补习系列(16)-springboot mongodb 数据库应用技巧
一、关于 MongoDB

MongoDB 目前非常流行,在最近的DB-Engine排名中居第5位,仅次于传统的关系型数据库如 Oracle、Mysql。

然而在非关系型数据库领域,MongoDB已经持续成为佼佼者一段时间了,这与 MongoDB的一些优势存在一定关系:
- 无模式(Schema),便于快速开发;
- 面向文档化的数据,基于BSON格式(类JSON),灵活性强
- 高性能,得益于其内存计算能力;
- 副本集、自动分片特性,提供了高可用及水平扩展能力
MongoDB 的主要对象包括数据库(database)、集合(collection)、文档对象(document),与关系型数据库的对应关系如下:
| MySql | MongoDB |
|---|---|
| schema | database |
| table | collection |
| record | document |
| column | field |
与关系型数据库一样,MongoDB也支持索引(不支持外键),然而其没有定义固定的列(Column),字段可以是任何类型的值,比如数值、数组或嵌套文档等。
在最近发布的4.0版本中,MongoDB开始支持事务。可见,在未来这些数据库之间的差异只会越来越少。
二、Spring-Data-Mongo
Spring-Data-Mongo 是Spring框架对于MongoDB 数据读写的ORM 封装,
与 大家熟悉的 JPA一样,其在MongoDB-Java-Driver基础之上做了一些封装,令应用开发更加简便。
如下是SpringData 整体框架的一个概要:
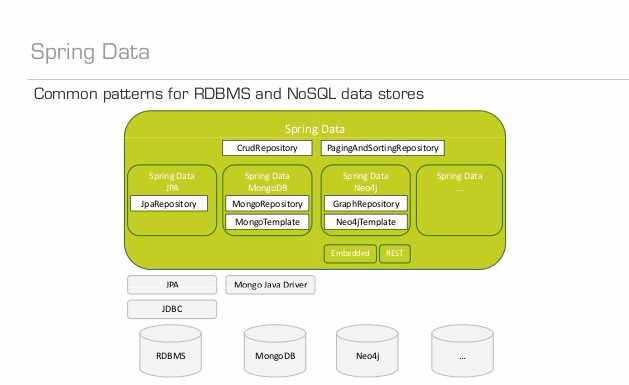
从上图中可以看出,SpringData 是基于分层设计的。从下之上,分别是:
- 数据库层;
- 驱动层(JDBC/Driver);
- ORM层(Repository);
三、整合 MongoDB CRUD
接下来的篇幅,主要针对如何在项目中使用框架进行MongoDB数据库的读写,部分代码可供参考。
A. 引入框架
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
<version>${spring-boot.version}</version>
</dependency>
其中 spring-boot-starter-mongodb 是一个胶水组件,声明对它的依赖会令项目自动引入spring-data-mongo、mongodb-java-driver等基础组件。
B. 数据库配置
我们在 application.properties 中声明一段配置:
spring.data.mongodb.host=127.0.0.1
spring.data.mongodb.port=27017
spring.data.mongodb.username=appuser
spring.data.mongodb.password=appuser@2016
spring.data.mongodb.database=appdb
不难理解,这里是数据库主机、端口、用户密码、数据库的设置。
C. 数据模型
接下来,要定义数据集合(collection) 的一个结构,以 Book实体为例:
@Document(collection = "book")
@CompoundIndexes({ @CompoundIndex(name = "idx_category_voteCount", def = "{'category': 1, 'voteCount': 1}"),
@CompoundIndex(name = "idx_category_createTime", def = "{'category': 1, 'createTime': 1}") })
public class Book {
@Id
private String id;
@Indexed
private String author;
private String category;
@Indexed
private String title;
private int voteCount;
private int price;
@Indexed
private Date publishDate;
private Date updateTime;
private Date createTime;
...
