Zip文件格式
Overview
This document describes the on-disk structure of a PKZip (Zip) file. The documentation currently only describes the file layout format and meta information but does not address the actual compression or encryption of the file data itself. This documentation also does not discuss Zip archives that span multiple files in great detail. This documentation was created using the official documentation provided by PKWare Inc.
General structure
Each Zip file is structured in the following manner:
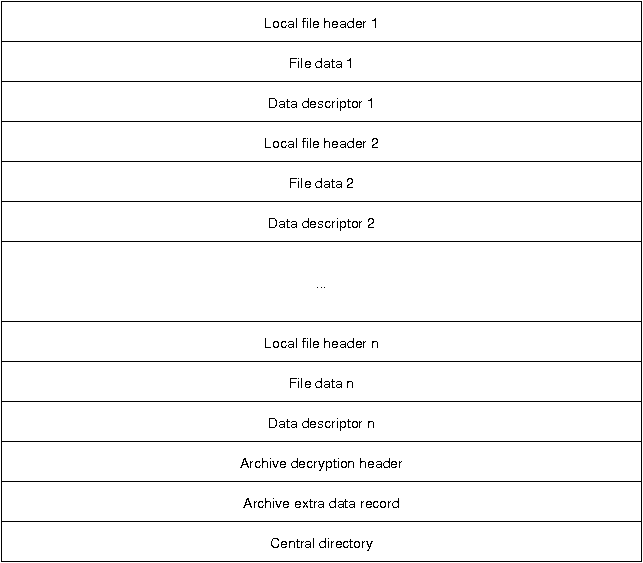
The archive consists of a series of local file descriptors, each containing a local file header, the actual compressed and/or encrypted data, as well as an optional data descriptor. Whether a data descriptor exists or not depends on a flag in the local file header.
Following the file descriptors is the archive decryption header, which only exists in PKZip file version 6.2 or greater. This header is only present if the central directory is encrypted and contains information about the encryption specification. The archive extra data record is also only for file of version 6.2 or greater and is not present in all Zip files. It is used in to support the encryption or compression of the central directory.
The central directory summarizes the local file descriptors and carries additional information regarding file attributes, file comments, location of the local headers, and multi-file archive information.
Local file headers
Each local file header has the following structure:
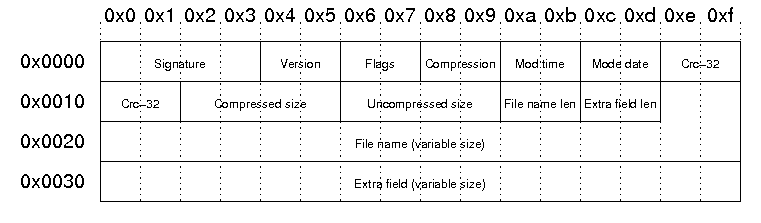
| Signature | The signature of the local file header. This is always '\x50\x4b\x03\x04'. |
| Version | PKZip version needed to extract |
| Flags | General purpose bit flag: Bit 00: encrypted file Bit 01: compression option Bit 02: compression option Bit 03: data descriptor Bit 04: enhanced deflation Bit 05: compressed patched data Bit 06: strong encryption Bit 07-10: unused Bit 11: language encoding Bit 12: reserved Bit 13: mask header values Bit 14-15: reserved |
| Compression method | 00: no compression 01: shrunk 02: reduced with compression factor 1 03: reduced with compression factor 2 04: reduced with compression factor 3 05: reduced with compression factor 4 06: imploded 07: reserved 08: deflated 09: enhanced deflated 10: PKWare DCL imploded 11: reserved 12: compressed using BZIP2 13: reserved 14: LZMA 15-17: reserved 18: compressed using IBM TERSE 19: IBM LZ77 z 98: PPMd version I, Rev 1 |
| File modification time | stored in standard MS-DOS format: Bits 00-04: seconds divided by 2 Bits 05-10: minute Bits 11-15: hour |
| File modification date | stored in standard MS-DOS format: Bits 00-04: day Bits 05-08: month Bits 09-15: years from 1980 |
