cgroup代码浅析(2)
info
- include/linux/memcontrol.h memcg相关的函数
数据结构
- mem_cgroup在每个node下,都有一个lruvec, 这个lruvec保存在mem_cgroup_per_node结构中
///////////// mem_cgroup
struct mem_cgroup {
struct cgroup_subsys_state css;
...
struct mem_cgroup_per_node *nodeinfo[0]; // memcg 在每个node下
}
struct cgroup_subsys_state {
struct cgroup *cgroup;
...
}
struct mem_cgroup_per_node {
struct lruvec lruvec;
unsigned long lru_zone_size[MAX_NR_ZONES][NR_LRU_LISTS];
struct mem_cgroup_reclaim_iter iter[DEF_PRIORITY + 1];
struct rb_node tree_node; /* RB tree node */
unsigned long usage_in_excess;/* Set to the value by which */
/* the soft limit is exceeded*/
bool on_tree;
bool writeback; /* memcg kswapd reclaim writeback */
bool dirty; /* memcg kswapd reclaim dirty */
bool congested; /* memcg has many dirty pages */
/* backed by a congested BDI */
struct mem_cgroup *memcg; /* Back pointer, we cannot */
/* use container_of */
};
//////////// lru结构
struct lruvec {
struct list_head lists[NR_LRU_LISTS];
struct zone_reclaim_stat reclaim_stat;
/* Evictions & activations on the inactive file list */
atomic_long_t inactive_age;
/* Refaults at the time of last reclaim cycle */
unsigned long refaults;
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMCG
struct pglist_data *pgdat;
#endif
};
Cgroup和Task的关联
task->css_set
struct task_struct {
struct css_set __rcu *cgroups; // 每个进程中,都对应有一个css_set结构体,css_set其实就是cgroup_subsys_state对象的集合,而每个cgroup_subsys_state代表一个subsystem
...
}
struct css_set {
struct cgroup_subsys_state *subsys[CGROUP_SUBSYS_COUNT];
...
}
css_set的初始化发生在kernel boot,从如下代码可见
asmlinkage __visible void __init start_kernel(void)
{
cpuset_init();
cgroup_init();
...
}
一个task可以属于多个cgroup,一个cgroup也可以拥有多个task,这种M:N的关系,linux kernel中是通过cgrp_cset_link结构体表示的:
/*
* A cgroup can be associated with multiple css_sets as different tasks may
* belong to different cgroups on different hierarchies. In the other
* direction, a css_set is naturally associated with multiple cgroups.
* This M:N relationship is represented by the following link structure
* which exists for each association and allows traversing the associations
* from both sides.
*/
struct cgrp_cset_link {
/* the cgroup and css_set this link associates */
struct cgroup *cgrp;
struct css_set *cset;
/* list of cgrp_cset_links anchored at cgrp->cset_links */
struct list_head cset_link;
/* list of cgrp_cset_links anchored at css_set->cgrp_links */
struct list_head cgrp_link;
};
这个结构其实就是一个link,cgrp就是这个link关联的cgroup,cset属于一个task,于是可以代表一个进程。
而cset_link是给struct cgroup查找struct cgrp_cset_link用的。那么怎么找呢?
我们首先来看如何把一个cgroup与一个css_set关联起来
/**
* link_css_set - a helper function to link a css_set to a cgroup
* @tmp_links: cgrp_cset_link objects allocated by allocate_cgrp_cset_links()
* @cset: the css_set to be linked
* @cgrp: the destination cgroup
*/
/* link_css_set函数的功能就是把一个css_set与一个cgroup通过struct */cgrp_cset_link联系起来。
static void link_css_set(struct list_head *tmp_links, struct css_set *cset, struct cgroup *cgrp)
{
struct cgrp_cset_link *link;
BUG_ON(list_empty(tmp_links));
if (cgroup_on_dfl(cgrp))
cset->dfl_cgrp = cgrp;
// 从已经分配好的一个cgrp_cset_link链表(表头为tmp_links)中拿一个出来,填上cgroup与css_set的指针
link = list_first_entry(tmp_links, struct cgrp_cset_link, cset_link);
link->cset = cset;
link->cgrp = cgrp;
// 把这个cgrp_cset_link从原来的链表中移出来,加入到cgrp(这个就是那个cgroup)的cset_links链表中
list_move_tail(&link->cset_link, &cgrp->cset_links);
// 把cgrp_cset_link的cgrp_link加入到cset的cgrp_links链表中
list_add_tail(&link->cgrp_link, &cset->cgrp_links);
if (cgroup_parent(cgrp))
cgroup_get(cgrp);
}
上面注释中提到,用于分配cgrp_cset_link(表头为tmp_links)的函数是allocate_cgrp_cset_links,其定义如下:
/**
* allocate_cgrp_cset_links - allocate cgrp_cset_links
* @count: the number of links to allocate
* @tmp_links: list_head the allocated links are put on
*
* Allocate @count cgrp_cset_link structures and chain them on @tmp_links
* through ->cset_link. Returns 0 on success or -errno.
