字典树Trie的使用
1. Trie树介绍
Trie,又称单词查找树、前缀树,是一种多叉树结构。如下图所示:
上图是一棵Trie树,表示了关键字集合{“a”, “to”, “tea”, “ted”, “ten”, “i”, “in”, “inn”} 。 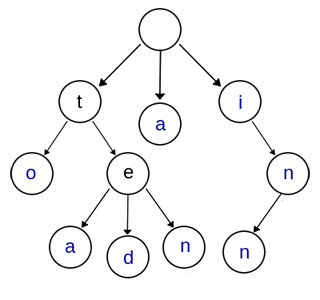
与二叉查找树不同,键不是直接保存在节点中,而是由节点在树中的位置决定。一个节点的所有子孙都有相同的前缀,也就是这个节点对应的字符串,而根节点对应空字符串。
2. trie树性质:
1.根节点不包含字符,除根节点外的每一个节点都只包含一个字符。
2.从根节点到某一节点,路径上经过的字符连接起来,为该节点对应的字符串。
3.每个节点的所有子节点包含的字符都不相同。
3. trie树典型应用:
(1) 字符串检索
查找某一个单词是否在树中。思路就是从根节点开始一个一个字符进行比较:
如果沿路比较,发现不同的字符,则表示该字符串在集合中不存在。
如果所有的字符全部比较完并且全部相同,还需判断最后一个节点的标志位(标记该节点是否代表字符串最后一个字符)。
从而trie树可以设计为:
struct trie_node
{
bool isKey; // 标记该节点是否代表一个关键字
trie_node *children[]; // 各个子节点
};
(2) 词频统计
Trie树常被搜索引擎系统用于文本词频统计。
思路:为了实现词频统计,我们可以修改节点结构,将ksKey用一个整型变量count来表示该节点为结尾的关键字的词频。对每一个关键字执行插入操作,若已存在,计数加1,若不存在,插入后count置1。
struct trie_node
{
int count; // 记录该节点代表的单词的个数
trie_node *children[]; // 各个子节点
};
(3) 去除重复单词
建立字典树的过程就是给字符串去重的过程。
(4) 字符串排序
Trie树可以对大量字符串按字典序进行排序,思路也很简单:遍历一次所有关键字,将它们全部插入trie树,树的每个结点的所有儿子很显然地按照字母表排序,然后先序遍历输出Trie树中所有关键字即可。
(5) 最长公共前缀
查找N个单词的最长公共前缀
(6) 前缀匹配:
比如要找以“an”为前缀的字符串
4. trie树设计
为了计算英语字符串词频,trie树设计可以参考3.(2)词频统计。
以上设计中因为是英文字符,父节点保存孩子节点时直接用一个数组children[26]来保存了孩子节点。这种方式最快,但是并不是所有节点都会有很多孩子,所以这种方式浪费的空间太多。可以用一个链表来代替数据。这样我们就可以省下不小的空间,但是缺点是搜索的时候需要遍历这个链表,增加了时间复杂度。如果存储汉字,可以把链表代替为map,这样既加快了速度,又不至于太浪费空间。
5. trie树优点:
(1) 查询快。对于长度为m的键值,最坏情况下只需花费O(m)的时间;而BST需要O(m log n)的时间。 虽然hash 表时间复杂度是O(1),但是,哈希搜索的效率通常取决于 hash 函数的好坏,若一个坏的 hash 函数导致很多的冲突,效率并不一定比Trie树高。
(2) 当存储大量字符串时,Trie耗费的空间较少。因为键值并非显式存储的,而是与其他键值共享子串。
6. trie树操作
(1) 初始化或清空:遍历Trie,删除所有节点,只保留根节点。
(2) 插入字符串
1. 设置当前节点为根节点,设置当前字符为插入字符串中的首个字符;
2. 在当前节点的子节点上搜索当前字符,若存在,则将当前节点设为值为当前字符的子节点;否则新建一个值为当前字符的子节点,并将当前结点设置为新创建的节点。
3. 将当前字符设置为串中的下个字符,若当前字符为0,则结束;否则转2.
