杨其菊201771010134《面向对象程序设计(java)》第六周学习总结
《面向对象程序设计(java)》第六周学习总结
第一部分:理论知识
2)Object:所有类的超类
4)对象包装器和自动打包
7)继承设计的技巧
第二部分:实验部分
继承定义与使用《代码测试和示例程序的注释》
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 理解继承的定义;
(2) 掌握子类的定义要求
(3) 掌握多态性的概念及用法;
(4) 掌握抽象类的定义及用途;//不能创建自己的对象,特殊类
(5) 掌握类中4个成员访问权限修饰符的用途;//public和private,
(6) 掌握抽象类的定义方法及用途;
(7)掌握Object类的用途及常用API;//最顶层的类,
(8) 掌握ArrayList类的定义方法及用法;//预定一类
(9) 掌握枚举类定义方法及用途。//预定一类
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第5章示例程序,测试并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
• 在elipse IDE中编辑、调试、运行程序5-1 (教材152页-153页) ;
• 掌握子类的定义及用法;
• 结合程序运行结果,理解并总结OO风格程序构造特点,理解Employee和Manager类的关系子类的用途,并在代码中添加注释。
- 1 package inheritance;
- 2
- 3 /**
- 4 * This program demonstrates inheritance.
- 5 * @version 1.21 2004-02-21
- 6 * @author Cay Horstmann
- 7 */
- 8 public class ManagerTest
- 9 {
- 10 public static void main(String[] args)
- 11 {
- 12 // 创建一个Manager类对象;
- 13 Manager boss = new Manager("Carl Cracker", 80000, 1987, 12, 15);
- 14 boss.setBonus(5000);
- 15
- 16 Employee[] staff = new Employee[3]; //定义一个雇员数组;
- 17
- 18 // 用管理者和雇员对象填充数组;
- 19
- 20 staff[0] = boss;
- 21 staff[1] = new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1);
- 22 staff[2] = new Employee("Tommy Tester", 40000, 1990, 3, 15);
- 23
- 24 // 输出所有雇员对象的信息;
- 25 for (Employee e : staff)
- 26 System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary());
- 27
- 28 }
- 29 }
- package inheritance;
- 2
- 3 import java.time.*;
- 4
- 5 public class Employee
- 6 {
- 7 //定义Employee属性;
- 8 private String name;
- 9 private double salary;
- 10 private LocalDate hireDay;
- 11 //构造Employee对象,及初始化其属性,
- 12 public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
- 13 {
- 14 this.name = name;
- 15 this.salary = salary;
- 16 hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day);
- 17 }