*/
static int allocate_cgrp_cset_links(int count, struct list_head *tmp_links)
{
struct cgrp_cset_link *link;
int i;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(tmp_links);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
link = kzalloc(sizeof(*link), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!link) {
free_cgrp_cset_links(tmp_links);
return -ENOMEM;
}
list_add(&link->cset_link, tmp_links);
}
return 0;
}
这个函数很简单,就是申请count个struct cgrp_cset_link,同时把它们一个个加到tmp_links这个链表里。这count的数据结构是通过struct cgrp_cset_link->cset_link连接起来的,但是前面说到这个变量是给struct cgroup用的。这是因为目前分配出来的这些个数据结构只是临时的,也就是说暂时借用一下这个变量,到后面会再来恢复这个变量的本来用途。这也是为什么link_css_set函数中cgrp_link成员用list_add,而cset_link用list_move。
于是,可以用下图来表示allocate_cgrp_cset_links的结果:
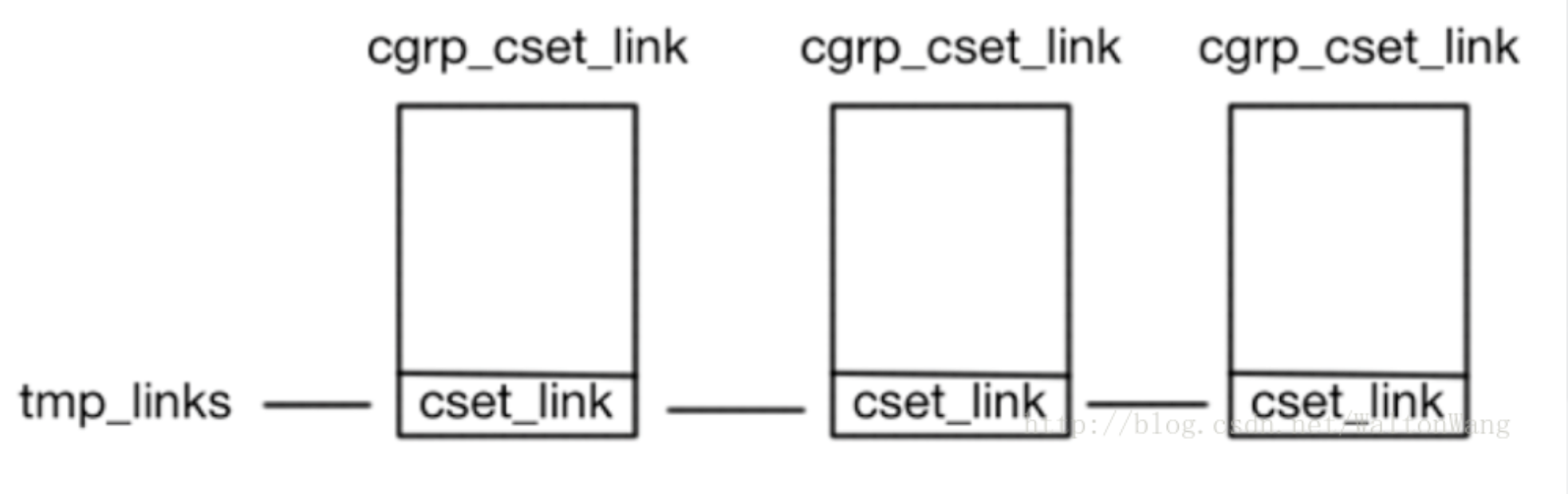
而link_css_set的结果则可以用下图来表示:

这张图也解释了linux代码中如何表现cgroup与subsystem之间多对多的关系。每个struct cgroup可以通过cgroup->cset_links和cgrp_cset_link->cset_link找到一串struct cgrp_cset_link,每个struct cgrp_cset_link都有着对应的css_set,这个css_set属于一个tast_struct(其实是多个),其中包含着subsystem。
于是通过遍历链表就能找到这个cgroup对应的所有task(其实找到的是css_set,但是对于Cgroups这个模块来说,关心的并不是task_struct,而是这个css_set)。反之亦然,通过task_struct的cgroups变量(类型为struct css_set*)就能找到这个进程属于的所有cgroup。
例如,给定一个task,我们想找到这个task在某个hierarchy中的cgroup,就可以调用如下函数:linux-4.4.19/kernel/cgroup.c
/*
* Return the cgroup for "task" from the given hierarchy. Must be
* called with cgroup_mutex and css_set_lock held.