(3) 查找字符串
搜索过程与插入操作类似,当字符找不到匹配时返回假;若全部字符都存在匹配,判断最终停留的节点是否为树叶,若是,则返回真,否则返回假。
(4) 输出字符串词频
(5) 删除字符串
首先查找该字符串,边查询边将经过的节点压栈,若找不到,则返回假;否则依次判断栈顶节点是否为树叶,若是则删除该节点,否则返回真。
(6) 输出字典树所有字符串
(7) 计算所有字符串的词频总数(包含重复或不重复)
(8) 计算字典树中所有单词的最长公共前缀及其长度
//使用字典树存储英文单词,使用的结构是26叉字典树。不区分单词的大小写
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream> /* trie的节点类型 */
template <int Size> //Size为字符表的大小
struct trie_node
{
int freq; //当前节点是否可以作为字符串的结尾,如果是freq>0,如果存在重复单词,freq表示该单词的词频
int node; //子节点的个数
trie_node *child[Size]; //指向子节点指针 /* 构造函数 */
trie_node() : freq(0), node(0) { memset(child, 0, sizeof(child)); }
}; /* trie */
template <int Size, typename Index> //Size为字符表的大小,Index为字符表的哈希函数
class trie
{
public:
/* 定义类型别名 */
typedef trie_node<Size> node_type;
typedef trie_node<Size>* link_type; /* 构造函数 */
trie(Index i = Index()) : index(i){ } /* 析构函数 */
~trie() { clear(); } /* 清空 */
void clear()
{
clear_node(root);
for (int i = 0; i < Size; ++i)
root.child[i] = 0;
} /* 插入字符串 */
template <typename Iterator>
void insert(Iterator begin, Iterator end)
{
link_type cur = &root; //当前节点设置为根节点
for (; begin != end; ++begin)
{
if (!cur->child[index[*begin]]) //若当前字符找不到匹配,则新建节点
{
cur->child[index[*begin]] = new node_type;
++cur->node; //当前节点的子节点数加一
}
cur = cur->child[index[*begin]]; //将当前节点设置为当前字符对应的子节点
}
(cur->freq)++; //设置存放最后一个字符的节点的可终止标志为真
} /* 插入字符串,针对C风格字符串的重载版本 */
void insert(const char *str)
{
insert(str, str + strlen(str));
} /* 查找字符串,算法和插入类似 */
template <typename Iterator>
int getfreq(Iterator begin, Iterator end)
{
link_type cur = &root;
for (; begin != end; ++begin)
{
if (!cur->child[index[*begin]])
return false;
cur = cur->child[index[*begin]];
}
return cur->freq;
} /* 查找字符串,针对C风格字符串的重载版本 */
bool find(const char *str)
{
int freq = getfreq(str, str + strlen(str));
return freq > 0;
} /* 查找字符串str的词频*/
int getfreq(const char* str)
{
return getfreq(str,str + strlen(str));
} /* 删除字符串 */
template <typename Iterator>
bool erase(Iterator begin, Iterator end)
{
bool result; //用于存放搜索结果
erase_node(begin, end, root, result);
return result;
} /* 删除字符串,针对C风格字符串的重载版本 */
bool erase(const char *str)
{
return erase(str, str + strlen(str));
} /* 按字典序遍历单词树的所有单词 */
template <typename Functor>
void traverse( Functor execute = Functor())
{
char word[100] = {0};
traverse_node(root, execute,word,0);
} /*输出字典树单词的总个数,包含重复字符串*/
int sizeAll()
{
sizeAll(root);
} int sizeAll(node_type& cur)
{
int size = cur.freq;
for(int i=0;i < Size; ++i)
{
if(cur.child[i] == 0)
continue;
size += sizeAll(*cur.child[i]);
}
return size;
} /*输出字典树单词的总个数,重复字符串按一个处理*/
int sizeNoneRedundant()
{
sizeNoneRedundant(root);
} int sizeNoneRedundant(node_type& cur)
{
int size = cur.freq>0?1:0;
for(int i=0;i < Size;++i)
{
if(cur.child[i] == 0)
continue;
size += sizeNoneRedundant(*cur.child[i]);
}
return size;
} /*求字符串最长的公共前缀的长度*/
int maxPrefix_length()
{
int length = maxPrefix_length(root);
return length - 1; //因为length包含了根节点,需要删除。
} int maxPrefix_length(node_type& cur)
{
int length = 0;
for(int i=0;i<Size;++i)
{
if(cur.child[i] != 0)
{
int tmp = maxPrefix_length(*cur.child[i]);
if(tmp > length)
{
length = tmp;
} }
}
if(length > 0 || cur.node >1 || cur.freq >0 && cur.node>0) //cur.node >1 处理"abcde"与"abcdf"这种情况;cur.freq>0 && cur.node>0处理"abcde"与"abcdef"这种情况
{
length++;
}
return length; }
/*求字符串最长的最共前缀*/
void maxPrefix(std::string& prefix)
{
maxPrefix(root,prefix);
std::string word(prefix);
int size = word.size();
for(int i=0;i<size;++i)
prefix[i] = word[size-1-i];
prefix.erase(size-1); //因为prefix包含了根节点字符,需要把它删除。 } void maxPrefix(node_type& cur,std::string& prefix)
