Python全栈开发:模块
模块,用一砣代码实现了某个功能的代码集合。
参考资源:http://www.cnblogs.com/alex3714/articles/5161349.html
类似于函数式编程和面向过程编程,函数式编程则完成一个功能,其他代码用来调用即可,提供了代码的重用性和代码间的耦合。而对于一个复杂的功能来,可能需要多个函数才能完成(函数又可以在不同的.py文件中),n个 .py 文件组成的代码集合就称为模块。
如:os 是系统相关的模块;file是文件操作相关的模块
模块分为三种:
- 自定义模块
- 内置模块
- 开源模块
自定义模块
1、定义模块
情景一:

情景二:

情景三:

2、导入模块
Python之所以应用越来越广泛,在一定程度上也依赖于其为程序员提供了大量的模块以供使用,如果想要使用模块,则需要导入。导入模块有一下几种方法:
|
1
2
3
4
|
import modulefrom module.xx.xx import xxfrom module.xx.xx import xx as rename from module.xx.xx import * |
导入模块其实就是告诉Python解释器去解释那个py文件
- 导入一个py文件,解释器解释该py文件
- 导入一个包,解释器解释该包下的 __init__.py 文件
那么问题来了,导入模块时是根据那个路径作为基准来进行的呢?即:sys.path
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
import sysprint sys.path 结果:['/Users/wupeiqi/PycharmProjects/calculator/p1/pp1', '/usr/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/setuptools-15.2-py2.7.egg', '/usr/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/distribute-0.6.28-py2.7.egg', '/usr/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/MySQL_python-1.2.4b4-py2.7-macosx-10.10-x86_64.egg', '/usr/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/xlutils-1.7.1-py2.7.egg', '/usr/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/xlwt-1.0.0-py2.7.egg', '/usr/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/xlrd-0.9.3-py2.7.egg', '/usr/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/tornado-4.1-py2.7-macosx-10.10-x86_64.egg', '/usr/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/backports.ssl_match_hostname-3.4.0.2-py2.7.egg', '/usr/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/certifi-2015.4.28-py2.7.egg', '/usr/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/pyOpenSSL-0.15.1-py2.7.egg', '/usr/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/six-1.9.0-py2.7.egg', '/usr/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/cryptography-0.9.1-py2.7-macosx-10.10-x86_64.egg', '/usr/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/cffi-1.1.1-py2.7-macosx-10.10-x86_64.egg', '/usr/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ipaddress-1.0.7-py2.7.egg', '/usr/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/enum34-1.0.4-py2.7.egg', '/usr/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/pyasn1-0.1.7-py2.7.egg', '/usr/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/idna-2.0-py2.7.egg', '/usr/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/pycparser-2.13-py2.7.egg', '/usr/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/Django-1.7.8-py2.7.egg', '/usr/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/paramiko-1.10.1-py2.7.egg', '/usr/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/gevent-1.0.2-py2.7-macosx-10.10-x86_64.egg', '/usr/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/greenlet-0.4.7-py2.7-macosx-10.10-x86_64.egg', '/Users/wupeiqi/PycharmProjects/calculator', '/usr/local/Cellar/python/2.7.9/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/lib/python27.zip', '/usr/local/Cellar/python/2.7.9/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/lib/python2.7', '/usr/local/Cellar/python/2.7.9/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/lib/python2.7/plat-darwin', '/usr/local/Cellar/python/2.7.9/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/lib/python2.7/plat-mac', '/usr/local/Cellar/python/2.7.9/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/lib/python2.7/plat-mac/lib-scriptpackages', '/usr/local/Cellar/python/2.7.9/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/lib/python2.7/lib-tk', '/usr/local/Cellar/python/2.7.9/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/lib/python2.7/lib-old', '/usr/local/Cellar/python/2.7.9/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/lib/python2.7/lib-dynload', '/usr/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages', '/Library/Python/2.7/site-packages'] |
如果sys.path路径列表没有你想要的路径,可以通过 sys.path.append('路径') 添加。
通过os模块可以获取各种目录,例如:
- import sys
- import os
- pre_path = os.path.abspath('../')
- sys.path.append(pre_path)
开源模块
一、下载安装
下载安装有两种方式:
- yum
- pip
- apt-get
- ...