- 18 //name属性访问器
- 19 public String getName()
- 20 {
- 21 return name;
- 22 }
- 23 //Salary属性访问器;
- 24 public double getSalary()
- 25 {
- 26 return salary;
- 27 }
- 28 //HireDay属性访问器
- 29 public LocalDate getHireDay()
- 30 {
- 31 return hireDay;
- 32 }
- 33 //raiseSalary方法;
- 34 public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
- 35 {
- 36 double raise = salary
- 37 salary +=raise;
- 38 }
- 1 package inheritance;
- 2
- 3 public class Manager extends Employee//定义新类Manager是Employee的子类;
- 4 {
- 5 private double bonus;//子类独有属性;
- 6
- 7 /**
- 8 * @param name the employee's name
- 9 * @param salary the salary
- 10 * @param year the hire year
- 11 * @param month the hire month
- 12 * @param day the hire day
- 13 */
- 14 //构造Manager对象并初始化其属性;super直接调用父类参数,name,salary, year, month, day,无返回值;
- 15
- 16 public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
- 17 {
- 18 super(name, salary, year, month, day);
- 19 bonus = 0; //Manager独有属性并初始化;
- 20 }
- 21 //Salary属性访问器,
- 22 public double getSalary()
- 23 {
- 24 //父类中的方法语句在子类中被重写成“独有方法”;
- 25 double baseSalary = super.getSalary();
- 26 return baseSalary + bonus;
- 27 }
- 28 //Bonus属性更改器;
- 29 public void setBonus(double b)
- 30 {
- 31 bonus = b;
- 32 }
- 33 }
实验结果截图:
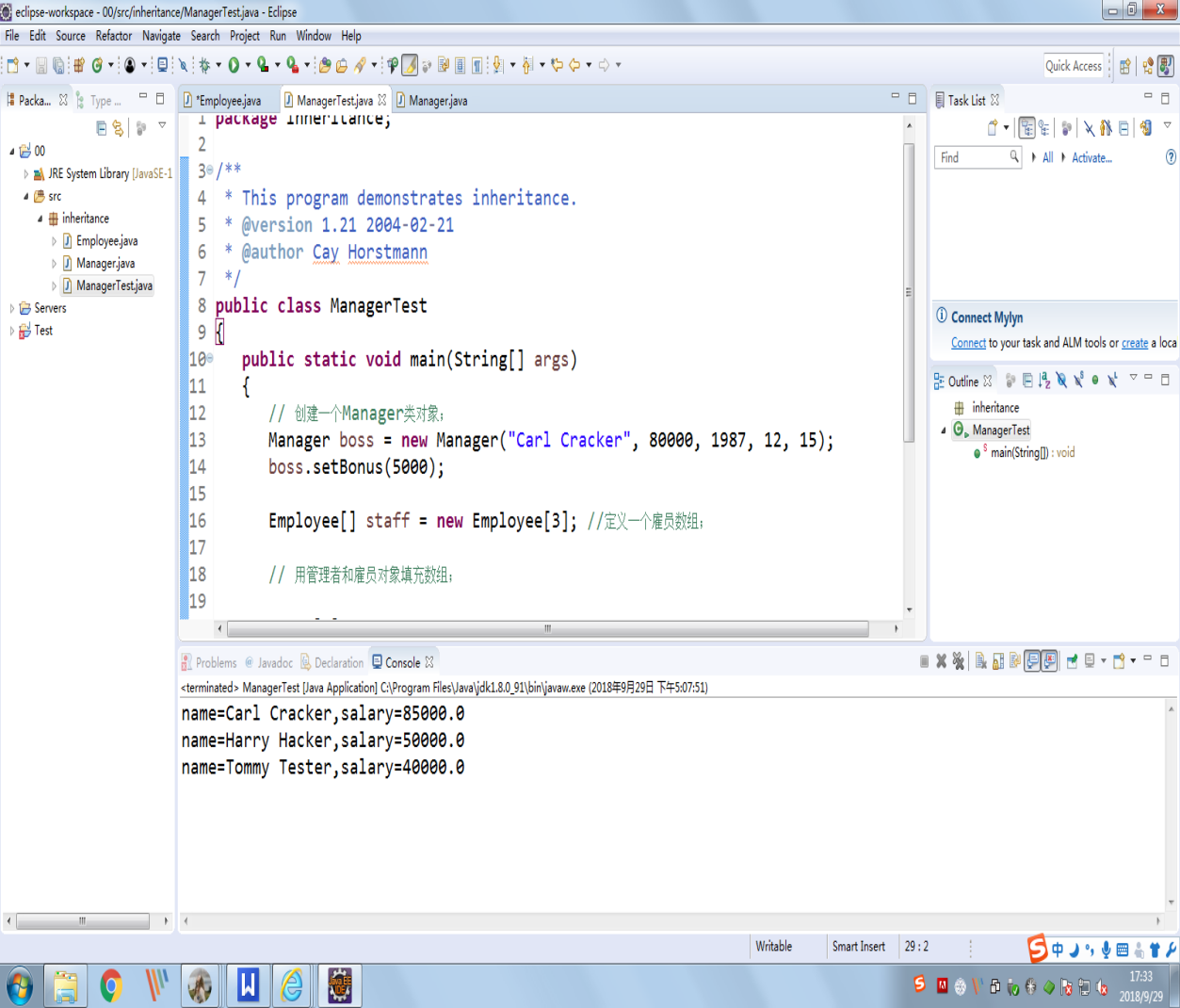
测试程序2:
• 编辑、编译、调试运行教材PersonTest程序(教材163页-165页);
• 掌握超类的定义及其使用要求;
• 掌握利用超类扩展子类的要求;
• 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释。
- package abstractClasses;
- /**
- * This program demonstrates abstract classes.
- * @version 1.01 2004-02-21
- * @author Cay Horstmann
- */
- public class PersonTest
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- Person[] people = new Person[2];
- // 用学生和雇员对象填充People数组;
- people[0] = new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1);
- people[1] = new Student("Maria Morris", "computer science");
