ArrayList相关方法介绍及源码分析
ArrayList简介:
java.util.ArrayList 是我们最常用的一个类,ArrayList 底层是动态数组,读者可以把它理解为数组的实现
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable{
}
如上代码我们可以看到 ArrayList 继承了 AbstractList() 抽象类,并实现了 List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, Serializable 接口
AbstractList :
public abstract class AbstractList<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements List<E> {}
可以看到AbstractList 继承了 AbstractCollection 接口, 并实现了List 接口
AbstractCollection :
public abstract class AbstractCollection<E> implements Collection<E> {}
AbstractCollection 是一个抽象类,实现了Collection 接口,并提供了某些方法的具体实现。
Collection:
Collection 是一个顶级接口,是很多集合类的顶级接口,继承了Iterable ,支持轻量级遍历其中元素
public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E> {}
List :
ArrayList 实现了List接口,List 也是一个和Collection 媲美的顶级接口,继承了Collection 接口
public interface List<E> extends Collection<E> {}
它是许多集合类的父类,
eg:
List list = new ArrayList();
List list2 = new LinkedList();
RandomAccess
RandomAccess 也是一个顶级接口,实现了此接口的类支持随机访问
Cloneable
Cloneable 接口是一个顶级接口,实现了此接口的类支持浅拷贝
Serializable
实现此接口的类支持序列化的功能
类之间的继承关系如图

ArrayList 相关方法介绍
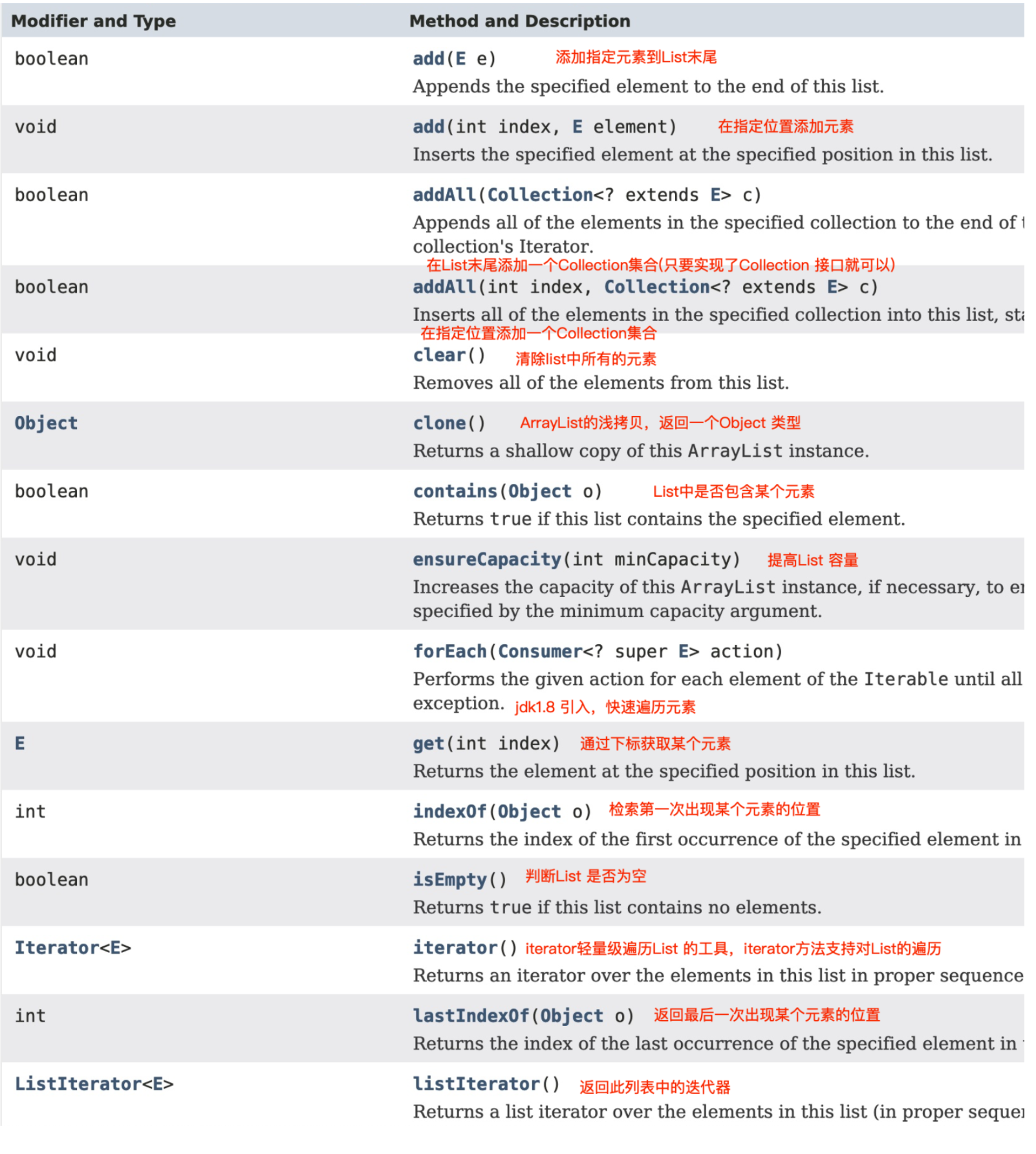
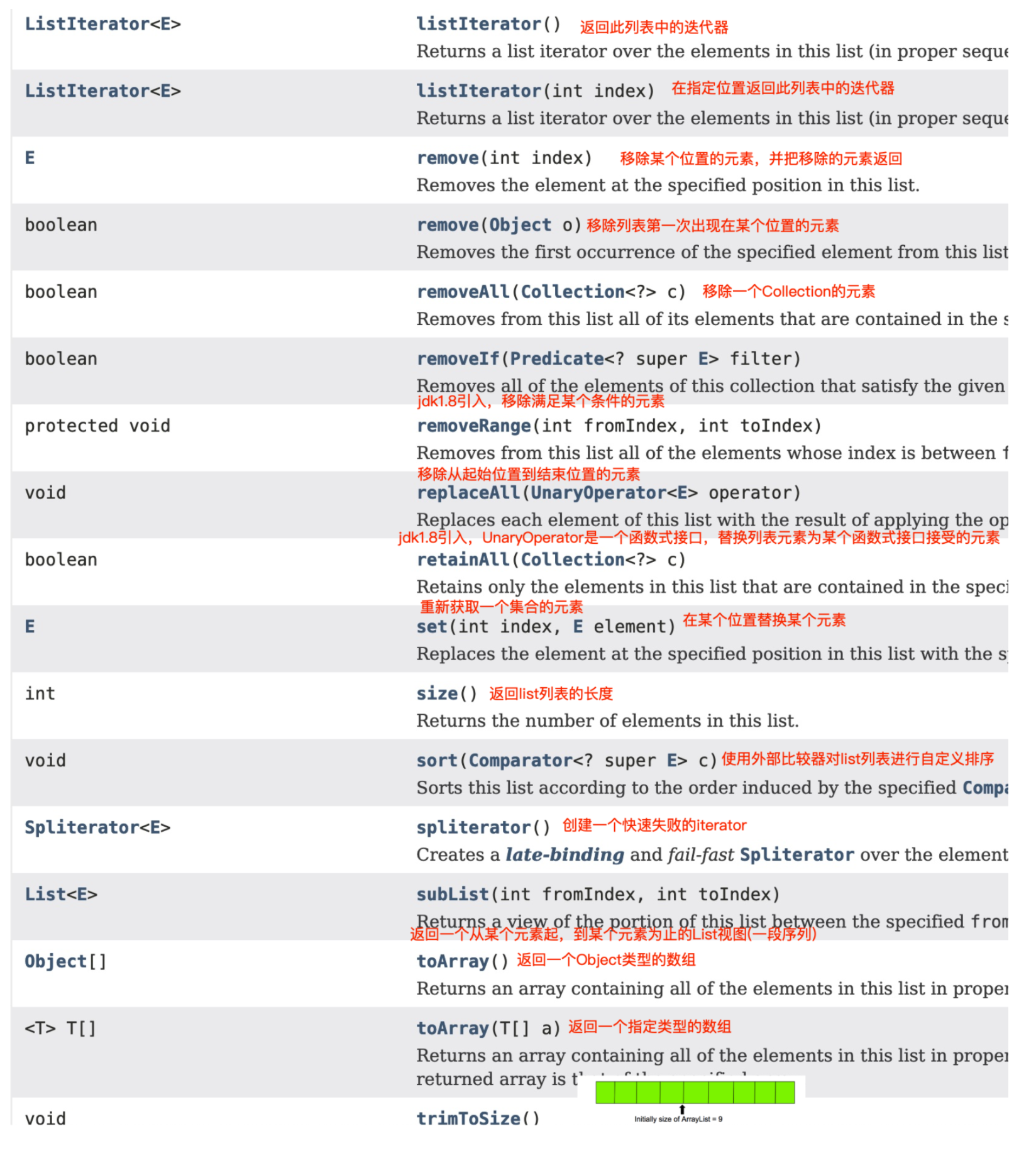
trimToSize()
代码表示
实践才是检验真理最好的方式:
import java.util.*;
/**
* 详述ArrayList 基本用法
*/
public class ArrayListTest {
private static class SortList implements Comparator<String> {
@Override
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
Integer i1 = Integer.valueOf(o1);
Integer i2 = Integer.valueOf(o2);
if(i1 < i2){
return -1;
}else if(i1 == i2){
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
}
// 使用可变参数,能够接受任意个参数
public Set<String> putSet(String...args){
Set<String> sets = new HashSet<>();
for(String str : args){
sets.add(str);
}
return sets;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("111");
list.add("222");
// 在指定位置添加元素
list.add(0,"333");
System.out.println(list);
// 进行外部排序
list.sort(new SortList());
System.out.println(list);
list.clear();
System.out.println(list.size());
// 使用addAll添加元素
ArrayListTest at = new ArrayListTest();
list.addAll(at.putSet("1","2","3"));
Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
// 移除所有元素
it.remove();
}