这里,我们给Book 实体定义了一些属性:
| 属性名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| id | 书籍ID |
| author | 作者 |
| category | 书籍分类 |
| title | 书籍标题 |
| voteCount | 投票数量 |
| price | 价格 |
| publishDate | 发布日期 |
| updateTime | 更新时间 |
| createTime | 创建时间 |
除此以外,我们还会用到几个注解:
| 注解 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| @Document | 声明实体为MongoDB文档 |
| @Id | 标记ID属性 |
| @Indexed | 单键索引 |
| @CompoundIndexes | 复合索引集 |
| @CompoundIndex | 复合索引 |
关于MongoDB索引形态,可以参考官方文档做一个详细了解。
D. 数据操作
ORM 框架可以让你通过操作对象来直接影响数据,这样一来,可以大大减少上手的难度,你不再需要熟悉大量驱动层的API了。
Spring-Data-Mongo 实现了类JPA的接口,通过预定义好的Repository可实现代码方法到数据库操作语句DML的映射。
下面是一些例子:
- BookRepository
public interface BookRepository extends MongoRepository<Book, String> {
public List<Book> findByAuthor(String author);
public List<Book> findByCategory(String category, Pageable pageable);
public Book findOneByTitle(String title);
}
我们所看到的 findByAttribute 将会直接被转换成对应的条件查询,如 findByAuthor 等价于
db.book.find({author:'Lilei'})
接下来,我们可以方便的在业务逻辑层(service层) 对Repository 进行调用,如下:
@Service
public class BookService {
@Autowired
private BookRepository bookRepository;
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(BookService.class);
/**
* 创建book
*
* @param category
* @param title
* @param author
* @param price
* @param publishDate
* @return
*/
public Book createBook(String category, String title, String author, int price, Date publishDate) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(category) || StringUtils.isEmpty(title) || StringUtils.isEmpty(author)) {
return null;
}
Book book = new Book();
book.setAuthor(author);
book.setTitle(title);
book.setCategory(category);
book.setPrice(price);
book.setPublishDate(publishDate);
book.setVoteCount(0);
book.setCreateTime(new Date());
book.setUpdateTime(book.getCreateTime());
return bookRepository.save(book);
}
/**
* 更新价格
*
* @param id
* @param price
* @return
*/
public boolean updatePrice(String id, int price) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(id)) {
return false;
}
Book book = bookRepository.findOne(id);
if (book == null) {
logger.info("the book '{}' is not exist", id);
return false;
}
book.setPrice(price);
book.setUpdateTime(new Date());
if (bookRepository.save(book) != null) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 根据获取book
*
* @param title
* @return
*/
public Book getBookByTitle(String title) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(title)) {
return null;
}
return bookRepository.findOneByTitle(title);
}
/**
* 获取投票排行列表
*
* @param category
* @param max
* @return
*/
public List<Book> listTopVoted(String category, int max) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(category) || max <= 0) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
// 按投票数倒序排序
Sort sort = new Sort(Direction.DESC, Book.COL_VOTE_COUNT);
PageRequest request = new PageRequest(0, max, sort);
return bookRepository.findByCategory(category, request);
}
/**
* 删除书籍
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
public boolean deleteBook(String id) {
Book book = bookRepository.findOne(id);
if (book == null) {
logger.info("the book '{}' is not exist", id);
return false;
}
bookRepository.delete(book);
return true;
}
}
关于Repository 映射规则,可以从这里找到详细介绍。
E. 自定义操作
有时候,Repository的方法映射无法较好的满足一些特定场景,比如高级检索、局部更新、覆盖索引查询等等,
此时可以使用框架提供的 MongoTemplate 工具类来完成这些定制,MongoTemplate 提供了大量的 Criteria API 来封装 Mongo-Java-Driver的实现。
我们一方面可以选择直接使用该API,另一方面,则可以更加"优雅"的整合到Repository 接口,如下面的代码:
- 声明 Custom 接口
public interface BookRepositoryCustom {
public PageResult<Book> search(String category, String title, String author, Date publishDataStart,
Date publishDataEnd, Pageable pageable);
public boolean incrVoteCount(String id, int voteIncr);
}
- 声明接口继承关系
public interface BookRepository extends MongoRepository<Book, String>, BookRepositoryCustom{
- 实现类
public class BookRepositoryImpl implements BookRepositoryCustom {
@Autowired
private MongoTemplate mongoTemplate;
public boolean incrVoteCount(String id, int voteIncr) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(id)) {
return false;
}