- //输出所有Person对象的名称和描述;
- for (Person p : people)
System.out.println(p.getName() + ", " + p.getDescription());
}
}
- package abstractClasses;
- public abstract class Person //定义抽象类型Person;
- {
public abstract String getDescription();
private String name;
public Person(String name) {- this.name = name;
}
//Name属性访问器;
public String getName() {- return name;
}
}
- package abstractClasses;
- import java.time.*;
- public class Employee extends Person //定义新类Employee是Person的子类
- {
//定义属性;
- private double salary;
- private LocalDate hireDay;
public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) {- super(name); //调用父类方法;
- this.salary = salary;//this代替当前对象;
hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day);//LocalDate方法;
}
//Salary属性访问器
public double getSalary()
{- return salary;
}- public LocalDate getHireDay()
{
return hireDay;
}
//Description属性访问器,String类型;
public String getDescription()
{- return String.format("an employee with a salary of $%.2f", salary);
}
//Employee类独有方法;
public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
//计算语句;
double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; salary += raise;
}
}
- package abstractClasses;
- public class Student extends Person//子类Student继承父类Person;
- {
- private String major;
- /**
- * @param nama the student's name
- * @param major the student's major
- */
- public Student(String name, String major)
- {
- // 将name传递给父类构造函数;
- super(name);
- this.major = major;
- }
- public String getDescription()
- {
- return "a student majoring in " + major;
- }
- }
运行结果如下:

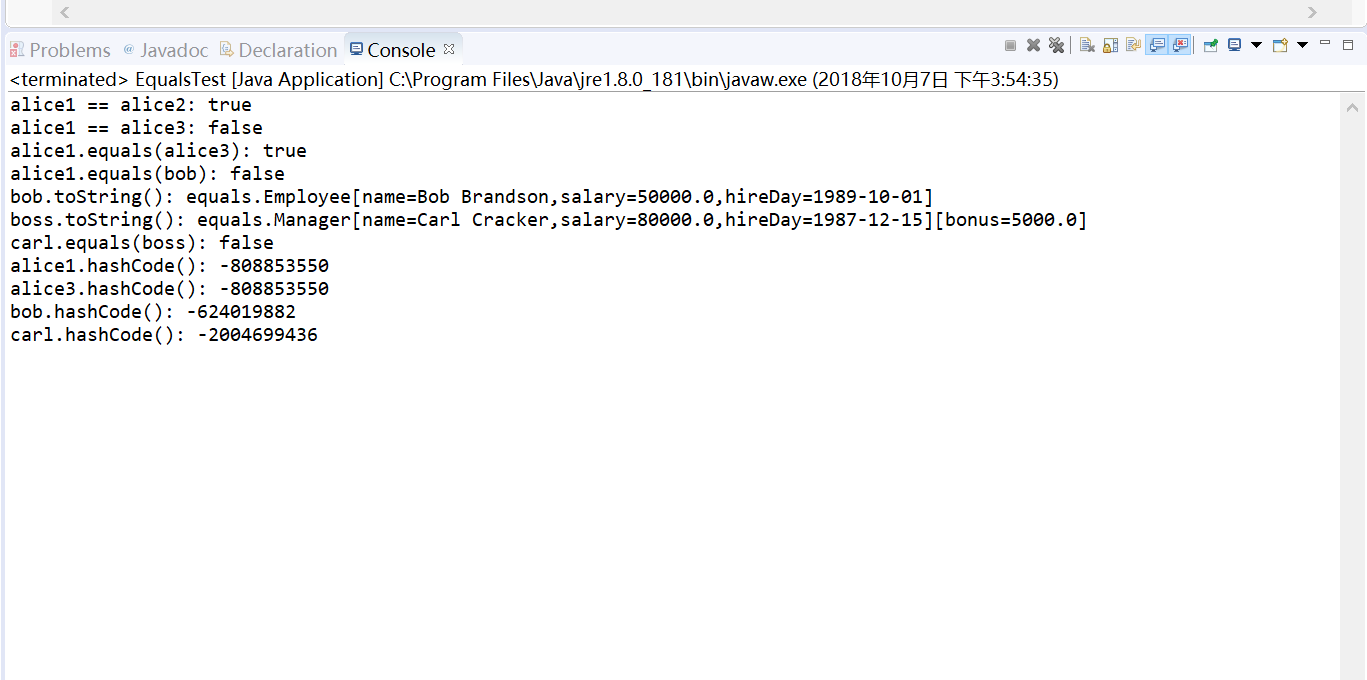
测试程序3:
• 编辑、编译、调试运行教材程序5-8、5-9、5-10,结合程序运行结果理解程序(教材174页-177页);
• 掌握Object类的定义及用法;
• 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释。
- package equals;
- /**
- * This program demonstrates the equals method.
