pytest 学习笔记一:参数化与组织分层
组织分层:
1、普通方式,和unittest分层类似:
setup_module() # 通常放在类外
setup_class(cls)
setup(self)
teardown(self)
teardown_class(cls)
teardown_module()
2、pytest特有的分层方式
@pytest.fixture() 装饰fixture
@pytest.mark.usefixtures() 使用fixture
例一:
@pytest.fixture() # 默认scope是function,等同于@pytest.fixture(scope="function"),作用于每个test用例
def before():
print u"清除数据" class TestClass(common): # 继承common类中setup_class def setup(self): # 可以和before并存,如果某个用例使用了before,共同生效。
print "start" def teardown(self):
print "end" @pytest.mark.usefixtures("before") #使用fixture的方法一
def test_one(self):
x = "this"
assert "h" in x def test_two(self,before): # 使用fixture的方法二
x = "hello"
assert x == "hello" if __name__=="__main__":
pytest.main("-s test_pt2.py") # 指定测试文件
执行后结果:

@pytest.fixture(scope="xxx") 有4个范围,function、class、module、session 。session是作用于整个项目。
例二:
#coding:utf8
import pytest class DB(object):
def __init__(self):
self.intransaction = []
def begin(self, name):
self.intransaction.append(name)
def rollback(self):
self.intransaction.pop() @pytest.fixture(scope="module")
def db(): # 工厂模式
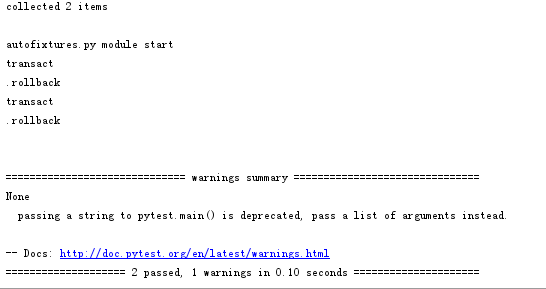
print "module start"
return DB() # @pytest.mark.usefixtures("transact") #作用于整个类,即对类中所有用例都生效
class TestClass(object):
@pytest.fixture(autouse=True) # 设置一个function级别的fixture, autouse=True 表示对所有用例生效 ,等效于在测试类前@pytest.mark.usefixtures("transact")
def transact(self,request, db):
db.begin(request.function.__name__)
print "transact"
yield # yield之后的内容可以当成teardown !!!
db.rollback()
print "rollback" def test_method1(self,db): # 这里需要引入db ,db是module范围,每个模块只运行一次
#module只运行一次,那么在这个module范围(module表示同一层目录中?)中所有的用例引用db得到的参数DB()是同一个。这里类似于module范围的一个全局变量
assert db.intransaction == ["test_method1"]
def test_method2(self,db):
assert db.intransaction == ["test_method2"]
if __name__=="__main__":
pytest.main("-s autofixtures.py")
执行结果:
参数化:
#参数化一,先定义函数,更灵活
@pytest.fixture(params=[2,3,4])
def before3(request): #request固定格式
param=request.param
print param
return param+1 再使用:
def test_four(self,before3): # 参数化
assert before3 !=3
# 参数化二,简便
@pytest.mark.parametrize("param", [1, 2, 3])
def test_three(self,param): # 参数化
assert param !=2 参数覆盖fixture: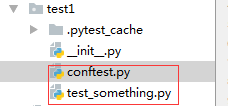
conftest.py :
import pytest @pytest.fixture
def username():
return 'username' @pytest.fixture
def other_username(username):
return 'other-' + username
test_something.py:
#coding:utf8
import pytest # 同一层级的fixture可以直接引用 @pytest.mark.parametrize('username', ['directly-overridden-username'])
def test_username(username): # conftest中的fixture:username,这里被参数username直接覆盖
assert username == 'directly-overridden-username' @pytest.mark.parametrize('username', ['directly-overridden-username-other'])
def test_username_other(other_username): # conftest中的fixture:other_username,other_username引用了username,这里被参数usename间接覆盖了
assert other_username == 'other-directly-overridden-username-other' if __name__=="__main__":
pytest.main("-s test_something.py") 更多fixture覆盖参考:https://blog.csdn.net/huitailang1991/article/details/74053781
pytest 学习笔记一:参数化与组织分层的更多相关文章
- [转载]pytest学习笔记
pytest学习笔记(三) 接着上一篇的内容,这里主要讲下参数化,pytest很好的支持了测试函数中变量的参数化 一.pytest的参数化 1.通过命令行来实现参数化 文档中给了一个简单的例子, ...