{
std::string word;
int length =0 ;
int k = 0;
for(int i=0;i<Size;++i)
{
if(cur.child[i] != 0)
{
maxPrefix(*cur.child[i],word);
if(word.size() > length)
{
length = word.size();
prefix.swap(word);
k = i;
} }
}
if(length > 0 || cur.node >1 || cur.freq >0 && cur.node>0) //cur.node >1 处理"abcde"与"abcdf"这种情况;cur.freq>0 && cur.node>0处理"abcde"与"abcdef"这种情况
{
prefix.push_back(k + 'a');
}
} private: template<typename Functor>
void traverse_node(node_type& cur, Functor execute,char* word,int index)
{
if(cur.freq)
{
std::string str = word;
execute(str,cur.freq);
}
for(int i=0; i < Size; ++i)
{
if(cur.child[i] != 0)
{
word[index++] = 'a' + i;
traverse_node(*cur.child[i],execute,word,index);
word[index] = 0;
index--;
}
} } /* 清除某个节点的所有子节点 */
void clear_node(node_type& cur)
{
for (int i = 0; i < Size; ++i)
{
if (cur.child[i] == 0) continue;
clear_node(*cur.child[i]);
delete cur.child[i];
cur.child[i] = 0;
if (--cur.node == 0) break;
}
} /* 边搜索边删除冗余节点,返回值用于向其父节点声明是否该删除该节点 */
template <typename Iterator>
bool erase_node(Iterator begin, Iterator end, node_type &cur, bool &result)
{
if (begin == end) //当到达字符串结尾:递归的终止条件
{
result = (cur.freq > 0); //如果当前节点的频率>0,则当前节点可以作为终止字符,那么结果为真
if(cur.freq)
cur.freq --; //如果当前节点为终止字符,词频减一
return cur.freq == 0 && cur.node == 0; //若该节点为树叶,那么通知其父节点删除它
}
//当无法匹配当前字符时,将结果设为假并返回假,即通知其父节点不要删除它
if (cur.child[index[*begin]] == 0) return result = false;
//判断是否应该删除该子节点
else if (erase_node((++begin)--, end, *(cur.child[index[*begin]]), result))
{
delete cur.child[index[*begin]]; //删除该子节点
cur.child[index[*begin]] = 0; //子节点数减一
//若当前节点为树叶,那么通知其父节点删除它
if (--cur.node == 0 && cur.freq == 0) return true;
}
return false; //其他情况都返回假
} /* 根节点 */
node_type root; /* 将字符转换为索引的转换表或函数对象 */
Index index;
}; //index function object
class IndexClass
{
public:
int operator[](const char key)
{
if(key>='a' && key <= 'z')
return key - 'a';
else if(key >= 'A' && key <= 'Z')
return key - 'A';
}
}; class StringExe
{
public:
void operator()(std::string& str,int freq)
{
std::cout<<str<<":"<<freq<<std::endl;
}
};
int main()
{
trie<26,IndexClass> t;
t.insert("tree");
t.insert("tree");
t.insert("tea");
t.insert("A");
t.insert("BABCDEGG");
t.insert("BABCDEFG"); t.traverse<StringExe>(); int sizeall = t.sizeAll();
std::cout<<"sizeAll:"<<sizeall<<std::endl; int size = t.sizeNoneRedundant();
std::cout<<"size:"<<size<<std::endl; std::string prefix;
int deep = t.maxPrefix_length();
t.maxPrefix(prefix);
std::cout<<"deep:"<<deep<<" prefix:"<<prefix<<std::endl; if(t.find("tree"))
std::cout<<"find tree"<<std::endl;
else
std::cout<<"not find tree"<<std::endl; int freq = t.getfreq("tree");
std::cout<<"tree freq:"<<freq<<std::endl; if(t.erase("tree"))
std::cout<<"delete tree"<<std::endl;
else
std::cout<<"not find tree"<<std::endl; freq = t.getfreq("tree");
std::cout<<"tree freq:"<<freq<<std::endl; if(t.erase("tree"))
std::cout<<"delete tree"<<std::endl;
else
std::cout<<"not find tree"<<std::endl; if(t.erase("tree"))
std::cout<<"delete tree"<<std::endl;
else
std::cout<<"not find tree"<<std::endl; sizeall = t.sizeAll();
std::cout<<"sizeAll:"<<sizeall<<std::endl; size = t.sizeNoneRedundant();
std::cout<<"size:"<<size<<std::endl; if(t.find("tre"))
std::cout<<"find tre"<<std::endl;
else
std::cout<<"not find tre"<<std::endl; t.traverse<StringExe>(); return 0;
}
字典树Trie的使用的更多相关文章
- [POJ] #1002# 487-3279 : 桶排序/字典树(Trie树)/快速排序
一. 题目 487-3279 Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 274040 Accepted: 48891 ...
