Tensorflow数学运算
一、Tensor 之间的运算规则
1) 相同大小 Tensor 之间的任何算术运算都会将运算应用到元素级
2) 不同大小 Tensor(要求dimension 0 必须相同) 之间的运算叫做广播(broadcasting)
3) Tensor 与 Scalar(0维 tensor) 间的算术运算会将那个标量值传播到各个元素
4) Note:TensorFLow 在进行数学运算时,一定要求各个 Tensor 数据类型一致
二、算术操作(+,-,*,/,Mod)
(1)tensor-tensor操作(element-wise)
大多数运算符都进行了重载操作,使我们可以快速使用 (+ - * /) 等,但是有一点不好的是使用重载操作符后就不能为每个操作命名了。
#两个tensor 运算
#运算规则:element-wise。即c[i,j,..,k]=a[i,j,..,k] op b[i,j,..,k]
ts1=tf.constant(1.0,shape=[2,2])
ts2=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2,2]))
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
#以ts1和ts2为例: #(1)加法+
ts_add1=tf.add(ts1,ts2,name=None)
ts_add2=ts1+ts2 #二者等价
#(2)减法-
ts_sub1=tf.subtract(ts1,ts2,name=None)
ts_sub2=ts1-ts2 #二者等价
#(3)乘法*
ts_mul1=tf.multiply(ts1,ts2,name=None)
ts_mul2=ts1*ts2
#(4)除法/
ts_div1=tf.divide(ts1,ts2,name=None)
ts_div2=tf.div(ts1,ts2,name=None) #div 支持 broadcasting(即shape可不同)
ts_div3=ts1/ts2
#另外还有truediv(x,y) x,y类型必须一致,floor_div等。
(2)tensor-scalar操作
#scalar-tensor操作。
#对tensor中所有element执行同样的操作(+,-,*,/)
#加法
ts_add=ts1+2
#减法
ts_sub=ts1-2
#乘法
ts_mul=ts1*2
#除法
ts_div=ts1/2
(3)基本数学函数
# 算术操作符:+ - * / %
tf.add(x, y, name=None) # 加法(支持 broadcasting)
tf.subtract(x, y, name=None) # 减法
tf.multiply(x, y, name=None) # 乘法
tf.divide(x, y, name=None) # 浮点除法, 返回浮点数(python3 除法)
tf.mod(x, y, name=None) # 取余 # 幂指对数操作符:^ ^2 ^0.5 e^ ln
tf.pow(x, y, name=None) # 幂次方
tf.square(x, name=None) # 平方
tf.sqrt(x, name=None) # 开根号,必须传入浮点数或复数
tf.exp(x, name=None) # 计算 e 的次方
tf.log(x, name=None) # 以 e 为底,必须传入浮点数或复数 # 取符号、负、倒数、绝对值、近似、两数中较大/小的
tf.negative(x, name=None) # 取负(y = -x).
tf.sign(x, name=None) # 返回 x 的符号
tf.reciprocal(x, name=None) # 取倒数
tf.abs(x, name=None) # 求绝对值
tf.round(x, name=None) # 四舍五入
tf.ceil(x, name=None) # 向上取整
tf.floor(x, name=None) # 向下取整
tf.rint(x, name=None) # 取最接近的整数
tf.maximum(x, y, name=None) # 返回两tensor中的最大值 (x > y ? x : y)
tf.minimum(x, y, name=None) # 返回两tensor中的最小值 (x < y ? x : y) # 三角函数和反三角函数
tf.cos(x, name=None)
tf.sin(x, name=None)
tf.tan(x, name=None)
tf.acos(x, name=None)
tf.asin(x, name=None)
tf.atan(x, name=None) # 其它
tf.div(x, y, name=None) # python 2.7 除法, x/y-->int or x/float(y)-->float
tf.truediv(x, y, name=None) # python 3 除法, x/y-->float
tf.floordiv(x, y, name=None) # python 3 除法, x//y-->int
tf.realdiv(x, y, name=None)
tf.truncatediv(x, y, name=None)
tf.floor_div(x, y, name=None)
tf.truncatemod(x, y, name=None)
tf.floormod(x, y, name=None)
tf.cross(x, y, name=None)
tf.add_n(inputs, name=None) # inputs: A list of Tensor objects, each with same shape and type
tf.squared_difference(x, y, name=None)
三、tensor大小 比较
#(1)相等equal (element-wise)
tf.equal(x, y, name=None) #Returns the truth value of (x == y) element-wise. #(2)不等not_equal
tf.not_equal(x, y, name=None) #(3)其他比较
tf.less(x, y, name=None)
tf.less_equal(x, y, name=None)
tf.greater(x, y, name=None)
tf.greater_equal(x, y, name=None)
四、恒等映射
#恒等映射
tf.identity(input, name=None) #Return a tensor with the same shape and contents as the input tensor or value.
