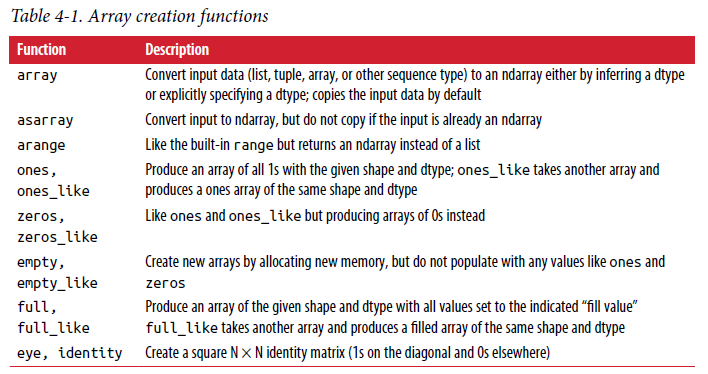
Python Numpy-基础教程
1. 为什么要学习numpy?
- numpy可以对整个array进行复杂计算,而不需要像list一样写loop
- 它的
ndarray提供了快速的基于array的数值运算 - memory-efficient container that provides fast numerical operations
- 学习pandas的必备
证明numpy比list优秀:
import numpy as np
my_arr = np.arange(1000000)
my_list = list(range(1000000))
%time for _ in range(10): my_arr2 = my_arr * 2 # Wall time: 25 ms
%time for _ in range(10): my_list2 = [x * 2 for x in my_list] # Wall time: 933 ms
2. Numpy基本用法
2.1. 创建np.ndarry
注意: numpy只能装同类型的数据
# Method 1: np.array()
## 1-D
a = np.array([1,2,3])
a.shape
a.dtype # int32, boolean, string, float
a.ndim
## 2-D
a = np.array([[0,1,2],[3,4,5]])
# Method 2:使用函数(arange, linspace, ones, zeros, eys, diag,random)创建
a = np.arange(10)
a = np.linspace(0,1,6, endpoint=False)
a = np.ones((3,3))
a = np.zeros((3,3))
a = np.eye(3)
a = np.diag(np.array([1,2,3,4]))
a = np.triu(np.ones((3,3)),1)
# Method 3: Random values
a = np.random.rand(4) # unifomr in [0,1]
a = np.random.randn(4) # Gaussian
np.random.seed(1234)
2.2. Indexing and Slicing
- Slice create a view on the original array(change will affect original array)
# 1-D
a = np.arange(10)
a[5], a[-1] # Index: 4,9
a[5:8] = 12 # Slice: all 5-8 is set as 12
arr[5:8].copy() # Slice without view
# 2-D
a = np.ones((3,3))
a[2] # second row
a[2].copy() # slice without view
a[0][2] # special value
a[:2]
a[:2, 1:] = 0
Boolean Index
names = np.array(['Bob', 'Joe', 'Will', 'Bob', 'Will', 'Joe', 'Joe'])
data = np.random.randn(7, 4)
data[names == 'Bob'] # select a row from data based on the if names equals Bob(boolean value)
data[~(names == 'Bob')] # not equal to Bob
data[(names == 'Bob') | (names == 'Will')] #e qual to Bob and Will
data[data<0] = 0
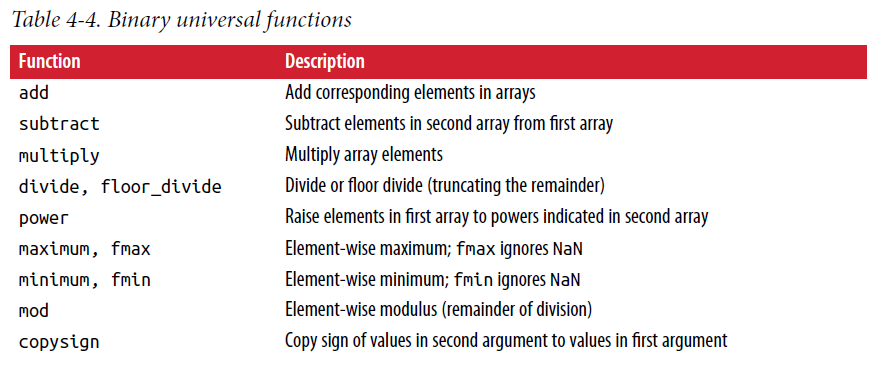
2.3. Universal Functions
a function that performs element-wise operations on data in ndarrays
a = np.arange(10)
b = np.arange(2,12)
# single
a + 1
a*2
np.sqrt(a)
np.exp(a)
np.sin(a)
# binary
a>b # return boolean ndarray
np.array_equal(a,b) # eual?
