[C#]基于命名管道的一对多进程间通讯
在工作中碰到了一个进程间通讯的问题,大概是这样的:
项目本身是.net Core做的,但是有部分功能Core中不方便实现,有的是依赖Framework,有的是因为权限和安全问题。
那基于这个问题,问了问度娘进程通讯的问题,但是一水大神都在说,Socket啊,WebApi啊,内存共享啊,文件共享啊,等等。好不容易有个人在问管道的问题,大家都是一个口气:“用这么古老的东西干什么?”
既然大家都说管道这个“老古董”,那我今天就来扒扒这个坟。
先来尝试一下管道通讯
首先要清楚什么是管道,有不少大神写了,我就这里就不废话了,给个链接 Windows中的管道技术
基础概念知道了,接下来看看网上的别人怎么做的 C#命名管道通信
这篇Blog中用的是 System.IO.Pipes 下的 NamedPipeClientStream 和 NamedPipeServerStream,从微软的官方看这个命名空间是System.Core.dll中提供的,无论是Framework还是Core都可以使用。
建立一个解决方案,下面两个控制台应用,一个Framework的作为服务端,一个Core的作为客户端。把Blog的代码粘进去,运行OK。(废话)
接下来修改代码,让程序支持半双工通讯。
为什么是半双工?不是单工或者双工?
C/S的沟通方式还是模拟的“请求-响应”模式,既然需要“响应”那么单工自然不满足需求,而服务端本身不需要在客户端发送请求数据的同时回传数据,自然全双工也没有意义,并发也不是靠双工解决的。所以选择了实现比较简单的半双工模式。
修改后的代码:
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.IO.Pipes; namespace Server
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
using (NamedPipeServerStream pipeServer = new NamedPipeServerStream("testpipe", PipeDirection.InOut, ))
{
try
{
pipeServer.WaitForConnection();
pipeServer.ReadMode = PipeTransmissionMode.Byte;
StreamWriter Writer = new StreamWriter(pipeServer);
StreamReader Reader = new StreamReader(pipeServer); while (true)
{
var input = Reader.ReadLine();
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(input))
{
break;
} Console.WriteLine($"Server Get Message:{input}");
Writer.WriteLine($"Server Get Message:{input}");
Writer.Flush();
}
}
catch (IOException e)
{
throw e;
}
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
服务端
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.IO.Pipes;
using System.Security.Principal;
using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Client
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
using (NamedPipeClientStream pipeClient = new NamedPipeClientStream("localhost", "testpipe", PipeDirection.InOut, PipeOptions.None, TokenImpersonationLevel.None))
{
pipeClient.Connect();//连接服务端
StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(pipeClient);
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(pipeClient);
while (true)
{
Console.WriteLine("SendMessage:");
var Input = Console.ReadLine();