- * @version 1.12 2012-01-26
- * @author Cay Horstmann
- */
- public class EqualsTest
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- Employee alice1 = new Employee("Alice Adams", 75000, 1987, 12, 15);
- Employee alice2 = alice1;
- Employee alice3 = new Employee("Alice Adams", 75000, 1987, 12, 15);
- Employee bob = new Employee("Bob Brandson", 50000, 1989, 10, 1);
- System.out.println("alice1 == alice2: " + (alice1 == alice2));
- System.out.println("alice1 == alice3: " + (alice1 == alice3));
- System.out.println("alice1.equals(alice3): " + alice1.equals(alice3));
- System.out.println("alice1.equals(bob): " + alice1.equals(bob));
- System.out.println("bob.toString(): " + bob);
- Manager carl = new Manager("Carl Cracker", 80000, 1987, 12, 15);
- Manager boss = new Manager("Carl Cracker", 80000, 1987, 12, 15);
- boss.setBonus(5000);
- System.out.println("boss.toString(): " + boss);
- System.out.println("carl.equals(boss): " + carl.equals(boss));
- System.out.println("alice1.hashCode(): " + alice1.hashCode());
- System.out.println("alice3.hashCode(): " + alice3.hashCode());
- System.out.println("bob.hashCode(): " + bob.hashCode());
- System.out.println("carl.hashCode(): " + carl.hashCode());
- }
- }
- package equals;
- import java.time.*;
- import java.util.Objects;
- public class Employee
- {
- private String name;
- private double salary;
- private LocalDate hireDay;
- public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
- {
- this.name = name;
- this.salary = salary;
- hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day);
- }
- public String getName()
- {
- return name;
- }
- public double getSalary()
- {
- return salary;
- }
- public LocalDate getHireDay()
- {
- return hireDay;
- }
- public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
- {
- double raise = salary * byPercent / 100;
- salary += raise;
- }
- public boolean equals(Object otherObject)
- {
- //快速检查对象是否相同
- if (this == otherObject) return true;
- //如果显示参数为null,则必须返回false;
- if (otherObject == null) return false;
- // 如果这些 类不匹配,他们不相等。
- if (getClass() != otherObject.getClass()) return false;
- // 现在我们知道另一个对象是非空雇员;
- Employee other = (Employee) otherObject;
- //测试字段是否具有相同的值;
- return Objects.equals(name, other.name) && salary == other.salary && Objects.equals(hireDay, other.hireDay);
- }
- public int hashCode()
- {
- return Objects.hash(name, salary, hireDay);
- }
- //toString方法;
- public String toString()
- {
- return getClass().getName() + "[name=" + name + ",salary=" + salary + ",hireDay=" + hireDay
- + "]";
- }
- }
- package equals;
- public class Manager extends //Employee子类Manager继承父类Employee
- {
// 定义属性;- private double bonus;
- public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
- {
- super(name, salary, year, month, day);//调用父类参数,无返回值;
- bonus = 0;
- }
- //Salary属性访问器;
- public double getSalary()
- {
- double baseSalary = super.getSalary();
- return baseSalary + bonus;
- }
- public void setBonus(double bonus)
- {
- this.bonus = bonus;
- }
- public boolean equals(Object otherObject)
- {
- if (!super.equals(otherObject)) return false;
- Manager other = (Manager) otherObject;
- // 检查这个是否与其他是否属于同一类;
