Codeforces Round #398 (Div. 2) A B C D 模拟 细节 dfs 贪心
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
According to an old legeng, a long time ago Ankh-Morpork residents did something wrong to miss Fortune, and she cursed them. She said that at some time n snacks of distinct sizes will fall on the city, and the residents should build a Snacktower of them by placing snacks one on another. Of course, big snacks should be at the bottom of the tower, while small snacks should be at the top.
Years passed, and once different snacks started to fall onto the city, and the residents began to build the Snacktower.
However, they faced some troubles. Each day exactly one snack fell onto the city, but their order was strange. So, at some days the residents weren't able to put the new stack on the top of the Snacktower: they had to wait until all the bigger snacks fell. Of course, in order to not to anger miss Fortune again, the residents placed each snack on the top of the tower immediately as they could do it.
Write a program that models the behavior of Ankh-Morpork residents.
The first line contains single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100 000) — the total number of snacks.
The second line contains n integers, the i-th of them equals the size of the snack which fell on the i-th day. Sizes are distinct integers from 1 to n.
Print n lines. On the i-th of them print the sizes of the snacks which the residents placed on the top of the Snacktower on the i-th day in the order they will do that. If no snack is placed on some day, leave the corresponding line empty.
3
3 1 2
3
2 1
5
4 5 1 2 3
5 4
3 2 1
In the example a snack of size 3 fell on the first day, and the residents immediately placed it. On the second day a snack of size 1 fell, and the residents weren't able to place it because they were missing the snack of size 2. On the third day a snack of size 2 fell, and the residents immediately placed it. Right after that they placed the snack of size 1 which had fallen before.
题意:有一个1到n的全排列,按顺序每一秒会到达一个数,你要把它们从n到1叠起来,如果能叠,你就马上叠,叠起来的意思是逆序输出。不能叠就输出换行。
比如n=3到达顺序312 ,那么你第一秒就叠3,第三秒叠21。
题解:模拟
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#define ll __int64
#define mod 1000000007
#define dazhi 2147483647
using namespace std;
int n;
int a[];
map<int,int> mp;
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
int maxn=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
maxn=max(a[i],maxn);
}
mp[maxn]=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if(a[i]!=maxn)
{
printf("\n");
mp[a[i]]=;
}
else
{
mp[a[i]]=;
while(mp[maxn]==)
{
printf("%d ",maxn);
maxn--;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Finally! Vasya have come of age and that means he can finally get a passport! To do it, he needs to visit the passport office, but it's not that simple. There's only one receptionist at the passport office and people can queue up long before it actually opens. Vasya wants to visit the passport office tomorrow.
He knows that the receptionist starts working after ts minutes have passed after midnight and closes after tf minutes have passed after midnight (so that (tf - 1) is the last minute when the receptionist is still working). The receptionist spends exactly t minutes on each person in the queue. If the receptionist would stop working within t minutes, he stops serving visitors (other than the one he already serves).
Vasya also knows that exactly n visitors would come tomorrow. For each visitor Vasya knows the point of time when he would come to the passport office. Each visitor queues up and doesn't leave until he was served. If the receptionist is free when a visitor comes (in particular, if the previous visitor was just served and the queue is empty), the receptionist begins to serve the newcomer immediately.
 "Reception 1"
"Reception 1"
For each visitor, the point of time when he would come to the passport office is positive. Vasya can come to the office at the time zero (that is, at midnight) if he needs so, but he can come to the office only at integer points of time. If Vasya arrives at the passport office at the same time with several other visitors, he yields to them and stand in the queue after the last of them.
Vasya wants to come at such point of time that he will be served by the receptionist, and he would spend the minimum possible time in the queue. Help him!
The first line contains three integers: the point of time when the receptionist begins to work ts, the point of time when the receptionist stops working tf and the time the receptionist spends on each visitor t. The second line contains one integer n — the amount of visitors (0 ≤ n ≤ 100 000). The third line contains positive integers in non-decreasing order — the points of time when the visitors arrive to the passport office.