sw.WriteLine(Input);
sw.Flush(); var Result = sr.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine($"Reply:{Result}");
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ex;
}
} }
}
客户端
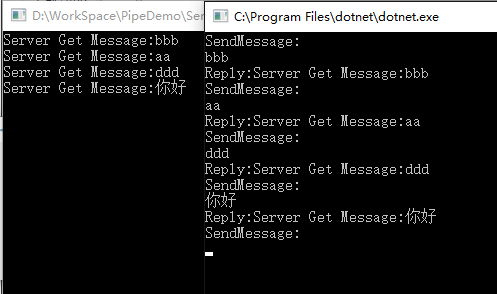
这样一个一对一的半双工通讯的程序就完成了
但是Web端肯定会有并发存在,如果这么一对一的通讯我总不能在Web后台长期阻塞等待服务器相应吧?如果采用消息列队就得不到服务器的响应了。
开始第一版踩坑设计
接下来说回正题,如何让管道进行“一对多”通讯。
首先客户端和服务端,再等待输入输出的时候线程都是阻塞的,那多个管道要进行同时通讯,就是要每个管道一个线程。
开始设计的“分发式”
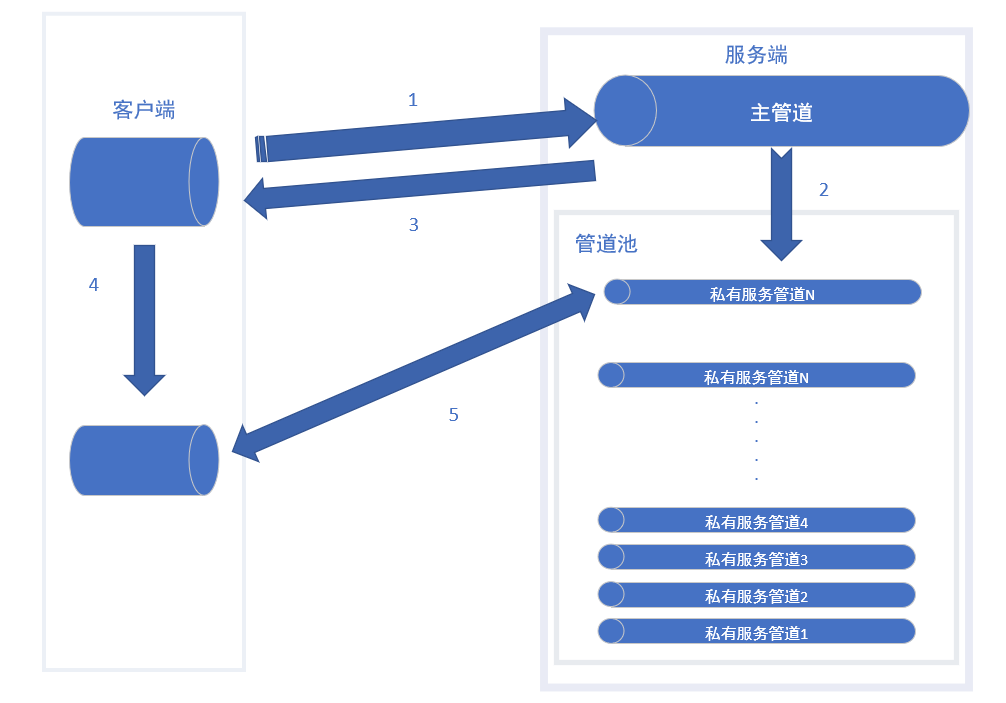
1、客户端 链接 服务端 的主管道
2、服务端根据客户端发过来的密钥,生成一个带安全认证的私有管道
3、私有管道的名称和密钥发送回客户端,之后断开链接等待其他客户端链接
4、客户端根据发回来密钥和名称来链接私有管道
5、开始正常私有管道通讯,客户端断开链接后,私有管道自动销毁。
这个设计有个3个问题
1、首先客户端需要创建2个管道
2、所有的客户端都要先链接主管道,即使极大的减少了管道处理量,但是依旧会产生阻塞
3、占用大量的管道名称
等代码都写完了,回头重新产看微软官方的文档的时候,发现其实这种“分发式”是极为的脑残的
微软爸爸早就提供了更优雅的解决方案,其实同名的管道可以存在多个实例,每个实例可以链接一个不同的客户端。
那么之前的设计就需要改改了
最终的来了
经过修改,改成了“自分裂式”
设计思路
1、创建一个管道池,保持内部有一个待链接的管道实例
2、客户端去链接,系统会自动分配给客户端一个等待链接的服务端实例
3、当服务端链接后,再创建一个新的待链接的管道实例
4、当客户端断开链接或者超时,那么将自动销毁服务端实例
保持管道池中至少有1个待链接的实例,但是不能超过上限数量。
我就不上图了,直接上代码
Pipeline.cs
作为管理管道用的类
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.IO.Pipes;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Server
{
public class Pipeline : IDisposable
{
public Guid ID { get; } private NamedPipeServerStream Server;
private Task Task;
private AutoResetEvent Get, Got;
private string inputContext;
private StreamWriter Writer;
private StreamReader Reader; public const int MaxServer = ;
public const string ServerName = "testpipe";
public const int ServerWaitReadMillisecs = ; //10s
public const int MaxTimeout = ; public Pipeline()
{
ID = Guid.NewGuid();
Get = new AutoResetEvent(false);
Got = new AutoResetEvent(false);
Server = new NamedPipeServerStream(ServerName, PipeDirection.InOut, MaxServer);
} public void Start()
{
Task = Task.Factory.StartNew(TaskRun);
} private void TaskRun()
{
Server.WaitForConnection();
PipelinePool.CreatePipeLineAsync();
try
{
Writer = new StreamWriter(Server);
Reader = new StreamReader(Server);
while (true)
{
var input = TryReadLine();
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(input)) break;
//Do Somethin....