| Crc-32 checksum | value computed over file data by CRC-32 algorithm with 'magic number' 0xdebb20e3 (little endian) |
| Compressed size | if archive is in ZIP64 format, this filed is 0xffffffff and the length is stored in the extra field |
| Uncompressed size | if archive is in ZIP64 format, this filed is 0xffffffff and the length is stored in the extra field |
| File name length | the length of the file name field below |
| Extra field length | the length of the extra field below |
| File name | the name of the file including an optional relative path. All slashes in the path should be forward slashes '/'. |
| Extra field | Used to store additional information. The field consistes of a sequence of header and data pairs, where the header has a 2 byte identifier and a 2 byte data size field. |
Example
Our sample zip file starts with a local file header:
00000000 50 4b 03 04 14 00 00 00 08 00 1c 7d 4b 35 a6 e1 |PK.........}K5..| 00000010 90 7d 45 00 00 00 4a 00 00 00 05 00 15 00 66 69 |.}E...J.......fi| 00000020 6c 65 31 55 54 09 00 03 c7 48 2d 45 c7 48 2d 45 |le1UT....H-E.H-E| 00000030 55 78 04 00 f5 01 f5 01 0b c9 c8 2c 56 00 a2 92 |Ux.........,V...|
This results in the following fields and field values:
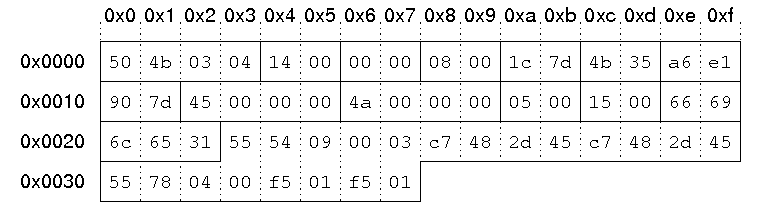
| Signature | '\x50\x4b\x03\x04'. |
| Version | 0x14 = 20 -> 2.0 |
| Flags | no flags |
| Compression method | 08: deflated |
| File modification time | 0x7d1c = 0111110100011100 hour = (01111)10100011100 = 15 minute = 01111(101000)11100 = 40 second = 01111101000(11100) = 28 = 56 seconds 15:40:56 |
| File modification date | 0x354b = 0011010101001011 year = (0011010)101001011 = 26 month = 0011010(1010)01011 = 10 day = 00110101010(01011) = 11 10/11/2006 |
| Crc-32 checksum | 0x7d90e1a6 |
| Compressed size | 0x45 = 69 bytes |
| Uncompressed size | 0x4a = 74 bytes |
| File name length | 5 bytes |
| Extra field length | 21 bytes |
| File name | "file1" |
| Extra field | id 0x5455: extended timestamp, size: 9 bytes Id 0x7855: Info-ZIP UNIX, size: 4 bytes |
Data descriptor
The data descriptor is only present if bit 3 of the bit flag field is set. In this case, the CRC-32, compressed size, and uncompressed size fields in the local header are set to zero. The data descriptor field is byte aligned and immediately follows the file data. The structure is as follows:

The example file does not contain a data descriptor.
Archive decryption header
This header is used to support the Central Directory Encryption Feature. It is present when the central directory is encrypted. The format of this data record is identical to the Decryption header record preceding compressed file data.
