曹工说Spring Boot源码(4)-- 我是怎么自定义ApplicationContext,从json文件读取bean definition的?
写在前面的话
相关背景及资源:
曹工说Spring Boot源码系列开讲了(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享
工程结构图:

大体思路
总体来说,bean definition是什么,我们前面几讲,说了个大概了;目前,我们将聚焦于怎么获取bean definition。
我们这次做个实验,就是将bean definition(一共两个bean,有依赖关系,依赖是手动指定的)定义在json文件内,然后自定义一个applicationcontext,从该文件内读取bean definiton,最后我们测试下是否能work。
注意哈,这里的依赖,依然和前面讲的一样,都是手动指定依赖,类似@Autowired这种,还会放到后面才会讲,开车也要先学手动档嘛,是伐?
建议大家直接拖源码下来看:
定义json文件
json文件内,要表达bean definition,按照我们前面说的,基本就包括几个必要的就行了,比如beanClassName。但我这里还是展示一个完整的,但我也是用fastjson先在之前的工程里生成了一个json,之后再拷贝到了json文件里:
// 这里获取到的bean definition的实际类型是 GenericBeanDefiniton,所以序列化出来的的json,就是一个
// GenericBeanDefiniton集合的json
List<BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionList = factory.getBeanDefinitionList()
JSON.toJSONString(beanDefinitionList)
json文件内容如下:
[
{
"abstract": false,
"autowireCandidate": true,
"autowireMode": 0,
"beanClass": "org.springframework.simple.TestService",
"beanClassName": "org.springframework.simple.TestService",
"constructorArgumentValues": {
"argumentCount": 0,
"empty": true,
"genericArgumentValues": [],
"indexedArgumentValues": {}
},
"dependencyCheck": 0,
"enforceDestroyMethod": true,
"enforceInitMethod": true,
"lazyInit": false,
"lenientConstructorResolution": true,
"methodOverrides": {
"empty": true,
"overrides": []
},
"nonPublicAccessAllowed": true,
"primary": false,
"propertyValues": {
"converted": false,
"empty": true,
"propertyValueList": [],
"propertyValues": []
},
"prototype": false,
"qualifiers": [],
"resolvedAutowireMode": 0,
"role": 0,
"scope": "",
"singleton": true,
"synthetic": false
},
{
"abstract": false,
"autowireCandidate": true,
"autowireMode": 0,
"beanClass": "org.springframework.simple.byconstructor.TestControllerByConstructor",
"beanClassName": "org.springframework.simple.byconstructor.TestControllerByConstructor",
"constructorArgumentValues": {
"argumentCount": 2,
"empty": false,
"genericArgumentValues": [],
"indexedArgumentValues": {
0: {
"converted": false,
"value": {
"beanName": "testService",
"toParent": false
}
},
1: {
"converted": false,
"value": "wire by constructor"
}
}
},
"dependencyCheck": 0,
"enforceDestroyMethod": true,
"enforceInitMethod": true,
"lazyInit": false,
"lenientConstructorResolution": true,
"methodOverrides": {
"empty": true,
"overrides": []
},
"nonPublicAccessAllowed": true,
"primary": false,
"propertyValues": {
"converted": false,
"empty": true,
"propertyValueList": [],
"propertyValues": []
},
"prototype": false,
"qualifiers": [],
"resolvedAutowireMode": 0,
"role": 0,
"scope": "",
"singleton": true,
"synthetic": false
}
]
大家可能看得有点懵,其实换成xml,就是类似下面这样的:
<bean name="testService" class="org.springframework.simple.TestService" />
<bean id="testController" class="org.springframework.simple.TestController">
<constructor-arg ref="testService"/>
</bean>
扩展 applicationContext
package org.springframework.beans.extend.json.applicationcontext;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.extend.json.JsonBeanDefinitionReader;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.ResourceEntityResolver;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ClassPathJsonApplicationContext extends AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext {
@Override
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
//其实主要内容和xmlapplicationcontext是一样的,主要就是下面这行不一样,new了一个json reader
JsonBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new JsonBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
// 这里通过json bean definiton reader去读取bean definition
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
/**
*通过json bean definiton reader去读取bean definition
**/
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(JsonBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
// 这里获取json文件的path,这个location是在new ClassPathJsonApplicationContext时传进来的
String[] configResources = getConfigLocations();
if (configResources != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