System.out.println("list是否为空 ? " + list.isEmpty());
list.add("111");
// 在指定位置添加一个set集合
list.addAll(0,at.putSet("1","2","3"));
System.out.println(list);
// 是否包含指定元素
if(list.contains("111")) {
list.remove("111");
}
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(list.indexOf("1"));
// 注意subList()这个方法是左开右闭区间,Java 中很多都是类似的
System.out.println(list.subList(0,3));
// 扩大list的容量
list.ensureCapacity(10);
// 去掉list空闲的容量
list.trimToSize();
// 获取某个特定的元素
System.out.println(list.get(1));
// 创建一个list的双向链表
ListIterator<String> listIterator = list.listIterator();
while(listIterator.hasNext()){
// 移到list的末端
System.out.println(listIterator.next());
}
System.out.println("--------------------------");
while (listIterator.hasPrevious()){
// 移到list的首端
System.out.println(listIterator.previous());
}
// 把list转换为数组
Object[] objects = list.toArray();
System.out.println("objects = " + objects);
}
}
相关方法源码分析
源码的具体分析是根据上面的代码示例得出,因为只看源码好像并不能看懂什么,需要根据具体的代码一步一步debug 进行跟踪
add()方法
解释:添加指定的元素在list的末尾
/**
* 添加指定的元素在list的末尾
*/
// 假设第一次添加的是 "111"
public boolean add(E e) {
// size是0,所以size + 1 传的是1
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1);
// elementData[0] = 111 , size++ = 1
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
// 此方法用来进行list 扩容
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
// 此时elementData 并没有存储元素,为0
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
// 则minCapacity 取默认初始容量和minCapacity 的最大值 (取1 和 10的最大值)
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
// 确保清晰的容量(最小容量与List元素的比较)
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
// 在list中添加了一个元素,所以会导致结构化的修改,"结构化的修改"见下面解释
// 此时minCapacity 为 10
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
// 次数 + 1
// 这个列表被修改结构的次数(比如添加和删除元素)会用modCount表示. 结构化修改是指的是能够
// 改变列表容量的操作,或者其他方式改变它,导致遍历的过程会产生错误的结果。
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
// 10 - 0 > 0 走grow 方法
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
/**
* 增加容量确保容纳足够的元素
*
* 参数传过来的是10
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
// oldCapacity = 0
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// newCapacity = 0
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
// newCapacity - minCapacity = -10
