];
head[b[0]].next.next.dx=(float)(a[0]-a[index-1])/(b[0]-b[index-1]);
head[b[0]].next.next.yMax=b[index-1];
}
}
}
else
{
if(head[b[index-1]]==null)
head[b[index-1]]=new Node(0,0,0);
head[b[index-1]].ymin=b[index-1];
if(head[b[index-1]].next==null) //该点是第一个插入的节点
{
head[b[index-1]].next=new Node(0,0,0);
head[b[index-1]].next.x=a[index-1];
head[b[index-1]].next.dx=(float)(a[0]-a[index-1])/(b[0]-b[index-1]);
head[b[index-1]].next.yMax=b[0]; //ymax为后一点的y
}
else { //该点不是第一个插入的节点
if(head[b[index-1]].next.next==null)
head[b[index-1]].next.next=new Node(0,0,0);
if((float)(a[0]-a[index-1])/(b[0]-b[index-1])<head[b[index-1]].next.dx) //当前插入x比之前存在的节点x小
{
head[b[index-1]].next.next.x=head[b[index-1]].next.x;
head[b[index-1]].next.next.dx=head[b[index-1]].next.dx;
head[b[index-1]].next.next.yMax=head[b[index-1]].next.yMax;
head[b[index-1]].next.x=a[index-1];
head[b[index-1]].next.dx=(float)(a[0]-a[index-1])/(b[0]-b[index-1]);
head[b[index-1]].next.yMax=b[0];
}
else
{
head[b[index-1]].next.next.x=a[index-1];
head[b[index-1]].next.next.dx=(float)(a[0]-a[index-1])/(b[0]-b[index-1]);
head[b[index-1]].next.next.yMax=b[0];
}
}
}
} for(int i=0;i<Ymax;i++)
if(head[i]!=null)
while(head[i].next!=null)
{ System.out.println("新编表y"+head[i].ymin+"新编表x"+head[i].next.x+"新编表dx"+head[i].next.dx+"新编表yMax"+head[i].next.yMax);
if(head[i].next.next!=null)
{ System.out.println("多的"+"新编表y"+head[i].ymin+"新编表x"+head[i].next.next.x+"新编表dx"+head[i].next.next.dx+"新编表yMax"+head[i].next.next.yMax);
}
break;
}
int YMIN=b[0];
for(int i=0;i<b.length;i++)
{
if(YMIN>b[i]&&b[i]!=0)
YMIN=b[i]; } classAndArray [] ca=new classAndArray [Ymax];
for(int i=YMIN;i<Ymax;i++)
ca[i]=new classAndArray();
//一个点一个点的全装入ca中再排序打印出点
for(int i=0;i<Ymax;i++)
{
if(head[i]!=null)
if(head[i].next!=null)
{
//System.out.println("新编表y"+head[i].ymin+"新编表x"+head[i].next.x+"新编表dx"+head[i].next.dx+"新编表yMax"+head[i].next.yMax);
for(int j=head[i].ymin;j<head[i].next.yMax;j++)
{ ca[i+j-head[i].ymin].list.add(head[i].next.x+(int)(0.5+((j-head[i].ymin)*head[i].next.dx)));
//System.out.print("ca[i+j-head[i].ymin]为"+(i+j-head[i].ymin)+"值为"+ca[i+j-head[i].ymin].list.toString());
//System.out.println("Ymin为"+i+" x为"+(head[i].next.x+(j-head[i].ymin)*head[i].next.dx));
} if(head[i].next.next!=null)
{ for(int j=head[i].ymin;j<head[i].next.next.yMax;j++)
{ ca[i+j-head[i].ymin].list.add(head[i].next.next.x+(int)(0.5+(j-head[i].ymin)*head[i].next.next.dx));
//System.out.print("next中ca[i+j-head[i].ymin]为"+(i+j-head[i].ymin)+"值为"+ca[i+j-head[i].ymin].list.toString());
//System.out.println("Ymin为"+i+" x为"+head[i].next.next.x+(j-head[i].ymin)*head[i].next.next.dx);
}
//System.out.println("多的"+"新编表y"+head[i].ymin+"新编表x"+head[i].next.next.x+"新编表dx"+head[i].next.next.dx+"新编表yMax"+head[i].next.next.yMax);
} }
} //
for(int i=YMIN;i<Ymax;i++)
{
ca[i].listSort();
for (int j = 0; j < ca[i].list.size(); j++) {
if(j%2==0||(j==0))
{
g2d.drawLine(ca[i].list.get(j), i, ca[i].list.get(j+1), i);
}
}
System.out.println(ca[i].list.toString());
}
}
} private static void createAndShowGUI() {
JFrame frame = new JFrame(); frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null); frame.setLayout(null);
JPanel jp=new JPanel(); frame.setVisible(true); frame.setContentPane(new PolygonScanning()); frame.setSize(600, 600);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
frame.setVisible(true);
} public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { createAndShowGUI(); }
}
效果截图(先在面板里点击点,鼠标移出面板填充)


JAVA实现扫描线算法的更多相关文章
- Spark案例分析
一.需求:计算网页访问量前三名 import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} /* ...
