jdk源码阅读笔记-LinkedHashMap
Map是Java collection framework 中重要的组成部分,特别是HashMap是在我们在日常的开发的过程中使用的最多的一个集合。但是遗憾的是,存放在HashMap中元素都是无序的,原因是我们在put或get数据的时候都是根据key的hash值来确定元素的位置。在具体的业务场景中,我们更多的希望对于HashMap集合能够进行顺序访问,好在 jdk 中已经给我们提供了一种解决方案,那就是LinkedHashMap。该类继承与HashMap,因此HashMap拥有的特性它都有,同时还具备其他的特性,比如实现了插入顺序排序和访问顺序排序,默认以插入顺序排序。同时也能够利用LinkedHashMap实现LRU算法。LinkedHashMap api很少,基本都是调用HashMap的方法,所以建议熟悉HashMap源码之后再来看这篇文章,我之前也写过【HashMap源码分析笔记】,大家可以点进去参考一下。
LRU算法: LRU是Least Recently Used的缩写,即最近最少使用,也就是说将热点数据放到最前面,冷门数据放到最后,当达到一定条件后会删除冷门数据,在一个缓存系统中经常会用到该算法。
一、LinkedHashMap与HashMap数据结构对比
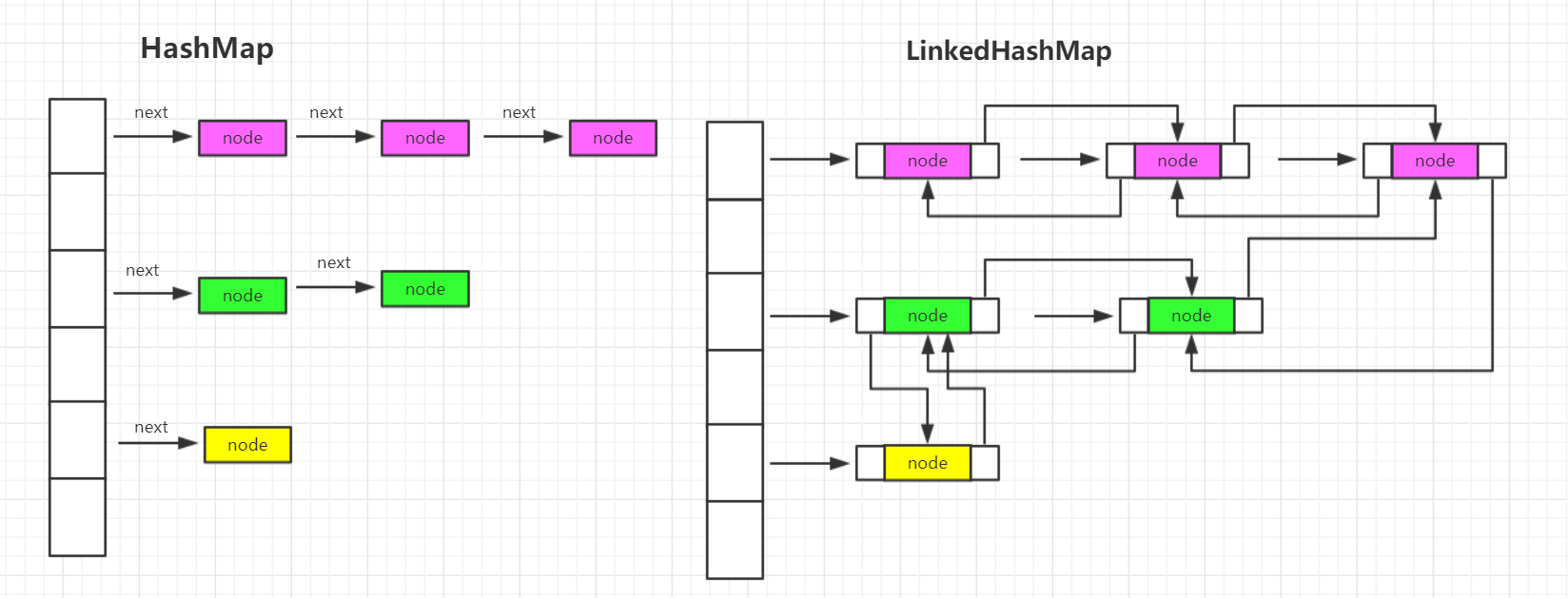
从上图可以看到HashMap的数据结构位数组+单向链表,数据存放在链表的node节点上,每个node节点上都有一个指针指向下一个节点,每个数组index上的链表跟其他的index上面的链表是部相互链接的。LinkedHashMap在部破坏HashMap的结构基础之上,每个node节点都额外增加了两个指针,分别指向了前一个节点和下一个节点,所以在HashMap上所有的node节点形成了一条双向链表,每次添加往LinkedHashMap put数据的时候都将节点放在双向链表的最后位置,从而实现了插入顺序排序。在LinkedHashMap中,节点的定义如下:
/**
* HashMap.Node subclass for normal LinkedHashMap entries.