Archive extra data record
This header is used to support the Central Directory Encryption Feature. When present, this record immediately precedes the central directory data structure. The size of this data record will be included in the Size of the Central Directory field in the End of Central Directory record. The structure is as follows:
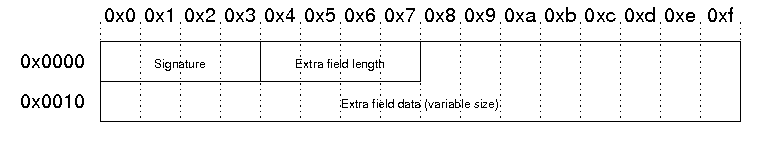
Central directory
The central directory contains more metadata about the files in the archive and also contains encryption information and information about Zip64 (64-bit zip archives) archives. Furthermore, the central directory contains information about archives that span multiple files. The structure of the central directory is as follows:
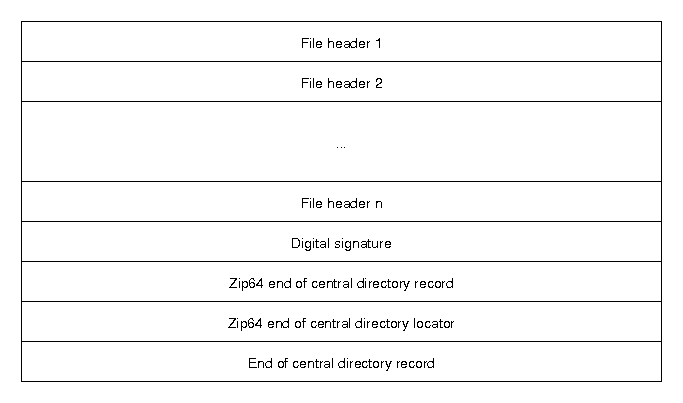
The file headers are similar to the local file headers, but contain some extra information. The Zip64 entries handle the case of a 64-bit Zip archive, and the end of the central directory record contains information about the archive itself.
Central directory file header
The structure of the file header in the central directory is as follows:
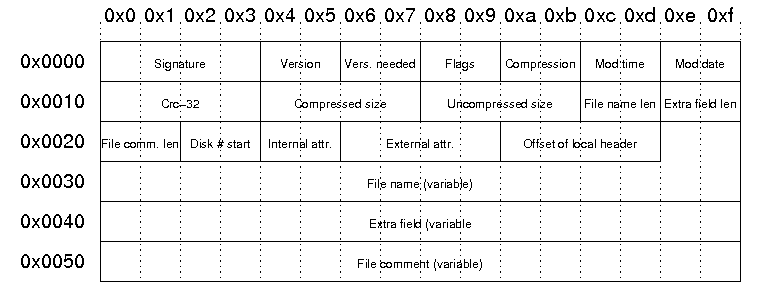
| Signature | The signature of the file header. This is always '\x50\x4b\x01\x02'. |
| Version | Version made by:
upper byte: lower byte: |
| Vers. needed |
PKZip version needed to extract |
| Flags | General purpose bit flag: Bit 00: encrypted file Bit 01: compression option Bit 02: compression option Bit 03: data descriptor Bit 04: enhanced deflation Bit 05: compressed patched data Bit 06: strong encryption Bit 07-10: unused Bit 11: language encoding Bit 12: reserved Bit 13: mask header values Bit 14-15: reserved |
| Compression method | 00: no compression 01: shrunk 02: reduced with compression factor 1 03: reduced with compression factor 2 04: reduced with compression factor 3 05: reduced with compression factor 4 06: imploded 07: reserved 08: deflated 09: enhanced deflated 10: PKWare DCL imploded 11: reserved 12: compressed using BZIP2 13: reserved 14: LZMA 15-17: reserved 18: compressed using IBM TERSE 19: IBM LZ77 z 98: PPMd version I, Rev 1 |
| File modification time | stored in standard MS-DOS format: Bits 00-04: seconds divided by 2 Bits 05-10: minute Bits 11-15: hour |
| File modification date | stored in standard MS-DOS format: Bits 00-04: day Bits 05-08: month Bits 09-15: years from 1980 |
| Crc-32 checksum | value computed over file data by CRC-32 algorithm with 'magic number' 0xdebb20e3 (little endian) |