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
// newCapacity = 10
newCapacity = minCapacity;
// MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = 数组分配的最大空间 = 2147483639
// 一般情况下不会比 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE 还要大
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
// 底层还是用的System.arraycopy(), 关于System.arrayCopy() 读者可以参考我的另一篇博客
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
相关常用的基本数据类型包装类的值: Java基本数据类型包装类常用的值
add(int index, E element)
解释:在list中指定位置插入指定的元素,如果当前位置有元素,就移动当前位置的元素
/**
* 在list中指定位置插入指定的元素,如果当前位置有元素,就移动当前位置的元素
* 要插入的位置的后面所有元素的位置向前 + 1
*
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
// 检查 0 这个位置是否越界
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
// 不再赘述,读者可以自行debug
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
// 因为从当前位置插入元素,所以当前位置及后面的元素都会向后移动
// 使用System.arraycopy 进行数组复制
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
// 为当前元素赋值
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
/**
* 为add 和 addall 提供的范围检查, 不符合条件,抛出IndexOutOfBoundsException 异常
*/
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index > size || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
Clear()
解释:移除列表中的所有元素
/**
* 移除list列表中所有的元素,列表会变为空列表在调用此方法后
*
*/
public void clear() {
// 修改次数 + 1
modCount++;
// clear to let GC do its work
// 把每个变量置空,GC进行回收
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
elementData[i] = null;
// 列表的长度变为0
size = 0;
}
这个方法的源码理解起来还是比较简单的
addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
解释: 把一个Collection集合添加到list末尾
/**
* 把一个Collection集合(实现了此接口的类)添加到list的末尾,按着迭代的顺序返回。
* 此操作的行为是如果在此方法调用的过程中修改了Collection(实现了此接口的类)的话,
* 那么这个操作不会成功
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
// 把Collection 转换为 Object[] 数组
Object[] a = c.toArray();
// 数组中有三个元素
int numNew = a.length;
// 因为上面的操作调用了一次list.clear()方法,所以list.size = 0
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
// 一句话解释: 把a 数组中0个位置的元素 复制到 elementData数组中 第size个位置的元素,
// 复制的长度为 numNew
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
// toArray()方法:
/**
* 返回一个数组,包含了所有的元素(从第一个元素到最后一个元素)
* 返回的数组是很"安全的"因为列表没有引用可以维持(换句话说,这个方法必须分配一个新数组)
* 调用者因此可以任意修改返回的数组
