进程&信号&管道实践学习记录
程序分析
exec1.c & exect2.c & exect3.c
程序代码 (以exect1.c为例,其他两个结构类似)
#include <stdio.h>#include <unistd.h>int main(){char *arglist[3];arglist[0] = "ls";arglist[1] = "-l";arglist[2] = 0 ;//NULLprintf("* * * About to exec ls -l\n");execvp( "ls" , arglist );printf("* * * ls is done. bye");return 0;}
运行结果:
结果显示代码“* * * ls is done. bye”没有打印出来。
原因:因为调用execvp,execlp,execv时,内核将新程序载入到当前进程,替代当前进程的代码和数据。
forkdemo1.c
程序代码:
#include <stdio.h>#include <sys/types.h>#include <unistd.h>int main(){int ret_from_fork, mypid;mypid = getpid();printf("Before: my pid is %d\n", mypid);ret_from_fork = fork();sleep(1);printf("After: my pid is %d, fork() said %d\n",getpid(), ret_from_fork);return 0;}
运行结果:
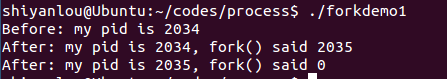
分析:fork()在父进程中返回子进程的pid,在子进程中返回0。
forkdemo2.c
程序代码:
#include <stdio.h>#include <unistd.h>int main(){printf("before:my pid is %d\n", getpid() );fork();fork();printf("aftre:my pid is %d\n", getpid() );return 0;}
运行结果:
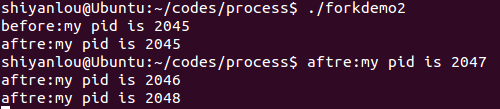
分析:两次fork()共产生3个子进程,加上父进程总共有4个进程。
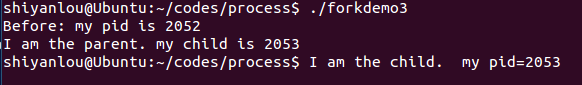
forkdemo3.c
程序代码:
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <unistd.h>int main(){int fork_rv;printf("Before: my pid is %d\n", getpid());fork_rv = fork(); /* create new process */if ( fork_rv == -1 ) /* check for error */perror("fork");else if ( fork_rv == 0 ){printf("I am the child. my pid=%d\n", getpid());exit(0);}else{printf("I am the parent. my child is %d\n", fork_rv);exit(0);}return 0;}
运行效果:
forkdemo4.c
程序代码:
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <unistd.h>int main(){int fork_rv;printf("Before: my pid is %d\n", getpid());fork_rv = fork(); /* create new process */if ( fork_rv == -1 ) /* check for error */perror("fork");else if ( fork_rv == 0 ){printf("I am the child. my pid=%d\n", getpid());printf("parent pid= %d, my pid=%d\n", getppid(), getpid());exit(0);}else{printf("I am the parent. my child is %d\n", fork_rv);sleep(10);exit(0);}return 0;}
运行结果:
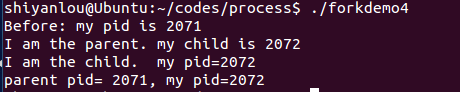
forkgdb.c
程序代码:
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <unistd.h>int gi=0;int main(){int li=0;static int si=0;int i=0;pid_t pid = fork();if(pid == -1){exit(-1);}else if(pid == 0){for(i=0; i<5; i++){printf("child li:%d\n", li++);sleep(1);printf("child gi:%d\n", gi++);printf("child si:%d\n", si++);}exit(0);}else{for(i=0; i<5; i++){printf("parent li:%d\n", li++);printf("parent gi:%d\n", gi++);sleep(1);printf("parent si:%d\n", si++);}exit(0);}return 0;}
运行效果:
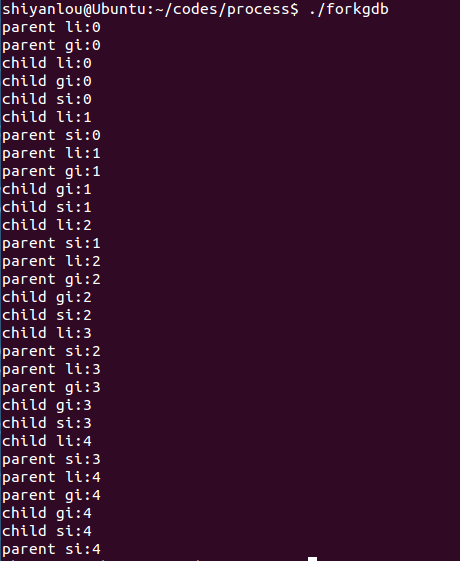
分析:运行结果说明了子进程与父进程并发运行。
psh1.c
