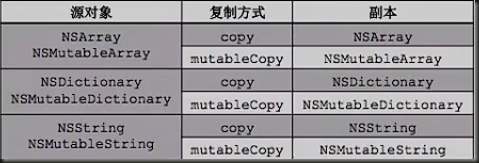
copy语法
copy 和 mutableCopy
一个对象使用copy或者mutableCopy方法可以创建对象的副本
---------------
copy - 需要先实现NSCopying协议,创建的是不可变副本(如NSString,NSArray,NSDictionary)
---------------
mutableCopy - 需要先实现NSMutableCopying协议,创建的是可变副本(如NSMutableString,NSMutableArray,NSMutableDictionary,默认都已经实现)
像自己创建 的 Person Student 是不可以拷贝的,因为没有实现这两个协议中的一个。
---------------
深拷贝:内容拷贝,源对象和副本指向的是不同的两个对象,源对象引用计数器不变,副本计数器设置为1。内容拷贝。区别:有没有产生新对象。
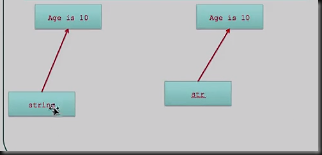
---------------
浅拷贝:指针拷贝,源对象和副本指向的是同一个对象。对象的引用计数器+1,其实相当于做了一次retain操作。地址拷贝。
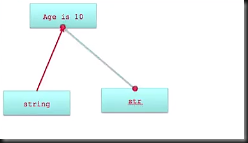
---------------
只有不可变对象创建的不可变副本(copy)才是浅复制,其他的都是深复制。
OC中copy语法存在的意义就是改变副本不影响源对象。
所以只跟调用的方法名有关系,跟源对象没关系。
内存管理回顾

#pragma mark mutablecopy
void stringMutablecopy(){
//string counter 1
NSString *string=[[NSString alloc] initWithFromat:@”age is %1”,10];
//str counter 1,string counter 1
// Create a new Object it’s counter is 1,source object counter is 1
NSMutableString *str=[string mutableCopy];
NSLog(@”str=%zi”,[str retainCount]); //1
NSLog(@”string=%zi”,[string retainCount]);//1
//so copy release
//not the same Object
NSLog(@”%i”,str==string);//0
//Modify str to check whether string change
[str appendString:@”abcd”];
NSLog(@”string:%@”,string);
NSLog(@”str:%@”,str);
[str release];//str:0
//string counter 0
[string release];
}
#pragma mark copy
void(){
NSString *string=[[NSString alloc] initWithFromat:@”age is %1”,10];
NSLog(@”%zi”,[string retainCount]);
NSString *str=[string copy];// Both can’t change
//浅拷贝 相当于retain ,因为str不可变,为了性能着想,所以返回源对象本身,计数器+1
NSLog(@”%i”,str==string);//1
NSLog(@”%zi”,[string retainCount]);
[str release];
[string release];
}
//结论不论是copy 还是 mutableCopy 都需要release
#praga mark mutable->copy 可变字符串的拷贝
void mutableStringCopy(){
NSMutableString * string=[NSMutableString stringWithFormat:@”age is %i”,10];
NString *str=[string copy];// 深拷贝
NSLog(@“%i”,str==string);
[str release];
}
void mutableStringMutableCopy(){
//肯定是深拷贝
NSMutableString * string=[NSMutableString stringWithFormat:@”age is %i”,10];
NSMutableString * str=[string mutableCopy];
[str appendString:@”1234”];
NSLog(@”str:%@”,str);
NSLog(@”string:%@”,string);
[str release];
}
自己创建的类来拷贝
Student.h
//@property (nonatomic ,retain) NSString *name;
Student.m
//retain代表set方法会release旧对象,retain新对象
-(void)setName:(NSString *)name{
if(_name!=name){
[_name release];
_name=[name retain];
}
}
-(void)dealloc{
[_name release];
[super dealloc];
}
Student.h
//修改外部的变量并不会影响到内部成员
@property (nonatomic ,copy) NSString *name;
Student.m
//copy代表set方法会release旧对象,copy新对象
-(void)setName:(NSString *)name{
if(_name!=name){
[_name release];
_name=[name copy];
}
}
-(void)dealloc{
[_name release];
[super dealloc];
}
//pragma mark show copy name of Student (前面的懂,这就模糊了)