- 下载源码
- 解压源码
- 进入目录
- 编译源码 python setup.py build
- 安装源码 python setup.py install
注:在使用源码安装时,需要使用到gcc编译和python开发环境,所以,需要先执行:
|
1
2
3
4
|
yum install gccyum install python-devel或apt-get python-dev |
安装成功后,模块会自动安装到 sys.path 中的某个目录中,如:
|
1
|
/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ |
二、导入模块
同自定义模块中导入的方式
三、模块 paramiko
paramiko是一个用于做远程控制的模块,使用该模块可以对远程服务器进行命令或文件操作,值得一说的是,fabric和ansible内部的远程管理就是使用的paramiko来现实。
1、下载安装
|
1
|
pip3 install paramiko |
或
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
# pycrypto,由于 paramiko 模块内部依赖pycrypto,所以先下载安装pycrypto# 下载安装 pycryptowget http://files.cnblogs.com/files/wupeiqi/pycrypto-2.6.1.tar.gztar -xvf pycrypto-2.6.1.tar.gzcd pycrypto-2.6.1python setup.py buildpython setup.py install# 进入python环境,导入Crypto检查是否安装成功# 下载安装 paramikowget http://files.cnblogs.com/files/wupeiqi/paramiko-1.10.1.tar.gztar -xvf paramiko-1.10.1.tar.gzcd paramiko-1.10.1python setup.py buildpython setup.py install# 进入python环境,导入paramiko检查是否安装成功 |
2、使用模块
- #!/usr/bin/env python
- #coding:utf-8
- import paramiko
- ssh = paramiko.SSHClient()
- ssh.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
- ssh.connect('192.168.1.108', 22, 'alex', '123')
- stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh.exec_command('df')
- print stdout.read()
- ssh.close();
- 执行命令 - 通过用户名和密码连接服务器
- import paramiko
- private_key_path = '/home/auto/.ssh/id_rsa'
- key = paramiko.RSAKey.from_private_key_file(private_key_path)
- ssh = paramiko.SSHClient()
- ssh.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
- ssh.connect('主机名 ', 端口, '用户名', key)
- stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh.exec_command('df')
- print stdout.read()
- ssh.close()
- 执行命令 - 过密钥链接服务器
- import os,sys
- import paramiko
- t = paramiko.Transport(('182.92.219.86',22))
- t.connect(username='wupeiqi',password='123')
- sftp = paramiko.SFTPClient.from_transport(t)
- sftp.put('/tmp/test.py','/tmp/test.py')
- t.close()
- import os,sys
- import paramiko
- t = paramiko.Transport(('182.92.219.86',22))
- t.connect(username='wupeiqi',password='123')
- sftp = paramiko.SFTPClient.from_transport(t)
- sftp.get('/tmp/test.py','/tmp/test2.py')
- t.close()
- 上传或者下载文件 - 通过用户名和密码
- import paramiko
- pravie_key_path = '/home/auto/.ssh/id_rsa'
- key = paramiko.RSAKey.from_private_key_file(pravie_key_path)
- t = paramiko.Transport(('182.92.219.86',22))
- t.connect(username='wupeiqi',pkey=key)
- sftp = paramiko.SFTPClient.from_transport(t)
- sftp.put('/tmp/test3.py','/tmp/test3.py')
- t.close()
- import paramiko
- pravie_key_path = '/home/auto/.ssh/id_rsa'
- key = paramiko.RSAKey.from_private_key_file(pravie_key_path)
- t = paramiko.Transport(('182.92.219.86',22))
- t.connect(username='wupeiqi',pkey=key)
- sftp = paramiko.SFTPClient.from_transport(t)
- sftp.get('/tmp/test3.py','/tmp/test4.py')
- t.close()
- 上传或下载文件 - 通过密钥
内置模块
一、os
用于提供系统级别的操作

- os.getcwd() 获取当前工作目录,即当前python脚本工作的目录路径
- os.chdir("dirname") 改变当前脚本工作目录;相当于shell下cd
- os.curdir 返回当前目录: ('.')
- os.pardir 获取当前目录的父目录字符串名:('..')
- os.makedirs('dirname1/dirname2') 可生成多层递归目录
- os.removedirs('dirname1') 若目录为空,则删除,并递归到上一级目录,如若也为空,则删除,依此类推
- os.mkdir('dirname') 生成单级目录;相当于shell中mkdir dirname
- os.rmdir('dirname') 删除单级空目录,若目录不为空则无法删除,报错;相当于shell中rmdir dirname
- os.listdir('dirname') 列出指定目录下的所有文件和子目录,包括隐藏文件,并以列表方式打印
- os.remove() 删除一个文件
- os.rename("oldname","newname") 重命名文件/目录
- os.stat('path/filename') 获取文件/目录信息
- os.sep 输出操作系统特定的路径分隔符,win下为"\\",Linux下为"/"
- os.linesep 输出当前平台使用的行终止符,win下为"\t\n",Linux下为"\n"
- os.pathsep 输出用于分割文件路径的字符串
- os.name 输出字符串指示当前使用平台。win->'nt'; Linux->'posix'
- os.system("bash command") 运行shell命令,直接显示
- os.environ 获取系统环境变量
- os.path.abspath(path) 返回path规范化的绝对路径
- os.path.split(path) 将path分割成目录和文件名二元组返回
- os.path.dirname(path) 返回path的目录。其实就是os.path.split(path)的第一个元素
- os.path.basename(path) 返回path最后的文件名。如何path以/或\结尾,那么就会返回空值。即os.path.split(path)的第二个元素
- os.path.exists(path) 如果path存在,返回True;如果path不存在,返回False
- os.path.isabs(path) 如果path是绝对路径,返回True
- os.path.isfile(path) 如果path是一个存在的文件,返回True。否则返回False
- os.path.isdir(path) 如果path是一个存在的目录,则返回True。否则返回False
- os.path.join(path1[, path2[, ...]]) 将多个路径组合后返回,第一个绝对路径之前的参数将被忽略
- os.path.getatime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后存取时间
- os.path.getmtime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后修改时间

更多猛击这里
二、sys
用于提供对解释器相关的操作

- sys.argv 命令行参数List,第一个元素是程序本身路径
- sys.exit(n) 退出程序,正常退出时exit(0)
- sys.version 获取Python解释程序的版本信息
- sys.maxint 最大的Int值
- sys.path 返回模块的搜索路径,初始化时使用PYTHONPATH环境变量的值
- sys.platform 返回操作系统平台名称
- sys.stdout.write('please:')
- val = sys.stdin.readline()[:-1]

更多猛击这里
三、hashlib
用于加密相关的操作,代替了md5模块和sha模块,主要提供 SHA1, SHA224, SHA256, SHA384, SHA512 ,MD5 算法
- import md5
- hash = md5.new()
- hash.update('admin')
- print hash.hexdigest()
- import sha
- hash = sha.new()
- hash.update('admin')
- print hash.hexdigest()
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
import hashlib# ######## md5 ########hash = hashlib.md5()hash.update('admin')print hash.hexdigest()# ######## sha1 ########hash = hashlib.sha1()hash.update('admin')print hash.hexdigest()# ######## sha256 ########hash = hashlib.sha256()hash.update('admin')print hash.hexdigest()# ######## sha384 ########hash = hashlib.sha384()hash.update('admin')print hash.hexdigest()# ######## sha512 ########hash = hashlib.sha512()hash.update('admin')print hash.hexdigest() |
以上加密算法虽然依然非常厉害,但时候存在缺陷,即:通过撞库可以反解。所以,有必要对加密算法中添加自定义key再来做加密。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
import hashlib# ######## md5 ########hash = hashlib.md5('898oaFs09f')hash.update('admin')print hash.hexdigest() |
还不够吊?python 还有一个 hmac 模块,它内部对我们创建 key 和 内容 再进行处理然后再加密
|
1
2
3
4
|
import hmach = hmac.new('wueiqi')h.update('hellowo')print h.hexdigest() |
不能再牛逼了!!!