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>#include <unistd.h>#define MAXARGS 20#define ARGLEN 100//将字符串内容当做命令来执行。int execute( char *arglist[] ){execvp(arglist[0], arglist);perror("execvp failed");exit(1);}char * makestring( char *buf ){char *cp;buf[strlen(buf)-1] = '\0';cp = malloc( strlen(buf)+1 );if ( cp == NULL ){fprintf(stderr,"no memory\n");exit(1);}strcpy(cp, buf);return cp;}int main(){char *arglist[MAXARGS+1];int numargs;char argbuf[ARGLEN];numargs = 0;while ( numargs < MAXARGS ){printf("Arg[%d]? ", numargs);if ( fgets(argbuf, ARGLEN, stdin) && *argbuf != '\n' )arglist[numargs++] = makestring(argbuf);else{if ( numargs > 0 ){arglist[numargs]=NULL;execute( arglist ); //将arglist中的字符串当做命令来执行。numargs = 0;}}}return 0;}
运行结果:
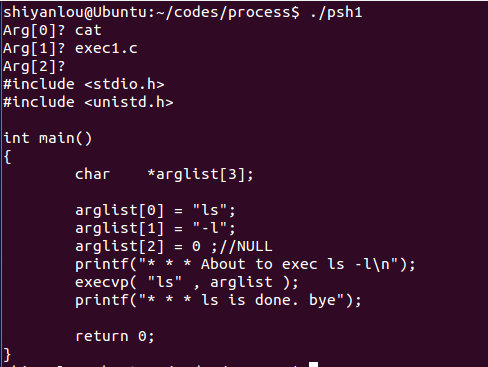
程序功能:输入字符串并将其当做命令执行。
psh2.c
程序代码:
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>#include <sys/types.h>#include <sys/wait.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <signal.h>#define MAXARGS 20#define ARGLEN 100char *makestring( char *buf ){char *cp;buf[strlen(buf)-1] = '\0';cp = malloc( strlen(buf)+1 );if ( cp == NULL ){fprintf(stderr,"no memory\n");exit(1);}strcpy(cp, buf);return cp;}void execute( char *arglist[] ){int pid,exitstatus;pid = fork();switch( pid ){case -1:perror("fork failed");exit(1);case 0:execvp(arglist[0], arglist);perror("execvp failed");exit(1);default:while( wait(&exitstatus) != pid );printf("child exited with status %d,%d\n",exitstatus>>8, exitstatus&0377);}}int main(){char *arglist[MAXARGS+1];int numargs;char argbuf[ARGLEN];numargs = 0;while ( numargs < MAXARGS ){printf("Arg[%d]? ", numargs);if ( fgets(argbuf, ARGLEN, stdin) && *argbuf != '\n' )arglist[numargs++] = makestring(argbuf);else{if ( numargs > 0 ){arglist[numargs]=NULL;execute( arglist );numargs = 0;}}}return 0;}
运行结果:
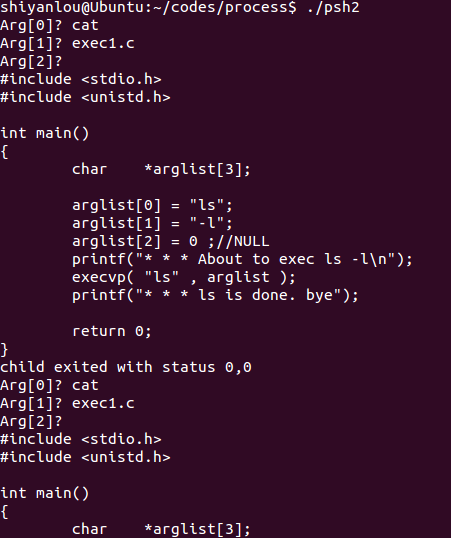
程序功能:不断产生新的子进程输入字符串命令。
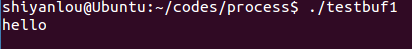
testbuf1
程序代码:
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>int main(){printf("hello");fflush(stdout);while(1);}
运行效果:
testbuf2
程序代码:
#include <stdio.h>int main(){printf("hello\n");while(1);}
运行效果:

testbuf3
程序代码:
#include <stdio.h>int main(){fprintf(stdout, "1234", 5);fprintf(stderr, "abcd", 4);}
运行效果:
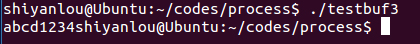
分析:在默认情况下,stdout是行缓冲的,他的输出会放在一个buffer里面,只有到换行的时候,才会输出到屏幕。而stderr是无缓冲的,会直接输出。所以输出结果为:abcd1234
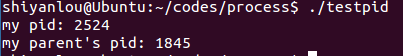
testpid.c
程序代码:
#include <stdio.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <sys/types.h>int main(){printf("my pid: %d \n", getpid());//获取当前进程pidprintf("my parent's pid: %d \n", getppid());//获取当前进程父进程pidreturn 0;}
运行效果:
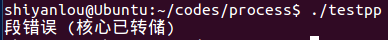
testpp.c
程序代码:
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>int main(){char **pp;pp[0] = malloc(20);return 0;}
运行效果:
testsystem.c
程序代码:
#include <stdlib.h>int main ( int argc, char *argv[] ){system(argv[1]);system(argv[2]);return EXIT_SUCCESS;}
- system函数:
system()会调用fork()产生子进程,由子进程来调用/bin/sh-c string来执行参数string字符串所代表的命令,此命令执行完后随即返回原调用的进程。在调用system()期间SIGCHLD 信号会被暂时搁置,SIGINT和SIGQUIT 信号则会被忽略。 返回值 =-1:出现错误 =0:调用成功但是没有出现子进程 >0:成功退出的子进程的id 如果system()在调用/bin/sh时失败则返回127,其他失败原因返回-1。若参数string为空指针(NULL),则返回非零值>。如果system()调用成功则最后会返回执行shell命令后的返回值,但是此返回值也有可能为 system()调用/bin/sh失败所返回的127,因此最好能再检查errno 来确认执行成功。