*/
static struct cgroup *task_cgroup_from_root(struct task_struct *task,
struct cgroup_root *root)
{
/*
* No need to lock the task - since we hold cgroup_mutex the
* task can't change groups, so the only thing that can happen
* is that it exits and its css is set back to init_css_set.
*/
return cset_cgroup_from_root(task_css_set(task), root);
}
/* look up cgroup associated with given css_set on the specified hierarchy */
static struct cgroup *cset_cgroup_from_root(struct css_set *cset,
struct cgroup_root *root)
{
struct cgroup *res = NULL;
lockdep_assert_held(&cgroup_mutex);
lockdep_assert_held(&css_set_lock);
if (cset == &init_css_set) {
res = &root->cgrp;
} else {
struct cgrp_cset_link *link;
list_for_each_entry(link, &cset->cgrp_links, cgrp_link) {
struct cgroup *c = link->cgrp;
if (c->root == root) {
res = c;
break;
}
}
}
BUG_ON(!res);
return res;
}
Cgroup与subsystem
linux-4.4.19/include/linux/cgroupsubsys.h中定义了所有的subsystem。
可以看到,共有cpuset, debug, cpu, cpuacct, memory, devices, freezer, netcls, blkio, perfevent, netprio, hugtlb等12个.
cpu subsystem
struct task_group就是cpu subsystem对应的子类, 代码见
/* task group related information */
struct task_group {
struct cgroup_subsys_state css;
#ifdef CONFIG_FAIR_GROUP_SCHED
/* schedulable entities of this group on each cpu */
struct sched_entity **se;
/* runqueue "owned" by this group on each cpu */
struct cfs_rq **cfs_rq;
unsigned long shares;
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
atomic_long_t load_avg;
#endif
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_RT_GROUP_SCHED
struct sched_rt_entity **rt_se;
struct rt_rq **rt_rq;
struct rt_bandwidth rt_bandwidth;
#endif
struct rcu_head rcu;
struct list_head list;
struct task_group *parent;
struct list_head siblings;
struct list_head children;
#ifdef CONFIG_SCHED_AUTOGROUP
struct autogroup *autogroup;
#endif
struct cfs_bandwidth cfs_bandwidth;
};
Cgroups通过VFS来和用户打交道, 用户通过将各个subsystem mount到某个目录下之后, cgroup文件系统会自动创建一系列虚拟文件, 用户通过向不同的文件读写数据控制Cgroups的行为. 具体对CPU subsystem来说, 有一个tasks文件, 向其中写入一些进程的pid, 就能将这些进程加入到这个cgroup. 另外还有个cpu.shares的文件, 向其中写入一个数字后就能设置这个cgroup的进程的weight.
每个文件系统(包括Cgroups对应的cgroup文件系统)拥有一个数据结构, 其中有一系列函数指针, 当对这个文件系统进行读写操作时, 内核会调用这个文件系统的对应函数指针. 因此当向一个VFS的文件写入数据时, 可以在这个函数指针指向的函数做一些其他事情. 具体对于CPU subsystem, 当向cpu.shares写入一个数字时, 内核执行的函数干的事情是修改这个cgroup对应的struct task_group中的shares变量. 这个函数是:
linux-4.4.19/kernel/sched/core.c #8270
static int cpu_shares_write_u64(struct cgroup_subsys_state *css,
struct cftype *cftype, u64 shareval)
{
return sched_group_set_shares(css_tg(css), scale_load(shareval));
}
其中, csstg函数是找到具体的subsystem子类, 这里就是struct taskcgroup. schedgroupset_shares这个函数的定义如下:
int sched_group_set_shares(struct task_group *tg, unsigned long shares)
{
int i;
unsigned long flags;
/*
* We can't change the weight of the root cgroup.