| Compressed size | if archive is in ZIP64 format, this filed is 0xffffffff and the length is stored in the extra field |
| Uncompressed size | if archive is in ZIP64 format, this filed is 0xffffffff and the length is stored in the extra field |
| File name length | the length of the file name field below |
| Extra field length | the length of the extra field below |
| File comm. len | the length of the file comment |
| Disk # start | the number of the disk on which this file exists |
| Internal attr. |
Internal file attributes: |
| External attr. | External file attributes: host-system dependent |
| Offset of local header | Relative offset of local header. This is the offset of where to find the corresponding local file header from the start of the first disk. |
| File name | the name of the file including an optional relative path. All slashes in the path should be forward slashes '/'. |
| Extra field | Used to store additional information. The field consistes of a sequence of header and data pairs, where the header has a 2 byte identifier and a 2 byte data size field. |
| File comment | An optional comment for the file. |
Example:
The corresponding file header from our local file header example above starts at byte 0x9a2 in the example file:
000009a0 28 f0 50 4b 01 02 17 03 14 00 00 00 08 00 1c 7d |(.PK...........}| 000009b0 4b 35 a6 e1 90 7d 45 00 00 00 4a 00 00 00 05 00 |K5...}E...J.....| 000009c0 0d 00 1c 00 00 00 01 00 00 00 a4 81 00 00 00 00 |................| 000009d0 66 69 6c 65 31 55 54 05 00 03 c7 48 2d 45 55 78 |file1UT....H-EUx| 000009e0 00 00 74 68 69 73 20 69 73 20 61 20 63 6f 6d 6d |..this is a comm| 000009f0 65 6e 74 20 66 6f 72 20 66 69 6c 65 20 31 50 4b |ent for file 1PK|
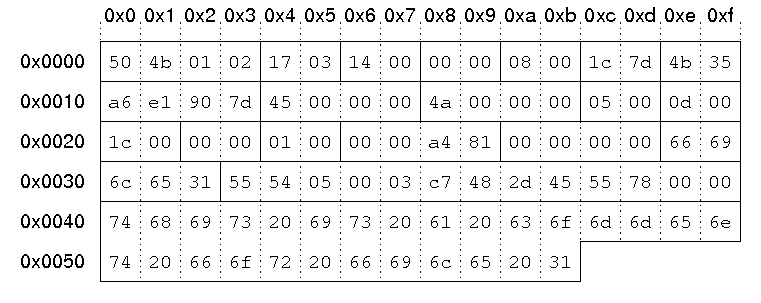
| Signature | '\x50\x4b\x01\x02'. |
| Version | 0x0317 upper byte: 03 -> UNIX lower byte: 23 -> 2.3 |
| Version needed | 0x14 = 20 -> 2.0 |
| Flags | no flags |
| Compression method | 08: deflated |
| File modification time | 0x7d1c = 0111110100011100 hour = (01111)10100011100 = 15 minute = 01111(101000)11100 = 40 second = 01111101000(11100) = 28 = 56 seconds 15:40:56 |
| File modification date | 0x354b = 0011010101001011 year = (0011010)101001011 = 26 month = 0011010(1010)01011 = 10 day = 00110101010(01011) = 11 10/11/2006 |
| Crc-32 checksum | 0x7d90e1a6 |
| Compressed size | 0x45 = 69 bytes |
| Uncompressed size | 0x4a = 74 bytes |
| File name length | 5 bytes |
| Extra field length | 13 bytes |