}
}
public ClassPathJsonApplicationContext(String configLocation) throws BeansException {
this(new String[] {configLocation}, true, null);
}
/**
* 这里一模一样,不需要任何变化
**/
public ClassPathJsonApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}
}
扩展jsonBeanDefinitionReader
package org.springframework.beans.extend.json;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanDefinitionStoreException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConstructorArgumentValues;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.RuntimeBeanReference;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinitionReader;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanNameGenerator;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.GenericBeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationBeanNameGenerator;
import org.springframework.core.NamedThreadLocal;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.EncodedResource;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import org.springframework.util.StreamUtils;
import org.xml.sax.InputSource;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.*;
/**
* 类似
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader}
* 只是本类是去json文件里读取bean definition
*
*/
@Slf4j
public class JsonBeanDefinitionReader extends AbstractBeanDefinitionReader {
private final ThreadLocal<Set<EncodedResource>> resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded =
new NamedThreadLocal<Set<EncodedResource>>("json bean definition resources currently being loaded");
public JsonBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
super(registry);
}
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// 以下照抄xmlbeanDefintionReader开始
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (currentResources == null) {
currentResources = new HashSet<EncodedResource>(4);
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
EncodedResource encodedResource = new EncodedResource(resource);
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
//照抄xmlbeanDefintionReader结束
//这里的encodedResource.getResource()就是我们的json文件,这里通过spring core里面的一个工具类读取为InputStream
String json = null;
try (InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream()) {
json = StreamUtils.copyToString(inputStream, Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("{}",e);
return 0;
} finally {
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
//熟悉的fastjson,熟悉的味道
List<GenericBeanDefinition> list = JSON.parseArray(json, GenericBeanDefinition.class);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(list)) {
return 0;
}
/**
* 1:因为GenericBeanDefinition,只有setBeanClassName,所以bean反序列化时,只序列化了这个字 * 段;实际我们知道,beanClass很重要,所以我们只能自己处理一下了
* 2:第二个问题,我们在下面解释
**/
for (GenericBeanDefinition genericBeanDefinition : list) {
/**
* 1、处理beanClass
*/
Class<?> clazz = null;
try {
clazz = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().loadClass(genericBeanDefinition.getBeanClassName());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
log.error("bean class cant be load for beandefinition: {}",genericBeanDefinition);
throw new RuntimeException();
}
genericBeanDefinition.setBeanClass(clazz);
/**
* 2、处理constructor问题,因为Object value = valueHolder.getValue();
* 是Object类型,但这个实际是一个可变类型,当构造器参数为String类型时,这个Object就是 * String类型的,当构造器参数类型为其他bean的引用时,这个object就是RuntimeBeanReference * 的,
* 因为fastjson把我的object转成jsonobject类型了,所以这里要手动搞成RuntimeBeanReference
*/
ConstructorArgumentValues constructorArgumentValues = genericBeanDefinition.getConstructorArgumentValues();
if (constructorArgumentValues.isEmpty()) {
continue;
}
Map<Integer, ConstructorArgumentValues.ValueHolder> map = constructorArgumentValues.getIndexedArgumentValues();
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(map)) {
continue;
}
for (ConstructorArgumentValues.ValueHolder valueHolder : map.values()) {
Object value = valueHolder.getValue();
if (value instanceof JSONObject) {
JSONObject jsonObject = (JSONObject) value;
