谣言检测(ClaHi-GAT)《Rumor Detection on Twitter with Claim-Guided Hierarchical Graph Attention Networks》
论文信息
论文标题:Rumor Detection on Twitter with Claim-Guided Hierarchical Graph Attention Networks
论文作者:Erxue Min, Yu Rong, Yatao Bian, Tingyang Xu, Peilin Zhao, Junzhou Huang,Sophia Ananiadou
论文来源:2021,EMNLP
论文地址:download
论文代码:download
Background
传播结构为谣言的真假提供了有用的线索,但是现有的谣言检测方法要么局限于用户相应关系,要么简化了对话结构。
本文说的 Claim 代表的是 Source post ,即源帖。
1 Introduction
如下为一个简单的 conversation thread 例子:
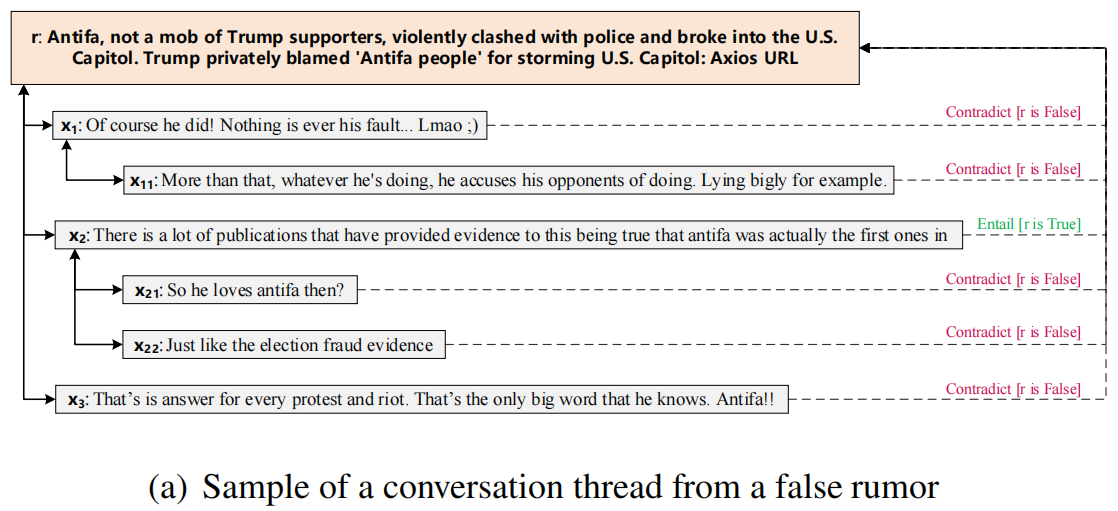
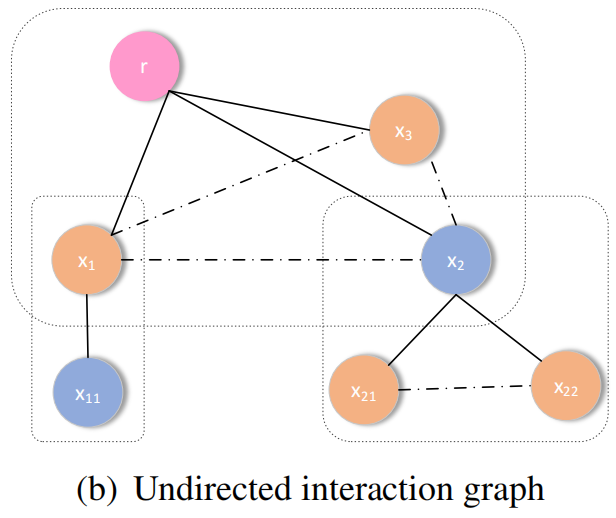
本文提出的点:考虑兄弟之间的关系,如下图虚线部分。
2 Claim-guided Hierarchical Graph Attention Networks
总体框架如下:
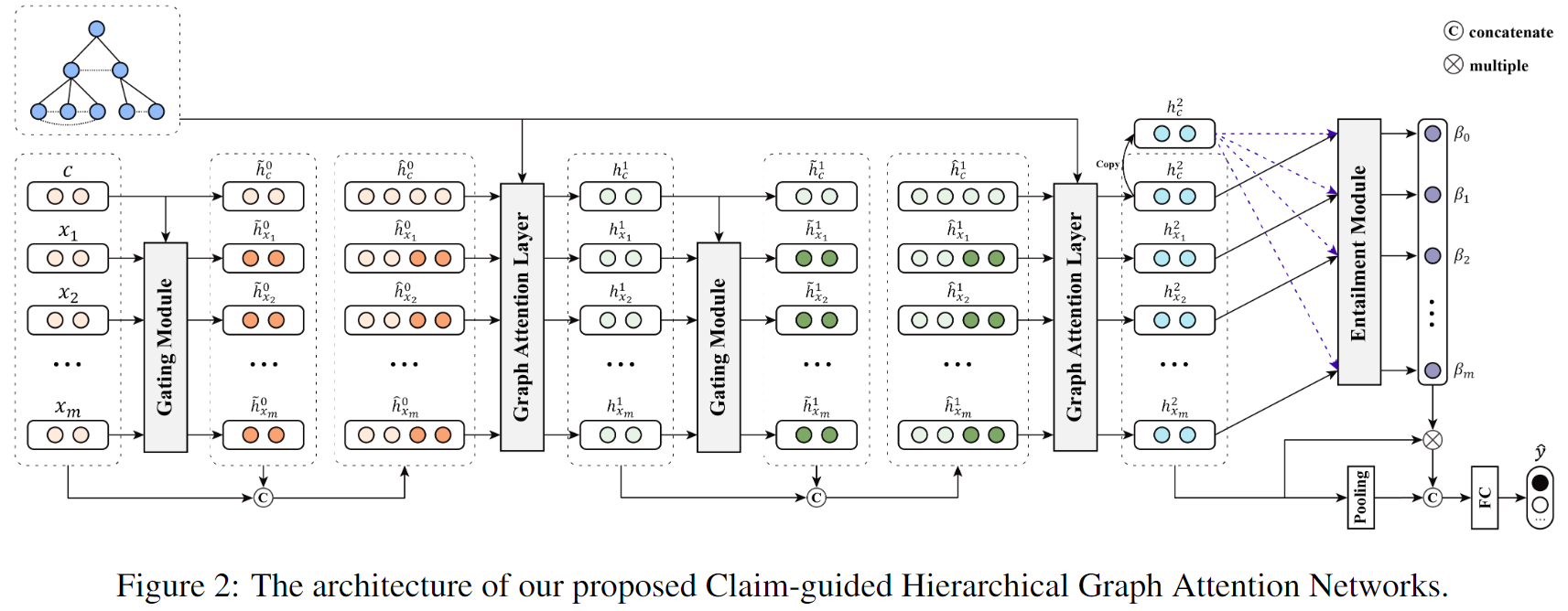
本文的模型包括两个注意力模块:
- A Graph Attention to capture the importance of different neighboring tweets
- A claim-guided hierarchical attention to enhance post content understanding
2.1 Claim-guided Hierarchical Attention
对于每个 tweet $x_i$ ,首先使用 Bi-LSTM 获得 Post 的特征矩阵 $X=\left[c, x_{1}, x_{2}, \cdots, x_{|\mathcal{V}|-1}\right]^{\top}$ ,其中 $c, x_{i} \in \mathbb{R}^{d}$。
为加强模型的主题一致性和语义推理:
Post-level Attention
