Ternary weight networks
Introduction
这两天看了一下这篇文章,我就这里分享一下,不过我还是只记录一下跟别人blog上没有,或者自己的想法(ps: 因为有时候翻blog时候发现每篇都一样还是挺烦的= =) 。为了不重复前人的工作,我post一个不小心翻到的博客权值简化(1):三值神经网络(Ternary Weight Networks),整个论文内容及实现都讲的很全面了,可以翻阅一下,我也借鉴一下。
文中主要工作的点在三个方面:
- 增加了网络的表达力(expressive ability)。在{1,0,1}基础上增加了 \(\alpha\) 作为scaled factor;
- 压缩模型大小。当然主要是weight的压缩。比起FPWN(full precision weight network)有16~32x的提升,但是BPWN(binary precision weight network)的2x大小(ps:当然在TWN的caffe代码里面,都由float double类型存储,因为这需要在应该上方面来实现);
- 减少计算需求。主要相比于BPWN增多了0,当然这方面也需硬件来获得提升,在该caffe代码里面并没有;
Ternary Quantization
在我的理解看来,文中最核心的内容是:将有约束的并且两变量之间互相依赖的优化问题,逐步拆分最后用具有先验的统计方法来近视解决。
最初的优化问题:

将\(W^{t}\)的约束具体化为:
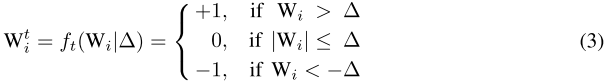
并将其带入公式(1),将\(W^{t*}\)的优化转化为\(\Delta^*\)的优化:
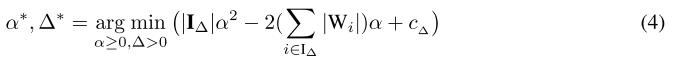
然后对公式(4)中的\(\alpha\)求偏导,得到:

因为\(\alpha\)和\(\Delta\)相互依赖,将(5)代入(4)消去\(\alpha\):

但问题来了,公式(6)依然没法求,而文中就根据先验知识,假设\(W_i\)服从\(N(0,\sigma^2)\)分布,近视的\(\Delta^*\)为\(0.6\sigma\)(\(0.6\sigma\)等于\(0.75E(|W|)\))。因此作者采用粗暴的方法,把\(\Delta^*\)设为\(\Delta^*\approx0.7E(|W|)\approx\frac{n}{0.7}\sum_{i=1}^n|W_i|\)
//caffe-twns
//blob.cpp
template <typename Dtype>
void Blob<Dtype>::set_delta(){
float scale_factor = TERNARY_DELTA * 1.0 / 10; //delta = 0.7
Dtype delta = (Dtype) scale_factor * this->asum_data() / this->count(); // 0.7*(E|W_i|)/num
delta = (delta <= 100) ? delta : 100;
delta = (delta >= -100) ? delta : -100;
this->delta_ = delta;
}
template <typename Dtype>
void Blob<Dtype>::set_delta(Dtype delta){
delta = (delta <= 100) ? delta : 100;
delta = (delta >= -100) ? delta : -100;
this->delta_ = delta;
}
Implement
我借用一张图
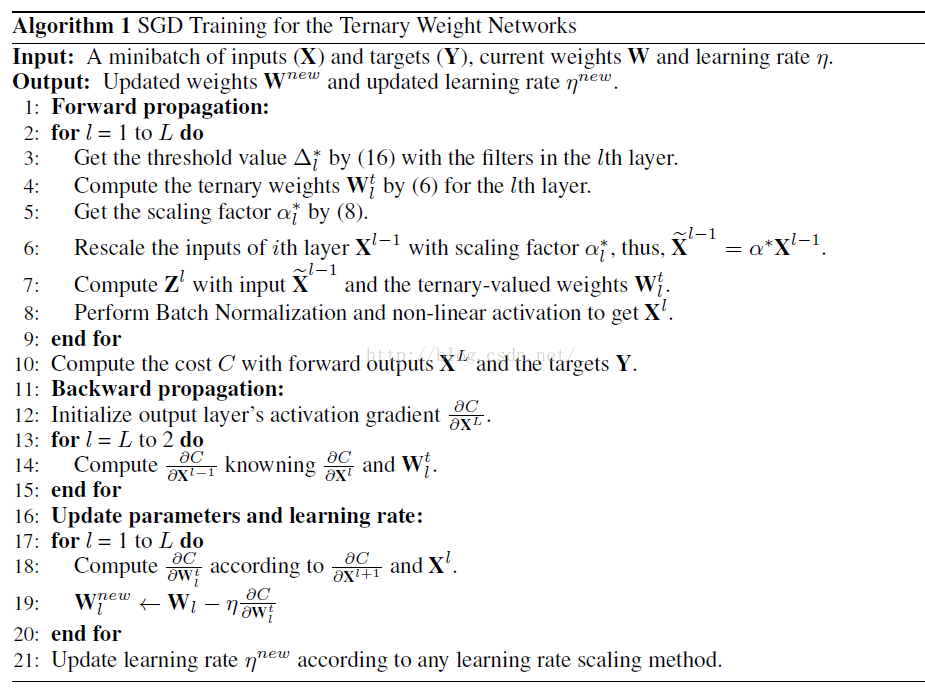
步骤3~5,其中第5步代码在上面:
template <typename Dtype>
void Blob<Dtype>::ternarize_data(Phase phase){
if(phase == RUN){
// if(DEBUG) print_head();
//LOG(INFO) << "RUN phase...";
// caffe_sleep(3);
return; // do nothing for the running phase
}else if(phase == TRAIN){
//LOG(INFO) << "TRAIN phase ...";
// caffe_sleep(3);
}else{
//LOG(INFO) << "TEST phase ...";
// caffe_sleep(3);
}
// const Dtype delta = 0; // default value;
// const Dtype delta = (Dtype) 0.8 * this->asum_data() / this->count();
this->set_delta(); //defualt 0.7*(E|W_i|)/num or set by user
const Dtype delta = this->get_delta();
Dtype alpha = 1;
if (!data_) { return; }
switch (data_->head()) {
case SyncedMemory::HEAD_AT_CPU:
{
caffe_cpu_ternary<Dtype>(this->count(), delta, this->cpu_data(), this->mutable_cpu_binary()); //quantized weight to ternary
alpha = caffe_cpu_dot(this->count(), this->cpu_binary(), this->cpu_data()); //scale-alpha: (E |W_i|) i belong to I_delta
alpha /= caffe_cpu_dot(this->count(), this->cpu_binary(), this->cpu_binary()); //(1/num_binary)*alpha