运行效果:
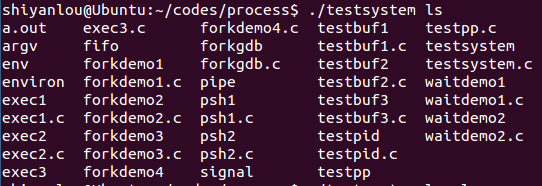
waitdemo1.c
程序代码:
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <sys/types.h>#include <sys/wait.h>#include <unistd.h>#define DELAY 4void child_code(int delay){printf("child %d here. will sleep for %d seconds\n", getpid(), delay);sleep(delay);printf("child done. about to exit\n");exit(17);}void parent_code(int childpid){int wait_rv=0; /* return value from wait() */wait_rv = wait(NULL);//子进程成功结束返回子进程PID,没有子进程则返回-1。printf("done waiting for %d. Wait returned: %d\n",childpid, wait_rv);}int main(){int newpid;printf("before: mypid is %d\n", getpid());if ( (newpid = fork()) == -1 )perror("fork");else if ( newpid == 0 )child_code(DELAY);elseparent_code(newpid);return 0;}
运行效果:
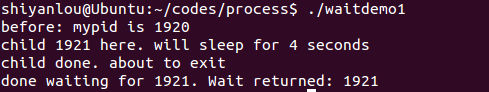
waitdemo2.c
程序代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define DELAY 10void child_code(int delay){printf("child %d here. will sleep for %d seconds\n", getpid(), delay);sleep(delay);printf("child done. about to exit\n");exit(27);}void parent_code(int childpid){int wait_rv;int child_status;int high_8, low_7, bit_7;wait_rv = wait(&child_status);printf("done waiting for %d. Wait returned: %d\n", childpid, wait_rv);high_8 = child_status >> 8; /* 1111 1111 0000 0000 */low_7 = child_status & 0x7F; /* 0000 0000 0111 1111 */bit_7 = child_status & 0x80; /* 0000 0000 1000 0000 */printf("status: exit=%d, sig=%d, core=%d\n", high_8, low_7, bit_7);}int main(){int newpid;printf("before: mypid is %d\n", getpid());if ( (newpid = fork()) == -1 )perror("fork");else if ( newpid == 0 )child_code(DELAY);elseparent_code(newpid);}
运行结果:
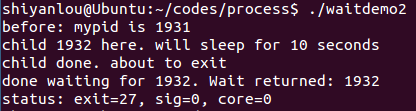
argtest.c
程序代码:
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include "argv.h"int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {char delim[] = " \t";int i;char **myargv;int numtokens;if (argc != 2) {fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s string\n", argv[0]);return 1;}if ((numtokens = makeargv(argv[1], delim, &myargv)) == -1) {fprintf(stderr, "Failed to construct an argument array for %s\n", argv[1]);return 1;}printf("The argument array contains:\n");for (i = 0; i < numtokens; i++)printf("%d:%s\n", i, myargv[i]);execvp(myargv[0], myargv);return 0;}
功能:将输入字符串当做系统命令执行。
运行结果:
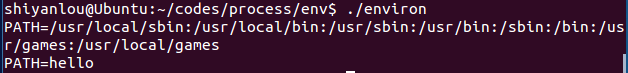
environ.c
程序代码:
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>int main(void){printf("PATH=%s\n", getenv("PATH"));setenv("PATH", "hello", 1);printf("PATH=%s\n", getenv("PATH"));#if 0printf("PATH=%s\n", getenv("PATH"));setenv("PATH", "hellohello", 0);printf("PATH=%s\n", getenv("PATH"));printf("MY_VER=%s\n", getenv("MY_VER"));setenv("MY_VER", "1.1", 0);printf("MY_VER=%s\n", getenv("MY_VER"));#endifreturn 0;}