*/
if (!tg->se[0])
return -EINVAL;
shares = clamp(shares, scale_load(MIN_SHARES), scale_load(MAX_SHARES));
mutex_lock(&shares_mutex);
if (tg->shares == shares)
goto done;
tg->shares = shares;
for_each_possible_cpu(i) {
struct rq *rq = cpu_rq(i);
struct sched_entity *se;
se = tg->se[i];
/* Propagate contribution to hierarchy */
raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&rq->lock, flags);
/* Possible calls to update_curr() need rq clock */
update_rq_clock(rq);
for_each_sched_entity(se)
update_cfs_shares(group_cfs_rq(se));
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&rq->lock, flags);
}
done:
mutex_unlock(&shares_mutex);
return 0;
}
变量
根组:
extern struct mem_cgroup *root_mem_cgroup;
函数
从page获取mem_cgroup: page_mem_cgroup()
static inline struct mem_cgroup *page_mem_cgroup(struct page *page)
{
return page->mem_cgroup;
}
从pgdata + memcg 获取lru: mem_cgroup_lruvec()
static inline struct lruvec *mem_cgroup_lruvec(struct pglist_data *pgdat,
struct mem_cgroup *memcg)
{
struct mem_cgroup_per_node *mz;
struct lruvec *lruvec;
// 如果没有开启memcg,则,lru等于node上的lru
if (mem_cgroup_disabled()) {
lruvec = node_lruvec(pgdat);
goto out;
}
// 获取memcg里对应的node的mz,mz里保存了这个memcg在这个node上的lruvec
mz = mem_cgroup_nodeinfo(memcg, pgdat->node_id);
lruvec = &mz->lruvec;
out:
/*
* Since a node can be onlined after the mem_cgroup was created,
* we have to be prepared to initialize lruvec->pgdat here;
* and if offlined then reonlined, we need to reinitialize it.
*/
if (unlikely(lruvec->pgdat != pgdat))
lruvec->pgdat = pgdat;
return lruvec;
}
例子:
static void reclaim_pages_from_memcg(struct mem_cgroup *memcg)
{
pg_data_t *pgdat;
struct lruvec *lruvec;
pgdat = NODE_DATA(nid);
lruvec = mem_cgroup_lruvec(pgdat, memcg);
}
常见函数
mem_cgroup_disabled()
打印相关:
memcg_stat_show()
charge 相关:
int mem_cgroup_try_charge(struct page *page, struct mm_struct *mm,
gfp_t gfp_mask, struct mem_cgroup **memcgp,
bool compound);
void mem_cgroup_commit_charge(struct page *page, struct mem_cgroup *memcg,
bool lrucare, bool compound);
void mem_cgroup_cancel_charge(struct page *page, struct mem_cgroup *memcg,
bool compound);
void mem_cgroup_uncharge(struct page *page);
void mem_cgroup_uncharge_list(struct list_head *page_list);
charge/uncharge
mem_cgroup_uncharge
void mem_cgroup_uncharge(struct page *page)
{
if (mem_cgroup_disabled())
return;
/* Don't touch page->lru of any random page, pre-check: */
if (!page->mem_cgroup)
return;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&page->lru);
uncharge_list(&page->lru);
}
memcg_stat_show
static int memcg_stat_show(struct seq_file *m, void *v)
{
struct mem_cgroup *memcg = mem_cgroup_from_css(seq_css(m));
unsigned long memory, memsw;
struct mem_cgroup *mi;
unsigned int i;
struct accumulated_stats acc;
BUILD_BUG_ON(ARRAY_SIZE(mem_cgroup_stat_names) !=
MEM_CGROUP_STAT_NSTATS);
BUILD_BUG_ON(ARRAY_SIZE(mem_cgroup_events_names) !=
MEM_CGROUP_EVENTS_NSTATS);
BUILD_BUG_ON(ARRAY_SIZE(mem_cgroup_lru_names) != NR_LRU_LISTS);
for (i = 0; i < MEM_CGROUP_STAT_NSTATS; i++) {
if (i == MEM_CGROUP_STAT_SWAP && !do_memsw_account())
continue;
seq_printf(m, "%s %lu\n", mem_cgroup_stat_names[i],
mem_cgroup_read_stat(memcg, i) * PAGE_SIZE);
}
for (i = 0; i < MEM_CGROUP_EVENTS_NSTATS; i++)
seq_printf(m, "%s %lu\n", mem_cgroup_events_names[i],
mem_cgroup_read_events(memcg, i));
for (i = 0; i < NR_LRU_LISTS; i++)
seq_printf(m, "%s %lu\n", mem_cgroup_lru_names[i],
mem_cgroup_nr_lru_pages(memcg, BIT(i)) * PAGE_SIZE);
Refs
https://www.cnblogs.com/yjf512/p/6003094.html
https://blog.csdn.net/WaltonWang/article/details/53899191
cgroup代码浅析(2)的更多相关文章
- cgroup代码浅析(1)
前置:这里使用的linux版本是4.8,x86体系. cgroup_init_early(); 聊这个函数就需要先了解cgroup. cgroup概念 这个函数就是初始化cgroup所需要的参数的.c ...