五、类型转化
tf.cast(x, dtype, name=None)
#Casts a tensor to a new type. #For example:
# tensor `a` is [1.8, 2.2], dtype=tf.float
#tf.cast(a, tf.int32) ==> [1, 2] dtype=tf.int32
六、矩阵运算相关数学函数
# 矩阵乘法(tensors of rank >= 2)
tf.matmul(a, b, transpose_a=False, transpose_b=False, adjoint_a=False, adjoint_b=False, a_is_sparse=False, b_is_sparse=False, name=None) # 转置,可以通过指定 perm=[1, 0] 来进行轴变换
tf.transpose(a, perm=None, name='transpose') # 在张量 a 的最后两个维度上进行转置
tf.matrix_transpose(a, name='matrix_transpose')
# Matrix with two batch dimensions, x.shape is [1, 2, 3, 4]
# tf.matrix_transpose(x) is shape [1, 2, 4, 3] # 求矩阵的迹
tf.trace(x, name=None) # 计算方阵行列式的值
tf.matrix_determinant(input, name=None) # 求解可逆方阵的逆,input 必须为浮点型或复数
tf.matrix_inverse(input, adjoint=None, name=None) # 奇异值分解
tf.svd(tensor, full_matrices=False, compute_uv=True, name=None) # QR 分解
tf.qr(input, full_matrices=None, name=None) # 求张量的范数(默认2)
tf.norm(tensor, ord='euclidean', axis=None, keep_dims=False, name=None) # 构建一个单位矩阵, 或者 batch 个矩阵,batch_shape 以 list 的形式传入
tf.eye(num_rows, num_columns=None, batch_shape=None, dtype=tf.float32, name=None)
# Construct one identity matrix.
tf.eye(2)
==> [[1., 0.],
[0., 1.]] # Construct a batch of 3 identity matricies, each 2 x 2.
# batch_identity[i, :, :] is a 2 x 2 identity matrix, i = 0, 1, 2.
batch_identity = tf.eye(2, batch_shape=[3]) # Construct one 2 x 3 "identity" matrix
tf.eye(2, num_columns=3)
==> [[ 1., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0.]] # 构建一个对角矩阵,rank = 2*rank(diagonal)
tf.diag(diagonal, name=None)
# 'diagonal' is [1, 2, 3, 4]
tf.diag(diagonal) ==> [[1, 0, 0, 0]
[0, 2, 0, 0]
[0, 0, 3, 0]
[0, 0, 0, 4]] # 其它
tf.diag_part
tf.matrix_diag
tf.matrix_diag_part
tf.matrix_band_part
tf.matrix_set_diag
tf.cholesky
tf.cholesky_solve
tf.matrix_solve
tf.matrix_triangular_solve
tf.matrix_solve_ls
tf.self_adjoint_eig
tf.self_adjoint_eigvals
七、Reduction:reduce various dimensions of a tensor
# 计算输入 tensor 所有元素的和,或者计算指定的轴所有元素的和
tf.reduce_sum(input_tensor, axis=None, keep_dims=False, name=None)
# 'x' is [[1, 1, 1]
# [1, 1, 1]]
tf.reduce_sum(x) ==> 6
tf.reduce_sum(x, 0) ==> [2, 2, 2]
tf.reduce_sum(x, 1) ==> [3, 3]
tf.reduce_sum(x, 1, keep_dims=True) ==> [[3], [3]] # 维度不缩减
tf.reduce_sum(x, [0, 1]) ==> 6 # 计算输入 tensor 所有元素的均值/最大值/最小值/积/逻辑与/或
# 或者计算指定的轴所有元素的均值/最大值/最小值/积/逻辑与/或(just like reduce_sum)
tf.reduce_mean(input_tensor, axis=None, keep_dims=False, name=None)
tf.reduce_max(input_tensor, axis=None, keep_dims=False, name=None)
tf.reduce_min(input_tensor, axis=None, keep_dims=False, name=None)
tf.reduce_prod(input_tensor, axis=None, keep_dims=False, name=None)
tf.reduce_all(input_tensor, axis=None, keep_dims=False, name=None) # 全部满足条件