运行效果:
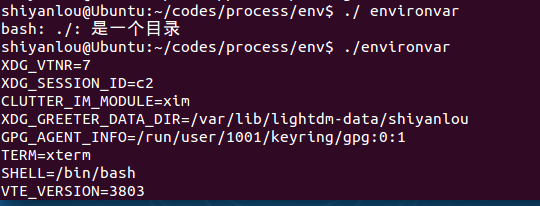
environvar.c
运行代码:
#include <stdio.h>int main(void){extern char **environ;int i;for(i = 0; environ[i] != NULL; i++)printf("%s\n", environ[i]);return 0;}
功能:打印环境变量。
运行效果:
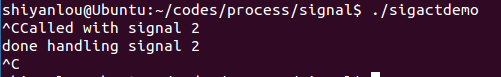
sigactdemo.c
程序代码:
#include <stdio.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <signal.h>#define INPUTLEN 100void inthandler();int main(){struct sigaction newhandler;sigset_t blocked;char x[INPUTLEN];newhandler.sa_handler = inthandler;//新的信号处理函数效果与signal()类似newhandler.sa_flags = SA_RESTART|SA_NODEFER|SA_RESETHAND;//设置信号处理相关操作sigemptyset(&blocked); //将blocked信号集初始化,并清空。sigaddset(&blocked, SIGQUIT);//将SIGQUIT信号加入参数blocked信号集。newhandler.sa_mask = blocked;//暂时将block信号阻塞if (sigaction(SIGINT, &newhandler, NULL) == -1)perror("sigaction");elsewhile (1) {fgets(x, INPUTLEN, stdin);printf("input: %s", x);}return 0;}void inthandler(int s){printf("Called with signal %d\n", s);sleep(s * 4);printf("done handling signal %d\n", s);}
sigation结构体:
struct sigaction {void (*sa_handler)(int);void (*sa_sigaction)(int, siginfo_t *, void *);sigset_t sa_mask;int sa_flags;void (*sa_restorer)(void);}
- sa_handler此参数和signal()的参数handler相同,代表新的信号处理函数,其他意义请参考signal()。
- sa_mask 指定在信号处理程序执行过程中,哪些信号应当被阻塞。默认当前信号本身被阻塞。
- sa_restorer 已过时,POSIX不支持它,不应再使用。
- sa_flags 用来设置信号处理的其他相关操作,下列的数值可用。
- sa_flags还可以设置其他标志:
- SA_RESETHAND:当调用信号处理函数时,将信号的处理函数重置为缺省值SIG_DFL
- SA_RESTART:如果信号中断了进程的某个系统调用,则系统自动启动该系统调用
- SA_NODEFER :一般情况下, 当信号处理函数运行时,内核将阻塞该给定信号。但是如果设置了 SA_NODEFER标记, 那么在该信号处理函数运行时,内核将不会阻塞该信号
运行效果:
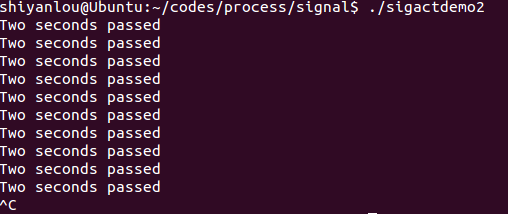
sigactdemo2.c
#include <unistd.h>#include <signal.h>#include <stdio.h>void sig_alrm( int signo ){/*do nothing*/}unsigned int mysleep(unsigned int nsecs){struct sigaction newact, oldact;unsigned int unslept;newact.sa_handler = sig_alrm;//设置处理函数sigemptyset( &newact.sa_mask );//清空newact的阻塞信号集newact.sa_flags = 0;//设置信号处理的其它操作为空sigaction( SIGALRM, &newact, &oldact );//显式取消阻塞信号alarm( nsecs );//设置闹钟pause();unslept = alarm ( 0 );//取消闹钟,并返回剩余时间sigaction( SIGALRM, &oldact, NULL );return unslept;}int main( void ){while( 1 ){mysleep( 2 );printf( "Two seconds passed\n" );}return 0;}
运行效果:
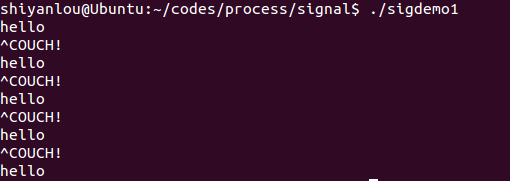
sigdemo1.c
#include <stdio.h>#include <signal.h>void f(int);int main(){int i;signal( SIGINT, f );//改变键盘ctril+C处理函数for(i=0; i<5; i++ ){printf("hello\n");sleep(2);}return 0;}void f(int signum){printf("OUCH!\n");}
运行效果:
sigdemo2.c
#include <stdio.h>#include <signal.h>main(){signal( SIGINT, SIG_IGN );//设置忽略Ctrl+C中断信号。printf("you can't stop me!\n");while( 1 ){sleep(1);printf("haha\n");}}
运行效果:

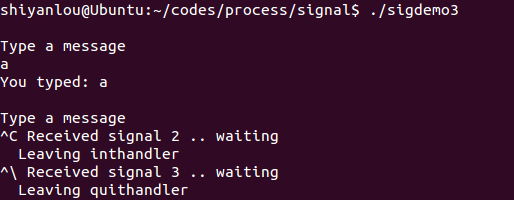
sigdemo3.c
程序代码:
#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>#include <signal.h>#include <unistd.h>#define INPUTLEN 100int main(int argc, char *argv[]){void inthandler(int);void quithandler(int);char input[INPUTLEN];int nchars;signal(SIGINT, inthandler);//^Csignal(SIGQUIT, quithandler);//^\do {printf("\nType a message\n");nchars = read(0, input, (INPUTLEN - 1));if (nchars == -1)perror("read returned an error");else {input[nchars] = '\0';printf("You typed: %s", input);}}while (strncmp(input, "quit", 4) != 0);return 0;}void inthandler(int s){printf(" Received signal %d .. waiting\n", s);sleep(2);printf(" Leaving inthandler \n");}void quithandler(int s){printf(" Received signal %d .. waiting\n", s);sleep(3);printf(" Leaving quithandler \n");}
运行效果:
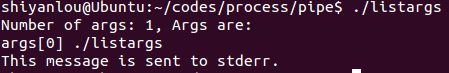
listargs.c
程序代码
#include <stdio.h>main( int ac, char *av[] ){int i;printf("Number of args: %d, Args are:\n", ac);//ac为传入参数的个数。for(i=0;i<ac;i++)printf("args[%d] %s\n", i, av[i]);fprintf(stderr,"This message is sent to stderr.\n");}
运行效果:

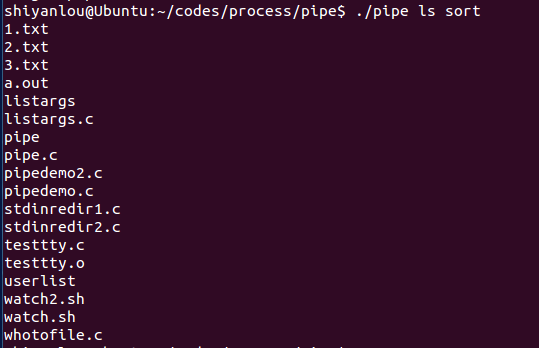
pipe.c
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <unistd.h>#define oops(m,x) { perror(m); exit(x); }int main(int ac, char **av){int thepipe[2],newfd,pid;//判断管道输入格式是否正确if ( ac != 3 ){fprintf(stderr, "usage: pipe cmd1 cmd2\n");exit(1);}//管道建立失败,输出错误信息if ( pipe( thepipe ) == -1 )oops("Cannot get a pipe", 1);//子进程创建失败,输出错误信息if ( (pid = fork()) == -1 )oops("Cannot fork", 2);if ( pid > 0 ){close(thepipe[1]);if ( dup2(thepipe[0], 0) == -1 )//将thepipe[0]重定向到标准输入oops("could not redirect stdin",3);close(thepipe[0]);execlp( av[2], av[2], NULL);//试着执行av[2]中的命令oops(av[2], 4);}close(thepipe[0]);if ( dup2(thepipe[1], 1) == -1 )//将thepipe[1]重定向到标准输出oops("could not redirect stdout", 4);close(thepipe[1]);execlp( av[1], av[1], NULL);//试着执行av[1]中的命令oops(av[1], 5);}
pipe():
头文件 #include<unistd.h>
定义函数: int pipe(int filedes[2]);
函数说明: pipe()会建立管道,并将文件描述词由参数filedes数组返回。
filedes[0]为管道里的读取端
filedes[1]则为管道的写入端。返回值: 若成功则返回零,否则返回-1,错误原因存于errno中。
execlp():
从PATH 环境变量所指的目录中查找符合参数file的文件名,找到后便执行该文件,然后将第二个以后的参数当做该文件的argv[0]、argv[1]……,最后一个参数必须用空指针(NULL)作结束。如果用常数0来表示一个空指针,则必须将它强制转换为一个字符指针,否则将它解释为整形参数,如果一个整形数的长度与char * 的长度不同,那么exec函数的实际参数就将出错。如果函数调用成功,进程自己的执行代码就会变成加载程序的代码,execlp()后边的代码也就不会执行了。
返回值:
如果执行成功则函数不会返回,执行失败则直接返回-1,失败原因存于errno 中。
运行效果:
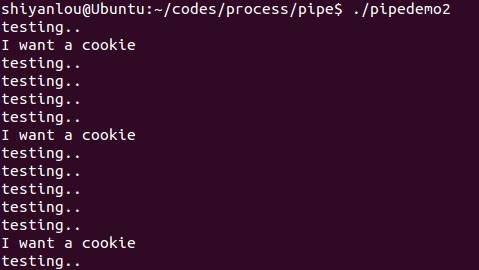
pipedemo2.c
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>#include <unistd.h>#define CHILD_MESS "I want a cookie\n"#define PAR_MESS "testing..\n"#define oops(m,x) { perror(m); exit(x); }main(){int pipefd[2];int len;char buf[BUFSIZ];int read_len;if ( pipe( pipefd ) == -1 )oops("cannot get a pipe", 1);switch( fork() ){case -1:oops("cannot fork", 2);case 0:len = strlen(CHILD_MESS);while ( 1 ){if (write( pipefd[1], CHILD_MESS, len) != len )oops("write", 3);sleep(5);}default:len = strlen( PAR_MESS );while ( 1 ){if ( write( pipefd[1], PAR_MESS, len)!=len )oops("write", 4);sleep(1);read_len = read( pipefd[0], buf, BUFSIZ );if ( read_len <= 0 )break;write( 1 , buf, read_len );}}}