| File comment length | 28 bytes |
| Disk # start | 0 |
| Internal attributes | Bit 0 set: ASCII/text file |
| External attributes | 0x81a40000 |
| Offset of local header | 0 |
| File name | "file1" |
| Extra field | id 0x5455: extended timestamp, size: 5 bytes Id 0x7855: Info-ZIP UNIX, size: 0 bytes |
| File comment | "this is a comment for file 1" |
End of central directory record
The structure of the end of central directory record is as follows:
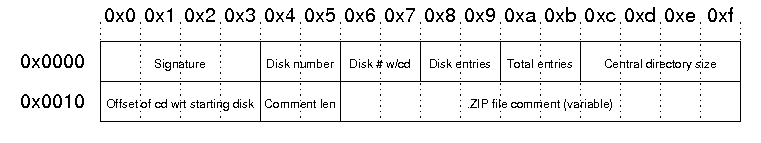
| Signature | The signature of end of central directory record. This is always '\x50\x4b\x05\x06'. |
| Disk Number | The number of this disk (containing the end of central directory record) |
| Disk # w/cd | Number of the disk on which the central directory starts |
| Disk entries | The number of central directory entries on this disk |
| Total entries | Total number of entries in the central directory. |
| Central directory size | Size of the central directory in bytes |
| Offset of cd wrt to starting disk | Offset of the start of the central directory on the disk on which the central directory starts |
| Comment len | The length of the following comment field |
| ZIP file comment | Optional comment for the Zip file |
Example:
The end of central directory in out example file starts at byte 0xb36:
00000b30 6f 6d 6d 65 6e 74 50 4b 05 06 00 00 00 00 04 00 |ommentPK........| 00000b40 04 00 94 01 00 00 a2 09 00 00 33 00 74 68 69 73 |..........3.this| 00000b50 20 69 73 20 61 0d 0a 6d 75 6c 74 69 6c 69 6e 65 | is a..multiline| 00000b60 20 63 6f 6d 6d 65 6e 74 20 66 6f 72 20 74 68 65 | comment for the| 00000b70 20 65 6e 74 69 72 65 20 61 72 63 68 69 76 65 | entire archive|
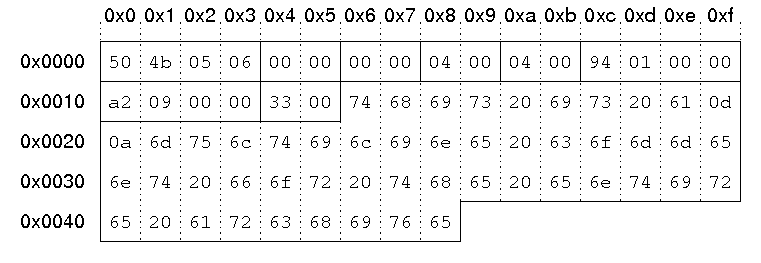
| Signature | '\x50\x4b\x05\x06'. |
| Disk Number | 0 |
| Disk # w/cd | 0 |
| Disk entries | 4 |
| Total entries | 4 |
| Central directory size | 0x194 = 404 bytes |
| Offset of cd wrt to starting disk | byte 0x9a2 = byte 2466 |
| Comment len | 0x33 = 51 bytes |
| ZIP file comment | "this is a multiline comment for the entire archive" |
Zip文件格式的更多相关文章
- 转(zip文件格式说明)
zip文件由三部分组成:压缩的文件内容源数据.压缩的目录源数据.目录结束标识结构 1. 压缩的文件内容源数据: 记录着压缩的所有文件的内容信息,其数据组织结构是对于每个文件都由file header ...
- ZIP压缩算法详细分析及解压实例解释
最近自己实现了一个ZIP压缩数据的解压程序,觉得有必要把ZIP压缩格式进行一下详细总结,数据压缩是一门通信原理和计算机科学都会涉及到的学科,在通信原理中,一般称为信源编码,在计算机科学里,一般称为数据 ...
- 彻底解决mysql中文乱码的办法,修改mysql解压缩版(免安装版或zip版)字符编码
MySQL会出现中文乱码的原因不外乎下列几点:1.server本身设定问题,例如server字符编码还停留在latin12.table的语系设定问题(包含character与collation)3.客 ...
