cJSON序列化工具解读一(结构剖析)
cJSON简介
JSON基本信息
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)是一种轻量级的数据交换格式。易于人阅读和编写。同时易于机器解析和生成。是一种很好地数据交换语言。
JSON构建:基于两种结构
“名称/值”对 的集合。
值得有序列表。
JSON具体结构表示
对象:一个”名称/值"对的集合 {名称:值,名称:值}
数组:值得有序集合[值,值]
值:str,num,true,false,null,object,array。可嵌套
字符串:由双引号包围的任意数量Unicode字符的集合,反斜杠转义
数值:类似C,java:没有8进制和具体的编码细节
cJSON源码解读
首先给出cJSON文件中头文件函数列表
我们将根据此进行模块化解读
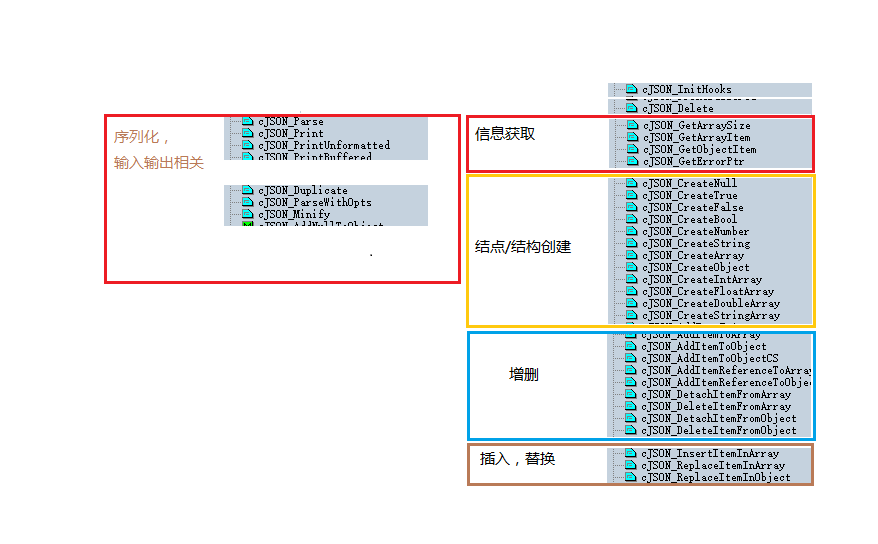
①结构描述
关于具体的结构图解描述,请参考官方描述
/* cJSON Types: */
#define cJSON_False 0
#define cJSON_True 1
#define cJSON_NULL 2
#define cJSON_Number 3
#define cJSON_String 4
#define cJSON_Array 5
#define cJSON_Object 6 #define cJSON_IsReference 256
#define cJSON_StringIsConst 512
以上是具体的类型区分描述,可以改进为使用enum实现更加安全
/* The cJSON structure: */
typedef struct cJSON {
struct cJSON *next, *prev; /* 如果是同一级别类型元素,使用双项链方式实现 */
struct cJSON *child; /* 如果是具体结构或者数组,第一个指针指向内部链 */ int type; /*根据以上定义描述所保存对象类型*/ char *valuestring; /* The item's string, if type==cJSON_String */
int valueint; /* The item's number, if type==cJSON_Number */
double valuedouble; /* The item's number, if type==cJSON_Number */ char *string; /* 对于key-value映射结构,表示其key/名称 */
}cJSON;
②关于内存管理
typedef struct cJSON_Hooks {
void *(*malloc_fn)(size_t sz);
void(*free_fn)(void *ptr);
} cJSON_Hooks;
注:cJSON的内存管理,提供了用户自主方式的接口。可以通过方法InitHooks来设置自己的内存管理,默认使用malloc,free
static void *(*cJSON_malloc)(size_t sz) = malloc;
static void(*cJSON_free)(void *ptr) = free; void cJSON_InitHooks(cJSON_Hooks* hooks)
{
if (!hooks) { /* Reset hooks */
cJSON_malloc = malloc;
cJSON_free = free;
return;
} cJSON_malloc = (hooks->malloc_fn) ? hooks->malloc_fn : malloc;
cJSON_free = (hooks->free_fn) ? hooks->free_fn : free;
}
③结点创建,删除结点
/* Internal constructor. */
static cJSON *cJSON_New_Item(void)
{
cJSON* node = (cJSON*)cJSON_malloc(sizeof(cJSON));
if (node) memset(node, , sizeof(cJSON));
return node;
} /* Delete a cJSON structure. */
//删除节点很简单, 先删除儿子,然后清理内存即可。
//总结一下就是对于 object 和 array 需要先删除儿子,然后删除自己。
//对于 字符串, 需要先释放字符串的内存, 再释放自己这块内存。
//对于其他节点,直接释放自己这块内存。
void cJSON_Delete(cJSON *c)
{
cJSON *next;
while (c)
{
next = c->next;
if (!(c->type&cJSON_IsReference) && c->child) cJSON_Delete(c->child); //
if (!(c->type&cJSON_IsReference) && c->valuestring) cJSON_free(c->valuestring);
if (!(c->type&cJSON_StringIsConst) && c->string) cJSON_free(c->string);
cJSON_free(c);
c = next;
}
}
有了结点设置,那么下面就是具体类型结点的实现了:设置类型,设置具体类型的值
/* These calls create a cJSON item of the appropriate type. */