* 这个方法是数组 和 集合之间的桥梁
*/
public Object[] toArray() {
return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
iterator(), hasNext(), next()
解释:Iterator方法用于遍历list中的元素,返回一个Itr 的内部类,hasNext()方法用于判断list 中是否还有未遍历的元素,next()方法用于获取下一个元素
/**
* 以适当的顺序返回此列表中元素的迭代器
* 返回的iterator 支持fail-fast 机制
*/
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
/**
* Itr 是一个内部类,实现了Iterator接口,可支持快速遍历
*/
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
// 下一个元素返回的下标
int cursor; // index of next element to return
// 最后一个元素返回的下标, 如果没有返回-1
int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such
// expectedModCount 期望的修改次数,默认是和modCount(修改次数相同,用于iterator判断fail-fast机制)
int expectedModCount = modCount;
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
// 判断遍历的过程中是否触发fail-fast机制
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void remove() {
// 如果lastRet < 0,说明 lastRet 没有被改变,
// 所以应该是没有调用next()就调用了remove()
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) {
Objects.requireNonNull(consumer);
final int size = ArrayList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size) {
return;
}
final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) {
consumer.accept((E) elementData[i++]);
}
cursor = i;
lastRet = i - 1;
checkForComodification();
}
// 如果修改次数不满足预期修改次数的话,抛出异常
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
addAll(int index,Collection<? extends E> c)
解释:在某个位置添加Collection集合
/**
* 在指定的位置下标插入一个Collection集合
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
// 需要移动的元素个数
int numMoved = size - index;
if (numMoved > 0)
// 第一次数组复制,从elementData中的index位置开始,复制到index + numNew位置上,复制numMoved个元素
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew,
numMoved);
// 第二次数组复制,从a 数组中的第0个位置开始,复制到elementData第index位置上你,复制numNew个元素
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
contains(Object o)
解释:判断list列表是否包含某个元素
/**
* 返回true,如果这个列表包含指定的元素
* 更进一步来说,当且仅当list包含至少一个元素的情况下,返回true
*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
/**
* 返回列表中第一次出现指定元素的下标值,如果不包含指定元素,则返回-1。
* 更进一步来说,返回最小的索引当(o == null ? get(i) == null : o.equals(get(i)))的时候
* 或者返回-1 没有此下标值
*
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
// 如果o这个对象等于null,就判断elementData中是否有空元素,如果有,返回