- java-a实现压缩与解压缩(zip、gzip)
zip扮演着归档和压缩两个角色:gzip并不将文件归档,仅只是对单个文件进行压缩,所以,在UNIX平台上,命令tar通常用来创建一个档案文件,然后命令gzip来将档案文件压缩. Java I/O类库还 ...
- ( 解压缩版 免安装版 或 zip版 )如何修改mysql5.6.24 字符编码
1.当我们把zip文件格式解压到指定目录后,并且完成基本环境配置后,打开mysql 5.6.24会发现名为[my-default.ini]的文件.我们用记事本打开该文件会发现并没有[default-c ...
- Java实现文件压缩与解压[zip格式,gzip格式]
Java实现ZIP的解压与压缩功能基本都是使用了Java的多肽和递归技术,可以对单个文件和任意级联文件夹进行压缩和解压,对于一些初学者来说是个很不错的实例. zip扮演着归档和压缩两个角色:gzip并 ...
- liux之我用过的zip解压命令
用途说明 zip文件是一种常用的压缩文件格式,WinZip.WinRar等压缩软件都支持zip文件格式,就连java的jar包也是zip格式 的,Firefox插件xpi文件也是zip格式的.Linu ...
- java基础---->Zip压缩的使用(转)
java中提供了对压缩格式的数据流的读写.它们封装到现成的IO 类中,以提供压缩功能.下面我们开始java中压缩文件的使用. 目录导航: 关于压缩的简要说明 GZIP压缩文件的使用 ZIP压缩文件的使 ...
- 用Python写一款属于自己的 简易zip压缩软件 附完成图(适合初学者)
一.软件描述 用Python tkinter模块写一款属于自己的压缩软件.zip文件格式是通用的文档压缩标准,在ziplib模块中,使用ZipFile来操作zip文件,具有功能:zip压缩功能,zip ...
随机推荐
- 企业搜索引擎开发之连接器connector(二十七)
ChangeQueue类实现ChangeSource接口,声明了拉取下一条Change对象的方法 * A source of {@link Change} objects. * * @since 2. ...
- 机器学习—集成学习(Adaboost)
一.原理部分: 二.sklearn实现: from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier from sklearn.datasets import lo ...
- Java反射API研究(2)——java.lang.reflect详细内容与关系
对于最新的java1.8而言,reflect中接口的结构是这样的: java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedType ...
- solr特点二:Facet(1)
一. Facet 简介 Facet 是 solr 的高级搜索功能之一 , 可以给用户提供更友好的搜索体验 . 在搜索关键字的同时 , 能够按照 Facet 的字段进行分组并统计 . 二. Fa ...
- docker容器日志清理
1.先查看磁盘空间 df -h 2.找到容器的containerId-json.log文件,并清理(治标不治本,log迟早还会大的) 查看各个容器的log文件大小 find /var/lib/dock ...
- PARTITION BY函数
1.PARTITION BY 开窗函数, 使用场景,在合同表里,获取所有房源在最新的合同编号.或者获取每个班级每次考试的第一名. 区别聚合函数:对于每个每个分组返回多行,而聚合函数对于每个分组只返回一 ...
- 在Windows子系统(WSL)中配置开机启动服务
在WSL中跑了一些测试服务 比如 mysql nginx等,但关机后每次都要手动开启甚是吃力,本想着用rc.local来编辑开机启动 ,无奈不支持啊!先看看非WSL环境中是怎么实现的. 在 Ubunt ...
- Luogu1438 无聊的数列(单点查询)&&加强版(区间查询)
题目链接:戳我 线段树中差分和前缀和的应用 其实对于加上等差数列的操作我们可以分成这样三步-- update(1,1,n,l,l,k); if(r>l) update(1,1,n,l+1,r,d ...
- 多线程并行计算数据总和 —— 优化计算思想(多线程去计算)—— C语言demo
多线程计算整型数组数据总和: #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <Windows.h> #includ ...
- 552. Student Attendance Record II
Given a positive integer n, return the number of all possible attendance records with length n, whic ...