- Mosquitto pub/sub服务实现代码浅析-主体框架
Mosquitto 是一个IBM 开源pub/sub订阅发布协议 MQTT 的一个单机版实现(目前也只有单机版),MQTT主打轻便,比较适用于移动设备等上面,花费流量少,解析代价低.相对于XMPP等来 ...
- VC 函数调用的 汇编代码 浅析
摘要:主要谈谈vc里面函数调用汇编成汇编代码的情形,首先针对之前的一个小程序,说说vc编译器的优化. 例子程序: #include <iostream>using namespace st ...
- 游戏音频技术备忘 (五)Wwise Unreal Engine 集成代码浅析 二
AkAmbientSound类的实现 Unreal Engine提供了一个基本对象的构造器ObjectInitializer,一般来说用户创建的类总是拥有很多变量,因此 AkAmbientSound ...
- 游戏音频技术备忘 (四) Wwise Unreal Engine 集成代码浅析 (一)
在Engine\Plugins\Wwise\Source下为主要Wwise相关代码,AkAudio文件夹下为运行时相关代码,AudiokineticTools下为编辑器工具相关代码,Audiokine ...
- TensorFlow教程——Bi-LSTM+CRF进行序列标注(代码浅析)
https://blog.csdn.net/guolindonggld/article/details/79044574 Bi-LSTM 使用TensorFlow构建Bi-LSTM时经常是下面的代码: ...
- jQuery on()方法绑定动态元素的点击事件实例代码浅析
之前就一直受这个问题的困扰,在jQuery1.7版本之后添加了on方法,之前就了解过,其优越性高于live(),bind(),delegate()等方法,在此之前项目中想用这个来测试结果发现,居然动态 ...
- Linux profile1,bashrc,.bash_profile,.bash_login,.profile,.bashrc,.bash_logout浅析 Part1
profile,bashrc,.bash_profile,.bash_login,.profile,.bashrc,.bash_logout浅析 Part 1 by:授客 QQ:103355312 ...
- cgroup 分析之CPU和内存部分
https://ggaaooppeenngg.github.io/zh-CN/2017/05/07/cgroups-%E5%88%86%E6%9E%90%E4%B9%8B%E5%86%85%E5%AD ...
随机推荐
- javascript总结02
1 如何打开和关闭一个新的窗口? 2 Window对象的哪个属性能返回上一个浏览页面? 3 一次或多次执行一段程序的函数是什么? 定时函数 4 如何查找并访问节点? 5 给表格新增行和单元格的方法分别 ...
- C#计算运行时间
using System.Diagnostics; private Stopwatch stw = new Stopwatch(); stw.Start(); stw.Stop(); MessageB ...
- 学习MAP 地图好地址
http://www.cnblogs.com/beniao/archive/2010/01/13/1646446.html Bēniaǒ成长笔记在IT江湖里我不是一名老手,我只是一名普通的程序员,愿意 ...
- 【Dairy】2016.10.23 观火&中彩记
...................... 就第一条可以! 观火10分钟,长郡附近老房子起火...
- FreeMarker:模板开发指南
ylbtech-FreeMarker:模板开发指南 1.返回顶部 1. Section Contents 入门 模板 + 数据模型 = 输出 数据模型一览 模板一览 数值,类型 基本内容 类型 模板 ...
- 国外知名IT网站(转载)
转自:http://supportopensource.iteye.com/blog/780566 =========================================== 1.Cnet ...
- "git rm" 和 "rm" 的区别(转载)
转自:http://yang3wei.github.io/blog/2013/02/03/git-rm-he-rm-de-qu-bie/ 这是一个比较肤浅的问题,但对于 git 初学者来说,还是有必要 ...
- bzoj 1646: [Usaco2007 Open]Catch That Cow 抓住那只牛【bfs】
满脑子dp简直魔性 模拟题意bfs转移即可 #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<queue> using na ...
- mvn 配置
<!-- 阿里云仓库1 --> <mirror> <id>alimaven-1</id> <name>al ...
- jQuery——表单应用(4)
HTML: <!--复选框应用--> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF- ...