- Pytest学习笔记8-参数化
前言 我们在实际自动化测试中,某些测试用例是无法通过一组测试数据来达到验证效果的,所以需要通过参数化来传递多组数据 在unittest中,我们可以使用第三方库parameterized来对数据进行参数 ...
- pytest学习笔记
From: https://blog.csdn.net/gaowg11/article/details/54910974 由于对测试框架了解比较少,所以最近看了下pytest测试框架,对学习心得做个记 ...
- pytest学习笔记(一)
这两天在学习pytest,之前有小用到pytest,觉得这个测试框架很灵巧,用在实现接口自动化(pytest+requests)非常的轻便,然后很有兴致的决定学习下,然后又发现了pytest-sele ...
- pytest学习笔记(三)
接着上一篇的内容,这里主要讲下参数化,pytest很好的支持了测试函数中变量的参数化 一.pytest的参数化 1.通过命令行来实现参数化 文档中给了一个简单的例子, test_compute.py ...
- pytest学习笔记(二)
继续文档的第二章 (一)pytest中可以在命令行中静态/动态添加option,这里没什么好讲的,略过... 这里面主要讲下如何试用skip/xfail,还有incremental(包含一些列的测试步 ...
- 学习笔记之TCP/IP协议分层与OSI參考模型
1.协议的分层 ISO在制定标准化OSI之前,对网络体系结构相关的问题进行了充分的讨论, 终于提出了作为通信协议设计指标的OSI參考模型.这一模型将通信协议中必要 的功能分成了7层.通过这些 ...
- pytest 学习笔记一 入门篇
前言 之前做自动化测试的时候,用的测试框架为Python自带的unittest框架,随着工作的深入,发现了另外一个框架就是pytest (官方地址文档http://www.pytest.org/en/ ...
- Pytest学习笔记3-fixture
前言 个人认为,fixture是pytest最精髓的地方,也是学习pytest必会的知识点. fixture用途 用于执行测试前后的初始化操作,比如打开浏览器.准备测试数据.清除之前的测试数据等等 用 ...
随机推荐
- 最好的ie版本检测方式
预备知识:NodeList的实时性 通过 document.getElementsByTagName,document.forms ,document.images 等方法获取到nodelist以后 ...
- 05python上
location 位置 untitled 未命名的 fullstack 全栈 interpreter 解释器 字符格式化输出 占位符 %s s = string %d d = digit 整数 %f ...
- spark基础知识介绍2
dataframe以RDD为基础的分布式数据集,与RDD的区别是,带有Schema元数据,即DF所表示的二维表数据集的每一列带有名称和类型,好处:精简代码:提升执行效率:减少数据读取; 如果不配置sp ...
- 01.VMware虚拟机上网络连接(network type)的三种模式--bridged、host-only、NAT
VMWare提供了三种工作模式,它们是bridged(桥接模式).NAT(网络地址转换模式)和host-only(主机模式).要想在网络管理和维护中合理应用它们,你就应该先了解一下这三种工作模式. 1 ...
- Java中,&&与&,||与|的区别
在java的逻辑运算符中,有这么四类:&&(短路与),&,|,||(短路或). &&和&都是表示与,区别是&&只要第一个条件不满足,后面 ...
- 爬虫--requests模块高级(代理和cookie操作)
代理和cookie操作 一.基于requests模块的cookie操作 引言:有些时候,我们在使用爬虫程序去爬取一些用户相关信息的数据(爬取张三“人人网”个人主页数据)时,如果使用之前requests ...
- Django--ORM(模型层)--多表(重重点)
一.数据库表关系 单表 重复的字段太多,所以需要一对多,多对多来简化 多表 多对一 多对多 一对一 =============================================== 一对 ...
- WDA-5-VIEW视图切换
这一部分介绍同一窗口下不同视图之间的链接跳转. 前提:完成上一步骤MAIN视图ALV显示. 1.效果展示 点击ALV物料下划线链接,页面跳转到物料明细页面. 2.实现过程 基于上一步骤在MAIN页面显 ...
- React Native,flexbox布局
Flexbox布局 flex:使组件在可利用的空间内动态地扩张或收缩.flex:1会使组件撑满空间.当有多个组件都指定了flex的值,那么谁的flex值大谁占得空间就大,占得大小的比例就是flex值的 ...
- select as table
select order_time, max(sum_price) from (SELECT order, sum(price) as sum_price FROM orders group by o ...