为了防止主题偏离和丢失 claim 的信息,本文采用 gate module 决定它应该接受 claim 多少信息,以更好地指导相关职位的重要性分配。claim-aware representation 具体如下:
$\begin{array}{l}g_{c \rightarrow x_{i}}^{(l)} &=&\operatorname{sigmoid}\left(W_{g}^{(l)} h_{x_{i}}^{(l)}+U_{g}^{(l)} h_{c}^{(l)}\right) \\\tilde{h}_{x_{i}}^{(l)} &=&g_{c \rightarrow x_{i}}^{(l)} \odot h_{x_{i}}^{(l)}+\left(1-g_{c \rightarrow x_{i}}^{(l)}\right) \odot h_{c}^{(l)}\end{array}$
其中,$g_{c \rightarrow x_{i}}^{(l)}$ 是一个 gate vector,$W_{g}^{(l)}$ 和 $U_{g}^{(l)}$ 是可学习参数。
然后,将 claim-aware representation 与 original representation 拼接起来,作为 $\text{Eq.1}$ 的输入去计算注意力权重:
$\begin{array}{l}\hat{h}_{x_{i}}^{(l)}=\left[\tilde{h}_{x_{i}}^{(l)} \| h_{x_{i}}^{(l)}\right] \\\hat{\alpha}_{i, j}^{(l)}=\operatorname{Atten}\left(\hat{h}_{x_{i}}^{(l)}, \hat{h}_{x_{j}}^{(l)}\right)\end{array}$
2.2 Graph Attention Networks
为了编码结构信息,本文使用 GAT encoder:
输入:$H^{(l)}=\left[h_{c}^{(l)}, h_{x_{1}}^{(l)}, h_{x_{2}}^{(l)}, \ldots, h_{x_{|\mathcal{V}|-1}}^{(l)}\right]^{\top}$
过程:
${\large \begin{aligned}\alpha_{i, j}^{(l)} &=\operatorname{Atten}\left(h_{x_{i}}^{(l)}, h_{x_{j}}^{(l)}\right) \\&=\frac{\exp \left(\phi\left(a^{\top}\left[W^{(l)} h_{x_{i}}^{(l)} \| W^{(l)} h_{x_{j}}^{(l)}\right]\right)\right)}{\sum_{j \in \mathcal{N}_{i}} \exp \left(\phi\left(a^{\top}\left[W^{(l)} h_{x_{i}}^{(l)} \| W^{(l)} h_{x_{j}}^{(l)}\right]\right)\right)}\end{aligned}} $
$h_{x_{i}}^{(l+1)}=\operatorname{Re} L U\left(\sum\limits_{j \in \mathcal{N}_{i}} \alpha_{i, j}^{(l)} W^{(l)} h_{x_{j}}^{(l)}\right)$
考虑多头注意力:
$h_{x_{i}}^{(l+1)}=\|_{k=1}^{K} \operatorname{ReLU}\left(\sum\limits _{j \in \mathcal{N}_{i}} \alpha_{i, j}^{(l, k)} W_{k}^{(l)} h_{x_{j}}^{(l)}\right)$
替换输出层的表示向量:
${\large h_{x_{i}}^{(L)}=\operatorname{Re} L U\left(\frac{1}{K} \sum\limits _{k=1}^{K} \sum\limits_{j \in \mathcal{N}_{i}} \alpha_{i, j}^{\left(l^{\prime}, k\right)} W_{k}^{\left(l^{\prime}\right)} h_{x_{j}}^{\left(l^{\prime}\right)}\right)} $
输出:图表示
$\bar{s}=\text { mean-pooling }\left(H^{(L)}\right)$
Event-level Attention
出发点:获得图表示的时候采用的 平均池化并不是一定有意义的,可能存在某些节点对于图分类来说更准确。
受到 Natural Language Inference (NLI) 的影响,本文考虑对 GAT 最后一层的 $h_{c}^{(L)}$ 和 $\left.h_{x_{i}}^{(L)}: 1\right)$ 做如下处理 :
1)concatenation $\left[h_{c}^{(L)} \| h_{x_{i}}^{(L)}\right]$
2)element-wise product $h_{\text {prod }}^{(L)}=h_{c}^{(L)} \odot h_{x_{i}}^{(L)}$