运行结果:
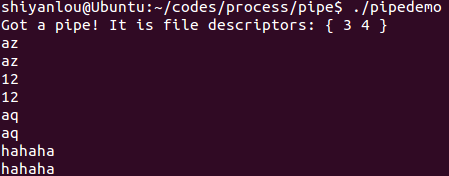
pipedemo.c
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>#include <unistd.h>int main(){int len, i, apipe[2];char buf[BUFSIZ];if ( pipe ( apipe ) == -1 ){perror("could not make pipe");exit(1);}printf("Got a pipe! It is file descriptors: { %d %d }\n",apipe[0], apipe[1]);while ( fgets(buf, BUFSIZ, stdin) ){len = strlen( buf );if ( write( apipe[1], buf, len) != len ){perror("writing to pipe");break;}for ( i = 0 ; i<len ; i++ )buf[i] = 'X' ;len = read( apipe[0], buf, BUFSIZ ) ;if ( len == -1 ){perror("reading from pipe");break;}if ( write( 1 , buf, len ) != len ){ //将标准输入写到标准输出perror("writing to stdout");break;}}}
运行结果:
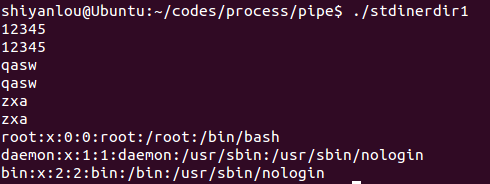
stdinerdir1.c
程序代码:
#include <stdio.h>#include <fcntl.h>int main(){int fd ;char line[100];fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );close(0);fd = open("/etc/passwd", O_RDONLY);//读取passwd文件到stdinif ( fd != 0 ){fprintf(stderr,"Could not open data as fd 0\n");exit(1);}fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );}
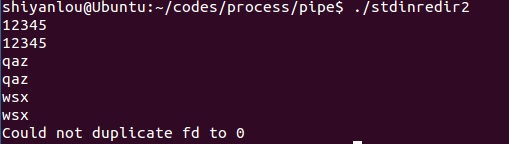
stdinredir2.c
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <fcntl.h>//#define CLOSE_DUP//#define USE_DUP2main(){int fd ;int newfd;char line[100];fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );fd = open("data", O_RDONLY);#ifdef CLOSE_DUPclose(0);newfd = dup(fd);#elsenewfd = dup2(fd,0); //将fd重定向到标准输入#endifif ( newfd != 0 ){fprintf(stderr,"Could not duplicate fd to 0\n");exit(1);}close(fd);fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );}
运行效果:(没有data文件,无法获取文件描述符,重定向失败)
testtty.c
#include <unistd.h>int main(){char *buf = "abcde\n";write(0, buf, 6);//将字符串写到标准输入}
运行效果:

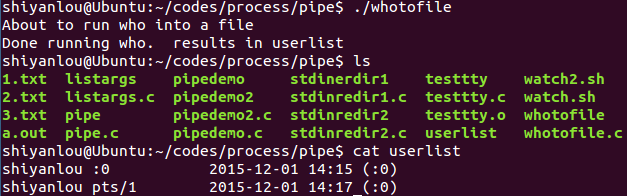
whotofile.c
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <unistd.h>int main(){int pid ;int fd;printf("About to run who into a file\n");if( (pid = fork() ) == -1 ){perror("fork"); exit(1);}if ( pid == 0 ){close(1); /* close, */fd = creat( "userlist", 0644 ); /* then open *///以写的方式创建一个文件,因为前面关闭了文件描述符1,所以fd=1,为标准输出。execlp( "who", "who", NULL ); /* and run *///执行who命令,输出到文件表描述符1中。perror("execlp");exit(1);}if ( pid != 0 ){wait(NULL);printf("Done running who. results in userlist\n");}return 0;}
运行结果:
consumer.c
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>#include <fcntl.h>#include <limits.h>#include <sys/types.h>#include <sys/stat.h>#define FIFO_NAME "/tmp/myfifo"#define BUFFER_SIZE PIPE_BUFint main(){int pipe_fd;int res;int open_mode = O_RDONLY;char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE + 1];int bytes = 0;memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));//数组置零printf("Process %d opeining FIFO O_RDONLY \n", getpid());pipe_fd = open(FIFO_NAME, open_mode);printf("Process %d result %d\n", getpid(), pipe_fd);if (pipe_fd != -1) {do {res = read(pipe_fd, buffer, BUFFER_SIZE);bytes += res;} while (res > 0);close(pipe_fd);} else {exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}printf("Process %d finished, %d bytes read\n", getpid(), bytes);exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);}