All times are set in minutes and do not exceed 1012; it is guaranteed that ts < tf. It is also guaranteed that Vasya can arrive at the passport office at such a point of time that he would be served by the receptionist.
Print single non-negative integer — the point of time when Vasya should arrive at the passport office. If Vasya arrives at the passport office at the same time with several other visitors, he yields to them and queues up the last. If there are many answers, you can print any of them.
10 15 2
2
10 13
12
8 17 3
4
3 4 5 8
2
In the first example the first visitor comes exactly at the point of time when the receptionist begins to work, and he is served for two minutes. At 12 minutes after the midnight the receptionist stops serving the first visitor, and if Vasya arrives at this moment, he will be served immediately, because the next visitor would only come at 13 minutes after midnight.
In the second example, Vasya has to come before anyone else to be served.
题意:给你起始时间 终止时间 n个人到来的时刻 每个人办事需要的时长 问你什么时刻来办事 等待的时间最短。
题解:细节题 枚举每个人到来时刻的前一秒 找到等待最小值的时刻。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#define ll __int64
#define mod 1000000007
#define dazhi 2147483647
using namespace std;
ll ts,tf,t,n;
ll a[];
ll b[];
map<ll,int> mp;
ll ans=;
int main()
{
scanf("%I64d %I64d %I64d",&ts,&tf,&t);
scanf("%d",&n);
int jishu=;
ll re;
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
{
scanf("%I64d",&a[i]);
mp[a[i]]++;
if(mp[a[i]]==)
b[jishu++]=a[i];
}
if(b[]!=)
{
if(b[]<=ts)
{
ans=ts-(b[]-);
re=b[]-;
}
else
{
ans=;
re=ts;
}
}
else
{
if(mp[b[]]==n)
ans=mp[b[]]*t;
else
{
if(ts+mp[b[]]*t<b[])
ans=;
else
ans=ts+mp[b[]]*t-(b[]-);
}
re=ans+ts;
}
ll now=max(b[],ts)+mp[b[]]*t;
for(int i=; i<jishu; i++)
{
if(now>=tf)
break;
ll exm=now-(b[i]-);
if(exm<)
exm=;
if(ans>exm)
{
ans=min(ans,max((ll),exm));
re=min(now,b[i]-);
}
now=max(now,b[i])+mp[b[i]]*t;
}
if(now<=(tf-t))
printf("%I64d\n",now);
else
printf("%I64d\n",re);
return ;
}
/*
2 10 2
3
2 4 5
2 10 2
4
2 4 5 15
4 5 1
1
7
100 200 50
2
20 150
*/
/*
61 1000000000 13
55
29 72 85 94 103 123 125 144 147 153 154 184 189 192 212 234 247 265 292 296 299 304 309 365 378 379 393 401 414 417 421 427 439 441 480 500 509 515 522 539 571 582 623 630 634 635 643 649 654 679 680 686 747 748 775
*/
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Once at New Year Dima had a dream in which he was presented a fairy garland. A garland is a set of lamps, some pairs of which are connected by wires. Dima remembered that each two lamps in the garland were connected directly or indirectly via some wires. Furthermore, the number of wires was exactly one less than the number of lamps.
There was something unusual about the garland. Each lamp had its own brightness which depended on the temperature of the lamp. Temperatures could be positive, negative or zero. Dima has two friends, so he decided to share the garland with them. He wants to cut two different wires so that the garland breaks up into three parts. Each part of the garland should shine equally, i. e. the sums of lamps' temperatures should be equal in each of the parts. Of course, each of the parts should be non-empty, i. e. each part should contain at least one lamp.

Help Dima to find a suitable way to cut the garland, or determine that this is impossible.
While examining the garland, Dima lifted it up holding by one of the lamps. Thus, each of the lamps, except the one he is holding by, is now hanging on some wire. So, you should print two lamp ids as the answer which denote that Dima should cut the wires these lamps are hanging on. Of course, the lamp Dima is holding the garland by can't be included in the answer.
The first line contains single integer n (3 ≤ n ≤ 106) — the number of lamps in the garland.