3)absolute element-wise difference $h_{\text {diff }}^{(L)}=\left|h_{c}^{(L)}-h_{x_{i}}^{(L)}\right|$
接着获得一个联合表示:
$h_{x_{i}}^{c}=\tanh \left(F C\left(\left[h_{c}^{(L)}\left\|h_{x_{i}}^{(L)}\right\| h_{\text {prod }}^{(L)} \| h_{\text {diff }}^{(L)}\right]\right)\right)$
通过使用该联合表示计算 Event-level Attention :
${\large \begin{array}{l}b_{i} &=&\tanh \left(F C\left(h_{x_{i}}^{c}\right)\right) \\\beta_{i} &=&\frac{\exp \left(b_{i}\right)}{\sum_{i} \exp \left(b_{i}\right)} \\\hat{s} &&=\sum_{i} \beta_{i} h_{x_{i}}^{(L)}\end{array}} $
最后将其 $\hat{S}$ 与 GAT 最后一层的平均池化图表示 $\bar{s}$ 拼接作为最终图表示,并进行分类:
$\hat{y}=\operatorname{softmax}(F C([\hat{s} \| \bar{s}]))$
3 Experiments
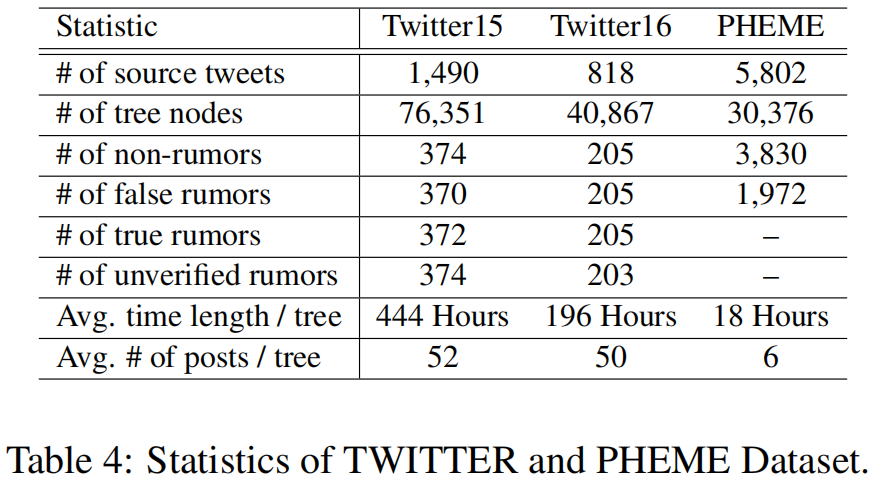
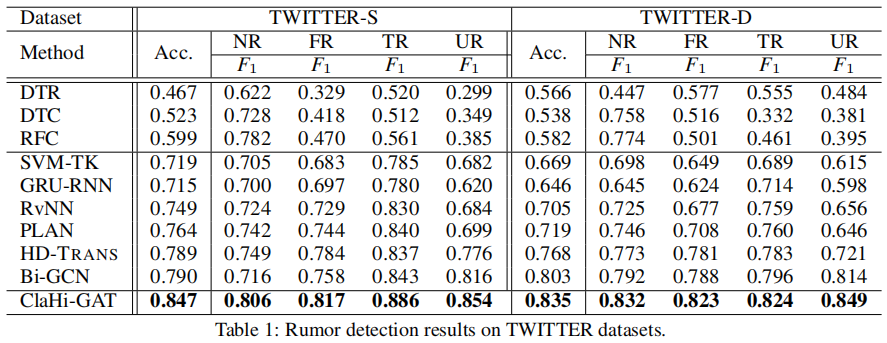
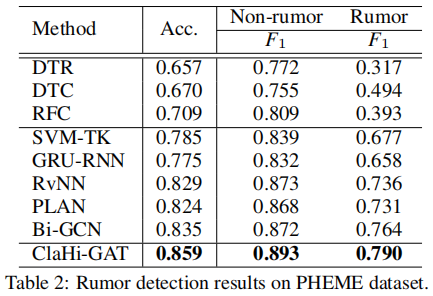
3.2 Rumor Classifification Performance
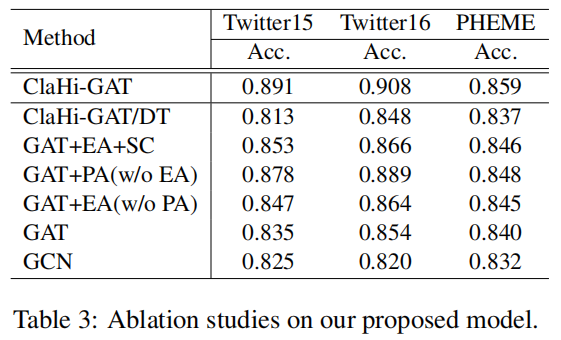
3.3 Ablation Study
1) ClaHi-GAT/DT: Instead of the undirected interaction graph, we use the directed trees as the model input.
2) GAT+EA+SC: We simply concatenate the features of the claim with the node features at each GAT layer, to replace the claim-aware representation.
