Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 2)A B C 模拟 水 并查集
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Hongcow is learning to spell! One day, his teacher gives him a word that he needs to learn to spell. Being a dutiful student, he immediately learns how to spell the word.
Hongcow has decided to try to make new words from this one. He starts by taking the word he just learned how to spell, and moves the last character of the word to the beginning of the word. He calls this a cyclic shift. He can apply cyclic shift many times. For example, consecutively applying cyclic shift operation to the word "abracadabra" Hongcow will get words "aabracadabr", "raabracadab" and so on.
Hongcow is now wondering how many distinct words he can generate by doing the cyclic shift arbitrarily many times. The initial string is also counted.
The first line of input will be a single string s (1 ≤ |s| ≤ 50), the word Hongcow initially learns how to spell. The string s consists only of lowercase English letters ('a'–'z').
Output a single integer equal to the number of distinct strings that Hongcow can obtain by applying the cyclic shift arbitrarily many times to the given string.
abcd
4
bbb
1
yzyz
2
For the first sample, the strings Hongcow can generate are "abcd", "dabc", "cdab", and "bcda".
For the second sample, no matter how many times Hongcow does the cyclic shift, Hongcow can only generate "bbb".
For the third sample, the two strings Hongcow can generate are "yzyz" and "zyzy".
题意:给你一个字符串 每次可以把最尾部的一个字符放到最前面 问形成的字符串有多少种?
题解:模拟
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#define ll __int64
#define mod 1000000007
#define dazhi 2147483647
#define bug() printf("!!!!!!!")
#define M 100005
using namespace std;
char s[];
map<string,int>mp;
int main()
{
scanf("%s",s);
string str;
str.assign(s);
mp[s]=;
int ans=;
int len=strlen(s);
int last=len-;
len--;
while(len)
{
len--;
char exm=s[last];
for(int i=last;i>=;i--)
{
s[i]=s[i-];
}
s[]=exm;
str.assign(s);
if(mp[str]==)
{
mp[str]++;
ans++;
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Hongcow likes solving puzzles.
One day, Hongcow finds two identical puzzle pieces, with the instructions "make a rectangle" next to them. The pieces can be described by an n by m grid of characters, where the character 'X' denotes a part of the puzzle and '.' denotes an empty part of the grid. It is guaranteed that the puzzle pieces are one 4-connected piece. See the input format and samples for the exact details on how a jigsaw piece will be specified.
The puzzle pieces are very heavy, so Hongcow cannot rotate or flip the puzzle pieces. However, he is allowed to move them in any directions. The puzzle pieces also cannot overlap.
You are given as input the description of one of the pieces. Determine if it is possible to make a rectangle from two identical copies of the given input. The rectangle should be solid, i.e. there should be no empty holes inside it or on its border. Keep in mind that Hongcow is not allowed to flip or rotate pieces and they cannot overlap, i.e. no two 'X' from different pieces can share the same position.
The first line of input will contain two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 500), the dimensions of the puzzle piece.
The next n lines will describe the jigsaw piece. Each line will have length m and will consist of characters '.' and 'X' only. 'X' corresponds to a part of the puzzle piece, '.' is an empty space.
It is guaranteed there is at least one 'X' character in the input and that the 'X' characters form a 4-connected region.
Output "YES" if it is possible for Hongcow to make a rectangle. Output "NO" otherwise.
2 3
XXX
XXX
YES
2 2
.X
XX
NO
5 5
.....
..X..
.....
.....
.....
YES
For the first sample, one example of a rectangle we can form is as follows
111222
111222
For the second sample, it is impossible to put two of those pieces without rotating or flipping to form a rectangle.
In the third sample, we can shift the first tile by one to the right, and then compose the following rectangle:
.....
..XX.
.....
.....
..... 题意:给你一个n*m的矩阵 由‘X’形成一个图形 问你是否可以用两个相同的图形拼成一个矩形(不可以旋转和翻折)
题解:确定给你的图形是否为一个矩形即可
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#define ll __int64
#define mod 1000000007
#define dazhi 2147483647
#define bug() printf("!!!!!!!")