Console.WriteLine($"Server {ID} Get Message:{input}");
Writer.WriteLine($"Server Get Message:{input}");
Writer.Flush();
}
}
catch (TimeoutException)
{
Console.WriteLine($"管道{ID}超时次数过多,视为丢失链接");
}
Console.WriteLine($"管道{ID}即将关闭");
Dispose();
} private void readerThread()
{
Get.WaitOne();
inputContext = Reader.ReadLine();
Got.Set();
} private string TryReadLine()
{
int TimeOutCount = ;
var thread = new Thread(readerThread);
thread.Start();
Get.Set();
while (!Got.WaitOne(ServerWaitReadMillisecs))
{
if (TimeOutCount++ > MaxTimeout)
{
thread.Abort();
throw new TimeoutException();
}
Console.WriteLine($"管道{ID}第{TimeOutCount}次超时");
}
return inputContext;
} public void Dispose()
{
Server.Close();
Server.Dispose();
Get.Dispose();
Got.Dispose();
PipelinePool.DisposablePipeLineAsync(ID);
}
}
}
其中值得一提的是 TryReadLine 这个方法。
在普通的ReadLine时候,线程是阻塞的,造成后面的代码无法为运行。
如果客户端因为某个问题早成死锁或者崩溃,但是又未丢掉链接,这个线程就会一直阻塞下去。也无法释放。
无奈上了下最大的同性交友技术交流网站Stackoverflow,大神的确多,找到了这么一个解决方案 How to add a Timeout to Console.ReadLine()?
经过修改,就成了上面的TryReadLine方法。
接下来池子就比较简单了
using System;
using System.Collections.Concurrent;
using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Server
{
public class PipelinePool
{
/// <summary>
/// 用于存储和管理管道的进程池
/// </summary>
private static ConcurrentDictionary<Guid, Pipeline> ServerPool = new ConcurrentDictionary<Guid, Pipeline>(); /// <summary>
/// 创建一个新的管道
/// </summary>
private static void CreatePipeLine()
{
lock (ServerPool)
{
if (ServerPool.Count < Pipeline.MaxServer)
{
var pipe = new Pipeline();
pipe.Start();
ServerPool.TryAdd(pipe.ID, pipe);
} }
Console.WriteLine($"管道池添加新管道 当前管道总数{ServerPool.Count}");
} /// <summary>
/// 根据ID从管道池中释放一个管道
/// </summary>
private static void DisposablePipeLine(Guid Id)
{
lock (ServerPool)
{
Console.WriteLine($"开始尝试释放,管道{Id}");
if (ServerPool.TryRemove(Id, out Pipeline pipe))
Console.WriteLine($"管道{Id},已经关闭,并完成资源释放");
else
Console.WriteLine($"未找到ID为{Id}的管道");
if (ServerPool.Count == )
CreatePipeLine();
}
} /// <summary>
/// (异步)创建一个新的管道进程
/// </summary>
public static async void CreatePipeLineAsync() => await Task.Run(new Action(CreatePipeLine)); /// <summary>
/// (异步)根据ID从管道池中释放一个管道
/// </summary>
/// <param name="id"></param>
public static async void DisposablePipeLineAsync(Guid id) => await Task.Run(() => { DisposablePipeLine(id); }); }
}
然后程序的入口方法
using System; namespace Server
{
class Program
{ static void Main(string[] args)