3) w/o EA: We discard the event-level (inference-based) attention as presented.
4) w/o PA: We neglect the post-level (claim-aware) attention by leaving out the gating module introduced.
5) GAT: The backbone model.
6) GCN: The vanilla graph convolutional networks with no attention.
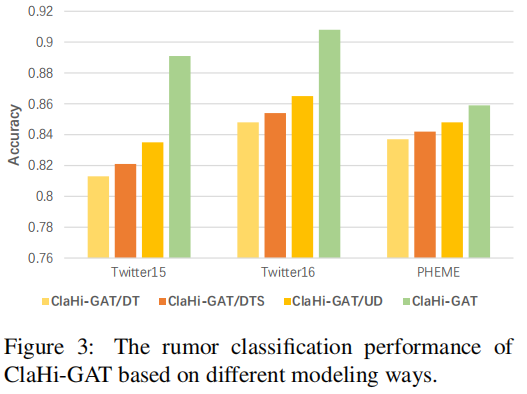
3.4 Evaluation of Undirected Interaction Graphs
- ClaHi-GAT/DT Utilize the directional tree applied in past influential works as the modeling way instead of our proposed undirected interaction graph.
- ClaHi-GAT/DTS Based on the directional tree structure similar to ClaHi-GAT/DT but the explicit interactions between sibling nodes are taken into account.
- ClaHi-GAT/UD The modeling way is our undirected interaction topology but without considering the explicit correlations between sibling nodes that reply to the same target.
- ClaHi-GAT In this paper, we propose to model the conversation thread as an undirected interaction graph for our claim-guided hierarchical graph attention networks.
3.5 Early Rumor Detection
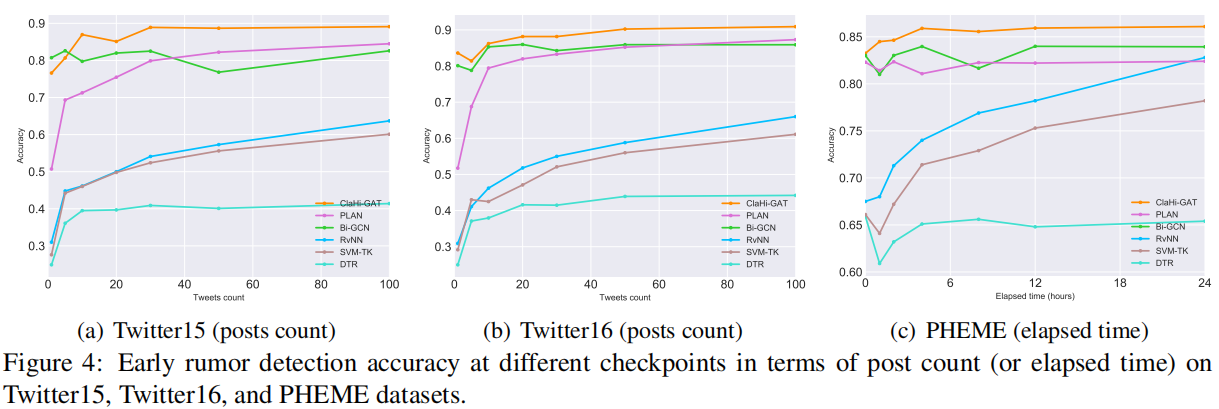
关键点:随着 claim 的传播,或多或少会产生更多的语义信息和噪声,所以使用 claim 的信息至关重要。
举例说明:false claim 的注意力分数得分图如下:

言下之意:错误的 post $x_2$ 会被赋予较小的权重,这就是为什么该模型早期谣言检测比较稳定的原因。
谣言检测(ClaHi-GAT)《Rumor Detection on Twitter with Claim-Guided Hierarchical Graph Attention Networks》的更多相关文章
- 论文解读(RvNN)《Rumor Detection on Twitter with Tree-structured Recursive Neural Networks》
论文信息 论文标题:Rumor Detection on Twitter with Tree-structured Recursive Neural Networks论文作者:Jing Ma, Wei ...
- 谣言检测(PSIN)——《Divide-and-Conquer: Post-User Interaction Network for Fake News Detection on Social Media》
论文信息 论文标题:Divide-and-Conquer: Post-User Interaction Network for Fake News Detection on Social Media论 ...