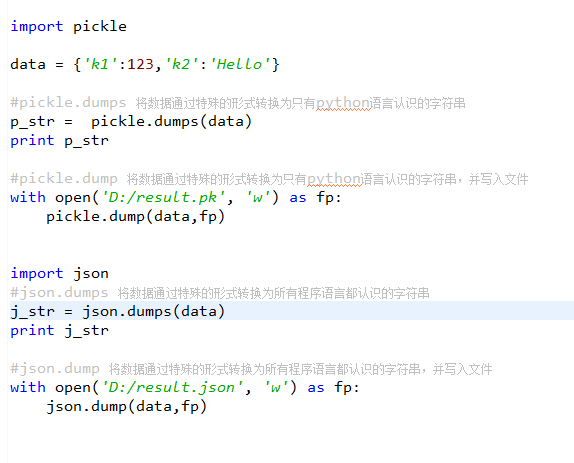
四、json 和 pickle
用于序列化的两个模块
- json,用于字符串 和 python数据类型间进行转换
- pickle,用于python特有的类型 和 python的数据类型间进行转换
Json模块提供了四个功能:dumps、dump、loads、load
pickle模块提供了四个功能:dumps、dump、loads、load
五、执行系统命令
可以执行shell命令的相关模块和函数有:
- os.system
- os.spawn*
- os.popen* --废弃
- popen2.* --废弃
- commands.* --废弃,3.x中被移除
- import commands
- result = commands.getoutput('cmd')
- result = commands.getstatus('cmd')
- result = commands.getstatusoutput('cmd')
以上执行shell命令的相关的模块和函数的功能均在 subprocess 模块中实现,并提供了更丰富的功能。
call
执行命令,返回状态码
|
1
2
|
ret = subprocess.call(["ls", "-l"], shell=False)ret = subprocess.call("ls -l", shell=True) |
shell = True ,允许 shell 命令是字符串形式
check_call
执行命令,如果执行状态码是 0 ,则返回0,否则抛异常
|
1
2
|
subprocess.check_call(["ls", "-l"])subprocess.check_call("exit 1", shell=True) |
check_output
执行命令,如果状态码是 0 ,则返回执行结果,否则抛异常
|
1
2
|
subprocess.check_output(["echo", "Hello World!"])subprocess.check_output("exit 1", shell=True) |
subprocess.Popen(...)
用于执行复杂的系统命令
参数:
- args:shell命令,可以是字符串或者序列类型(如:list,元组)
- bufsize:指定缓冲。0 无缓冲,1 行缓冲,其他 缓冲区大小,负值 系统缓冲
- stdin, stdout, stderr:分别表示程序的标准输入、输出、错误句柄
- preexec_fn:只在Unix平台下有效,用于指定一个可执行对象(callable object),它将在子进程运行之前被调用
- close_sfs:在windows平台下,如果close_fds被设置为True,则新创建的子进程将不会继承父进程的输入、输出、错误管道。
所以不能将close_fds设置为True同时重定向子进程的标准输入、输出与错误(stdin, stdout, stderr)。 - shell:同上
- cwd:用于设置子进程的当前目录
- env:用于指定子进程的环境变量。如果env = None,子进程的环境变量将从父进程中继承。
- universal_newlines:不同系统的换行符不同,True -> 同意使用 \n
- startupinfo与createionflags只在windows下有效
将被传递给底层的CreateProcess()函数,用于设置子进程的一些属性,如:主窗口的外观,进程的优先级等等
- import subprocess
- ret1 = subprocess.Popen(["mkdir","t1"])
- ret2 = subprocess.Popen("mkdir t2", shell=True)
终端输入的命令分为两种:
- 输入即可得到输出,如:ifconfig
- 输入进行某环境,依赖再输入,如:python
- import subprocess
- obj = subprocess.Popen("mkdir t3", shell=True, cwd='/home/dev',)
- 复制代码
- import subprocess
- obj = subprocess.Popen(["python"], stdin=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
- obj.stdin.write('print 1 \n ')
- obj.stdin.write('print 2 \n ')
- obj.stdin.write('print 3 \n ')
- obj.stdin.write('print 4 \n ')
- obj.stdin.close()
- cmd_out = obj.stdout.read()
- obj.stdout.close()
- cmd_error = obj.stderr.read()
- obj.stderr.close()
- print cmd_out
- print cmd_error
- 复制代码
- 复制代码
- import subprocess
- obj = subprocess.Popen(["python"], stdin=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
- obj.stdin.write('print 1 \n ')
- obj.stdin.write('print 2 \n ')
- obj.stdin.write('print 3 \n ')
- obj.stdin.write('print 4 \n ')
- out_error_list = obj.communicate()
- print out_error_list
- 复制代码
- import subprocess
- obj = subprocess.Popen(["python"], stdin=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
- out_error_list = obj.communicate('print "hello"')
- print out_error_list
更多猛击这里
六、shutil
高级的 文件、文件夹、压缩包 处理模块
shutil.copyfileobj(fsrc, fdst[, length])
将文件内容拷贝到另一个文件中,可以部分内容
- def copyfileobj(fsrc, fdst, length=16*1024):
- """copy data from file-like object fsrc to file-like object fdst"""
- while 1:
- buf = fsrc.read(length)
- if not buf:
- break
- fdst.write(buf)
shutil.copyfile(src, dst)
拷贝文件
- def copyfile(src, dst):
- """Copy data from src to dst"""
- if _samefile(src, dst):
- raise Error("`%s` and `%s` are the same file" % (src, dst))
- for fn in [src, dst]:
- try:
- st = os.stat(fn)
- except OSError:
- # File most likely does not exist
- pass
- else:
- # XXX What about other special files? (sockets, devices...)