Query query = new Query();
query.addCriteria(Criteria.where("id").is(id));
Update update = new Update();
update.inc(Book.COL_VOTE_COUNT, voteIncr);
update.set(Book.COL_UPDATE_TIME, new Date());
WriteResult result = mongoTemplate.updateFirst(query, update, Book.class);
return result != null && result.getN() > 0;
}
@Override
public PageResult<Book> search(String category, String title, String author, Date publishDataStart,
Date publishDataEnd, Pageable pageable) {
Query query = new Query();
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(category)) {
query.addCriteria(Criteria.where(Book.COL_CATEGORY).is(category));
}
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(author)) {
query.addCriteria(Criteria.where(Book.COL_AUTHOR).is(author));
}
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(title)) {
query.addCriteria(Criteria.where(Book.COL_TITLE).regex(title));
}
if (publishDataStart != null || publishDataEnd != null) {
Criteria publishDateCond = Criteria.where(Book.COL_PUBLISH_DATE);
if (publishDataStart != null) {
publishDateCond.gte(publishDataStart);
}
if (publishDataEnd != null) {
publishDateCond.lt(publishDataEnd);
}
query.addCriteria(publishDateCond);
}
long totalCount = mongoTemplate.count(query, Book.class);
if (totalCount <= 0) {
return new PageResult<Book>();
}
if (pageable != null) {
query.with(pageable);
}
List<Book> books = mongoTemplate.find(query, Book.class);
return PageResult.of(totalCount, books);
}
}
利用 AOP的魔法 ,Spring 框架会自动将我们这段代码实现织入 到Bean对象中,
这样一来,我们原先对Repository的依赖引用方式就不需要改变了。
四、高级技巧
SpringBoot中完成Mongodb的自动化配置,是通过MongoAutoConfiguration、MongoDataAutoConfiguration完成的。
其中MongoAutoConfiguration的实现如下:
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(MongoClient.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(MongoProperties.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(type = "org.springframework.data.mongodb.MongoDbFactory")
public class MongoAutoConfiguration {
private final MongoProperties properties;
private final MongoClientOptions options;
private final Environment environment;
private MongoClient mongo;
public MongoAutoConfiguration(MongoProperties properties,
ObjectProvider<MongoClientOptions> options, Environment environment) {
this.properties = properties;
this.options = options.getIfAvailable();
this.environment = environment;
}
@PreDestroy
public void close() {
if (this.mongo != null) {
this.mongo.close();
}
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public MongoClient mongo() throws UnknownHostException {
this.mongo = this.properties.createMongoClient(this.options, this.environment);
return this.mongo;
}
}
从上面的代码可见,如果应用代码中未声明 MongoClient、MongoDbFactory,那么框架会根据配置文件自动做客户端的初始化。
通过声明,可以取消这些自动化配置:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAutoConfiguration(exclude = { EmbeddedMongoAutoConfiguration.class, MongoDataAutoConfiguration.class,
MongoAutoConfiguration.class })
public class DemoBoot {
...
真实线上的项目中,会对MongoDB 客户端做一些定制,下面的介绍几个用法
1. 连接池配置
@Configuration
public class MongoConfig {
@Bean
public MongoDbFactory mongoFactory(MongoProperties mongo) throws Exception {
MongoClientOptions.Builder builder = new MongoClientOptions.Builder();
// 连接池配置
builder.maxWaitTime(1000 * 60 * 1).socketTimeout(30 * 1000).connectTimeout(10 * 1000).connectionsPerHost(60)
.minConnectionsPerHost(60).socketKeepAlive(true);
// 设置鉴权信息
MongoCredential credential = null;
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(mongo.getUsername())) {
credential = MongoCredential.createCredential(mongo.getUsername(), mongo.getDatabase(),
mongo.getPassword());
}
MongoClientOptions mongoOptions = builder.build();
List<ServerAddress> addrs = Arrays.asList(new ServerAddress(mongo.getHost(), mongo.getPort()));
MongoClient mongoClient = null;
if (credential != null) {
mongoClient = new MongoClient(addrs, Arrays.asList(credential), mongoOptions);
} else {
mongoClient = new MongoClient(addrs, mongoOptions);
}
return new SimpleMongoDbFactory(mongoClient, mongo.getDatabase());
}
我们所关心的,往往是连接池大小、超时参数阈值、队列这几个,如下:
//连接池最小值
private int minConnectionsPerHost;
//连接池最大值
private int maxConnectionsPerHost = 100;
//线程等待连接阻塞系数
private int threadsAllowedToBlockForConnectionMultiplier = 5;
//选择主机超时
private int serverSelectionTimeout = 1000 * 30;
//最大等待
private int maxWaitTime = 1000 * 60 * 2;
//最大连接闲时
private int maxConnectionIdleTime;
//最大连接存活
private int maxConnectionLifeTime;
//TCP建立连接超时
private int connectTimeout = 1000 * 10;
//TCP读取超时
private int socketTimeout = 0;
//TCP.keepAlive是否启用
private boolean socketKeepAlive = true;
//心跳频率
private int heartbeatFrequency = 10000;
//最小心跳间隔
private int minHeartbeatFrequency = 500;
//心跳TCP建立连接超时
private int heartbeatConnectTimeout = 20000;
//心跳TCP读取超时
private int heartbeatSocketTimeout = 20000;
2. 去掉_class属性
通过 SpringDataMongo 定义的实体,会自动写入一个_class属性,大多数情况下这个不是必须的,可以通过配置去掉:
@Bean
public MongoTemplate mongoTemplate(MongoDbFactory mongoDbFactory, MongoMappingContext context) {
DbRefResolver dbRefResolver = new DefaultDbRefResolver(mongoDbFactory);
MappingMongoConverter converter = new MappingMongoConverter(dbRefResolver, context);
converter.setTypeMapper(new DefaultMongoTypeMapper(null));
converter.afterPropertiesSet();
MongoTemplate mongoTemplate = new MongoTemplate(mongoDbFactory, converter);
return mongoTemplate;
}
3. 自定义序列化
一些基础的字段类型,如 int 、long、string,通过JDK 装箱类就可以完成,
对于内嵌的对象类型,SpringDataMongo框架会将其转换为 DBObject对象(java driver 实体)。
一般情况下这已经足够了,但某些场景下你不得不实现自己的序列化方式,比如通过文档存储某些特殊格式的内容。
这需要用到 Converter 接口,如下面的代码:
@Bean
public MongoTemplate mongoTemplate(MongoDbFactory mongoDbFactory, MongoMappingContext context) {
DbRefResolver dbRefResolver = new DefaultDbRefResolver(mongoDbFactory);
MappingMongoConverter converter = new MappingMongoConverter(dbRefResolver, context);
converter.setTypeMapper(new DefaultMongoTypeMapper(null));
// 自定义转换
converter.setCustomConversions(customConversions());
converter.afterPropertiesSet();
MongoTemplate mongoTemplate = new MongoTemplate(mongoDbFactory, converter);
return mongoTemplate;
}
private CustomConversions customConversions() {
List<Converter<?, ?>> converters = new ArrayList<Converter<?, ?>>();
converters.add(new BasicDBObjectWriteConverter());
converters.add(new BasicDBObjectReadConverter());
return new CustomConversions(converters);
}
/**
* 写入序列化
*/
@WritingConverter
public static class BasicDBObjectWriteConverter implements Converter<BasicDBObject, String> {
public String convert(BasicDBObject source) {
if (source == null) {
return null;
}
return source.toJson();
}
}
/**
* 读取反序列化
*/
@ReadingConverter
public static class BasicDBObjectReadConverter implements Converter<String, BasicDBObject> {
public BasicDBObject convert(String source) {
if (source == null || source.length() <= 0) {
return null;
}
return BasicDBObject.parse(source);
}
}
4. 读写分离
MongoDB 本身支持读写分离的实现,前提是采用副本集、分片副本集的架构,
通过声明客户端的 ReadPreference 级别可以达到优先读主、优先读备的控制。
@Configuration
public class MongoConfig {
@Bean(name="secondary")
public MongoDbFactory mongoFactory(MongoProperties mongo) throws Exception {
MongoClientOptions.Builder builder = new MongoClientOptions.Builder();
// 连接池配置
builder.maxWaitTime(1000 * 60 * 1).socketTimeout(30 * 1000).connectTimeout(10 * 1000).connectionsPerHost(60)
.minConnectionsPerHost(60).socketKeepAlive(true);
// 优先读备节点
builder.readPreference(ReadPreference.secondaryPreferred());
...
上面的代码中,将会为MongoClient 设置 secondaryPreferred 的读级别。
ReadPreference 级别包括以下几种:
| 级别 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| primary | 默认值,只从主节点读,主节点不可用时报错 |
| primaryPreferred | 优先主节点(primary)读,主节点不可用时到从节点(secondary)读 |
| secondary | 仅从备节点(secondary)读取数据 |
| secondaryPreferred | 优先从备节点读,从节点不可用时到主节点读取 |
| nearest | 到网络延迟最低的节点读取数据,不管是主节点还是从节点 |
小结
MongoDB 是当下 NoSQL 数据库的首选,也有不少服务化架构采用了 MongoDB作为主要数据库,
其在 4.x版本中即将推出事务功能,在未来该文档数据库相对于RDBMS的差距将会大大缩小。
也正由于MongoDB 具备 简单、易扩展、高性能等特性,其社区活跃度非常高,是非常值得关注和学习的。
欢迎继续关注"美码师的补习系列-springboot篇" ,期待更多精彩内容-
补习系列(16)-springboot mongodb 数据库应用技巧的更多相关文章
- 补习系列(17)-springboot mongodb 内嵌数据库
目录 简介 一.使用 flapdoodle.embed.mongo A. 引入依赖 B. 准备测试类 C. 完善配置 D. 启动测试 细节 二.使用Fongo A. 引入框架 B. 准备测试类 C.业 ...