*/
static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
}
节点继承与HashMap的 Node内部类,但是又额外添加了两个属性,before和after,分别指向前一个节点和后一个节点,形成一个双向链表。
二、LinkedHashMap类结构
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V>
extends HashMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>
{
.......
}
LinkedHashMap继承了HashMap,所以拥有HashMap的所有特性。
三、成员变量
/**
* The head (eldest) of the doubly linked list.
*/
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> head; /**
* The tail (youngest) of the doubly linked list.
*/
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> tail; /**
* The iteration ordering method for this linked hash map: <tt>true</tt>
* for access-order, <tt>false</tt> for insertion-order.
*
* @serial
*/
final boolean accessOrder;
LinkedHashMap在HashMap的基础之上添加了head、tail和accessOrder属性:
head:双向链表的表头
tail: 双向链表的表尾
accessOrder:排序的标志。默认为false,按插入顺序排序。可以通过构造方法设置为true,按访问顺序排序。
四、构造方法
/**
* Constructs an empty insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance
* with the specified initial capacity and load factor.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadFactor the load factor
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
accessOrder = false;
} /**
* Constructs an empty insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance
* with the specified initial capacity and a default load factor (0.75).
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
*/
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
super(initialCapacity);
accessOrder = false;
} /**
* Constructs an empty insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance
* with the default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75).
*/
public LinkedHashMap() {
super();
accessOrder = false;
} /**
* Constructs an insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance with
* the same mappings as the specified map. The <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt>
* instance is created with a default load factor (0.75) and an initial
* capacity sufficient to hold the mappings in the specified map.
*
* @param m the map whose mappings are to be placed in this map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null
*/
public LinkedHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
super();
accessOrder = false;
putMapEntries(m, false);
} /**
* Constructs an empty <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance with the
* specified initial capacity, load factor and ordering mode.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadFactor the load factor
* @param accessOrder the ordering mode - <tt>true</tt> for
* access-order, <tt>false</tt> for insertion-order
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor,
boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}
5个构造方法都是直接调用父类HashMap的构造方法。
五、添加数据put(Object key,V value)
LinkedHashMap中并没有对HashMap进行复写,也就是说添加数据的时候其实就是调用的HashMap的put方法,那么它是怎么进行排序的呢?下面我们一起来看看HashMap中是怎么添加数据的吧。
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == )
n = (tab = resize()).length;
/**
* 通过位与的方式来确定下标位置,判断当前下标位置是否为空,如果为空直接放入到该位置上
* 不为空则通过equals方法来寻找当前位置上面的元素,如果有相同的key,则将覆盖掉,如果没有则将node放置在对应
* 位置上面
*/
if ((p = tab[i = (n - ) & hash]) == null)//直接放到数组中
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);//创建新节点
else {//当前位置不为空
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))//已存在相同的key的数据,将其覆盖
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)//当前位置是红黑树,将Node节点放到红黑树中
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);//创建新树节点
else {//为链表的情况
for (int binCount = ; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);//创建新节点
//链表的长度超过转换红黑数的阈值,则将该链表转成红黑树
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - ) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))//覆盖相同key的node
break;
p = e;
}
}
//map中已经存在了相同的key,将原来的数据替换掉