- if stat.S_ISFIFO(st.st_mode):
- raise SpecialFileError("`%s` is a named pipe" % fn)
- with open(src, 'rb') as fsrc:
- with open(dst, 'wb') as fdst:
- copyfileobj(fsrc, fdst)
shutil.copymode(src, dst)
仅拷贝权限。内容、组、用户均不变
- def copymode(src, dst):
- """Copy mode bits from src to dst"""
- if hasattr(os, 'chmod'):
- st = os.stat(src)
- mode = stat.S_IMODE(st.st_mode)
- os.chmod(dst, mode)
shutil.copystat(src, dst)
拷贝状态的信息,包括:mode bits, atime, mtime, flags
- def copystat(src, dst):
- """Copy all stat info (mode bits, atime, mtime, flags) from src to dst"""
- st = os.stat(src)
- mode = stat.S_IMODE(st.st_mode)
- if hasattr(os, 'utime'):
- os.utime(dst, (st.st_atime, st.st_mtime))
- if hasattr(os, 'chmod'):
- os.chmod(dst, mode)
- if hasattr(os, 'chflags') and hasattr(st, 'st_flags'):
- try:
- os.chflags(dst, st.st_flags)
- except OSError, why:
- for err in 'EOPNOTSUPP', 'ENOTSUP':
- if hasattr(errno, err) and why.errno == getattr(errno, err):
- break
- else:
- raise
shutil.copy(src, dst)
拷贝文件和权限
- def copy(src, dst):
- """Copy data and mode bits ("cp src dst").
- The destination may be a directory.
- """
- if os.path.isdir(dst):
- dst = os.path.join(dst, os.path.basename(src))
- copyfile(src, dst)
- copymode(src, dst)
shutil.copy2(src, dst)
拷贝文件和状态信息
- def copy2(src, dst):
- """Copy data and all stat info ("cp -p src dst").
- The destination may be a directory.
- """
- if os.path.isdir(dst):
- dst = os.path.join(dst, os.path.basename(src))
- copyfile(src, dst)
- copystat(src, dst)
shutil.ignore_patterns(*patterns)
shutil.copytree(src, dst, symlinks=False, ignore=None)
递归的去拷贝文件
例如:copytree(source, destination, ignore=ignore_patterns('*.pyc', 'tmp*'))
- def ignore_patterns(*patterns):
- """Function that can be used as copytree() ignore parameter.
- Patterns is a sequence of glob-style patterns
- that are used to exclude files"""
- def _ignore_patterns(path, names):
- ignored_names = []
- for pattern in patterns:
- ignored_names.extend(fnmatch.filter(names, pattern))
- return set(ignored_names)
- return _ignore_patterns
- def copytree(src, dst, symlinks=False, ignore=None):
- """Recursively copy a directory tree using copy2().
- The destination directory must not already exist.
- If exception(s) occur, an Error is raised with a list of reasons.
- If the optional symlinks flag is true, symbolic links in the
- source tree result in symbolic links in the destination tree; if
- it is false, the contents of the files pointed to by symbolic
- links are copied.
- The optional ignore argument is a callable. If given, it
- is called with the `src` parameter, which is the directory
- being visited by copytree(), and `names` which is the list of
- `src` contents, as returned by os.listdir():
- callable(src, names) -> ignored_names
- Since copytree() is called recursively, the callable will be
- called once for each directory that is copied. It returns a
- list of names relative to the `src` directory that should
- not be copied.
- XXX Consider this example code rather than the ultimate tool.
- """
- names = os.listdir(src)
- if ignore is not None:
- ignored_names = ignore(src, names)
- else:
- ignored_names = set()
- os.makedirs(dst)
- errors = []
- for name in names:
- if name in ignored_names:
- continue
- srcname = os.path.join(src, name)
- dstname = os.path.join(dst, name)
- try:
- if symlinks and os.path.islink(srcname):
- linkto = os.readlink(srcname)
- os.symlink(linkto, dstname)
- elif os.path.isdir(srcname):
- copytree(srcname, dstname, symlinks, ignore)
- else:
- # Will raise a SpecialFileError for unsupported file types
- copy2(srcname, dstname)
- # catch the Error from the recursive copytree so that we can
- # continue with other files
- except Error, err:
- errors.extend(err.args[0])
- except EnvironmentError, why:
- errors.append((srcname, dstname, str(why)))
- try:
- copystat(src, dst)
- except OSError, why:
- if WindowsError is not None and isinstance(why, WindowsError):
- # Copying file access times may fail on Windows
- pass
- else:
- errors.append((src, dst, str(why)))
- if errors:
- raise Error, errors
shutil.rmtree(path[, ignore_errors[, onerror]])
递归的去删除文件
- def rmtree(path, ignore_errors=False, onerror=None):
- """Recursively delete a directory tree.
- If ignore_errors is set, errors are ignored; otherwise, if onerror
- is set, it is called to handle the error with arguments (func,
- path, exc_info) where func is os.listdir, os.remove, or os.rmdir;
- path is the argument to that function that caused it to fail; and
- exc_info is a tuple returned by sys.exc_info(). If ignore_errors
- is false and onerror is None, an exception is raised.
- """
- if ignore_errors:
- def onerror(*args):
- pass
- elif onerror is None:
- def onerror(*args):
- raise
- try:
- if os.path.islink(path):
- # symlinks to directories are forbidden, see bug #1669
- raise OSError("Cannot call rmtree on a symbolic link")
- except OSError:
- onerror(os.path.islink, path, sys.exc_info())
- # can't continue even if onerror hook returns
- return
- names = []
- try:
- names = os.listdir(path)
- except os.error, err:
- onerror(os.listdir, path, sys.exc_info())
- for name in names:
- fullname = os.path.join(path, name)
- try:
- mode = os.lstat(fullname).st_mode
- except os.error:
- mode = 0
- if stat.S_ISDIR(mode):
- rmtree(fullname, ignore_errors, onerror)
- else:
- try:
- os.remove(fullname)
- except os.error, err:
- onerror(os.remove, fullname, sys.exc_info())
- try:
- os.rmdir(path)
- except os.error:
- onerror(os.rmdir, path, sys.exc_info())
shutil.move(src, dst)
递归的去移动文件
- def move(src, dst):
- """Recursively move a file or directory to another location. This is
- similar to the Unix "mv" command.