#import “Student.h”
void studentNameCopy(){
Student *stu=[[[Student alloc] init]autorelease];
NSMutableString *string=[NSMutableString stringWithFormat:@”age is %i”,10];
stu.name=string;
[string appendString;@“123”];
NSLog(@”name=%@”,stu.name);//10
NSLog(@”string=%@”,string);//10123
}
//字符串建议一般用copy,其他对象一般用retain
#pragma mark copy Student copy
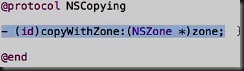
Student.h
@interface Student:NSObject<NSCopying>
@property (nonatomic,copy) NSString *name;
+(id)studentWithName:(NSString *)name;
@end
Student.m
@implementation Student
+(id)studentWithName:(NSString *)name{
//Student *stu=[[[Studeent alloc]init]autorelease];
Student *stu=[[[[self class]alloc]init]autorelease];
//self 指向方法调用者
stu.name=name;
return stu;
}
-(void)dealloc{
[_name release];
[super dealloc];
}
//description 你能打印 self 会死循环的
-(NSString *)description{
return [NSString stringWithFormat:@“[name=%@]”,_name];
//后面GoodStudent需要
}
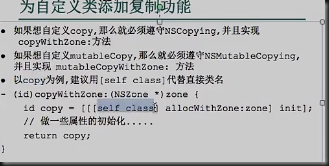
#pagma mark method in copying protocol zone 指向新的存储空间
-(id)copyWithZone:(NSZone *)zone{
Student *copy=[[[self class]allocWithZone:zone]init];//此处不要求释放
copy.name=self.name;//拷贝名字给副本对象
return copy;//谁调用谁释放,交给外界释放
}
@end
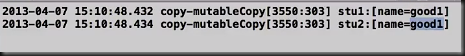
void student Copy(){
Student stu1=[Student studentWithName:@”stu1”];
Student stu2=[stu1 copy];
//print stu1 & stu2
NSLog(@”stu1:%@”,stu1);//stu1
NSLog(@”stu2:%@”,stu2);//stu1
stu2.name=@”stu2”;
NSLog(@”stu1:%@”,stu1);//stu1
NSLog(@”stu2:%@”,stu2);//stu2
[stu2 release];
}
#pragma mark GoodStudent inherit Student
GoodStudent.h
@interface GoodStudent : Student
@property (nonatomic,assign) int age;
+(id)goodStudentWithAge:(int)age name:(NSString *)name;
@end
GoodStudent.m
@implemrntation GoodStudent
+(id)goodStudentWithAge:(int)age name:(NSString *)name{
GoodStudent *good=[GoodStudent studentWithName:name];
//这样写返回的good是student对象
//所以student 方法应该是 Student *stu=[[[[self class]alloc]init]autorelease];
good.age=age;
return good;
}
-(id)copyWithZone:(NSZone *)zone{
//一定要调用父类的方法
GoodStudent *copy=[super copyWithZone:zone];
copy.age=self.age;
return copy;
}
-(NSString *)description {
return [NSString stringWithFomat:@”[name=%@,age=%i]”,self.name,_age];
//注意访问不了_name ,_name是Student内部私有
}
@end
main.m
#import “GoodStudent.h”
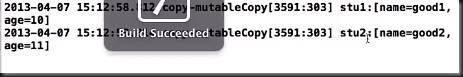
void goodStudentCopy(){
GoodStudent *stu1=[GoodStudent goodStudentWithAge:10 name;@”good1”];
GoodStudeent *stu2=[stu1 copy];
NSLog(@”stu1:%@”,stu1);
NSLog(@”stu2:%@”,stu2);
stu2.name=@”good2”;
stu2.age=@”11”;
NSLog(@”stu1:%@”,stu1);
NSLog(@”stu2:%@”,stu2);
}
key point:
copy语法的更多相关文章
- OC之Copy语法
转载请注明:http://www.cnblogs.com/letougaozao/p/3631105.html 概念 内存管理 NSString的copy实例 对象的copy实例 一.概念 目的:在改 ...