caffe_cpu_scale(this->count(), alpha, this->cpu_binary(), this->mutable_cpu_binary());
// this->set_alpha(alpha);
}
return;
case SyncedMemory::HEAD_AT_GPU:
case SyncedMemory::SYNCED:
#ifndef CPU_ONLY
{
caffe_gpu_ternary<Dtype>(this->count(), delta, this->gpu_data(), this->mutable_gpu_binary());
Dtype* pa = new Dtype(0);
caffe_gpu_dot(this->count(), this->gpu_binary(), this->gpu_data(), pa);
Dtype* pb = new Dtype(0);
caffe_gpu_dot(this->count(), this->gpu_binary(), this->gpu_binary(), pb);
alpha = (*pa) / ((*pb) + 1e-6);
this->set_alpha(alpha);
caffe_gpu_scale(this->count(), alpha, this->gpu_binary(), this->mutable_gpu_binary());
// this->set_alpha((Dtype)1);
// LOG(INFO) << "alpha = " << alpha;
// caffe_sleep(3);
}
return;
#else
NO_GPU;
#endif
case SyncedMemory::UNINITIALIZED:
return;
default:
LOG(FATAL) << "Unknown SyncedMemory head state: " << data_->head();
}
}
步骤6~7,其中在第6步作者在caffe-twns直接采用传统caffe的方法,而$Z=XW\approx X(\alpha W^t)=(\alpha X)\bigoplus W^t $更偏向与在硬件加速的优化(因为本身在caffe-twns的ternary就采用float或者double,并且用blas或cudnn加速也无法直接跳过0值):
//conv_layer.cpp
template <typename Dtype>
void ConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
// const Dtype* weight = this->blobs_[0]->cpu_data();
if(BINARY){
this->blobs_[0]->binarize_data();
}
if(TERNARY){
this->blobs_[0]->ternarize_data(this->phase_); //quantized from blob[0] to ternary sand stored in cpu_binary()
/*
Dtype alpha = (Dtype) this->blobs_[0]->get_alpha();
for(int i=0; i<bottom.size(); i++){
Blob<Dtype>* blob = bottom[i];
caffe_cpu_scale(blob->count(), alpha, blob->cpu_data(), blob->mutable_cpu_data());
}
*/
}
const Dtype* weight = (BINARY || TERNARY) ? this->blobs_[0]->cpu_binary() : this->blobs_[0]->cpu_data();
...
}
步骤11~19,weight的Update是在full precision上,而计算gradient则是用ternary weight:
//conv_layer.cpp
template <typename Dtype>
void ConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) {
const Dtype* weight = this->blobs_[0]->cpu_data();
Dtype* weight_diff = this->blobs_[0]->mutable_cpu_diff();
for (int i = 0; i < top.size(); ++i) {
...
if (this->param_propagate_down_[0] || propagate_down[i]) {
for (int n = 0; n < this->num_; ++n) {
// gradient w.r.t. weight. Note that we will accumulate diffs.
if (this->param_propagate_down_[0]) {
this->weight_cpu_gemm(bottom_data + n * this->bottom_dim_,
top_diff + n * this->top_dim_, weight_diff);
}
// gradient w.r.t. bottom data, if necessary.
if (propagate_down[i]) {
this->backward_cpu_gemm(top_diff + n * this->top_dim_, weight,
bottom_diff + n * this->bottom_dim_);
}
}
}
}
}
Ternary weight networks的更多相关文章
- 论文翻译:Ternary Weight Networks
目录 Abstract 1 Introduction 1.1 Binary weight networks and model compression 2 Ternary weight network ...