- If the destination is a directory or a symlink to a directory, the source
- is moved inside the directory. The destination path must not already
- exist.
- If the destination already exists but is not a directory, it may be
- overwritten depending on os.rename() semantics.
- If the destination is on our current filesystem, then rename() is used.
- Otherwise, src is copied to the destination and then removed.
- A lot more could be done here... A look at a mv.c shows a lot of
- the issues this implementation glosses over.
- """
- real_dst = dst
- if os.path.isdir(dst):
- if _samefile(src, dst):
- # We might be on a case insensitive filesystem,
- # perform the rename anyway.
- os.rename(src, dst)
- return
- real_dst = os.path.join(dst, _basename(src))
- if os.path.exists(real_dst):
- raise Error, "Destination path '%s' already exists" % real_dst
- try:
- os.rename(src, real_dst)
- except OSError:
- if os.path.isdir(src):
- if _destinsrc(src, dst):
- raise Error, "Cannot move a directory '%s' into itself '%s'." % (src, dst)
- copytree(src, real_dst, symlinks=True)
- rmtree(src)
- else:
- copy2(src, real_dst)
- os.unlink(src)
shutil.make_archive(base_name, format,...)
创建压缩包并返回文件路径,例如:zip、tar
- base_name: 压缩包的文件名,也可以是压缩包的路径。只是文件名时,则保存至当前目录,否则保存至指定路径,
如:www =>保存至当前路径
如:/Users/wupeiqi/www =>保存至/Users/wupeiqi/ - format: 压缩包种类,“zip”, “tar”, “bztar”,“gztar”
- root_dir: 要压缩的文件夹路径(默认当前目录)
- owner: 用户,默认当前用户
- group: 组,默认当前组
- logger: 用于记录日志,通常是logging.Logger对象
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
#将 /Users/wupeiqi/Downloads/test 下的文件打包放置当前程序目录import shutilret = shutil.make_archive("wwwwwwwwww", 'gztar', root_dir='/Users/wupeiqi/Downloads/test')#将 /Users/wupeiqi/Downloads/test 下的文件打包放置 /Users/wupeiqi/目录import shutilret = shutil.make_archive("/Users/wupeiqi/wwwwwwwwww", 'gztar', root_dir='/Users/wupeiqi/Downloads/test') |
- def make_archive(base_name, format, root_dir=None, base_dir=None, verbose=0,
- dry_run=0, owner=None, group=None, logger=None):
- """Create an archive file (eg. zip or tar).
- 'base_name' is the name of the file to create, minus any format-specific
- extension; 'format' is the archive format: one of "zip", "tar", "bztar"
- or "gztar".
- 'root_dir' is a directory that will be the root directory of the
- archive; ie. we typically chdir into 'root_dir' before creating the
- archive. 'base_dir' is the directory where we start archiving from;
- ie. 'base_dir' will be the common prefix of all files and
- directories in the archive. 'root_dir' and 'base_dir' both default
- to the current directory. Returns the name of the archive file.
- 'owner' and 'group' are used when creating a tar archive. By default,
- uses the current owner and group.
- """
- save_cwd = os.getcwd()
- if root_dir is not None:
- if logger is not None:
- logger.debug("changing into '%s'", root_dir)
- base_name = os.path.abspath(base_name)
- if not dry_run:
- os.chdir(root_dir)
- if base_dir is None:
- base_dir = os.curdir
- kwargs = {'dry_run': dry_run, 'logger': logger}
- try:
- format_info = _ARCHIVE_FORMATS[format]
- except KeyError:
- raise ValueError, "unknown archive format '%s'" % format
- func = format_info[0]
- for arg, val in format_info[1]:
- kwargs[arg] = val
- if format != 'zip':
- kwargs['owner'] = owner
- kwargs['group'] = group
- try:
- filename = func(base_name, base_dir, **kwargs)
- finally:
- if root_dir is not None:
- if logger is not None:
- logger.debug("changing back to '%s'", save_cwd)
- os.chdir(save_cwd)
- return filename
shutil 对压缩包的处理是调用 ZipFile 和 TarFile 两个模块来进行的,详细:
- import zipfile
- # 压缩
- z = zipfile.ZipFile('laxi.zip', 'w')
- z.write('a.log')
- z.write('data.data')
- z.close()
- # 解压
- z = zipfile.ZipFile('laxi.zip', 'r')
- z.extractall()
- z.close()
- 复制代码
- 复制代码
- import tarfile
- # 压缩
- tar = tarfile.open('your.tar','w')
- tar.add('/Users/wupeiqi/PycharmProjects/bbs2.zip', arcname='bbs2.zip')
- tar.add('/Users/wupeiqi/PycharmProjects/cmdb.zip', arcname='cmdb.zip')
- tar.close()
- # 解压
- tar = tarfile.open('your.tar','r')
- tar.extractall() # 可设置解压地址
- tar.close()
- 复制代码
- 复制代码
- class ZipFile(object):
- """ Class with methods to open, read, write, close, list zip files.
- z = ZipFile(file, mode="r", compression=ZIP_STORED, allowZip64=False)
- file: Either the path to the file, or a file-like object.
- If it is a path, the file will be opened and closed by ZipFile.
- mode: The mode can be either read "r", write "w" or append "a".
- compression: ZIP_STORED (no compression) or ZIP_DEFLATED (requires zlib).
- allowZip64: if True ZipFile will create files with ZIP64 extensions when
- needed, otherwise it will raise an exception when this would
- be necessary.
- """
- fp = None # Set here since __del__ checks it
- def __init__(self, file, mode="r", compression=ZIP_STORED, allowZip64=False):
- """Open the ZIP file with mode read "r", write "w" or append "a"."""