- [OC Foundation框架 - 17] copy语法
一个对象使用copy或mutableCopy方法可以创建对象的副本 1.copy 需要实现NSCopying协议 创建出来的是不可变副本,如NSString, NSArray, NSDictionar ...
- OC中@property属性关键字的使用(assign/weak/strong/copy)
OC中@property属性关键字的使用(assign/weak/strong/copy) 一.assign 用于 ‘基本数据类型’.‘枚举’.‘结构体’ 等非OC对象类型 eg:int.bool等 ...
- spring BeanUtils 工具实现对象之间的copy
一般我们会开发中会遇到返回用户信息的时候,不需要返回密码或者其他参数,这时候我们需要重新定义一个VO类去除不需要的参数,将原对象copy到VO类中 使用spring的BeanUtils可以实现对象的c ...
- oc总结 --oc基础语法相关知识
m是OC源文件扩展名,入口点也是main函数,第一个OC程序: #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> int main(int argc, const cha ...
- OC总结 【OC基础语法相关知识】
m是OC源文件扩展名,入口点也是main函数,第一个OC程序: #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> int main(int argc, const cha ...
- OC Copy and MutableCopy的使用
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h> @interface Student : NSObject <NSCopying> // copy代表set ...
- Docker指令集
FROM 语法:FROM <image>[:<tag>] 解释:设置要制作的镜像基于哪个镜像,FROM指令必须是整个Dockerfile ...
- ios深拷贝,浅拷贝,拷贝自定义对象的简单介绍(转)
copy语法的目的:改变副本的时候,不会影响到源对象: 深拷贝:内容拷贝,会产生新的对象.新对象计数器置为1,源对象计数器不变. 浅拷贝:指针拷贝,不会产生新的对象.源对象计数器+1. 拷贝有下面两个 ...
随机推荐
- linux tcp listen函数的参数backlog
1 listen函数(http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man2/listen.2.html) int listen(int sockfd, int backlog); ...
- 怎样查看Redis的版本号
Q: 怎样查看Redis版本 A: 下面两条命令都可以查看redis 版本: redis-server --version redis-server -v
- hdu 2846 字典树变形
mark: 题目有字串匹配的过程 有两点 1.为了高效的匹配子串 可以把所有的子串都预处理进去 然后字典树计数就放在最后面 2.在同一个母串处理自串的时候 会有重复的时候 比如abab 这里去重用个 ...
- Django2.0 应用 Xadmin 报错二
以上错误是运行点击添加数据等报异常,全是度年解决,并记录解决方法 1.报异常 ‘某个字段类型 ‘ object has no attribute ‘rel‘,点击报异常的地方,把.rel 修改为.re ...
- 【原创】大叔经验分享(76)confluence和jira配置
一 下载 confluence https://product-downloads.atlassian.com/software/confluence/downloads/atlassian-conf ...
- JS ES7
指数运算符(幂) ** console.log(3 ** 2); //9 判断数组中包含 Array.prototype.includes(value) var arr1 = [1,2,'a','b' ...
- 小程序点击图片,png转jpg,再预览方法
//页面数据初始化添加参数:isSignCanvassShow //通过canvas将图片转为jpg,使图片生成白色底便于查看预览 //list为原图片数组列表,index表示当前图片下标, //im ...
- mysql启动失败,unit not found
1 mysql启动 Failed to start mysqld.service: Unit not found. 2 查询/etc/init.d/下是否存在mysqld ll /etc/init ...
- centos所有版本镜像下载地址
centos所有版本镜像下载地址 版本号 下载地址 更新时间 centos2.1 iso镜像下载 2.1/ 2009/8/19 1:36 centos3.1 iso镜像下载 3.1/ 2005/ ...
- java -为什么重写equals(),还需要重写hashCode()?
1.先post这两个方法的基本定义: equals()的定义: 浅谈Java中的equals和==(转) hashCode()的定义: java中hashCode()方法的作用 Java中hashCo ...