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
// 如果不为null,返回这个值的存储位置
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
remove(Object o)
解释:移除list中的某个元素
/**
* 如果存在,则移除list中某个第一次出现的元素。如果这个list不包含指定元素,就不会改变
*
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
//快速移除某个指定元素
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/*
* 私有的移除方法,并且不返回被移除的元素,这个源码比较简单
*/
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
}
indexOf(Object o)
解释:检索某个元素的位置
此源码和contains(Object o)中调用的indexOf 源码相同
subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
解释:返回list列表的一个片段
/**
* 返回list列表中的一部分视图(相当于list片段),[fromIndex,toIndex),如果fromIndex 和
* toIndex 相同的话,表明这个list为空,这个返回的list被返回,所以在list中并没有结构的改变
* 这个返回的list片段支持所有的list操作
*/
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
// subList 范围检查
subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size);
return new SubList(this, 0, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
static void subListRangeCheck(int fromIndex, int toIndex, int size) {
if (fromIndex < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("fromIndex = " + fromIndex);
if (toIndex > size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("toIndex = " + toIndex);
if (fromIndex > toIndex)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromIndex(" + fromIndex +
") > toIndex(" + toIndex + ")");
}
private class SubList extends AbstractList<E> implements RandomAccess {
private final AbstractList<E> parent;
private final int parentOffset;
private final int offset;
int size;
SubList(AbstractList<E> parent,
int offset, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
this.parent = parent;
this.parentOffset = fromIndex;
this.offset = offset + fromIndex;
this.size = toIndex - fromIndex;
this.modCount = ArrayList.this.modCount;
}
}
ensureCapacity(int minCapacity)
解释:扩大list的容量
/**
* 增加ArrayList实例的容量,如果必须的话,确保它能持有最小容量的元素
*/
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
int minExpand = (elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA)
// any size if not default element table
? 0
// larger than default for default empty table. It's already
// supposed to be at default size.
: DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
if (minCapacity > minExpand) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
}
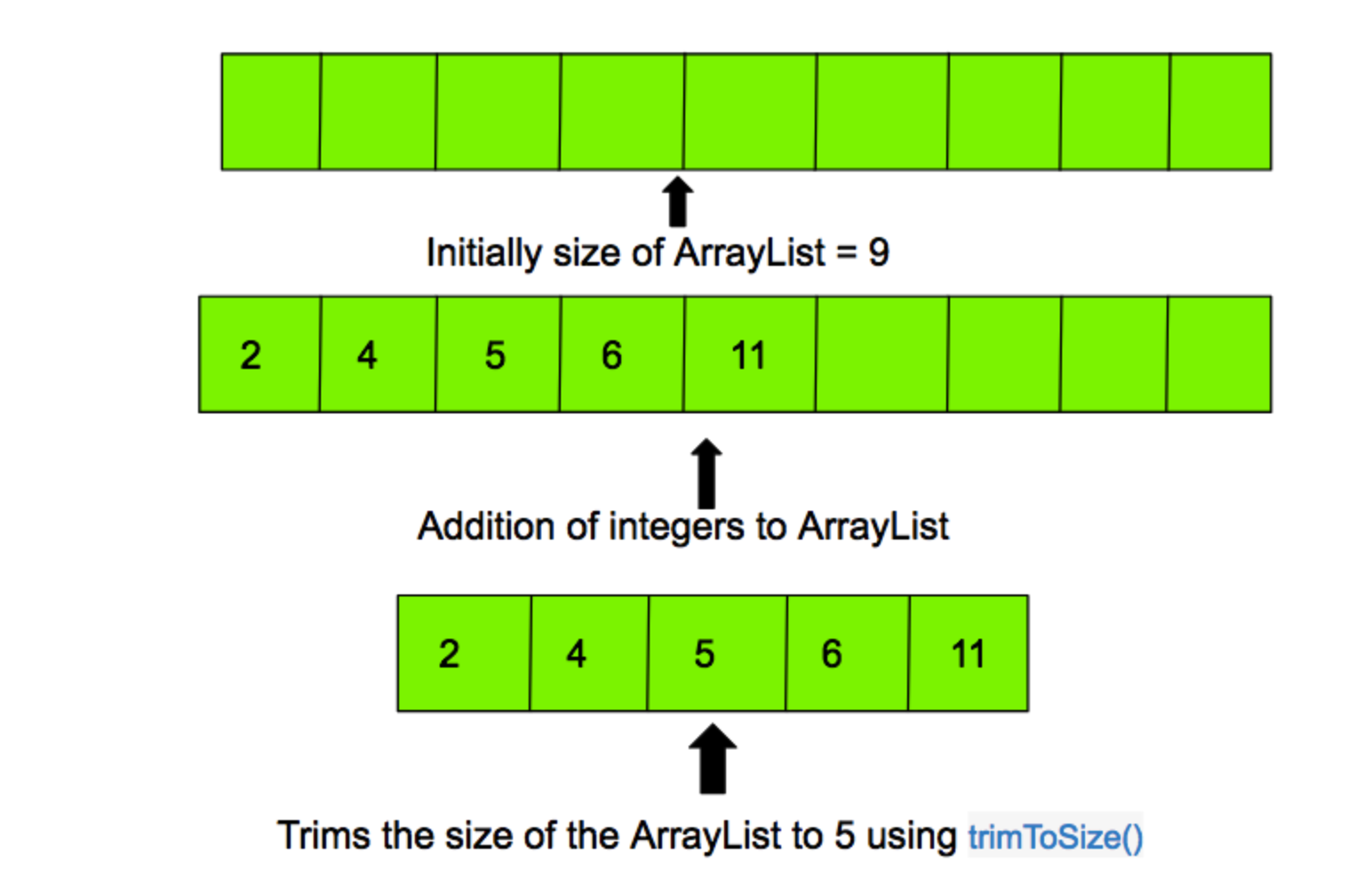
trimToSize()
解释:去掉list空闲的容量
/**
* 去掉ArrayList中的多余空间
*/
public void trimToSize() {
modCount++;
if (size < elementData.length) {
elementData = (size == 0)
? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
: Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
}
sort(Comparator<? super E> c)
sort 方法接收一个自定义比较器进行自定义比较,下面来看具体的源码
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {
// 根据上面代码分析,此时modCounnt 已经被修改过三次(添加了三个元素)
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
// 数组外部排序
Arrays.sort((E[]) elementData, 0, size, c);
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
modCount++;
}
ArrayList相关方法介绍及源码分析的更多相关文章
- ArrayList实现原理及源码分析之JDK8
转载 ArrayList源码分析 一.ArrayList介绍 Java 集合框架主要包括两种类型的容器: 一种是集合(Collection),存储一个元素集合. 一种是图(Map),存储键/值对映射. ...