np.maximum(a, b) # find max value between each pair values
np.logical_or(a,b) # Attentions, a and b must be boolean array

2.4. Array-oriented
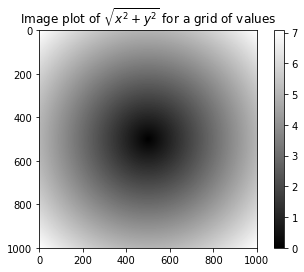
- Probelm 1
we wished to evaluate the function `sqrt(x^2 + y^2)`` across a regular grid of values.
The np.meshgrid function takes two 1D arrays and produces two 2D matrices corresponding to all pairs of (x, y) in the two arrays:
points = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.01) # 1000 equally spaced points
xs, ys = np.meshgrid(points, points)
z = np.sqrt(xs ** 2 + ys ** 2)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
plt.imshow(z, cmap=plt.cm.gray); plt.colorbar()
plt.title("Image plot of $\sqrt{x^2 + y^2}$ for a grid of values")
- Problem 2
we have two array(x,y) and one boolean array, we want select x if boolean=True, while select y if boolean=False->np.where()
xarr = np.array([1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5])
yarr = np.array([2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4, 2.5])
cond = np.array([True, False, True, True, False])
result = np.where(cond, xarr, yarr) # array([1.1, 2.2, 1.3, 1.4, 2.5])
np.where的后面两个参数可以是array,数字. 是数字的话就可以做替换工作,比如我们将随机生成的array中大于0的替换为2,小于0的替换为-2
arr = np.random.randn(4, 4)
np.where(arr > 0, 2, -2) # 大于0改为2,小于0改为-2
np.where(arr > 0, 2, arr) # 大于0改为2,小于0不变
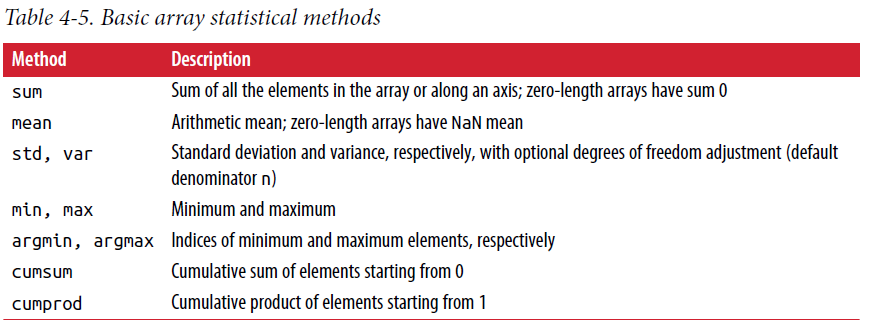
2.5. Mathematical Operations
a = np.random.randn(5, 4)
np.mean(a)
np.mean(a, axis = 1)
np.sum(a)
a.consum()
a.sort()
a.argmax() # index of maxium
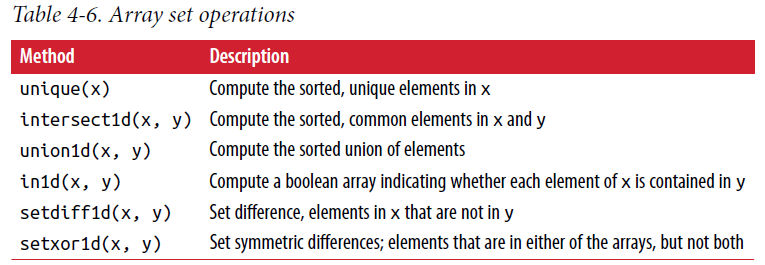
names = np.array(['Bob', 'Joe', 'Will', 'Bob', 'Will', 'Joe', 'Joe'])
np.unique(names)
sorted(set(names))
Python Numpy-基础教程的更多相关文章
- Python Numpy基础教程
Python Numpy基础教程 本文是一个关于Python numpy的基础学习教程,其中,Python版本为Python 3.x 什么是Numpy Numpy = Numerical + Pyth ...
- Python数据分析基础教程
Python数据分析基础教程(第2版)(高清版)PDF 百度网盘 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1_FsReTBCaL_PzKhM0o6l0g 提取码:nkhw 复制这段内容后 ...