tf.reduce_any(input_tensor, axis=None, keep_dims=False, name=None) #至少有一个满足条件 -------------------------------------------
# 分界线以上和 Numpy 中相应的用法完全一致
------------------------------------------- # inputs 为一 list, 计算 list 中所有元素的累计和,
# tf.add(x, y, name=None)只能计算两个元素的和,此函数相当于扩展了其功能
tf.accumulate_n(inputs, shape=None, tensor_dtype=None, name=None) # Computes log(sum(exp(elements across dimensions of a tensor)))
tf.reduce_logsumexp(input_tensor, axis=None, keep_dims=False, name=None) # Computes number of nonzero elements across dimensions of a tensor
tf.count_nonzero(input_tensor, axis=None, keep_dims=False, name=None)
八、Scan:perform scans (running totals) across one axis of a tensor
# Compute the cumulative sum of the tensor x along axis
tf.cumsum(x, axis=0, exclusive=False, reverse=False, name=None)
# Eg:
tf.cumsum([a, b, c]) # => [a, a + b, a + b + c]
tf.cumsum([a, b, c], exclusive=True) # => [0, a, a + b]
tf.cumsum([a, b, c], reverse=True) # => [a + b + c, b + c, c]
tf.cumsum([a, b, c], exclusive=True, reverse=True) # => [b + c, c, 0] # Compute the cumulative product of the tensor x along axis
tf.cumprod(x, axis=0, exclusive=False, reverse=False, name=None)
九、Segmentation
沿着第一维(x 轴)根据 segment_ids(list)分割好相应的数据后再进行操作
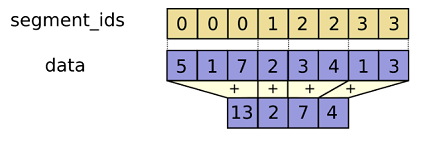
# Computes the sum/mean/max/min/prod along segments of a tensor
tf.segment_sum(data, segment_ids, name=None)
# Eg:
m = tf.constant([5,1,7,2,3,4,1,3])
s_id = [0,0,0,1,2,2,3,3]
s.run(tf.segment_sum(m, segment_ids=s_id))
>array([13, 2, 7, 4], dtype=int32) tf.segment_mean(data, segment_ids, name=None)
tf.segment_max(data, segment_ids, name=None)
tf.segment_min(data, segment_ids, name=None)
tf.segment_prod(data, segment_ids, name=None) # 其它
tf.unsorted_segment_sum
tf.sparse_segment_sum
tf.sparse_segment_mean
tf.sparse_segment_sqrt_n
十、 序列比较与索引提取
# 比较两个 list 或者 string 的不同,并返回不同的值和索引
tf.setdiff1d(x, y, index_dtype=tf.int32, name=None) # 返回 x 中的唯一值所组成的tensor 和原 tensor 中元素在现 tensor 中的索引
tf.unique(x, out_idx=None, name=None) # x if condition else y, condition 为 bool 类型的,可用tf.equal()等来表示
# x 和 y 的形状和数据类型必须一致
tf.where(condition, x=None, y=None, name=None) # 返回沿着坐标轴方向的最大/最小值的索引
tf.argmax(input, axis=None, name=None, output_type=tf.int64)
tf.argmin(input, axis=None, name=None, output_type=tf.int64) # x 的值当作 y 的索引,range(len(x)) 索引当作 y 的值
# y[x[i]] = i for i in [0, 1, ..., len(x) - 1]
tf.invert_permutation(x, name=None) # 其它
tf.edit_distance
参考文献:
https://blog.csdn.net/zywvvd/article/details/78593618
https://blog.csdn.net/vcvycy/article/details/78489378
Tensorflow数学运算的更多相关文章
- Java学习笔记 06 数字格式化及数学运算
一.数字格式化 DecimalFormat类 >>DecimalFormat是NumberFormat的子类,用于格式化十进制数,可以将一些数字格式化为整数.浮点数.百分数等.通过使用该类 ...