RuntimeBeanReference runtimeBeanReference = jsonObject.toJavaObject(RuntimeBeanReference.class);
valueHolder.setValue(runtimeBeanReference);
}
}
}
//这里new一个BeanNameGenerator,这是自带的
setBeanNameGenerator(new AnnotationBeanNameGenerator());
BeanNameGenerator beanNameGenerator = getBeanNameGenerator();
// 获取BeanDefinitionRegistry,bean factory默认实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = getRegistry();
//注册bean definition到BeanDefinitionRegistry里面去
for (GenericBeanDefinition genericBeanDefinition : list) {
String beanName = beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(genericBeanDefinition, registry);
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName,genericBeanDefinition);
}
return list.size();
}
}
收工了,测试一下
public class BootStrap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// new一个我们的自定义json上下文
ClassPathJsonApplicationContext context = new ClassPathJsonApplicationContext("beanDefinition.json");
// getBean试一下
TestControllerByConstructor bean = context.getBean(TestControllerByConstructor.class);
System.out.println(bean);
}
}
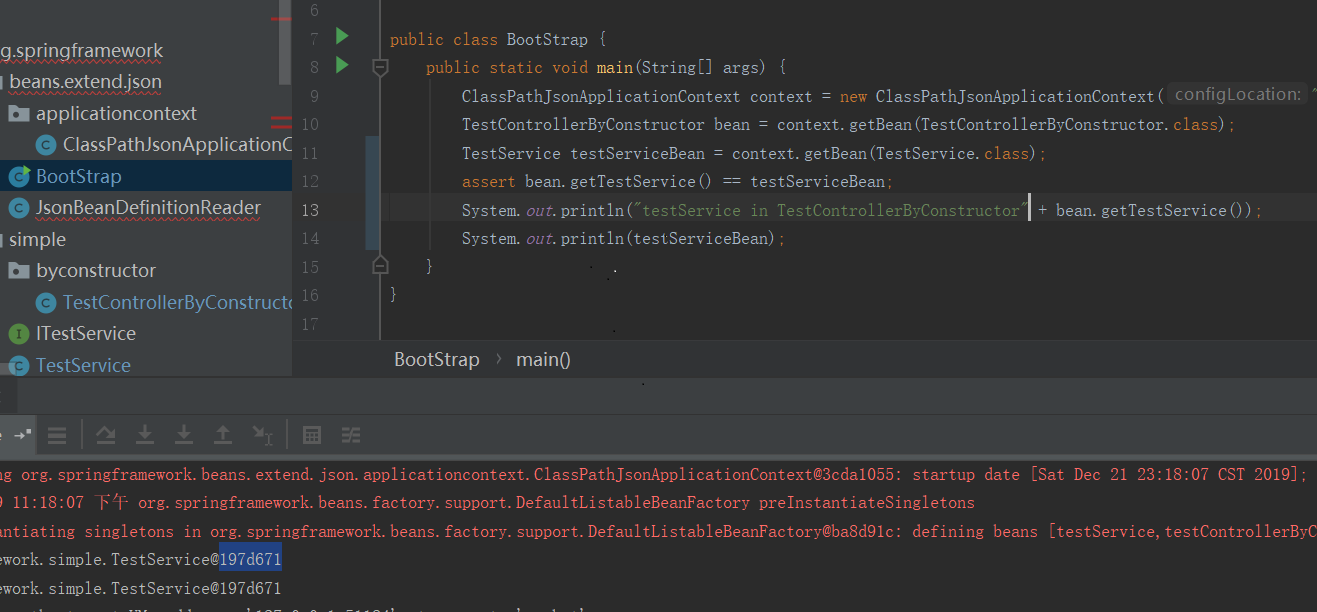
可以看到,已经注入进去了。没有什么问题。
总结
今天比较晚,写得也比较急,有问题的话,请大家务必指出,谢谢大家
源码地址:
曹工说Spring Boot源码(4)-- 我是怎么自定义ApplicationContext,从json文件读取bean definition的?的更多相关文章
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码系列开讲了(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享
写在前面的话&&About me 网上写spring的文章多如牛毛,为什么还要写呢,因为,很简单,那是人家写的:网上都鼓励你不要造轮子,为什么你还要造呢,因为,那不是你造的. 我不是要 ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,咱们对着接口,逐个方法讲解
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码系列开讲了(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 工程代码地址 思维导图地址 工程结构图: 正 ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(3)-- 手动注册Bean Definition不比游戏好玩吗,我们来试一下
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码系列开讲了(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 工程代码地址 思维导图地址 工程结构图: 大 ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(5)-- 怎么从properties文件读取bean
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(6)-- Spring怎么从xml文件里解析bean的
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(7)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(上)
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(8)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(util命名空间)
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(9)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(context命名空间上)
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
- # 曹工说Spring Boot源码(10)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(context:annotation-config 解析)
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
随机推荐
- PostGIS 存储过程返回类型
Postgresql存储过程返回值的方式有很多,在此先只记录一下自己用到过的,慢慢拓展 1.type型,这里geometry可以是任何postgresql支持的类型(integer/text/char ...
- 记录用户登陆信息,你用PHP是如何来实现的
对于初入门的PHP新手来说,或许有一定的难度.建议大家先看看PHP中session的基础含义,需要的朋友可以选择参考. 下面我们就通过具体的代码示例,为大家详细的介绍PHP中session实现记录用户 ...
- 2019-10-2,html作业,简历源码
<html> <head> <title>简历作业</title> </head> <body bgcolor=#cccccc> ...
- day 17 re模块 正则表达式
import re 引用re模块 查找 finall:匹配所有,每一项都是列表中的一个元素 search:只匹配从左到右的第一个,得到的不是直接的结果而是一个变量,通过group方法获取结果,没 ...
- 2019/12/1 智能硬件实验室(ROS方向)
浅谈安装ubuntu与ros感想 ubuntu 以前看电脑软件安装管家上的教程尝试在另一台电脑上安装ubuntu(虚拟机上),但是后面遇到了无法解决的问题,放弃了.这次因为选的ros方向,所以昨天在学 ...
- 仿微信 即时聊天工具 - SignalR (一)
话不多说,先上图 背景: 微信聊天,经常会遇见视频发不了,嗯,还有聊天不方便的问题,于是我就自己买了服务器,部署了一套可以直接在微信打开的网页进行聊天,这样只需要发送个url给朋友,就能聊天了! 由于 ...
- solr数据操作
本文介绍solr的基本数据操作,基于solr 8.2.solr支持多种数据格式,包括XML,JSON,CSV等,并提供多种脚本和工具来操作数据.本文讲解curl请求和JSON数据格式的处理方式. 本文 ...
- kubectl: Error from server: error dialing backend: remote error: tls: internal error
使用kubectl logs,发现报了tls的错误,然后查看kubelet的日志,发现报了上面的错误,然后通过命令kubectl get csr查看发现有很多处于pending状态 最后通过命令 ku ...
- 点击查看大图滑动预览(h5,pc通用)
点击预览大图并滑动观看,支持手机端和pc端,具体功能如下图: 一. touchTouch 的js和css 以及jquery依赖库 <link rel="stylesheet" ...
- PHP fsockopen受服务器KeepAlive影响的解决
在开发过程中常常遇到这样的需求,模拟浏览器访问某接口,并获取返回数据.我们比较常使用的方法是fsockopen与接口建立连接,然后发出指令,然后通过fgets接受返回值. 但是我们发现,通过PHP模拟 ...