#define M 100005
using namespace std;
int n,m;
char a[][];
int main()
{
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
getchar();
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
scanf("%s",a[i]);
int l=m-,r=,u=n-,d=;
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=;j<m;j++)
{
if(a[i][j]=='X')
{
l=min(l,j);
r=max(r,j);
u=min(u,i);
d=max(d,i);
}
}
}
for(int i=u;i<=d;i++)
{
for(int j=l;j<=r;j++)
{
if(a[i][j]=='.')
{
printf("NO\n");
return ;
}
}
}
printf("YES\n");
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Hongcow is ruler of the world. As ruler of the world, he wants to make it easier for people to travel by road within their own countries.
The world can be modeled as an undirected graph with n nodes and m edges. k of the nodes are home to the governments of the k countries that make up the world.
There is at most one edge connecting any two nodes and no edge connects a node to itself. Furthermore, for any two nodes corresponding to governments, there is no path between those two nodes. Any graph that satisfies all of these conditions is stable.
Hongcow wants to add as many edges as possible to the graph while keeping it stable. Determine the maximum number of edges Hongcow can add.
The first line of input will contain three integers n, m and k (1 ≤ n ≤ 1 000, 0 ≤ m ≤ 100 000, 1 ≤ k ≤ n) — the number of vertices and edges in the graph, and the number of vertices that are homes of the government.
The next line of input will contain k integers c1, c2, ..., ck (1 ≤ ci ≤ n). These integers will be pairwise distinct and denote the nodes that are home to the governments in this world.
The following m lines of input will contain two integers ui and vi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n). This denotes an undirected edge between nodes ui and vi.
It is guaranteed that the graph described by the input is stable.
Output a single integer, the maximum number of edges Hongcow can add to the graph while keeping it stable.
4 1 2
1 3
1 2
2
3 3 1
2
1 2
1 3
2 3
0
For the first sample test, the graph looks like this:
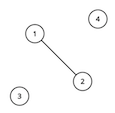 Vertices 1 and 3 are special. The optimal solution is to connect vertex 4 to vertices 1 and 2. This adds a total of 2 edges. We cannot add any more edges, since vertices 1 and 3 cannot have any path between them.
Vertices 1 and 3 are special. The optimal solution is to connect vertex 4 to vertices 1 and 2. This adds a total of 2 edges. We cannot add any more edges, since vertices 1 and 3 cannot have any path between them.
For the second sample test, the graph looks like this:
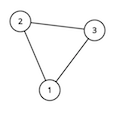 We cannot add any more edges to this graph. Note that we are not allowed to add self-loops, and the graph must be simple.
We cannot add any more edges to this graph. Note that we are not allowed to add self-loops, and the graph must be simple.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#define ll __int64
#define mod 1000000007
#define dazhi 2147483647
#define bug() printf("!!!!!!!")
#define M 100005
using namespace std;
int n,m,k;
int a[];
int fa[];
int l,r;
map<int,int>mp;
map<int,int>mpp;
int find(int root)
{
if(root!=fa[root])
return fa[root]=find(fa[root]);
else
return root;
}
void unio(int a,int b)
{
int aa=find(a);
int bb=find(b);
if(aa!=bb)
{
fa[aa]=bb;
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d %d %d",&n,&m,&k);
for(int i=;i<=k;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
fa[i]=i;
for(int i=;i<=m;i++)
{
scanf("%d %d",&l,&r);
unio(l,r);
}
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
int x=find(i);
mp[fa[i]]++;
}
int maxn=;
int sum=;
int re=;
for(int i=;i<=k;i++)
{
maxn=max(maxn,mp[fa[a[i]]]);
sum+=mp[fa[a[i]]];
mpp[fa[a[i]]]=;
re=re+ mp[fa[a[i]]]*(mp[fa[a[i]]]-)/;
}
int b[];
int jishu=;
int ans=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if(mpp[fa[i]]==)
{
b[jishu++]=mp[fa[i]];
re=re+mp[fa[i]]*(mp[fa[i]]-)/;
mpp[fa[i]]=;
}
}
for(int i=;i<jishu;i++)
{
for(int j=i+;j<jishu;j++)
{
ans+=(b[i]*b[j]);
}
}
printf("%d\n",re-m+(n-sum)*maxn+ans);
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 2)A B C 模拟 水 并查集的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #396 (Div. 2) D. Mahmoud and a Dictionary 并查集
D. Mahmoud and a Dictionary 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/766/problem/D Description Mahmoud wa ...