- [综述]Deep Compression/Acceleration深度压缩/加速/量化
Survey Recent Advances in Efficient Computation of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks, [arxiv '18] A ...
- zz神经网络模型量化方法简介
神经网络模型量化方法简介 https://chenrudan.github.io/blog/2018/10/02/networkquantization.html 2018-10-02 本文主要梳理了 ...
- deeplearning模型量化实战
deeplearning模型量化实战 MegEngine 提供从训练到部署完整的量化支持,包括量化感知训练以及训练后量化,凭借"训练推理一体"的特性,MegEngine更能保证量化 ...
- Understanding the Effective Receptive Field in Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
Understanding the Effective Receptive Field in Deep Convolutional Neural Networks 理解深度卷积神经网络中的有效感受野 ...
- [C6] Andrew Ng - Convolutional Neural Networks
About this Course This course will teach you how to build convolutional neural networks and apply it ...
- [CS231n-CNN] Training Neural Networks Part 1 : activation functions, weight initialization, gradient flow, batch normalization | babysitting the learning process, hyperparameter optimization
课程主页:http://cs231n.stanford.edu/ Introduction to neural networks -Training Neural Network ________ ...
- 【转】Artificial Neurons and Single-Layer Neural Networks
原文:written by Sebastian Raschka on March 14, 2015 中文版译文:伯乐在线 - atmanic 翻译,toolate 校稿 This article of ...
- 一天一经典Reducing the Dimensionality of Data with Neural Networks [Science2006]
别看本文没有几页纸,本着把经典的文多读几遍的想法,把它彩印出来看,没想到效果很好,比在屏幕上看着舒服.若用蓝色的笔圈出重点,这篇文章中几乎要全蓝.字字珠玑. Reducing the Dimensio ...
随机推荐
- 数据可视化之powerBI技巧(十二)学会这几个度量值,轻松获取前N名
数据中的明细项一般都有很多,可是我们关注的往往只是前几名,所以在报表中只展示关注的部分,就十分常用. 有了上篇(这几个示例,帮你深入理解RANKX排名)关于排名的铺垫,仅显示前N名就简单多了. 依然以 ...
- 用Tableau制作官网流量周报
好久没写博客了,上班摸鱼时间分享一下在工作中做的东西吧,先上图. 数据方面取自百度统计,身处传统类型公司,官网没有数据库,只好将就一下啦,反正是免费的,体验也还可以. 关于百度统计注册.添加管理站点和 ...
- 数据库分布式事务XA规范介绍及Mysql底层实现机制
1. 引言 分布式事务主要应用领域主要体现在数据库领域.微服务应用领域.微服务应用领域一般是柔性事务,不完全满足ACID特性,特别是I隔离性,比如说saga不满足隔离性,主要是通过根据分支事务执行成功 ...
- 高效C++:模板和泛型编程
模板和泛型编程的关注重点在编译期,所有的行为都在编译期确定,因此其规则和玩法也有自己特殊的一套,和其他模块不通用. 了解隐式接口和编译期多态 元编程------编译器多态,决定哪个重载函数被调用 cl ...
- tk.mybatis selectByPrimaryKey无法正确识别主键
selectByPrimaryKey无法正确识别主键,查看日志,发现报如下错误: ==> Preparing: SELECT username,password,name,age,sex,bir ...
- 搞定 CompletableFuture,并发异步编程和编写串行程序还有什么区别?你们要的多图长文
你有一个思想,我有一个思想,我们交换后,一个人就有两个思想 If you can NOT explain it simply, you do NOT understand it well enough ...
- CSS过渡时间
CSS过渡时间 基础知识 在了解CSS过渡时间之前,你应该先了解一下CSS的变形动画,可以参考之前的一篇博客. 我们的元素在属性发生变化时,如果没有特地的为它设置过渡时间,整个变化过程其实是以毫秒级别 ...
- Dart中final和const关键字
final和const 如果您从未打算更改一个变量,那么使用 final 或 const,不是var,也不是一个类型. 一个 final 变量只能被设置一次,两者区别在于:const 变量是一个编译时 ...
- element-ui的el-progress组件增加修改status状态
需求:实现进度条增长中呈现百分比,达到100%后将el-progress的status设置为“success” 想法:element对于status只给出了'success', 'exception' ...
- element上传功能携带参数
在写element的上传功能时,需要对上传的文件携带参数,但是参数比较多,就需要一个对象合并的方法,Object.assign() Object.assign(target, source1, sou ...