Then n lines follow. The i-th of them contain the information about the i-th lamp: the number lamp ai, it is hanging on (and 0, if is there is no such lamp), and its temperature ti ( - 100 ≤ ti ≤ 100). The lamps are numbered from 1 to n.
If there is no solution, print -1.
Otherwise print two integers — the indexes of the lamps which mean Dima should cut the wires they are hanging on. If there are multiple answers, print any of them.
6
2 4
0 5
4 2
2 1
1 1
4 2
1 4
6
2 4
0 6
4 2
2 1
1 1
4 2
-1
The garland and cuts scheme for the first example:
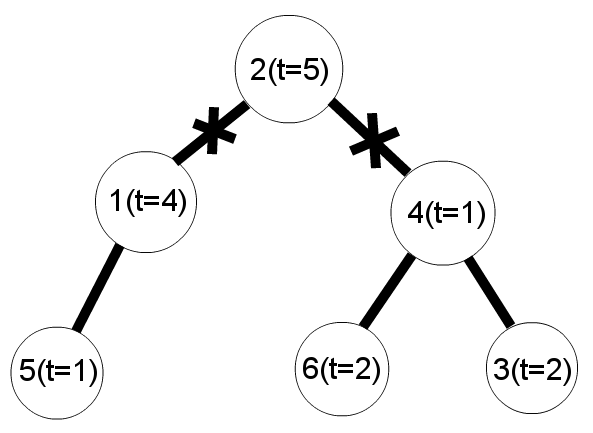
题意:有一棵给定根的树,有点权,要求剪掉两条边使得三个联通块权值和相等
题解:dfs处理 注意root
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#define ll __int64
#define mod 1000000007
#define dazhi 2147483647
using namespace std;
int n;
int a[];
struct node
{
int ed;
int pre;
}N[];
int pre[],he[],mp[];
int nedge=;
int to;
int sum=;
int root;
vector<int>re;
void add(int st,int ed)
{
nedge++;
N[nedge].ed=ed;
N[nedge].pre=pre[st];
pre[st]=nedge;
}
int getdfs(int x,int y)
{
he[x]=a[x];
for(int i=pre[x];i;i=N[i].pre)
{
if(N[i].ed!=y)
{
he[x]+=getdfs(N[i].ed,x);
}
}
if(he[x]==sum&&x!=root){
re.push_back(x);
he[x]=;
}
return he[x];
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n); for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d %d",&to,&a[i]);
sum+=a[i];
if(to==)
root=i;
else{
add(to,i);
}
}
if(sum%!=)
{
printf("-1\n");
return ;
}
sum=sum/;
getdfs(root,root);
if(re.size()<)
printf("-1\n");
else
printf("%d %d\n",re[],re[]);
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Olya likes milk very much. She drinks k cartons of milk each day if she has at least k and drinks all of them if she doesn't. But there's an issue — expiration dates. Each carton has a date after which you can't drink it (you still can drink it exactly at the date written on the carton). Due to this, if Olya's fridge contains a carton past its expiry date, she throws it away.
Olya hates throwing out cartons, so when she drinks a carton, she chooses the one which expires the fastest. It's easy to understand that this strategy minimizes the amount of cartons thrown out and lets her avoid it if it's even possible.
 Milk. Best before: 20.02.2017.
Milk. Best before: 20.02.2017.
The main issue Olya has is the one of buying new cartons. Currently, there are n cartons of milk in Olya's fridge, for each one an expiration date is known (how soon does it expire, measured in days). In the shop that Olya visited there are m cartons, and the expiration date is known for each of those cartons as well.
Find the maximum number of cartons Olya can buy so that she wouldn't have to throw away any cartons. Assume that Olya drank no cartons today.
In the first line there are three integers n, m, k (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 106, 1 ≤ k ≤ n + m) — the amount of cartons in Olya's fridge, the amount of cartons in the shop and the number of cartons Olya drinks each day.