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateNull(void);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateTrue(void);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateFalse(void);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateBool(int b);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateNumber(double num);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateString(const char *string);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateArray(void);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateObject(void); /* These utilities create an Array of count items. */
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateIntArray(const int *numbers, int count);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateFloatArray(const float *numbers, int count);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateDoubleArray(const double *numbers, int count);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateStringArray(const char **strings, int count);
/* Create basic types: */
cJSON *cJSON_CreateNull(void)
{
cJSON *item = cJSON_New_Item();
if (item)
item->type = cJSON_NULL;
return item;
} /* Create Arrays: */
cJSON *cJSON_CreateIntArray(const int *numbers, int count)
{
int i; cJSON *n = , *p = ,
*a = cJSON_CreateArray(); for (i = ; a && i < count; i++)
{
n = cJSON_CreateNumber(numbers[i]); //申请N个几点
if (!i)
a->child = n;//第一个结点链接使用child
else
suffix_object(p, n);//其他结点 :连接prev next
p = n;
}return a;
}
④结点操作
/* Append item to the specified array/object. */
extern void cJSON_AddItemToArray(cJSON *array, cJSON *item);
extern void cJSON_AddItemToObject(cJSON *object, const char *string, cJSON *item);
extern void cJSON_AddItemToObjectCS(cJSON *object, const char *string, cJSON *item); /* Use this when string is definitely const (i.e. a literal, or as good as), and will definitely survive the cJSON object */ /* Append reference to item to the specified array/object. Use this when you want to add an existing cJSON to a new cJSON,
but don't want to corrupt your existing cJSON. */
extern void cJSON_AddItemReferenceToArray(cJSON *array, cJSON *item);
extern void cJSON_AddItemReferenceToObject(cJSON *object, const char *string, cJSON *item); /* Remove/Detatch items from Arrays/Objects. */
//Detatch脱离,使item从arr链中脱离,便于delete
extern cJSON *cJSON_DetachItemFromArray(cJSON *array, int which);
extern void cJSON_DeleteItemFromArray(cJSON *array, int which);
extern cJSON *cJSON_DetachItemFromObject(cJSON *object, const char *string);
extern void cJSON_DeleteItemFromObject(cJSON *object, const char *string); /* Update array items. */
extern void cJSON_InsertItemInArray(cJSON *array, int which, cJSON *newitem); /* Shifts pre-existing items to the right. */
extern void cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(cJSON *array, int which, cJSON *newitem);
extern void cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(cJSON *object, const char *string, cJSON *newitem);
注:①
Detach 是什么东西呢?