- hdu-1542 Atlantis(离散化+线段树+扫描线算法)
题目链接: Atlantis Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) ...
- JAVA实现种子填充算法
种子填充算法原理在网上很多地方都能找到,这篇是继上篇扫描线算法后另一种填充算法,直接上实现代码啦0.0 我的实现只是实现了种子填充算法,但是运行效率不快,如果大佬有改进方法,欢迎和我交流,谢谢! 最后 ...
- 故障重现(内存篇2),JAVA内存不足导致频繁回收和swap引起的性能问题
背景起因: 记起以前的另一次也是关于内存的调优分享下 有个系统平时运行非常稳定运行(没经历过大并发考验),然而在一次活动后,人数并发一上来后,系统开始卡. 我按经验开始调优,在每个关键步骤的加入如 ...
- Elasticsearch之java的基本操作一
摘要 接触ElasticSearch已经有一段了.在这期间,遇到很多问题,但在最后自己的不断探索下解决了这些问题.看到网上或多或少的都有一些介绍ElasticSearch相关知识的文档,但个人觉得 ...
- 论:开发者信仰之“天下IT是一家“(Java .NET篇)
比尔盖茨公认的IT界领军人物,打造了辉煌一时的PC时代. 2008年,史蒂夫鲍尔默接替了盖茨的工作,成为微软公司的总裁. 2013年他与微软做了最后的道别. 2013年以后,我才真正看到了微软的变化. ...
- 故障重现, JAVA进程内存不够时突然挂掉模拟
背景,服务器上的一个JAVA服务进程突然挂掉,查看产生了崩溃日志,如下: # Set larger code cache with -XX:ReservedCodeCacheSize= # This ...
- 死磕内存篇 --- JAVA进程和linux内存间的大小关系
运行个JAVA 用sleep去hold住 package org.hjb.test; public class TestOnly { public static void main(String[] ...
- 【小程序分享篇 一 】开发了个JAVA小程序, 用于清除内存卡或者U盘里的垃圾文件非常有用
有一种场景, 手机内存卡空间被用光了,但又不知道哪个文件占用了太大,一个个文件夹去找又太麻烦,所以我开发了个小程序把手机所有文件(包括路径下所有层次子文件夹下的文件)进行一个排序,这样你就可以找出哪个 ...
随机推荐
- [STL] Implement "map", "set"
练习热身 Ref: STL中map的数据结构 C++ STL中标准关联容器set, multiset, map, multimap内部采用的就是一种非常高效的平衡检索二叉树:红黑树,也成为RB树(Re ...
- 浅谈HDFS(二)之NameNode与SecondaryNameNode
NN与2NN工作机制 思考:NameNode中的元数据是存储在哪里的? 假设存储在NameNode节点的硬盘中,因为经常需要随机访问和响应客户请求,必然效率太低,所以是存储在内存中的 但是,如果存储在 ...
- SpringBootSecurity学习(05)网页版登录内存中配置默认用户
默认用户 前面的例子中我们使用的都是配置文件中配置好的默认用户: 除了可以配置账号密码,还可以在配置文件中配置角色: 这个角色是后面实现权限过滤的重要内容,后面会重点讨论. 在内存中配置默认用户 这样 ...
- freemarker属性配置
freemarker属性配置: spring.freemarker.allow-request-override=false # Set whether HttpServletRequest attr ...
- 使用VirtualBox虚拟机搭建hadoop运行环境,
最近学了一下大数据,包括hadoop环境的搭建,搭建工具:centos6.5,hadoop2.6.4,eclipse Mars.1 Release (4.5.1),jdk1.8 第一步.网络与ip地址 ...
- 基于vue-cli、elementUI的Vue超简单入门小例子
- 这个例子还是比较简单的,独立完成后,能大概知道vue是干嘛的,可以写个todoList的小例子. - 开始写例子之前,先对环境的部署做点简单的介绍,其实和Vue官方的差不多. #如若没有安装过vu ...
- uC/OS-III 任务详解(四)
uC/OS系统的任务一般都放在最开始介绍,我放在第四章主要是对模糊的概念作清晰的讲解. 从用户的角度来看,uC/OS-III 中的任务可以分为5 种状态,分别是休眠态.就绪态.运行态.挂起态和中断态, ...
- 死磕 java线程系列之自己动手写一个线程池
欢迎关注我的公众号"彤哥读源码",查看更多源码系列文章, 与彤哥一起畅游源码的海洋. (手机横屏看源码更方便) 问题 (1)自己动手写一个线程池需要考虑哪些因素? (2)自己动手写 ...
- Springboot + Mysql8实现读写分离
在实际的生产环境中,为了确保数据库的稳定性,我们一般会给数据库配置双机热备机制,这样在master数据库崩溃后,slave数据库可以立即切换成主数据库,通过主从复制的方式将数据从主库同步至从库,在业务 ...
- Senparc.Weixin.MP SDK 微信公众平台开发教程(二十二):在 .NET Core 2.0/3.0 中使用 MessageHandler 中间件
概述 在 <Senparc.Weixin.MP SDK 微信公众平台开发教程(六):了解MessageHandler> 中我们已经了解了 MessageHandler 的运行原理和使用方法 ...