- return bonus == other.bonus;
- }
- public int hashCode()
- {
- return java.util.Objects.hash(super.hashCode(), bonus);
- }
- public String toString()
- {
- return super.toString() + "[bonus=" + bonus + "]";
- }
- }
测试程序4:
• 在elipse IDE中调试运行程序5-11(教材182页),结合程序运行结果理解程序;
• 掌握ArrayList类的定义及用法;
• 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释。
- package arrayList;
- import java.util.*;
- /**
- * This program demonstrates the ArrayList class.
- * @version 1.11 2012-01-26
- * @author Cay Horstmann
- */
- public class ArrayListTest
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- // 用雇员对象填充staff数组;
- ArrayList<Employee> staff = new ArrayList<>();
- staff.add(new Employee("Carl Cracker", 75000, 1987, 12, 15));
- staff.add(new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1));
- staff.add(new Employee("Tony Tester", 40000, 1990, 3, 15));
- //把每个雇员的薪水提高5%;
- for (Employee e : staff)
- e.raiseSalary(5);
- // 打印所有雇员对象的信息;
- for (Employee e : staff)
- System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary() + ",hireDay="
- + e.getHireDay());
- }
- }
- package arrayList;
- import java.time.*;
- public class Employee
- {
- private String name;
- private double salary;
- private LocalDate hireDay;
- public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
- {
//注意this的用法;- this.name = name;
- this.salary = salary;
- hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day);
- }
- public String getName()
- {
- return name;
- }
- public double getSalary()
- {
- return salary;
- }
- public LocalDate getHireDay()
- {
- return hireDay;
- }
- public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
- {
- double raise = salary * byPercent / 100;
- salary += raise;
- }
- }

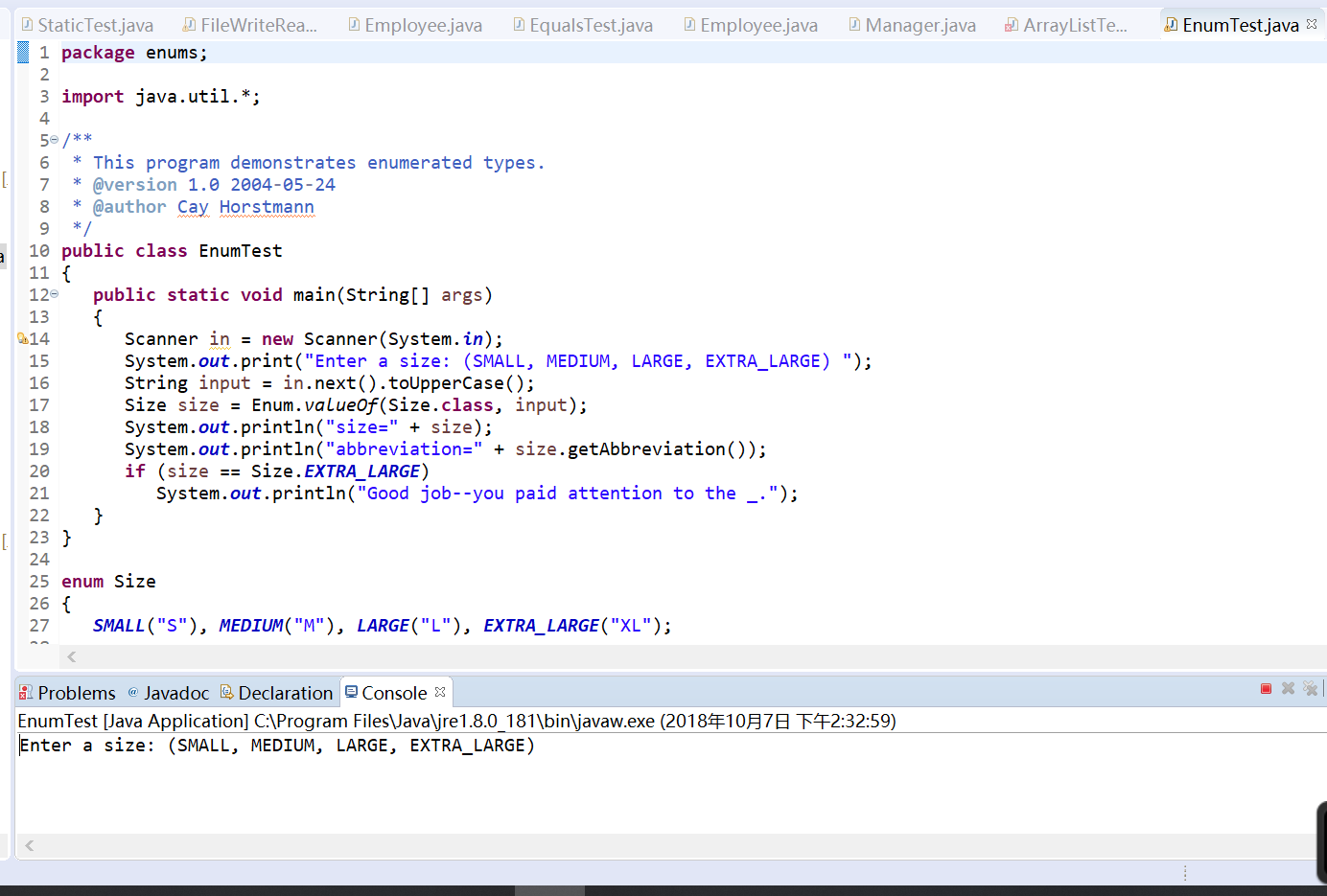
测试程序5:
• 编辑、编译、调试运行程序5-12(教材189页),结合运行结果理解程序;
• 掌握枚举类的定义及用法;
• 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释。
- package enums;
- import java.util.*;
- /**
- * This program demonstrates enumerated types.
- * @version 1.0 2004-05-24
- * @author Cay Horstmann
- */
- public class EnumTest
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- System.out.print("Enter a size: (SMALL, MEDIUM, LARGE, EXTRA_LARGE) ");
- String input = in.next().toUpperCase();
- Size size = Enum.valueOf(Size.class, input);
- System.out.println("size=" + size);
- System.out.println("abbreviation=" + size.getAbbreviation());
- if (size == Size.EXTRA_LARGE)
- System.out.println("Good job--you paid attention to the _.");
- }
- }
- enum Size
- {
- SMALL("S"), MEDIUM("M"), LARGE("L"), EXTRA_LARGE("XL");
- private Size(String abbreviation) { this.abbreviation = abbreviation; }
- public String getAbbreviation() { return abbreviation; }
- private String abbreviation;
- }
实验2:编程练习1
• 定义抽象类Shape:
属性:不可变常量double PI,值为3.14;
方法:public double getPerimeter();public double getArea())。
• 让Rectangle与Circle继承自Shape类。
• 编写double sumAllArea方法输出形状数组中的面积和和double sumAllPerimeter方法输出形状数组中的周长和。
• main方法中
1)输入整型值n,然后建立n个不同的形状。如果输入rect,则再输入长和宽。如果输入cir,则再输入半径。
2) 然后输出所有的形状的周长之和,面积之和。并将所有的形状信息以样例的格式输出。
3) 最后输出每个形状的类型与父类型,使用类似shape.getClass()(获得类型),shape.getClass().getSuperclass()(获得父类型);
思考sumAllArea和sumAllPerimeter方法放在哪个类中更合适?