- Python机器学习基础教程-第2章-监督学习之决策树集成
前言 本系列教程基本就是摘抄<Python机器学习基础教程>中的例子内容. 为了便于跟踪和学习,本系列教程在Github上提供了jupyter notebook 版本: Github仓库: ...
- Python机器学习基础教程-第2章-监督学习之决策树
前言 本系列教程基本就是摘抄<Python机器学习基础教程>中的例子内容. 为了便于跟踪和学习,本系列教程在Github上提供了jupyter notebook 版本: Github仓库: ...
- Python机器学习基础教程-第2章-监督学习之线性模型
前言 本系列教程基本就是摘抄<Python机器学习基础教程>中的例子内容. 为了便于跟踪和学习,本系列教程在Github上提供了jupyter notebook 版本: Github仓库: ...
- Python机器学习基础教程-第2章-监督学习之K近邻
前言 本系列教程基本就是摘抄<Python机器学习基础教程>中的例子内容. 为了便于跟踪和学习,本系列教程在Github上提供了jupyter notebook 版本: Github仓库: ...
- Python机器学习基础教程-第1章-鸢尾花的例子KNN
前言 本系列教程基本就是摘抄<Python机器学习基础教程>中的例子内容. 为了便于跟踪和学习,本系列教程在Github上提供了jupyter notebook 版本: Github仓库: ...
- 小白必看Python视频基础教程
Python的排名从去年开始就借助人工智能持续上升,现在它已经成为了第一名.Python的火热,也带动了工程师们的就业热.可能你也想通过学习加入这个炙手可热的行业,可以看看Python视频基础教程,小 ...
- Python机器学习基础教程
介绍 本系列教程基本就是搬运<Python机器学习基础教程>里面的实例. Github仓库 使用 jupyternote book 是一个很好的快速构建代码的选择,本系列教程都能在我的Gi ...
- Python 3基础教程1-环境安装和运行环境
本系列开始介绍Python3的基础教程,为什么要选中Python 3呢?之前呢,学Python 2,看过笨方法学Python,学了不到一个礼拜,就开始用Python写Selenium脚本.最近看到一些 ...
随机推荐
- MAC 地址(单播、组播、广播地址分类)
简介 一个制造商在生产制造网卡之前,必须先向 IEEE 注册,以获取到一个长度为 24bit 的厂商代码,也称为 OUI(Organizationally-Unique Identifier).制造商 ...
- spark之JDBC开发(实战)
一.概述 Spark Core.Spark-SQL与Spark-Streaming都是相同的,编写好之后打成jar包使用spark-submit命令提交到集群运行应用$SPARK_HOME/bin#. ...
- angularjs_百度地图API_根据经纬度定位_示例
百度API--Demo地址: http://lbsyun.baidu.com/jsdemo.htm#i8_4 本例是在angular.js使用的百度地图根据经纬度定位的API:(正常的页面写法基本 ...
- WPF 获取DataGrid 控件选中的单元格信息
获取 DataGrid 选中的单元格的信息DataGridCellInfo cell_Info = this.studentTable.SelectedCells[0]; studentTableIt ...
- C# 输出字符串到文本文件中
写个博客记录下,方便以后使用: public class WriteHelper { public static void WriteFile(object data) { try { string ...
- Tomcat日志设定
1 Tomcat 日志概述 Tomcat 日志信息分 为 两 类 : 一.是运行中的日志,它主要 记录 运行的一些信息,尤其是一些异常 错误 日志信息 .二.是 访问 日志信息,它 记录 的 访 ...
- 买or不买?如何测试博彩公司赔率是否合理?
世界杯期间,烧烤店.酒吧都热闹起来了,柔柔我的朋友圈也热闹起来了,有酱紫的: 还有酱紫的: 然后还有酱紫的: 酱紫的: 当然天台也是一如既然的热闹: 似乎人人都在输钱,那真正的赢家在哪里呢?博彩业的真 ...
- Maven(七)Eclipse使用Maven命令
由于没有mvn compile (其余命令类似) 可以点解上面框中选项手动输入compile
- undefined 与 xx is not defined 的区别
undefined 与 xx is not defined 的区别 1. undefined 表示是javascript中的一种数据类型,当被定义的变量没有被赋值或者某个被调用的函数没有定义返回值时候 ...
- H5和PC实现点击复制当前文字的功能,兼容ios,安卓
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