In the second line there are n integers f1, f2, ..., fn (0 ≤ fi ≤ 107) — expiration dates of the cartons in Olya's fridge. The expiration date is expressed by the number of days the drinking of this carton can be delayed. For example, a 0 expiration date means it must be drunk today, 1 — no later than tomorrow, etc.
In the third line there are m integers s1, s2, ..., sm (0 ≤ si ≤ 107) — expiration dates of the cartons in the shop in a similar format.
If there's no way for Olya to drink the cartons she already has in her fridge, print -1.
Otherwise, in the first line print the maximum number x of cartons which Olya can buy so that she wouldn't have to throw a carton away. The next line should contain exactly x integers — the numbers of the cartons that should be bought (cartons are numbered in an order in which they are written in the input, starting with 1). Numbers should not repeat, but can be in arbitrary order. If there are multiple correct answers, print any of them.
3 6 2
1 0 1
2 0 2 0 0 2
3
1 2 3
3 1 2
0 0 0
1
-1
2 1 2
0 1
0
1
1
In the first example k = 2 and Olya has three cartons with expiry dates 0, 1 and 1 (they expire today, tomorrow and tomorrow), and the shop has 3 cartons with expiry date 0 and 3 cartons with expiry date 2. Olya can buy three cartons, for example, one with the expiry date 0 and two with expiry date 2.
In the second example all three cartons Olya owns expire today and it means she would have to throw packets away regardless of whether she buys an extra one or not.
In the third example Olya would drink k = 2 cartons today (one she alreay has in her fridge and one from the shop) and the remaining one tomorrow.
题意:每瓶牛奶一个保质期Ai,然后必须在保质期前喝完它,每天只能喝k瓶牛奶。求最多可以从商店买几瓶。
题解:Ai范围很小,从后往前,让每一瓶冰箱里的牛奶尽可能晚喝掉,看看能否喝完冰箱里的。
如果能喝完,就把商店的牛奶排序一下,从后往前对每一个还能喝的天,都尽可能的买,即可。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#define ll __int64
#define mod 1000000007
#define dazhi 2147483647
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int w;
int pos;
}N[];
int f[];
int ans[];
int n,m,k;
bool cmp(struct node aa,struct node bb)
{
return aa.w<bb.w;
}
int main()
{
memset(f,,sizeof(f));
scanf("%d %d %d",&n,&m,&k);
int maxn=;
int x;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&x);
maxn=max(x,maxn);
f[x]++;
}
for(int i=;i<=m;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&N[i].w);
N[i].pos=i;
}
sort(N+,N++m,cmp);
for(int i=maxn;i>;i--)
{
if(f[i]>=k)
{
f[i-]+=f[i]-k;
f[i]=;
}
else
{
f[i]=k-f[i];
}
}
if(f[]>k)
{
printf("-1\n");
return ;
}
else
f[]=k-f[];
for(int i=maxn+;i<=;i++) f[i]=k;
int j=m;
int jishu=;
for(int i=;i>=;i--)
{
while(j>=&&N[j].w>=i&&f[i]>)
{
f[i]--;
ans[jishu]=N[j].pos;
jishu++;
j--;
}
}
printf("%d\n",jishu-);
for(int i=;i<jishu;i++)
printf("%d ",ans[i]);
printf("\n"); return ;
}
Codeforces Round #398 (Div. 2) A B C D 模拟 细节 dfs 贪心的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #398 (Div. 2)
Codeforces Round #398 (Div. 2) A.Snacktower 模拟 我和官方题解的命名神相似...$has$ #include <iostream> #inclu ...
- Codeforces Round #367 (Div. 2) B. Interesting drink (模拟)
Interesting drink 题目链接: http://codeforces.com/contest/706/problem/B Description Vasiliy likes to res ...
- Codeforces Round #398 (Div. 2) A. Snacktower 模拟
A. Snacktower 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/767/problem/A Description According to an old lege ...
- Codeforces Round #398 (Div. 2) C. Garland —— DFS
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/767/problem/C 题解:类似于提着一串葡萄,用剪刀剪两条藤,葡萄分成了三串.问怎样剪才能使三串葡萄的质量相等. 首先要做 ...