输入样例:
- 3
- rect
- 1 1
- rect
- 2 2
- cir
- 1
输出样例:
- 18.28
- 8.14
- [Rectangle [width=1, length=1], Rectangle [width=2, length=2], Circle [radius=1]]
- class Rectangle,class Shape
- class Rectangle,class Shape
- class Circle,class Shape
- package Attention;
- import java.math.*;
- import java.util.*;
- import Attention.Shape;
- import Attention.Rectangle;
- import Attention.Circle;
- public class sum
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
- String rect = "rect";
- String cir = "cir";
- System.out.print("请输入形状个数:");
- int n = in.nextInt();
- Shape[] score = new Shape[n];
- for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
- {
- System.out.println("请输入形状类型 (rect or cir):");
- String input = in.next();
- if(input.equals(rect))
- {
- double length = in.nextDouble();
- double width = in.nextDouble();
- System.out.println("Rectangle["+"length:"+length+" width:"+width+"]");
- score[i] = new Rectangle(width,length);
- }
- if(input.equals(cir))
- {
- double radius = in.nextDouble();
- System.out.println("Circle["+"radius:"+radius+"]");
- score[i] = new Circle(radius);
- }
- }
- Shape c = new Shape();
- System.out.println(c.sumAllPerimeter(score));
- System.out.println(c.sumAllArea(score));
- for(Shape s:score)
- {
- System.out.println(s.getClass()+", "+s.getClass().getSuperclass());
- }
- }
- public double sumAllArea(Shape core[])
- {
- double sum = 0;
- Object score;
- for(int i = 0;i<score.length;i++)
- sum+= score[i].getArea();
- return sum;
- }
- public double sumAllPerimeter(Shape score[])
- {
- double sum = 0;
- for(int i = 0;i<score.length;i++)
- sum+= score[i].getPerimeter();
- return sum;
- }
- }
- package Attention;
- public abstract class Shape
- {
- double PI = 3.14;//不可变常量double PI,值为3.14;
- //方法:public double getPerimeter();public double getArea());
- public abstract double getPerimeter();
- public abstract double getArea();
- }
- package Attention;
- public class Rectangle extends Shape //Rectangle继承自Shape类;
- {
- private double width;
- private double length;
- public Rectangle(double w,double l)
- {
- this.width=w;
- this.length=l;
- }
- public double getPerimeter()
- {
- double Perimeter = (width+length)*2;
- return Perimeter;
- }
- public double getArea()
- {
- double Area = width*length;
- return Area;
- }
- public String toString()
- {
- return getClass().getName() + "[ width=" + width + "]"+ "[length=" + length + "]";
- }
- }
- package Attention;
- public class Circle extends Shape//Circle继承自Shape类
- {
- private double radius;
- public Circle(double r)
- {
- radius = r;
- }
- public double getPerimeter()
- {
- double Perimeter = 2*PI*radius;
- return Perimeter;
- }
- public double getArea()
- {
- double Area = PI*radius*radius;
- return Area;
- }
- public String toString()
- {
- return getClass().getName() + "[radius=" + radius + "]";
- }
- }
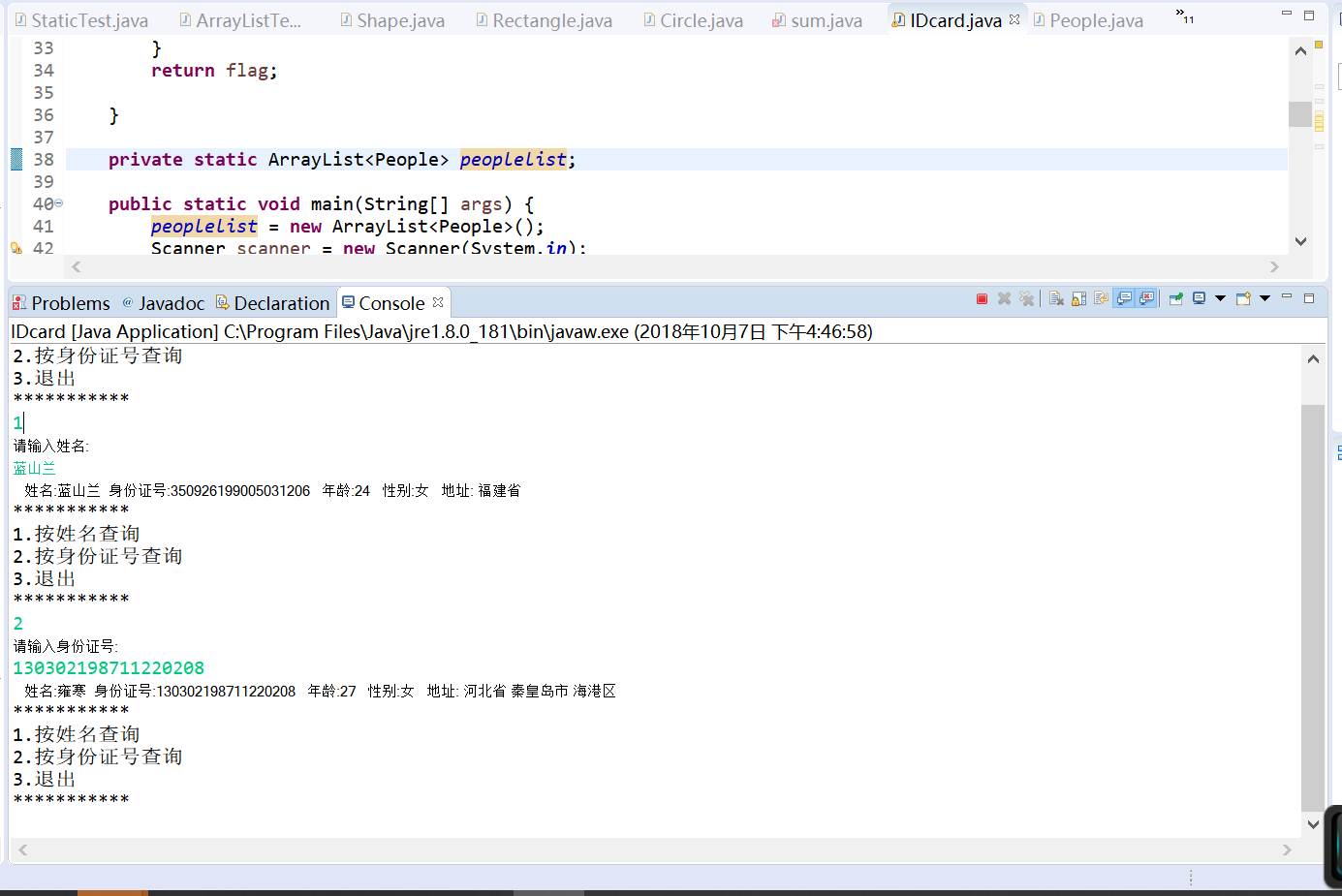
实验3: 编程练习2
编制一个程序,将身份证号.txt 中的信息读入到内存中,输入一个身份证号或姓名,查询显示查询对象的姓名、身份证号、年龄、性别和出生地。
- package Id;
- import java.io.BufferedReader;
- import java.io.File;
- import java.io.FileInputStream;
- import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
- import java.io.IOException;
- import java.io.InputStreamReader;
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.Scanner;
- public class ID {
- public static People findPeopleByname(String name) {
- People flag = null;
- for (People people : peoplelist) {
- if(people.getName().equals(name)) {
- flag = people;
- }
- }
- return flag;
- }