- 补习系列(17)-springboot mongodb 内嵌数据库【华为云技术分享】
目录 简介 一.使用 flapdoodle.embed.mongo A. 引入依赖 B. 准备测试类 C. 完善配置 D. 启动测试 细节 二.使用Fongo A. 引入框架 B. 准备测试类 C.业 ...
- 补习系列(14)-springboot redis 整合-数据读写
目录 一.简介 二.SpringBoot Redis 读写 A. 引入 spring-data-redis B. 序列化 C. 读写样例 三.方法级缓存 四.连接池 小结 一.简介 在 补习系列(A3 ...
- 补习系列(15)-springboot 分布式会话原理
目录 一.背景 二.SpringBoot 分布式会话 三.样例程序 四.原理进阶 A. 序列化 B. 会话代理 C. 数据老化 小结 一.背景 在 补习系列(3)-springboot 几种scope ...
- 补习系列(18)-springboot H2 迷你数据库
目录 关于 H2 一.H2 用作本地数据库 1. 引入依赖: 2. 配置文件 3. 样例数据 二.H2 用于单元测试 1. 依赖包 2. 测试配置 3. 测试代码 小结 关于 H2 H2 数据库是一个 ...
- 补习系列(6)- springboot 整合 shiro 一指禅
目标 了解ApacheShiro是什么,能做什么: 通过QuickStart 代码领会 Shiro的关键概念: 能基于SpringBoot 整合Shiro 实现URL安全访问: 掌握基于注解的方法,以 ...
- 补习系列(19)-springboot JPA + PostGreSQL
目录 SpringBoot 整合 PostGreSQL 一.PostGreSQL简介 二.关于 SpringDataJPA 三.整合 PostGreSQL A. 依赖包 B. 配置文件 C. 模型定义 ...
- 补习系列(10)-springboot 之配置读取
目录 简介 一.配置样例 二.如何注入配置 1. 缺省配置文件 2. 使用注解 3. 启动参数 还有.. 三.如何读取配置 @Value 注解 Environment 接口 @Configuratio ...
- 补习系列(8)-springboot 单元测试之道
目录 目标 一.About 单元测试 二.About Junit 三.SpringBoot-单元测试 项目依赖 测试样例 四.Mock测试 五.最后 目标 了解 单元测试的背景 了解如何 利用 spr ...
随机推荐
- 创建servlet的三种方式
第一种方式,实现Servlet接口 package com.example.servlet; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.Serv ...
- 0516js综合练习
<!DOCTYPE html><html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> ...
- CF#483(div2 C)
http://codeforces.com/contest/984/problem/C C. Finite or not time limit per test 1 second memory lim ...
- mysql数据库死锁的产生原因及解决办法
这篇文章主要介绍了mysql数据库锁的产生原因及解决办法,需要的朋友可以参考下 数据库和操作系统一样,是一个多用户使用的共享资源.当多个用户并发地存取数据 时,在数据库中就会产生多个事务同时存取同 ...
- java正则表达式验证金额
String reg_money = "\\d+(\\.\\d{1,2})?";// 金额正则,可以没有小数,小数最多不超过两位 Pattern pattern = Pattern ...
- CentOS7快速搭建LNMP环境
名词解释: LNMP:Linux+Nginx+MySql+PHPLAMP:LInux+Apache+MySql+PHPNginx的正确读法应该是Engine X我们使用CentOS自带的YUM来安装 ...
- 如何离线安装python的whl库
对于使用公司内网环境办公的人来说,可能无法使用pip install 命令安装python的whl库.对于这种情况,我们可以用以下的方法安装一个whl库. 1 下载whl文件,下载时注意,whl文件的 ...
- springMVC框架在js中使用window.location.href请求url时IE不兼容问题解决
是使用springMVC框架时,有时候需要在js中使用window.location.href来请求url,比如下面的路径: window.location.href = 'forecast/down ...
- 吐槽一下--最近多次在腾讯以及万科的面试经历---Web前端与PHP后端开发
前端时间,由于职业发展等,想要换一份工作,于是投递了一些国内还算知名的公司,列如: 腾讯.万科之类的: (1)首先说一下这两家公司的反馈情况: 腾讯:投递到反馈,(初次人事打电话沟通)大约1周,三次不 ...
- Prometheus监控数据格式学习
本文大纲: • prometheus metrics的概念• k/v的数据形式• prometheus exporter的使⽤(pull形式采集数据)• prometheus pushgateway的 ...