我们把一个节点从 json 树中删除, 但是不释放内存,而是先保留这个节点的指针, 这样储存在这个节点的信息都保留了下来。
接下来我们就可以做很多事了, 合适的时候添加到其他对象中, 合适的时候释放内存。
比如上面的 delete 函数, 就需要真实的删除了, 这个时候我们删除即可。
而 detach 实现也比较简单, 只是少了一步删除操作。
//将结点从结构中脱离
cJSON *cJSON_DetachItemFromArray(cJSON *array, int which)
{
cJSON *c = array->child;
while (c && which>)
c = c->next, which--;
if (!c)
return ;
if (c->prev)
c->prev->next = c->next;
if (c->next)
c->next->prev = c->prev;
if (c == array->child)
array->child = c->next;
c->prev = c->next = ;
return c;
}
void cJSON_DeleteItemFromArray(cJSON *array, int which)
{
cJSON_Delete(cJSON_DetachItemFromArray(array, which));
}
②关于以上相关方法,简单的增加结点就是个链表操作了,然后对于
cJSON_AddItemReferenceToArray这个方法说明
cJSON除了实现简单的增加结点到结构之外,还有简单考虑效率问题。
比如同时增加一个结点到两棵树中,那么如果有深浅拷贝问题时,cJSON做法是,增加一个结点为Reference类型,在另一棵树中。这里的做法可以是引用计数,写实拷贝等
我们来看看cJSON实现吧
/* Utility for handling references. */
static cJSON *create_reference(cJSON *item)
{
cJSON *ref = cJSON_New_Item();
if (!ref)
return ;
memcpy(ref, item, sizeof(cJSON)); //浅拷贝所有值-->最终保存了结点的value部分
ref->string = ; //k-v中的值清空,以便于重新设置
ref->type |= cJSON_IsReference; //结点类性是具体item类型的同时也是reference
ref->next = ref->prev = ; //只是当前节点的引用,去除引用的链接
return ref;
} void cJSON_AddItemReferenceToArray(cJSON *array, cJSON *item)
{
cJSON_AddItemToArray(array, create_reference(item)); //创建应用结点之后加入目的数组
}
void cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(cJSON *array, int which, cJSON *newitem)
{
cJSON *c = array->child;
while (c && which>)
c = c->next, which--; //找到具体位置
if (!c)
return;
newitem->next = c->next;
newitem->prev = c->prev; //连入结构中
if (newitem->next)
newitem->next->prev = newitem;//修改后指针 if (c == array->child) //如果是个孩子,
array->child = newitem;
else
newitem->prev->next = newitem; //修改后指针
c->next = c->prev = ;//释放被代替的结点
cJSON_Delete(c);
}
⑤查找相关
/* Get Array size/item / object item. */
int cJSON_GetArraySize(cJSON *array)
{
cJSON *c = array->child;
int i = ;
while (c)
i++, c = c->next;
return i;
}
cJSON *cJSON_GetArrayItem(cJSON *array, int item)
{
cJSON *c = array->child;
while (c && item>)
item--, c = c->next;
return c;
}
//结构中结点的设置,需要通过变量名来查找
cJSON *cJSON_GetObjectItem(cJSON *object, const char *string)
{
cJSON *c = object->child;
while (c && cJSON_strcasecmp(c->string, string))
c = c->next;
return c;
}
⑥总结部分:
通过以上对于cJSON结构的简单学习和剖析,我们不难联想到广义表。其实这个结构的实现就是类似广义表实现:由child递归为广义结构
关于具体的cJSON数据解析部分,请参考博客《cJONS序列化工具解读②(数据解析)》
cJSON序列化工具解读一(结构剖析)的更多相关文章
- cJONS序列化工具解读二(数据解析)
cJSON数据解析 关于数据解析部分,其实这个解析就是个自动机,通过递归或者解析栈进行实现数据的解析 /* Utility to jump whitespace and cr/lf *///用于跳过a ...