- 从零开始学习Node.js例子四 多页面实现数学运算 续二(client端和server端)
1.server端 支持数学运算的服务器,服务器的返回结果用json对象表示. math-server.js //通过监听3000端口使其作为Math Wizard的后台程序 var math = r ...
- Linux shell 变量 数学 运算
Abstract : 1) Linux shell 中使用 let , [ ] ,(( )) 三种运算符操作 shell 变量进行简单的基本运算: 2)Linux shell 中使用 expr 与 ...
- 认真学习shell的第一天-数学运算
shell中的数学运算有三种方式: (1)let,用let的时候,变量名称前不用添加$ (2)[],[]中变量可使用也可不使用$ (3)(())变量名之前必须添加$
- 6 让我们的C#程序开始做点数学运算
请相信我你只需要懂得最基本的数学运算,就可以从事大多数的软件项目的开发工作.千万不要一提编程,就让数学把你吓跑了.大多数的程序开发人员从事的编程工作是应用系统的开发.这些系统的绝大多数功能,只需要最基 ...
- shell编程之数学运算
shell数学运算支持整数运算的四种方法 1.let命令 no1=4; no2=5; let result=no1+no2 2.[]操作符 result=$[ no1 + no2] 3.(())操作符 ...
- 玩转变量、环境变量以及数学运算(shell)
变量和环境变量 var=value 给变量赋值,输出语句:$ echo $var或者是$ echo ${var},记住中间有个空格 例如:name="coffee" age ...
- css3 calc():css简单的数学运算-加减乘除
css3 calc():css简单的数学运算–加减乘除 多好的东西啊,不用js,一个css就解决了. .box{ border:1px solid #ddd; width:calc(100% - 10 ...
- Linux Shell 数学运算
Linux Shell 数学运算 在Linux中直接使用数学运算符进行数学运算往往得不到我们想要的计算结果.要在Shell中进行数学运算,我们需要借助点小手段.目前,Linux Shell中进行数学运 ...
随机推荐
- Mysql存储
BEGIN # 统计视频使用的模板数 UPDATE VideoTemplate vt INNER JOIN ( SELECT TemplateId, COUNT(TemplateId) AS Tota ...
- Go小爬虫测试
package main import ( "fmt" "io/ioutil" "log" "net/http" ) t ...
- 16.python-I/O模型
一.事件驱动模型1.什么是事件驱动模型:本身是一种编程范式,这里程序的执行是由外部事件来决定的.它的特点是包含一个事件循环,当外部事件发生时使用回调机制来触发相应的处理.常见的编程范式(单线程)同步以 ...
- 渗透测试学习 二、Windows基础
系统目录 服务 端口 注册表 黑客常用DOS命令(在拿到shell时会用到) 一. 系统目录 Windows目录 系统的安装目录 System32àconfigàSAM文件 是用户密码的 ...
- uva 202
#include <iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> # ...
- win10连接宽带,拨号提示错误720:不能建立到远程计算机的连接,解决方法
使用账号密码登录时,一直报720错误.解决方法是卸载以下IP驱动.卸载之后重新连接就正常了.亲测有效
- win10刻录光盘失败,一直显示有准备好写入到光盘中的文件
这是因为前面刻录留下的缓存导致的 解决方法是,删除系统刻录缓存文件 刻录缓存路径大概在以下位置(其中ase那个地方需要修改,改成自己的登录用户账号名即可) C:\Users\ase\AppData\L ...
- 18.25 JLink调试程序步骤
S3C2440开发板启动时候选择NandFlash启动,然后输入如下命令: r /*复位cpu*/ h ...
- 华为4K机顶盒EC6108V9U从原联通更换为电信的IPTV账号成功经验
4K设备直接在淘宝上买30块钱升级4K机顶盒,i视视手机app控制电视和手机投屏 硬件设备:EC6108V9U由X省联通更换为四川电信 采坑经验: 1.要从现有的机顶盒获取mac地址.stbid.ip ...
- RK3399/NanoPC-T4开发板低级格式化SD卡,恢复SD卡和TF卡 方法
恢复SD卡和TF卡 方法:Windows下运行:HDDLLF.4.40.exe执行Low-Level format然后拔插,重新插在win10下提示格式化,则执行格式化操作,即可恢复. 应用场合:使用 ...