- Codeforces Round #250 (Div. 1) B. The Child and Zoo 并查集
B. The Child and Zoo Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/438/ ...
- Codeforces Round #360 (Div. 1) D. Dividing Kingdom II 暴力并查集
D. Dividing Kingdom II 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/687/problem/D Description Long time a ...
- Codeforces Round #212 (Div. 2) D. Fools and Foolproof Roads 并查集+优先队列
D. Fools and Foolproof Roads You must have heard all about the Foolland on your Geography lessons. ...
- Codeforces Round #254 (Div. 2) B. DZY Loves Chemistry (并查集)
题目链接 昨天晚上没有做出来,刚看题目的时候还把题意理解错了,当时想着以什么样的顺序倒,想着就饶进去了, 也被题目下面的示例分析给误导了. 题意: 有1-n种化学药剂 总共有m对试剂能反应,按不同的 ...
- Codeforces Round #260 (Div. 1) C. Civilization 树的中心+并查集
题目链接: 题目 C. Civilization time limit per test1 second memory limit per test256 megabytes inputstandar ...
- Codeforces Round #250 (Div. 2) D. The Child and Zoo 并查集
D. The Child and Zoo time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standar ...
- Codeforces Round #329 (Div. 2) D. Happy Tree Party(LCA+并查集)
题目链接 题意:就是给你一颗这样的树,用一个$y$来除以两点之间每条边的权值,比如$3->7$,问最后的y的是多少,修改操作是把权值变成更小的. 这个$(y<=10^{18})$除的权值如 ...
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2) B. Bakery (模拟)
Bakery 题目链接: http://codeforces.com/contest/707/problem/B Description Masha wants to open her own bak ...
随机推荐
- 获取Java线程返回值的几种方式
在实际开发过程中,我们有时候会遇到主线程调用子线程,要等待子线程返回的结果来进行下一步动作的业务. 那么怎么获取子线程返回的值呢,我这里总结了三种方式: 主线程等待. Join方法等待. 实现Call ...
- Echarts-K线图提示框改头换面
工作: 使用Hbuilder建web工程,加入echarts相关库,根据需要更改K线图及其的提示样式,去除默认提示,使用异步加载echarts的数据,数据格式为json. 需要注意的K线图和5日均线, ...
- Linux内核学习笔记(5)-- 进程调度概述
进程调度程序是多任务操作系统的基础,它是确保进程能有效工作的一个内核子系统,负责决定哪个进程投入运行.何时运行以及运行多长时间.只有通过进程调度程序的合理调度,系统资源才能够最大限度地发挥作用,多进程 ...
- C语言—栈
栈的操作:进栈和出栈 #include "stdafx.h" #include "stack.h" #define maxsize 20 typedef int ...
- Fedora 26/27/28网易云音乐安装
信息从 https://www.southcity-oldboy.com/1474.html获取,感谢站长南城旧少年! 以下为前辈网页上的内容 1.安装 RPM Fusion 源 (free): ht ...
- Qt 编程指南
Qt 编程指南 持续关注一本正在编写的Qt编程指南,期待作者早日完成创作.
- AutoCAD 自动管理字体插件[使用ObjectARX C++]
概述: 使用AutoCAD的过程中,我们常常因为缺失字体而烦恼,本插件就是为了解决这个问题. 插件采用WEB服务器 + CAD插件方式.WEB服务器使用Python编写,部署在百度BAE上:CAD插件 ...
- pager-taglib2.0中文传参乱码问题
1.重现问题 在web项目中有时会用到pager-taglib来作为分页的标签,如上图红色框标识所示,当我们需要把页面参数保持的时候我们会在<pg:param />标签中把参数进行传递. ...
- php命名空间学习笔记。
为什么要用命名空间? 在PHP中,命名空间用来解决在编写类库或应用程序时创建可重用的代码如类或函数时碰到的两类问题: 用户编写的代码 与 PHP内部的类/函数/常量或第三方类/函数/常量之间的名字冲 ...
- qq浏览器的用户体验
用户界面: qq浏览器的用户界面简介,把一些不必要的东西去点,可以很容易让用户找到自己想看的网页,很方便. 记住用户的选择: qq浏览器和QQ相连,可是用QQ账户登录,并且会记住自己访问的高频网页,以 ...