- cJONS序列化工具解读三(使用案例)
cJSON使用案例 由了解了cJSON的数据结构,接口以及实现之后,那么我们来举例说明其使用. 本例子是一个简单的学生信息表格管理,我们通过键值对的方式向json中增加元素信息. 然后可以格式化输出结 ...
- 网络传输数据序列化工具Protostuff
一直在物色比较好用的网络传输数据序列化工具,看了诸如marshalling,protobuff等,但是均有一个共同特点,使用起来异常繁杂,有没有比较好用同时性能又不会太差的组件呢?答案当然是有的,那就 ...
- 数据序列化工具——flatbuffer
flatbuffer是一款类似于protobuf的数据序列化工具.所有数据序列化,简单来说,就是将某程数据结构按照一定的格式进行编码与解码,以方便在不同的进程间传递后,能够正确的还原成之前的数据结构. ...
- UNDO内存结构剖析
UNDO内存结构剖析 一.场景 Oracle的 C事物从早上9:00开始读取A表全部10w行数据,这个而读取需要经历5分钟.在9:01的时候,B事物将A表删除100条记录,那么,当9:05的时候,事物 ...
- spring-data-redis注册fastjson序列化工具
使用spring-data-redis的时候,其序列化工具自带:
- Google FlatBuffers——开源、跨平台的新一代序列化工具
前段时间刚试用了一个序列化工具cereal,请看cereal:C++实现的开源序列化库,打算再总结下我对google proto buf序列化库的使用呢, 结果还没动手,大Google又出了一个新的. ...
- $.ajax、$.post、from表单序列化工具
$.ajax\$.post <script type="text/javascript" language="javascript" src=" ...
- 用序列化工具写入xml
标本: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="true"?> //文 ...
随机推荐
- 使用jQuery为文本框、单选框、多选框、下拉框、下拉多选框设值及返回值的处理
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/ ...
- docker——安装
Docker划分为CE和EE.CE即社区版(免费,支持后期三个月),EE即企业版,强调安全,付费使用. #安装依赖包 yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-pe ...
- PHP生成名片、网址二维码
PHP生成名片.网址二维码 php生成名片(vcard)二维码: <?php$vname = 'test'; $vtel = '13800000000'; generateQRfromGoo ...
- 搭建 maven 项目 搭建 maven web 项目及遇到 JDK 的问题
临时起意搭建一个 maven web 项目.使用的servlet 3.0 及 1.8 JDK. maven 默认创建了一个JDK 1.5 版本的项目. 注意此处选择一下WAR包.不然在配置中配置的话会 ...
- Linux系统常用命令示例
1.在跟下创建一个目录,目录的名字为data # mkdir /data2.在data目录里创建一个文件,文件名为yunjisuan.txt # touch /data/yunjisuan.txt3. ...
- PKU 3318 Matrix Multiplication(神奇的输入)
#include<cstdio> using namespace std; ][]; ][],C[][]; int Read() { ; ; while((ch=getchar())==' ...
- topcoder SRM712 Div1 LR
题目: Problem Statement We have a cyclic array A of length n. For each valid i, element i-1 the l ...
- Python的socket网络编程(一)
(注:本文部分内容摘自互联网,由于作者水平有限,不足之处,还望留言指正.) 先写首诗,抒抒情. 一. 食堂.校园 见过你那么多次 卑微的我 只敢偷偷瞄上一眼 心扑通 扑通 春天真好 不是么 二. 学子 ...
- $Python常用内置函数典型用法
Python中有许多功能丰富的内置函数,本文基于Python 2.7,就常用的一些函数的典型用法做一些积累,不断更新中. sorted函数的三种用法 # coding:utf-8 # sorted函数 ...
- zookeeper No route to host
2017-10-12 07:25:59,270 [myid:1] - WARN [QuorumPeer[myid=1]/0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0:2181:QuorumCnxManager@36 ...