{
PipelinePool.CreatePipeLineAsync();
Console.ReadKey();
} } }
服务端的修改就完成了
客户端其实保持不变就可以
为了测试,修改一下
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.IO.Pipes;
using System.Security.Principal;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Models; namespace Client
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<PipeTest> list = new List<PipeTest>();
for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
list.Add(new PipeTest(i));
list.ForEach(a => Task.Factory.StartNew(a.run));
Console.ReadKey();
}
} public class PipeTest
{
public int id { get; } public PipeTest(int id)
{
this.id = id;
} private List<string> Message = new List<string> { "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd", "eee", "fff", "ggg" }; public void run()
{
try
{
using (NamedPipeClientStream pipeClient = new NamedPipeClientStream(
PipeCommunicationConfiguration.ServerName, PipeCommunicationConfiguration.PipeName,
PipeDirection.InOut, PipeOptions.None, TokenImpersonationLevel.None)
)
{
pipeClient.Connect(PipeCommunicationConfiguration.ClientConnectTimeout);//连接服务端
StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(pipeClient);
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(pipeClient);
foreach(string msg in Message)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Client {id} SendMessage:" + msg);
sw.WriteLine(msg);//传递消息到服务端
sw.Flush();//注意一定要有,同服务端一样 string temp = sr.ReadLine();//获取服务端返回信息
if (!pipeClient.IsConnected)
{
Console.WriteLine("Pipe is Broken");
break;
}
Console.WriteLine("replyContent:" + temp);
}
pipeClient.Close();
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
}
Console.WriteLine($"Client {id} end of conversation");
}
}
}
这样客户端就可以同时启动多个线程,并向服务端通讯
运行结果
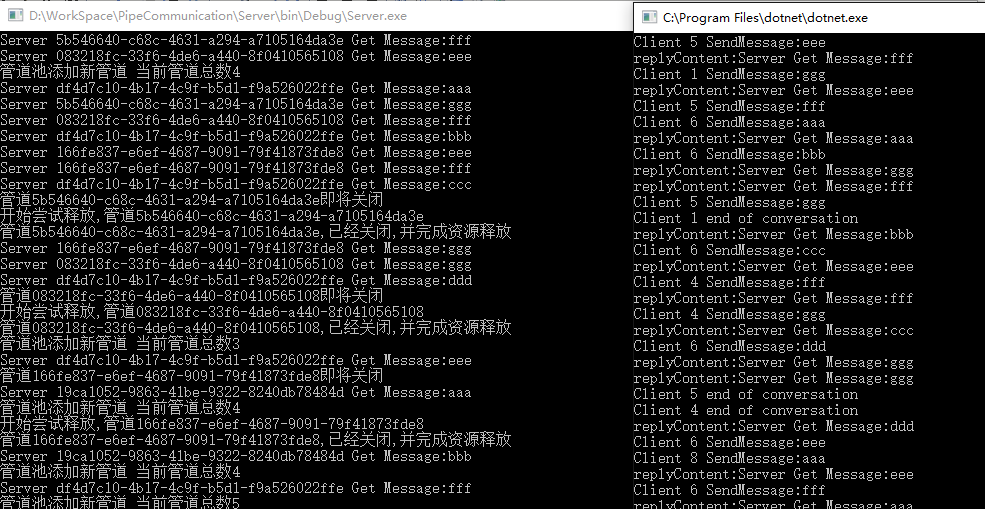
测试成功!
总结:
管道本身只能实现一对一进行通信,这个是不能改变的。
那多管道通信就成了必然,对管道数量的伸缩和进程的管理就成了主要的问题。
一开始没有好好看文档走了不少弯路,还整了个“分发式”...笑哭
[C#]基于命名管道的一对多进程间通讯的更多相关文章
- 【LINUX/UNIX网络编程】之使用消息队列,信号量和命名管道实现的多进程服务器(多人群聊系统)
RT,使用消息队列,信号量和命名管道实现的多人群聊系统. 本学期Linux.unix网络编程的第三个作业. 先上实验要求: 实验三 多进程服务器 [实验目的] 1.熟练掌握进程的创建与终止方法: 2 ...
- Windows进程间通信—命名管道
命名管道是通过网络来完成进程间的通信,它屏蔽了底层的网络协议细节.我们在不了解网络协议的情况下,也可以利用命名管道来实现进程间的通信.与Socket网络通信相比,命名管道不再需要编写身份验证的代码.将 ...
- 采用虚拟命名管道的字符设备和阻塞型I/O实现进程间的通信实现KWIC程序
采用虚拟命名管道的字符设备和阻塞型I/O实现进程间的通信实现KWIC程序专业程序代写c++程序代写
- Delphi 简单命名管道在两个进程间通讯
服务器端代码: unit Unit1; interface uses Windows, Messages, SysUtils, Variants, Classes, Graphics, Control ...