- ThreadLocal介绍以及源码分析
ThreadLocal 线程主变量 前面部分引用其他优秀博客,后面源码自己分析的,如有冒犯请私聊我. 用Java语言开发的同学对 ThreadLocal 应该都不会陌生,这个类的使用场景很多,特别是在 ...
- Redis 专栏(使用介绍、源码分析、常见问题...)
一.介绍相关 说Redis : 介绍Redis特性,使用场景,使用Jedis操作Redis等. 二.源码分析 1. 数据结构 Redis源码分析(sds):Redis自己封装的C语言字符串类型. Re ...
- ArrayList总结及部分源码分析
ArrayList源码阅读笔记 1. ArrayList继承的抽象类和实现的接口 ArrayList类实现的接口 List接口:里面定义了List集合的基本接口,ArrayList进行了实现 Rand ...
- 4.Java集合-ArrayList实现原理及源码分析
一.ArrayList概述: ArrayList 是基于数组实现的,是一个动态数组,其容量能自动增长,类似于C语言中的动态申请内存,动态增长内存 ArrayList不是线程安全的,只能用在单线程的情况 ...
- Spring AOP介绍及源码分析
转自:http://www.uml.org.cn/j2ee/201301102.asp 软件开发经历了从汇编语言到高级语言和从过程化编程到面向对象编程:前者是为了提高开发效率,而后者则使用了归纳法,把 ...
- Spring Security(3):配置与自动配置的介绍及源码分析
基于注解的配置(Java Configuration)从Spring Security 3.2开始就已经支持,本篇基于Spring boot注解的配置进行讲解,如果需要基于XML配置(Security ...
- java ArrayList 迭代器快速失败源码分析
先来看一个例子: @Test void test2() { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); list.add ...
- ArrayList增加扩容问题 源码分析
public class ArrayList<E>{ private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;//默认的容量是10 private s ...
随机推荐
- VMware Workstation虚拟机安装Windows 7系统
1.进入VMware Workstation虚拟机软件界面,选择新建虚拟机
- Java探索之旅(16)——异常处理
1.异常与异常处理 在<java编程思想>中这样定义 异常:阻止当前方法或作用域继续执行的问题.虽然java中有异常处理机制,但是要明确一点,决不应该用"正常"的态度来 ...
- Python及R安装包版本查看方法
R包查询 查询已安装的所有的包:library() 或installed.packages()(括号内为空,区别以上两项) 查询具体包的信息: help(package="pheatmap& ...
- PAM认证
PAM认证 摘自: http://www.cnblogs.com/shenxm/p/8451889.html PAM(Pluggable Authentication Modules) Sun公司于1 ...
- Linux包管理
1.yum(Yellow dog Updater, Modified) yum是一个在Fedora(基于Linux的操作系统)和RedHat(基于Linux的操作系统)以及SUSE(基于Linux的操 ...
- 微信小程序open-data获取用户的信息样式设置
效果图 wxml代码 <view class="userinfo"> <!-- 用户头像 --> <view class="userinfo ...
- ejs使用文档
EJS是一个javascript模板库,用来从json数据中生成HTML字符串. 功能:缓存功能,能够缓存好的HTML模板: <% code %>用来执行javascript代码 ejs模 ...
- Xuzhou Winter Camp 1C(模拟)
#include<iostream>#include<cstdio>#include<algorithm>#include<cmath>#include ...
- [Xcode 实际操作]五、使用表格-(4)设置UITableView单元格数据库源
目录:[Swift]Xcode实际操作 本文将演示如何自定义表格的数据来源. 在项目导航区,打开视图控制器的代码文件[ViewController.swift] import UIKit //首先添加 ...
- 解读人:李思奇,Development of a sensitive, scalable method for spatial, cell-type-resolved proteomics of the human brain. (一种用于研究人类大脑基于空间或细胞类型的蛋白质组学的灵敏方法)
发表时间:(2019年4月) 一. 概述: 本文报道了一种可研究人类大脑组织中特定神经细胞的蛋白质组学的方法.作者通过激光捕获显微切割技术(LCM)从逝者大脑中分离出目的神经元细胞,接着尝试了一系列不 ...