- Codeforces Round #398 (div.2)简要题解
这场cf时间特别好,周六下午,于是就打了打(谁叫我永远1800上不去div1) 比以前div2的题目更均衡了,没有太简单和太难的...好像B题难度高了很多,然后卡了很多人. 然后我最后做了四题,E题感 ...
- Codeforces Round #398 (Div. 2) A,B,C,D
A. Snacktower time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input ...
- Codeforces Round #398 (Div. 2) B,C
B. The Queue time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input o ...
- 【DFS】Codeforces Round #398 (Div. 2) C. Garland
设sum是所有灯泡的亮度之和 有两种情况: 一种是存在结点U和V,U是V的祖先,并且U的子树权值和为sum/3*2,且U不是根,且V的子树权值和为sum/3. 另一种是存在结点U和V,他们之间没有祖先 ...
- 【枚举】【贪心】 Codeforces Round #398 (Div. 2) B. The Queue
卡题意……妈的智障 一个人的服务时间完整包含在整个工作时间以内. 显然,如果有空档的时间,并且能再下班之前完结,那么直接输出即可,显然取最左侧的空档最优. 如果没有的话,就要考虑“挤掉”某个人,就是在 ...
随机推荐
- 题解 CF191C 【Fools and Roads】
树上差分半裸题 常规思路是进行三次DFS,然后常规运算即可 这里提供两次dfs的思路(wyz tql orz) 我们以样例2为例 我们考虑任意一条路径,令其起点为u终点为v,每走一次当前路径则v的访问 ...
- vue 与jq 的对比
vue.react和angular,众所周知,他们是前端框架的3个大佬.这篇主要想对比一下用vue和用jq的区别,至于和其他框架的对比,我想vue的官网说的更为详细. 我算是独自用vue写过一个小型项 ...
- mysql 启动报错
之前用我这个机器做mysql的测试来,今天启动准备搭建一套线上的主从,结果起不来了... 错误日志: ;InnoDB: End of page dump 170807 11:37:02 InnoDB: ...
- android4.3 Bluetooth分析之扫描分析
android4.3中引入了蓝牙低能耗le(low energy),相应的也有一些方法/类.不过代码里,并没有找到初始调用的地方.所以这里还是先只分析下bt普通的扫描流程(类似android 4.2) ...
- java面试95题
1.面向对象的特征有哪些方面? 答:面向对象的特征主要有以下几个方面: - 抽象:抽象是将一类对象的共同特征总结出来构造类的过程,包括数据抽象和行为抽象两方面.抽象只关注对象有哪些属性和行为,并不关注 ...
- YaoLingJump开发者日志(三)
开始第二关的筹建. 增加了地刺和会移动的砖块. 每次增加一个新东西都要改好多代码,好累吖. 把第二关搞出来后发现太难了,强行调整难度. 修复了一些bug. 调整难度后还是发现太 ...
- bwapp之xss(blog)
存储型XSS,持久化,代码是存储在服务器中的,如在个人信息或发表文章等地方,加入代码,如果没有过滤或过滤不严,那么这些代码将储存到服务器中,用户访问该页面的时候触发代码执行.这种XSS比较危险,容易造 ...
- MongoDb企业应用实战(一) 写在MongoDB应用介绍之前(ii)
上一篇: MongoDb企业应用实战(一) 写在MongoDB应用介绍之前(i) 有段时间没跟大家去分享和探讨过一些问题,分享过一些经验了(失败过的,痛苦过的才最有看点啊,不知道各位同仁们怎么去看这个 ...
- C的强制转换和C++的强制转换(转)
C的强制转换: (type)<expression> 其中,type为类型描述符,如int,float等.<expression>为表达式.经强制类型转换运算符运算后,返回一个 ...
- go的IO函数,整理下最基本的IO处理函数,工欲善其事必先利其器
bufio.NewScanner()函数是一行一行地读,但是对/proc/函数,这里不是个好方法,最好是把所有的数据一次读完,然后再去读,有没有这样读的接口呢?把所有数据都读入到内存中然后再通过通过搜 ...