运行效果:
文件不存在,打开失败。
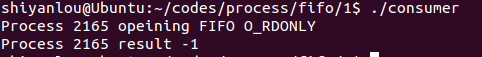
文件存在读取成功。

producer.c
程序代码:
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>#include <fcntl.h>#include <limits.h>#include <sys/types.h>#include <sys/stat.h>#define FIFO_NAME "/tmp/myfifo"#define BUFFER_SIZE PIPE_BUF#define TEN_MEG (1024 * 1024 * 10)int main(){int pipe_fd;int res;int open_mode = O_WRONLY;int bytes = 0;char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE + 1];//判断文件是否存在。if (access(FIFO_NAME, F_OK) == -1) {res = mkfifo(FIFO_NAME, 0777);//创建一个FIFO文件if (res != 0) {fprintf(stderr, "Could not create fifo %s \n",FIFO_NAME);exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}}printf("Process %d opening FIFO O_WRONLY\n", getpid());pipe_fd = open(FIFO_NAME, open_mode);printf("Process %d result %d\n", getpid(), pipe_fd);if (pipe_fd != -1) {while (bytes < TEN_MEG) {res = write(pipe_fd, buffer, BUFFER_SIZE);if (res == -1) {fprintf(stderr, "Write error on pipe\n");exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}bytes += res;}close(pipe_fd);} else {exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}printf("Process %d finish\n", getpid());exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);}
access():
判断是否具有存取文件的权限
相关函数
stat,open,chmod,chown,setuid,setgid
表头文件include<unistd.h>
定义函数
int access(const char * pathname, int mode);
函数说明
access()会检查是否可以读/写某一已存在的文件。参数mode有几种情况组合:
R_OK,W_OK,X_OK 和F_OK。
R_OK,W_OK与X_OK用来检查文件是否具有读取、写入和执行的权限。
F_OK则是用来判断该文件是否存在。由于access()只作权限的核查,并不理会文件形态或文件内容,因此,如果一目录表示为“可写入”,表示可以在该目录中建立新文件等操作,而非意味此目录可以被当做文件处理。例如,你会发现DOS的文件都具有“可执行”权限,但用execve()执行时则会失败。
返回值
若所有欲查核的权限都通过了检查则返回0值,表示成功,只要有一权限被禁止则返回-1。
mkfifo()
mkfifo函数的作用是在文件系统中创建一个文件(该文件之前必须不存在),该文件用于提供FIFO功能,即命名管道。前边讲的那些管道都没有名字,因此它们被称为匿名管道,或简称管道。
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>int mkfifo( const char *pathname, mode_t mode );
mkfifo函数需要两个参数,第一个参数(pathname)是将要在文件系统中创建的一个专用文件。第二个参数(mode)用来规定FIFO的读写权限。Mkfifo函数如果调用成功的话,返回值为0;如果调用失败返回值为-1。
运行结果:
遇到的问题及解决
1.sigactdemo.c中的inthandler中的参数int s是怎么传进去的?
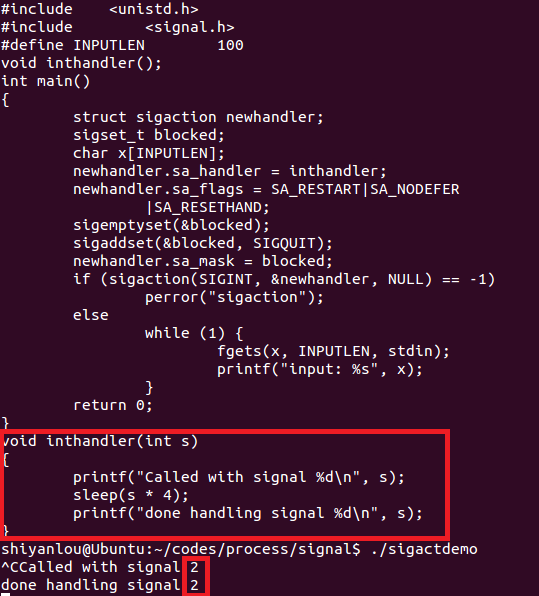
解决方法:在博客园提问。
inthandler被当做函数指针传给了newhandler.sa_handler
后面调用int sigaction(int signum,const struct sigaction *act ,struct sigaction *oldact);
它的第一个参数signum指定的信号编号就是用来设置这个信号的处理函数的。信号SIGINT序号为2。
命令kill -l可以查看各信号的序号。
2.运行testpp时遇到段错误(核心已转储)。
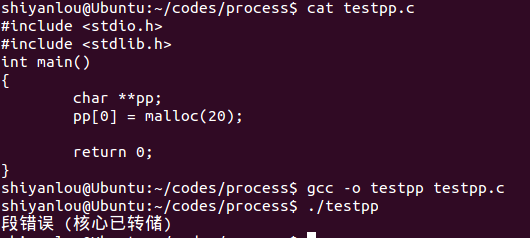
解决方法:在博客园提问。
二维数组越界申请空间。
将代码改为
pp=malloc(20);
即可编译成功。
参考资料
《深入理解计算机系统》第8章异常控制流
进程&信号&管道实践学习记录的更多相关文章
- PHP 中的多进程使用,进程通信、进程信号等详解
多进程环境要求 Linux 系统 php-cli 模式 pcntl 扩展 或 swoole 扩展 pcntl 扩展 <?php $str = "hello world!" . ...