- public static People findPeopleByid(String id) {
- People flag = null;
- for (People people : peoplelist) {
- if(people.getnumber().equals(id)) {
- flag = people;
- }
- }
- return flag;
- }
- private static ArrayList<People> peoplelist;
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- peoplelist = new ArrayList<People>();
- Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
- File file = new File("E:\\面向对象程序设计Java\\实验\\身份证号.txt");
- try {
- FileInputStream files = new FileInputStream(file);
- BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(files));
- String temp = null;
- while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) {
- Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp);
- linescanner.useDelimiter(" ");
- String name = linescanner.next();
- String number = linescanner.next();
- String sex = linescanner.next();
- String age = linescanner.next();
- String place = linescanner.nextLine();
- People people = new People();
- people.setName(name);
- people.setnumber(number);
- people.setage(age);
- people.setsex(sex);
- people.setplace(place);
- peoplelist.add(people);
- }
- } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
- System.out.println("文件未找到");
- e.printStackTrace();
- } catch (IOException e) {
- System.out.println("文件读取错误");
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- boolean isTrue = true;
- while (isTrue) {
- System.out.println("***********");
- System.out.println("1.按姓名查询");
- System.out.println("2.按身份证号查询");
- System.out.println("3.退出");
- System.out.println("***********");
- int nextInt = scanner.nextInt();
- switch (nextInt) {
- case 1:
- System.out.println("请输入姓名:");
- String peoplename = scanner.next();
- People person = findPeopleByname(peoplename);
- if (people != null) {
- System.out.println(" 姓名:"+
- person.getName() + " 身份证号:"+ person.getnumber() + " 年龄:"+ person.getage()+ " 性别:"+ person.getsex()+ " 地址:"+ person.getplace() ); } else { System.out.println("
- 此人不存在"); } break; case 2: System.out.println("请输入身份证号:"); String peopleid = scanner.next(); People person1 = findPeopleByid(peopleid); if (people1 != null) { System.out.println(" 姓名:"+person
- 1.getName()+ " 身份证号:"+ person1.getnumber()+ " 年龄:"+ person1.getage()+ " 性别:"+ person1.getsex()+ " 地址:"+ person1.getplace()); } else { System.out.println("此人不存在"); } break; case 3: isTrue = false; System.out.println("byebye!"); break; default: System.out.println("输入有误"); } } } }
- package Id;
- public class Person{
- private String name;
- private String number;
- private String age;
- private String sex;
- private String place;
- public String getName()
- {
- return name;
- }
- public void setName(String name)
- {
- this.name = name;
- }
- public String getnumber()
- {
- return number;
- }
- public void setnumber(String number)
- {
- this.number = number;
- }
- public String getage()
- {
- return age;
- }
- public void setage(String age )
- {
- this.age = age;
- }
- public String getsex()
- {
- return sex;
- }
- public void setsex(String sex )
- {
- this.sex = sex;
- }
- public String getplace()
- {
- return place;
- }
- public void setplace(String place)
- {
- this.place = place;
- }
- }
第三部分:总结
上周实验课助教老师的详细讲解对我的来说有很大帮助,以及老师在课堂带领我们阅读代码 让我学到很多。总的来说,能力还是很低下,我意识到自己的自主学习能力比较差,这与自身素质方面有很大关系,希望我可以通过这次彻底的认识到自己的问题,提高自己的能力。
杨其菊201771010134《面向对象程序设计(java)》第六周学习总结的更多相关文章
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第九周学习总结
第九周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 异常.断言和调试.日志 1.捕获 ...