- if mode not in ("r", "w", "a"):
- raise RuntimeError('ZipFile() requires mode "r", "w", or "a"')
- if compression == ZIP_STORED:
- pass
- elif compression == ZIP_DEFLATED:
- if not zlib:
- raise RuntimeError,\
- "Compression requires the (missing) zlib module"
- else:
- raise RuntimeError, "That compression method is not supported"
- self._allowZip64 = allowZip64
- self._didModify = False
- self.debug = 0 # Level of printing: 0 through 3
- self.NameToInfo = {} # Find file info given name
- self.filelist = [] # List of ZipInfo instances for archive
- self.compression = compression # Method of compression
- self.mode = key = mode.replace('b', '')[0]
- self.pwd = None
- self._comment = ''
- # Check if we were passed a file-like object
- if isinstance(file, basestring):
- self._filePassed = 0
- self.filename = file
- modeDict = {'r' : 'rb', 'w': 'wb', 'a' : 'r+b'}
- try:
- self.fp = open(file, modeDict[mode])
- except IOError:
- if mode == 'a':
- mode = key = 'w'
- self.fp = open(file, modeDict[mode])
- else:
- raise
- else:
- self._filePassed = 1
- self.fp = file
- self.filename = getattr(file, 'name', None)
- try:
- if key == 'r':
- self._RealGetContents()
- elif key == 'w':
- # set the modified flag so central directory gets written
- # even if no files are added to the archive
- self._didModify = True
- elif key == 'a':
- try:
- # See if file is a zip file
- self._RealGetContents()
- # seek to start of directory and overwrite
- self.fp.seek(self.start_dir, 0)
- except BadZipfile:
- # file is not a zip file, just append
- self.fp.seek(0, 2)
- # set the modified flag so central directory gets written
- # even if no files are added to the archive
- self._didModify = True
- else:
- raise RuntimeError('Mode must be "r", "w" or "a"')
- except:
- fp = self.fp
- self.fp = None
- if not self._filePassed:
- fp.close()
- raise
- def __enter__(self):
- return self
- def __exit__(self, type, value, traceback):
- self.close()
- def _RealGetContents(self):
- """Read in the table of contents for the ZIP file."""
- fp = self.fp
- try:
- endrec = _EndRecData(fp)
- except IOError:
- raise BadZipfile("File is not a zip file")
- if not endrec:
- raise BadZipfile, "File is not a zip file"
- if self.debug > 1:
- print endrec
- size_cd = endrec[_ECD_SIZE] # bytes in central directory
- offset_cd = endrec[_ECD_OFFSET] # offset of central directory
- self._comment = endrec[_ECD_COMMENT] # archive comment
- # "concat" is zero, unless zip was concatenated to another file
- concat = endrec[_ECD_LOCATION] - size_cd - offset_cd
- if endrec[_ECD_SIGNATURE] == stringEndArchive64:
- # If Zip64 extension structures are present, account for them
- concat -= (sizeEndCentDir64 + sizeEndCentDir64Locator)
- if self.debug > 2:
- inferred = concat + offset_cd
- print "given, inferred, offset", offset_cd, inferred, concat
- # self.start_dir: Position of start of central directory
- self.start_dir = offset_cd + concat
- fp.seek(self.start_dir, 0)
- data = fp.read(size_cd)
- fp = cStringIO.StringIO(data)
- total = 0
- while total < size_cd:
- centdir = fp.read(sizeCentralDir)
- if len(centdir) != sizeCentralDir:
- raise BadZipfile("Truncated central directory")
- centdir = struct.unpack(structCentralDir, centdir)
- if centdir[_CD_SIGNATURE] != stringCentralDir:
- raise BadZipfile("Bad magic number for central directory")
- if self.debug > 2:
- print centdir
- filename = fp.read(centdir[_CD_FILENAME_LENGTH])
- # Create ZipInfo instance to store file information
- x = ZipInfo(filename)
- x.extra = fp.read(centdir[_CD_EXTRA_FIELD_LENGTH])
- x.comment = fp.read(centdir[_CD_COMMENT_LENGTH])
- x.header_offset = centdir[_CD_LOCAL_HEADER_OFFSET]
- (x.create_version, x.create_system, x.extract_version, x.reserved,
- x.flag_bits, x.compress_type, t, d,
- x.CRC, x.compress_size, x.file_size) = centdir[1:12]
- x.volume, x.internal_attr, x.external_attr = centdir[15:18]
- # Convert date/time code to (year, month, day, hour, min, sec)
- x._raw_time = t
- x.date_time = ( (d>>9)+1980, (d>>5)&0xF, d&0x1F,
- t>>11, (t>>5)&0x3F, (t&0x1F) * 2 )
- x._decodeExtra()
- x.header_offset = x.header_offset + concat
- x.filename = x._decodeFilename()
- self.filelist.append(x)
- self.NameToInfo[x.filename] = x
- # update total bytes read from central directory
- total = (total + sizeCentralDir + centdir[_CD_FILENAME_LENGTH]
- + centdir[_CD_EXTRA_FIELD_LENGTH]
- + centdir[_CD_COMMENT_LENGTH])
- if self.debug > 2:
- print "total", total
- def namelist(self):
- """Return a list of file names in the archive."""
- l = []
- for data in self.filelist:
- l.append(data.filename)
- return l
- def infolist(self):
- """Return a list of class ZipInfo instances for files in the
- archive."""
- return self.filelist
- def printdir(self):
- """Print a table of contents for the zip file."""
- print "%-46s %19s %12s" % ("File Name", "Modified ", "Size")
- for zinfo in self.filelist:
- date = "%d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d" % zinfo.date_time[:6]
- print "%-46s %s %12d" % (zinfo.filename, date, zinfo.file_size)
- def testzip(self):
- """Read all the files and check the CRC."""
- chunk_size = 2 ** 20
- for zinfo in self.filelist:
- try:
- # Read by chunks, to avoid an OverflowError or a
- # MemoryError with very large embedded files.