- linux 进程通信 管道
1. 管道概述及相关API应用 1.1 管道相关的关键概念 管道是Linux支持的最初Unix IPC形式之一,具有以下特点: 管道是半双工的,数据只能向一个方向流动:需要双方通信时,需要建立起两个管 ...
- 进程信号的未决状态(pending status)
这两天看了apue有关进程信号的部分,觉得未决状态这个词很是不一般,呵呵.一开始当我看到这个词,我不理解,什么意思呢,读了好几遍.不知道是书里面讲的晦涩难懂,还是脑子越来越不行了,就是没有搞明白.后来 ...
- Linux 两组信号对比(关闭和停止进程信号)
之前看信号的时候,没有太注意不同信号的对比.今天再次看到的时候,突然感觉对一些信号,非常相似,乃至非常容易混淆.今天周末就抽空总结一下. 一.关闭进程信号 常见的4中关闭进程信号是SIGKILL,SI ...
- 【C】——sigprocmask 阻塞进程信号
1.有时候不希望在接到信号时就立即停止当前执行,去处理信号,同时也不希望忽略该信号,而是延时一段时间去调用信号处理函数.这种情况是通过阻塞信号实现的. 2.信号阻塞和忽略信号的区别. 阻塞的概念和忽略 ...
- 进程通信方式-管道pipe
管道是两个进程间进行单向通信的机制.因为管道传递数据的单向性,管道又称之为半双工管道. 1.数据只能从一个进程流向另一个进程(其中一个写管道,另一个读管道):如果要进行全双工通信,需要建立两个管道. ...
- linux进程的管道通信
linux进程的管道通信 要求 编程实现进程的管道通信,掌握管道通信的同步和互斥机制. 相关函数 pipe管道 指用于连接一个读进程和一个写进程以实现他们之间通信的一个共享文件,又名pipe文件.向管 ...
- Cobalt Strike系列教程第四章:文件/进程管理与键盘记录
Cobalt Strike系列教程分享如约而至,新关注的小伙伴可以先回顾一下前面的内容: Cobalt Strike系列教程第一章:简介与安装 Cobalt Strike系列教程第二章:Beacon详 ...
- 进程-IPC 管道 (一)
详见:https://github.com/ZhangzheBJUT/linux/blob/master/IPC(%E4%B8%80).md 一 IPC 概述 进程间通信就是在不同进程之间传播或交换信 ...
随机推荐
- MYSQL的慢查询两个方法
对于排查问题找出性能瓶颈来说,最容易发现并解决的问题就是MYSQL的慢查询以及没有得用索引的查询. ================================================== ...
- log4net资料收集
Log4net 日志使用介绍 http://www.cnblogs.com/jys509/p/4699813.html log4net Tutorial http://www.codeproject. ...
- Effective Java 09 Always override hashCode when you override equals
Failure to do so will result in a violation of the general contract for Object.hashCode, which will ...
- docker-3 基础命令
创建镜像 创建镜像的方法有三种: 基于已有的容器创建 基于本地模板导入 基于dockerfile 基于已有的容器创建 主要使用docker commit 命令,命令格式: docker commit ...
- Java SWT 做计算器。
java -- swt - - 计算器 环境搭建 安装java.eclipse.以及对应的swt插件. 开始工程 建立工程: 在java下建立一个在其他 —- WindowsBuilder — ...
- 用shell脚本批量修改文件后缀名
早上本想将一些照片上传到相册中,但是由于所有照片的扩展名都是JPG而不是小写的jpg,因此造成了“格式不正确”而不能上传照片.此刻就产生了这样一个问题:使用shell脚本如何批量将所有文件的扩展名JP ...
- USACO section1.1 Broken Necklace
/* ID: vincent63 LANG: C TASK: beads */ #include <stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include&l ...
- Listview的点击事件
上篇文章总结了如何自定义listview的显示内容,然而listview不能只是提供显示功能,还必须能够点击它显示一些东西: listView.setOnItemClickListener(new O ...
- CentOS安装Hypernetes相关问题解法
1.手动编译hyper缺少libdevmapper.h git clone -b v2_02_103 https://git.fedorahosted.org/git/lvm2.git /usr/lo ...
- 最小生成树 kruskal hdu 5723 Abandoned country
题目链接:hdu 5723 Abandoned country 题目大意:N个点,M条边:先构成一棵最小生成树,然后这个最小生成树上求任意两点之间的路径长度和,并求期望 /************** ...