- 『字典树 trie』
字典树 (trie) 字典树,又名\(trie\)树,是一种用于实现字符串快速检索的树形数据结构.核心思想为利用若干字符串的公共前缀来节约储存空间以及实现快速检索. \(trie\)树可以在\(O(( ...
- 字典树trie学习
字典树trie的思想就是利用节点来记录单词,这样重复的单词可以很快速统计,单词也可以快速的索引.缺点是内存消耗大 http://blog.csdn.net/chenleixing/article/de ...
- 字典树(Trie)详解
详解字典树(Trie) 本篇随笔简单讲解一下信息学奥林匹克竞赛中的较为常用的数据结构--字典树.字典树也叫Trie树.前缀树.顾名思义,它是一种针对字符串进行维护的数据结构.并且,它的用途超级广泛.建 ...
- 字典树(Trie Tree)
在图示中,键标注在节点中,值标注在节点之下.每一个完整的英文单词对应一个特定的整数.Trie 可以看作是一个确定有限状态自动机,尽管边上的符号一般是隐含在分支的顺序中的.键不需要被显式地保存在节点中. ...
- 字典树(Trie树)实现与应用
一.概述 1.基本概念 字典树,又称为单词查找树,Tire数,是一种树形结构,它是一种哈希树的变种. 2.基本性质 根节点不包含字符,除根节点外的每一个子节点都包含一个字符 从根节点到某一节点.路径上 ...
- 字典树(Trie树)的实现及应用
>>字典树的概念 Trie树,又称字典树,单词查找树或者前缀树,是一种用于快速检索的多叉树结构,如英文字母的字典树是一个26叉树,数字的字典树是一个10叉树.与二叉查找树不同,Trie树的 ...
- 字典树trie的学习与练习题
博客详解: http://www.cnblogs.com/huangxincheng/archive/2012/11/25/2788268.html http://eriol.iteye.com/bl ...
- [转载]字典树(trie树)、后缀树
(1)字典树(Trie树) Trie是个简单但实用的数据结构,通常用于实现字典查询.我们做即时响应用户输入的AJAX搜索框时,就是Trie开始.本质上,Trie是一颗存储多个字符串的树.相邻节点间的边 ...
- Codevs 4189 字典(字典树Trie)
4189 字典 时间限制: 1 s 空间限制: 256000 KB 题目等级 : 大师 Master 传送门 题目描述 Description 最经,skyzhong得到了一本好厉害的字典,这个字典里 ...
随机推荐
- excel表格定义导入到powerdesigner脚本
打开powerdesigner,shift + ctrl + X 打开脚本窗口 输入执行的脚本,点 run 即可. 简单的导入Excel脚本 '开始 Option Explicit Dim mdl ' ...
- 通信协议之sdp---sdp会话协议
(1)sdp 描述格式 (2)sdp example (3) sdp (1)sdp 描述格式 m=video 1234 RTP/AVP 96a=rtpmap:96 H264a=framerate:15 ...
- WCF服务返回XML或JSON格式数据
第一种方式public string GetData( string format) { string res = null; Student stu = new Student { StuID = ...
- C#高级编程 第十五章 反射
(二)自定义特性 使自定义特性非常强大的因素时使用反射,代码可以读取这些元数据,使用它们在运行期间作出决策. 1.编写自定义特性 定义一个FieldName特性: [AttributeUsage(At ...
- struts2 eclipse集成jdk与tomcat (2)
Eclipse 中集成jdk与tomcat 1. 首次打开Eclipse为让你选择工作空间,选择合适即可. 添加JDK (1) 在Eclipse的菜单中选择window选项,单击 perference ...
- mongo数据库中一条记录中某个属性是数组情形时 数据结构的定义
package entity; import java.util.Date; import com.mongodb.BasicDBList;import com.mongodb.DBObject; p ...
- 【CISCO强烈推荐】生成树 《路由协议》 卷一二 拥塞:网络延迟 阻塞:进程中 MTU QS:服务质量 OSPF RIP ISIS BGP 生成树 《路由协议》 卷一二
协议 CP/IP路由技术第一卷 作 者 (美)多伊尔,(美)卡罗尔
- Hadoop实战-Flume之Sink Failover(十六)
a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 k2 a1.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source a1.sources.r1.type ...
- hdu 4927 java程序
/*对于本题题意非常easy 关键在于求杨辉三角时的二项式是没实用到优化,导致超时. 对于第n行的二项式的第i个可有第i-1个乘于一个数处于一个数得到,要用到大数.java比較方便. 假如n=6,i= ...
- quick-cocos2d-x 系列之——环境搭建(Mac版)
quick-cocos2d-x简单介绍 何为quick-cocos2d-x? ? 简单一句话:quick-cocos2d-x是採用lua语言,通过tolua++工具对cocos2d-x进一步封装, ...