- with self.open(zinfo.filename, "r") as f:
- while f.read(chunk_size): # Check CRC-32
- pass
- except BadZipfile:
- return zinfo.filename
- def getinfo(self, name):
- """Return the instance of ZipInfo given 'name'."""
- info = self.NameToInfo.get(name)
- if info is None:
- raise KeyError(
- 'There is no item named %r in the archive' % name)
- return info
- def setpassword(self, pwd):
- """Set default password for encrypted files."""
- self.pwd = pwd
- @property
- def comment(self):
- """The comment text associated with the ZIP file."""
- return self._comment
- @comment.setter
- def comment(self, comment):
- # check for valid comment length
- if len(comment) > ZIP_MAX_COMMENT:
- import warnings
- warnings.warn('Archive comment is too long; truncating to %d bytes'
- % ZIP_MAX_COMMENT, stacklevel=2)
- comment = comment[:ZIP_MAX_COMMENT]
- self._comment = comment
- self._didModify = True
- def read(self, name, pwd=None):
- """Return file bytes (as a string) for name."""
- return self.open(name, "r", pwd).read()
- def open(self, name, mode="r", pwd=None):
- """Return file-like object for 'name'."""
- if mode not in ("r", "U", "rU"):
- raise RuntimeError, 'open() requires mode "r", "U", or "rU"'
- if not self.fp:
- raise RuntimeError, \
- "Attempt to read ZIP archive that was already closed"
- # Only open a new file for instances where we were not
- # given a file object in the constructor
- if self._filePassed:
- zef_file = self.fp
- should_close = False
- else:
- zef_file = open(self.filename, 'rb')
- should_close = True
- try:
- # Make sure we have an info object
- if isinstance(name, ZipInfo):
- # 'name' is already an info object
- zinfo = name
- else:
- # Get info object for name
- zinfo = self.getinfo(name)
- zef_file.seek(zinfo.header_offset, 0)
- # Skip the file header:
- fheader = zef_file.read(sizeFileHeader)
- if len(fheader) != sizeFileHeader:
- raise BadZipfile("Truncated file header")
- fheader = struct.unpack(structFileHeader, fheader)
- if fheader[_FH_SIGNATURE] != stringFileHeader:
- raise BadZipfile("Bad magic number for file header")
- fname = zef_file.read(fheader[_FH_FILENAME_LENGTH])
- if fheader[_FH_EXTRA_FIELD_LENGTH]:
- zef_file.read(fheader[_FH_EXTRA_FIELD_LENGTH])
- if fname != zinfo.orig_filename:
- raise BadZipfile, \
- 'File name in directory "%s" and header "%s" differ.' % (
- zinfo.orig_filename, fname)
- # check for encrypted flag & handle password
- is_encrypted = zinfo.flag_bits & 0x1
- zd = None
- if is_encrypted:
- if not pwd:
- pwd = self.pwd
- if not pwd:
- raise RuntimeError, "File %s is encrypted, " \
- "password required for extraction" % name
- zd = _ZipDecrypter(pwd)
- # The first 12 bytes in the cypher stream is an encryption header
- # used to strengthen the algorithm. The first 11 bytes are
- # completely random, while the 12th contains the MSB of the CRC,
- # or the MSB of the file time depending on the header type
- # and is used to check the correctness of the password.
- bytes = zef_file.read(12)
- h = map(zd, bytes[0:12])
- if zinfo.flag_bits & 0x8:
- # compare against the file type from extended local headers
- check_byte = (zinfo._raw_time >> 8) & 0xff
- else:
- # compare against the CRC otherwise
- check_byte = (zinfo.CRC >> 24) & 0xff
- if ord(h[11]) != check_byte:
- raise RuntimeError("Bad password for file", name)
- return ZipExtFile(zef_file, mode, zinfo, zd,
- close_fileobj=should_close)
- except:
- if should_close:
- zef_file.close()
- raise
- def extract(self, member, path=None, pwd=None):
- """Extract a member from the archive to the current working directory,
- using its full name. Its file information is extracted as accurately
- as possible. `member' may be a filename or a ZipInfo object. You can
- specify a different directory using `path'.
- """
- if not isinstance(member, ZipInfo):
- member = self.getinfo(member)
- if path is None:
- path = os.getcwd()
- return self._extract_member(member, path, pwd)
- def extractall(self, path=None, members=None, pwd=None):
- """Extract all members from the archive to the current working
- directory. `path' specifies a different directory to extract to.
- `members' is optional and must be a subset of the list returned
- by namelist().
- """
- if members is None:
- members = self.namelist()
- for zipinfo in members:
- self.extract(zipinfo, path, pwd)
- def _extract_member(self, member, targetpath, pwd):
- """Extract the ZipInfo object 'member' to a physical
- file on the path targetpath.
- """
- # build the destination pathname, replacing
- # forward slashes to platform specific separators.
- arcname = member.filename.replace('/', os.path.sep)
- if os.path.altsep:
- arcname = arcname.replace(os.path.altsep, os.path.sep)
- # interpret absolute pathname as relative, remove drive letter or
- # UNC path, redundant separators, "." and ".." components.
- arcname = os.path.splitdrive(arcname)[1]
- arcname = os.path.sep.join(x for x in arcname.split(os.path.sep)
- if x not in ('', os.path.curdir, os.path.pardir))
- if os.path.sep == '\\':
- # filter illegal characters on Windows
- illegal = ':<>|"?*'
- if isinstance(arcname, unicode):
- table = {ord(c): ord('_') for c in illegal}
- else:
- table = string.maketrans(illegal, '_' * len(illegal))
- arcname = arcname.translate(table)
- # remove trailing dots
- arcname = (x.rstrip('.') for x in arcname.split(os.path.sep))
- arcname = os.path.sep.join(x for x in arcname if x)
- targetpath = os.path.join(targetpath, arcname)
- targetpath = os.path.normpath(targetpath)
- # Create all upper directories if necessary.