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);//替换数据被视为更新数据,所以调用访问排序方法。
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;//快速失败机制
if (++size > threshold)//每次插入数据都要判断一下当前存储的数据是否需要扩容
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);//插入数据后进行插入排序
return null;
}
HashMap 插入数据的核心方法为 putVal方法,每次插入数据都调用newNode方法,这个方法LinkedHashMap 中已经重写了:
Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
new LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
linkNodeLast(p);
return p;
}
第一:因为已经重写了父类的newNode方法,所以在插入数据时创建新节点实际是调用了LinkedHashMap的newNode方法,该方法中每次创建新节点都想LinkedHashMap自身维护的双向链表的尾部添加一个当前新创节点,我们继续看看linkNodeLast方法:
private void linkNodeLast(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last = tail;
tail = p;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
}
这个方法很简单,如果链表为空则将新节点设置为头部和尾部,否则将新节点放到链表的最后,将新节点的前指针指向原尾部的节点,原尾部节点的后指针指向新节点。如果不明白具体的插入流程,可参考我之前的【ArrayList源码阅读笔记】,里面有详细插入各个位置的流程。
第二:创建新节点完成后,将新节点放入对象的链表或树中,如果新节点的key在HashMap中已经存在,那么就会原来的value覆盖掉,此时被视为修改了节点,调用afterNodeAccess(e)方法,LinkedHashMap对这个方法进行了重写,我们看一下源码:
/**
* 每次访问节点后将该节点放在最后
* @param e
*/
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) { // move node to last
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last;
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
p.after = null;
if (b == null)
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
if (a != null)
a.before = b;
else
last = b;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
tail = p;
++modCount;
}
}
该方法中,如果 accessOrder 为true并且访问节点不为空,那么就会将访问过的节点移动到最后。这也就是实现了LRU算法,具体移动路程如下:

第三:插入数据全部完成之后,执行afterNodeInsertion(evict)方法,evict为true,LinkedHashMap重写的该方法:
void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { // possibly remove eldest
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> first;
if (evict && (first = head) != null && removeEldestEntry(first)) {
K key = first.key;
removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true);
}
}
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K,V> eldest) {
return false;
}
afterNodeInsertion方法是用来删除最旧最少使用的数据,上面提到过,每次访问、修改map中的数据的时候都会将该节点放在链表的最后面,因此约靠前的数据使用的频率的越低,我们称之为冷数据,该方法就是将最冷门的数据删除掉。removeEldestEntry方法默认返回false,所以LinkedHashMap本身并不提供LRU算法,需要自己手动实现LinkedHashMap,然后重写removeEldestEntry方法,根据自己具体的业务决定何时删除冷数据。
总结:这里只总结LinkedHashMap实现部分。在put数据的时候,LinkedHashMap不仅将数据放在HashMap中,同时也将该数据放在自己维护的双向链表的最后,以实现顺序排序。如果put进去的数据的key已经存在与Map中,则将该数据移动到链表的最后位置。插入数据完成后,根据子类具体实现情况是否将第一个数据删除。
六、获取数据get(key)
/**
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,
* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key
* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code (key==null ? k==null :
* key.equals(k))}, then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise
* it returns {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)
*
* <p>A return value of {@code null} does not <i>necessarily</i>
* indicate that the map contains no mapping for the key; it's also
* possible that the map explicitly maps the key to {@code null}.
* The {@link #containsKey containsKey} operation may be used to
* distinguish these two cases.
*/
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null)
return null;
if (accessOrder)
afterNodeAccess(e);
return e.value;
}
这个方法看起来也比较简单,如果accessOrder为true,即按访问顺序排序,那个每次都将该数据放到链表的最后面。
七、其他方法
LinkedHashMap本身的方法比较少,而且大部分都是调用父类的方法,所以在这里就不说了,可以看看HashMap的源码。
八、总结
LinkedHashMap继承与HashMap,因此它有HashMap一样的特性。同时也弥补了HashMap无法顺序遍历的缺点。LinkedHashMap可以实现插入顺序排序(默认排序),也可以根据访问顺序排序,也就是访问的元素次数越多,该元素就越靠前。实现顺序遍历的底层原理是,LinkedHashMap自身维护了一张双向链表,为此插入、访问或修改数据的时候都将该节点放在链表最后面。按默认排序方式的话,在遍历的时候就从表头开始遍历,按访问顺序排序就从链表表尾开始遍历。另外,LinkedHashMap也可以用来搭建一个缓存系统底层存储结构,后面如果我有空的话,可能也会手写一个简单的缓存demo。最后,如果文章有什么写的不对的地方,欢迎大家提出来,我的qq:1170971295。
jdk源码阅读笔记-LinkedHashMap的更多相关文章
- JDK源码学习笔记——LinkedHashMap
HashMap有一个问题,就是迭代HashMap的顺序并不是HashMap放置的顺序,也就是无序. LinkedHashMap保证了元素迭代的顺序.该迭代顺序可以是插入顺序或者是访问顺序.通过维护一个 ...