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第十周学习总结
第8章泛型程序设计学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 主要内容: 什么是泛型程序设计 泛型类的声明及实例化的方法 泛型方法的定义 ...
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第八周学习总结
第八周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 一.接口.lambda和内部类: Comparator与comparable接口: 1.comparable接口的方法是compareTo,只有一个参数:comp ...
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十六周学习总结
第十六周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 1. 程序是一段静态的代码,它是应用程序执行的蓝本.进程是程序的一次动态执行,它对应了从代码加载.执行至执行完毕的一个完整过程.操作系统为每个进程分配一段独立的内 ...
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第十二周学习总结
第十二周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 内容概要: AWT与Swing简介:框架的创建:图形程序设计: 显示图像: 1.AWT组件: 2.Swing 组件层次关系 3 .AWT与Swing的关系:大部分 ...
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第七周学习总结
第七周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 1.继承是面向对象程序设计(Object Oriented Programming-OOP)中软件重用的关键技术.继承机制使用已经定义的类作为基础建立新的类定义,新 ...
- 201871010132-张潇潇《面向对象程序设计(java)》第一周学习总结
面向对象程序设计(Java) 博文正文开头 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cn ...
- 扎西平措 201571030332《面向对象程序设计 Java 》第一周学习总结
<面向对象程序设计(java)>第一周学习总结 正文开头: 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 ...
- 杨其菊201771010134《面向对象程序设计Java》第二周学习总结
第三章 Java基本程序设计结构 第一部分:(理论知识部分) 本章主要学习:基本内容:数据类型:变量:运算符:类型转换,字符串,输入输出,控制流程,大数值以及数组. 1.基本概念: 1)标识符:由字母 ...
- 201871010124 王生涛《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第一周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/xbsf/ ...
随机推荐
- Spark资源配置(核数与内存)
转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/zrc199021/article/details/54020692 关于所在节点核数怎么看? =========================== ...
- 将图片嵌入到markdown文档中
转自KFXW的专栏 将图片嵌入Markdown文档中一直是一个比较麻烦的事情.通常的做法是将图片存入本地某个路径或者网络存储空间,使用URL链接的形式插入图片: ![image][url_to_ima ...
- <realsense D400>同步采集深度图和彩色图
利用深度相机采集深度图和彩色图会面临一个问题,如何实现同步采集数据? 以下是我搜集到的两点方法: 1)高翔博士提到他的orbslam2教程有这么一步工作,具体目录为 example/RGBD/. (等 ...
- Zookeeper 在Windows下的安装过程及测试
安装jdk 安装Zookeeper. 在官网http://zookeeper.apache.org/下载zookeeper.我下载的是zookeeper-3.4.6版本. 解压zookeeper-3. ...
- 阿里Java开发手册
1.1 命名风格 (1)常量命名全部大写,单词间用下划线隔开. (2)抽象类命名以Abstract或Base开头:异常类命名以Exception结尾:测试类命名以它要测试的类名开始,以Test结尾. ...
- LeetCode【100. 相同的树】
看到这道题,第一思考是结构和节点完全相同 第一次,就没有思考null的情况 if(p.val == q.val && p.left.val == q.left.val &&am ...
- 01.JDBC操作数据库-快速入门操作
/** * 简单入门操作 * 注:先将mysql-connector-java-5.1.36.jar 构建 Build Path环境当中去 * @param args * @throws Except ...
- git打tag
亲们支持我的新博客哦==>地址(以后更新会尽量在新博客更新,欢迎大家访问加入我的后宫w) ) 标签分类 git标签分为两种类型:轻量标签和附注标签.轻量标签是指向提交对象的引用,附注标签 ...
- 【Servlet】(1)Servlet简介、Servlet底层原理、Servlet实现方式、Servlet生命周期
一.Servlet简介 1.Servlet定义: Servlet(Server Applet)是Java Servlet的简称,是为小服务程序或服务连接器,用Java编写的服务器端程序,主要功能在于交 ...
- 某大型跨境电商JVM调优总结
前提:某大型跨境电商业务发展非常快,线上机器扩容也很频繁,但是对于线上机器的运行情况,特别是jvm内存的情况,一直没有一个统一的标准来给到各个应用服务的owner.经过618大促之后,和运维的同学讨论 ...