- 谣言检测——《MFAN: Multi-modal Feature-enhanced Attention Networks for Rumor Detection》
论文信息 论文标题:MFAN: Multi-modal Feature-enhanced Attention Networks for Rumor Detection论文作者:Jiaqi Zheng, ...
- 谣言检测——(PSA)《Probing Spurious Correlations in Popular Event-Based Rumor Detection Benchmarks》
论文信息 论文标题:Probing Spurious Correlations in Popular Event-Based Rumor Detection Benchmarks论文作者:Jiayin ...
- 谣言检测(GACL)《Rumor Detection on Social Media with Graph Adversarial Contrastive Learning》
论文信息 论文标题:Rumor Detection on Social Media with Graph AdversarialContrastive Learning论文作者:Tiening Sun ...
- 谣言检测(PLAN)——《Interpretable Rumor Detection in Microblogs by Attending to User Interactions》
论文信息 论文标题:Interpretable Rumor Detection in Microblogs by Attending to User Interactions论文作者:Ling Min ...
- 谣言检测(RDEA)《Rumor Detection on Social Media with Event Augmentations》
论文信息 论文标题:Rumor Detection on Social Media with Event Augmentations论文作者:Zhenyu He, Ce Li, Fan Zhou, Y ...
- 谣言检测()《Data Fusion Oriented Graph Convolution Network Model for Rumor Detection》
论文信息 论文标题:Data Fusion Oriented Graph Convolution Network Model for Rumor Detection论文作者:Erxue Min, Yu ...
- 谣言检测()《Rumor Detection with Self-supervised Learning on Texts and Social Graph》
论文信息 论文标题:Rumor Detection with Self-supervised Learning on Texts and Social Graph论文作者:Yuan Gao, Xian ...
随机推荐
- Linux 加密安全和私有CA的搭建方法
常用安全技术 3A: 认证:身份确认 授权:权限分配 审计:监控做了什么 安全通信 加密算法和协议 对称加密: 非对称加密 单向加密:哈希(hash)加密 认证协议 对称加密: 加密和解密使用的是同一 ...
- React + Antd Menu组件实现菜单树
准备好两个变量,一个用来保存平级菜单列表,一个用来保存遍历后的菜单树. 推荐后端返回平级菜单树,假如菜单比较多,可以直接结合find方法找到菜单,做搜索功能很省事. const [menuList, ...
- HMS Core音频编辑服务音源分离与空间音频渲染,助力快速进入3D音频的世界
从单声道.立体声.环绕声发展到三维声,音频回放技术的迭代演进是为了还原真实世界的声音.其中,三维声技术使用信号处理的方法对到达两耳的声音信号进行模拟,将声场还原为三维空间,更接近真实世界.凭借这个技术 ...
- DZY Loves Math II
简要题面 对于正整数 \(S, n\),求满足如下条件的素数数列 \((p_1,p_2,\cdots,p_k)\)(\(k\) 为任意正整数) 的个数: \(p_1\le p_2\le\cdots\l ...
- Swift高仿iOS网易云音乐Moya+RxSwift+Kingfisher+MVC+MVVM
效果 列文章目录 因为目录比较多,每次更新这里比较麻烦,所以推荐点击到主页,然后查看iOS Swift云音乐专栏. 目简介 这是一个使用Swift(还有OC版本)语言,从0开发一个iOS平台,接近企业 ...
- YII的延迟加载
类的映射表 use app\model\order \Yii::$classMap['app\models\Order'] = "D:\wamp\www\...\models\Order.p ...
- Nginx 浏览器缓存配置指令
# 浏览器缓存 # 当浏览器第一次访问服务器资源的时候,服务器返回到浏览器后,浏览器进行缓存 # 缓存的大概内容有: # 1.缓存过期的日期和时间 # 2.设置和缓存相关的配置信息 # 3.请求资源最 ...
- 用JavaScript写一个进度条
var porpressBar = document.getElementById('progressBar') var info = document.getElementById('info') ...
- Luogu2938 [USACO09FEB]股票市场Stock Market (DP,多重背包)
第n天不卖,视为卖了又原价买回 #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include ...
- Luogu3870 [TJOI2009]开关 (分块)
线段树做法很简单,但分块好啊 #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include & ...