- Linux进程间通信之管道(pipe)、命名管道(FIFO)与信号(Signal)
整理自网络 Unix IPC包括:管道(pipe).命名管道(FIFO)与信号(Signal) 管道(pipe) 管道可用于具有亲缘关系进程间的通信,有名管道克服了管道没有名字的限制,因此,除具有管道 ...
- 邮槽 匿名管道 命名管道 剪贴板 进程通讯 转自http://www.cnblogs.com/kzloser/archive/2012/11/04/2753367.html#
邮槽 通信流程: 服务器 客户端 注意: 邮槽是基于广播通信体系设计出来的,它采用无连接的不可靠的数据传输 邮槽可以实现一对多的单向通信,我们可以利用这个特点编写一个网络会议通知系统,而且实现这一的系 ...
- High Performance Networking in Google Chrome 进程间通讯(IPC) 多进程资源加载
小结: 1. 小文件存储于一个文件中: 在内部,磁盘缓存(disk cache)实现了它自己的一组数据结构, 它们被存储在一个单独的缓存目录里.其中有索引文件(在浏览器启动时加载到内存中),数据文件( ...
- 【windows 操作系统】进程间通信(IPC)简述|无名管道和命名管道 消息队列、信号量、共享存储、Socket、Streams等
一.进程间通信简述 每个进程各自有不同的用户地址空间,任何一个进程的全局变量在另一个进程中都看不到,所以进程之间要交换数据必须通过内核,在内核中开辟一块缓冲区,进程1把数据从用户空间拷到内核缓冲区,进 ...
- 管道实现进程间通讯 、WaitNamedPipe
一.管道实现进程间通讯 主要的理论知识 1.什么是管道以及分类 管道是两个头的东西,每一个头各连接一个进程或者同一个进程的不同代码,依照管道的类别分有两种管道,匿名的和命名的:依照管道的传输方向分也能 ...
随机推荐
- 2015四川省acm B题
Carries frog has n integers a1,a2,-,an, and she wants to add them pairwise. Unfortunately, frog is s ...
- UVA - 10723 类似LCS
思路:dp(i, j)表示第一个串前i个字符和第二个串前j个字符需要的最短字符串长度,cnt(i, j)表示第一个串前i个字符和第二个串前j个字符需要的最短字符串的个数. 转移方程: if(s1[i] ...
- nginx的环境配置的问题
在安装好nginx之后,运行nginx,报错: nginx dyld: Library not loaded: /usr/local/lib/libpcre.1.dylib Referenced fr ...
- web前端研发工程师编程能力成长之路
[背景] 如果你是刚进入WEB前端研发领域,想试试这潭水有多深,看这篇文章吧:如果你是做了两三年WEB产品前端研发,迷茫找不着提高之路,看这篇文章吧:如果你是四五年的前端开发高手,没有难题能难得住你的 ...
- 304和浏览器http缓存
浏览器虽然发现了本地有该资源的缓存,但是不确定是否是最新的,于是想服务器询问,若服务器认为浏览器的缓存版本还可用,那么便会返回304. 浏览器缓存分为强缓存和协商缓存. 1.浏览器请求某资源,通过he ...
- c#判断外部可执行程序是否已打开(若未打开则打开)
#region 通过当前代码执行路径向上找到相关exe,并根据processes.Length判断是否已启动 private bool CheckAndOpenExe(string exeName) ...
- 关于echarts
昨天随手玩了下echarts,看见同事纠结于echarts的兼容问题. 最简单的echarts(官网的): <div id="main" style="width: ...
- xWorks下的硬盘启动方法
在VxWorks下进行开发调试,在目标机上加载VxWorks映像很重要,在目标机上加载VxWorks映像,最重要的是三个步骤: 第一步,修改config.h文件,在config.h文件里包括硬盘驱动. ...
- hi3531的i2c部分
一.关于编译Hi3531 SDK: 之前编译SDK时编译到make uImage总出错,一是找不到.config文件,这个问题是必须先make menuconfig 然后保存.config文件. 二是 ...
- TI AM335X处理器介绍
AM335X是美国TI(德州仪器)公司基于 ARM Cortex-A8内核的AM335X微处理器,在图像.图形处理.外设方面进行了增强,并全面支持诸如 EtherCAT 和 PROFIBUS等工业接口 ...