- jdk源码阅读笔记-HashSet
通过阅读源码发现,HashSet底层的实现源码其实就是调用HashMap的方法实现的,所以如果你阅读过HashMap或对HashMap比较熟悉的话,那么阅读HashSet就很轻松,也很容易理解了.我之 ...
- jdk源码阅读笔记-ArrayList
一.ArrayList概述 首先我们来说一下ArrayList是什么?它解决了什么问题?ArrayList其实是一个数组,但是有区别于一般的数组,它是一个可以动态改变大小的动态数组.ArrayList ...
- jdk源码阅读笔记
1.环境搭建 http://www.komorebishao.com/2020/idea-java-jdk-funyard/ 2. 好的源码阅读资源 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.co ...
- jdk源码阅读笔记-Integer
public final class Integer extends Number implements Comparable<Integer> Integer 由final修饰了,所以该 ...
- jdk源码阅读笔记-HashMap
文章出处:[noblogs-it技术博客网站]的博客:jdk1.8源码分析 在Java语言中使用的最多的数据结构大概右两种,第一种是数组,比如Array,ArrayList,第二种链表,比如Array ...
- jdk源码阅读笔记-LinkedList
一.LinkedList概述 LinkedList的底层数据结构为双向链表结构,与ArrayList相同的是LinkedList也可以存储相同或null的元素.相对于ArrayList来说,Linke ...
- jdk源码阅读笔记-AbstractStringBuilder
AbstractStringBuilder 在java.lang 包中,是一个抽象类,实现 Appendable 接口和 CharSequence 接口,这个类的诞生是为了解决 String 类在创建 ...
- jdk源码阅读笔记-String
本人自学java两年,有幸初入这个行业,所以功力尚浅,本着学习与交流的态度写一些学习随笔,什么错误的地方,热烈地希望园友们提出来,我们共同进步!这是我入园写的第一篇文章,写得可能会很乱. 一.什么是S ...
随机推荐
- Day2_元组_字典_集合_字符编码_文件处理
元组: 作用:存多个值,元组不可变,主要用来读 age=(11,22,33,44,55) print(age[2]) #取出元组内的值 print(age[1:4]) #取出元组内的某些值 print ...
- Install PIL with Jpeg support on Ubuntu Oneiric 64bit
from:http://jj.isgeek.net/2011/09/install-pil-with-jpeg-support-on-ubuntu-oneiric-64bits/ I am posti ...
- virtualenv 中 install flask 的小问题
最经在学习Python flask 框架 ,用virtualenv建立好我的flask虚拟环境后,执行 sudo pip install flask 并没有报错 我以为已经装上了flask,但当我进入 ...
- Django REST framework+Vue 打造生鲜超市(七)
目录 生鲜超市(一) 生鲜超市(二) 生鲜超市(三) 生鲜超市(四) 生鲜超市(五) 生鲜超市(六) 生鲜超市(七) 生鲜超市(八) 生鲜超市(九) 生鲜超市(十) ...
- Python3实现ICMP远控后门(中)之“嗅探”黑科技
ICMP后门 前言 第一篇:Python3实现ICMP远控后门(上) 第二篇:Python3实现ICMP远控后门(上)_补充篇 在上两篇文章中,详细讲解了ICMP协议,同时实现了一个具备完整功能的pi ...
- PAT1116: Come on! Let's C
1116. Come on! Let's C (20) 时间限制 200 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue &quo ...
- java反射获取类的类名、属性名、属性类型、方法、执行方法、构造函数
public class Demo02 { @SuppressWarnings("all") public static void main(String[] args) thro ...
- 基于SpringBoot + Mybatis实现SpringMVC Web项目
一.热身 一个现实的场景是:当我们开发一个Web工程时,架构师和开发工程师可能更关心项目技术结构上的设计.而几乎所有结构良好的软件(项目)都使用了分层设计.分层设计是将项目按技术职能分为几个内聚的部分 ...
- Switch在swift中的使用
switch的简单使用: 相比 C 和 objective - C 中的 switch 语句,Swift 中的 switch 语句不会默认的掉落到每个 case 的下面进入 另一个 case.相反,第 ...
- 静态资源压缩(GZIP) 专题
1.开GZIP有什么好处?答:Gzip开启以后会将输出到用户浏览器的数据进行压缩的处理,这样就会减小通过网络传输的数据量,提高浏览的速度.Tips:如果网站的用户分布比较分散,并且静态文件过大,可以将 ...