- upperdirs = os.path.dirname(targetpath)
- if upperdirs and not os.path.exists(upperdirs):
- os.makedirs(upperdirs)
- if member.filename[-1] == '/':
- if not os.path.isdir(targetpath):
- os.mkdir(targetpath)
- return targetpath
- with self.open(member, pwd=pwd) as source, \
- file(targetpath, "wb") as target:
- shutil.copyfileobj(source, target)
- return targetpath
- def _writecheck(self, zinfo):
- """Check for errors before writing a file to the archive."""
- if zinfo.filename in self.NameToInfo:
- import warnings
- warnings.warn('Duplicate name: %r' % zinfo.filename, stacklevel=3)
- if self.mode not in ("w", "a"):
- raise RuntimeError, 'write() requires mode "w" or "a"'
- if not self.fp:
- raise RuntimeError, \
- "Attempt to write ZIP archive that was already closed"
- if zinfo.compress_type == ZIP_DEFLATED and not zlib:
- raise RuntimeError, \
- "Compression requires the (missing) zlib module"
- if zinfo.compress_type not in (ZIP_STORED, ZIP_DEFLATED):
- raise RuntimeError, \
- "That compression method is not supported"
- if not self._allowZip64:
- requires_zip64 = None
- if len(self.filelist) >= ZIP_FILECOUNT_LIMIT:
- requires_zip64 = "Files count"
- elif zinfo.file_size > ZIP64_LIMIT:
- requires_zip64 = "Filesize"
- elif zinfo.header_offset > ZIP64_LIMIT:
- requires_zip64 = "Zipfile size"
- if requires_zip64:
- raise LargeZipFile(requires_zip64 +
- " would require ZIP64 extensions")
- def write(self, filename, arcname=None, compress_type=None):
- """Put the bytes from filename into the archive under the name
- arcname."""
- if not self.fp:
- raise RuntimeError(
- "Attempt to write to ZIP archive that was already closed")
- st = os.stat(filename)
- isdir = stat.S_ISDIR(st.st_mode)
- mtime = time.localtime(st.st_mtime)
- date_time = mtime[0:6]
- # Create ZipInfo instance to store file information
- if arcname is None:
- arcname = filename
- arcname = os.path.normpath(os.path.splitdrive(arcname)[1])
- while arcname[0] in (os.sep, os.altsep):
- arcname = arcname[1:]
- if isdir:
- arcname += '/'
- zinfo = ZipInfo(arcname, date_time)
- zinfo.external_attr = (st[0] & 0xFFFF) << 16L # Unix attributes
- if compress_type is None:
- zinfo.compress_type = self.compression
- else:
- zinfo.compress_type = compress_type
- zinfo.file_size = st.st_size
- zinfo.flag_bits = 0x00
- zinfo.header_offset = self.fp.tell() # Start of header bytes
- self._writecheck(zinfo)
- self._didModify = True
- if isdir:
- zinfo.file_size = 0
- zinfo.compress_size = 0
- zinfo.CRC = 0
- zinfo.external_attr |= 0x10 # MS-DOS directory flag
- self.filelist.append(zinfo)
- self.NameToInfo[zinfo.filename] = zinfo
- self.fp.write(zinfo.FileHeader(False))
- return
- with open(filename, "rb") as fp:
- # Must overwrite CRC and sizes with correct data later
- zinfo.CRC = CRC = 0
- zinfo.compress_size = compress_size = 0
- # Compressed size can be larger than uncompressed size
- zip64 = self._allowZip64 and \
- zinfo.file_size * 1.05 > ZIP64_LIMIT
- self.fp.write(zinfo.FileHeader(zip64))
- if zinfo.compress_type == ZIP_DEFLATED:
- cmpr = zlib.compressobj(zlib.Z_DEFAULT_COMPRESSION,
- zlib.DEFLATED, -15)
- else:
- cmpr = None
- file_size = 0
- while 1:
- buf = fp.read(1024 * 8)
- if not buf:
- break
- file_size = file_size + len(buf)
- CRC = crc32(buf, CRC) & 0xffffffff
- if cmpr:
- buf = cmpr.compress(buf)
- compress_size = compress_size + len(buf)
- self.fp.write(buf)
- if cmpr:
- buf = cmpr.flush()
- compress_size = compress_size + len(buf)
- self.fp.write(buf)
- zinfo.compress_size = compress_size
- else:
- zinfo.compress_size = file_size
- zinfo.CRC = CRC
- zinfo.file_size = file_size
- if not zip64 and self._allowZip64:
- if file_size > ZIP64_LIMIT:
- raise RuntimeError('File size has increased during compressing')
- if compress_size > ZIP64_LIMIT:
- raise RuntimeError('Compressed size larger than uncompressed size')
- # Seek backwards and write file header (which will now include
- # correct CRC and file sizes)
- position = self.fp.tell() # Preserve current position in file
- self.fp.seek(zinfo.header_offset, 0)
- self.fp.write(zinfo.FileHeader(zip64))
- self.fp.seek(position, 0)
- self.filelist.append(zinfo)
- self.NameToInfo[zinfo.filename] = zinfo
- def writestr(self, zinfo_or_arcname, bytes, compress_type=None):
- """Write a file into the archive. The contents is the string
- 'bytes'. 'zinfo_or_arcname' is either a ZipInfo instance or
- the name of the file in the archive."""
- if not isinstance(zinfo_or_arcname, ZipInfo):
- zinfo = ZipInfo(filename=zinfo_or_arcname,
- date_time=time.localtime(time.time())[:6])
- zinfo.compress_type = self.compression
- if zinfo.filename[-1] == '/':
- zinfo.external_attr = 0o40775 << 16 # drwxrwxr-x
- zinfo.external_attr |= 0x10 # MS-DOS directory flag
- else:
- zinfo.external_attr = 0o600 << 16 # ?rw-------
- else:
- zinfo = zinfo_or_arcname
- if not self.fp:
- raise RuntimeError(
- "Attempt to write to ZIP archive that was already closed")
- if compress_type is not None:
- zinfo.compress_type = compress_type
- zinfo.file_size = len(bytes) # Uncompressed size
- zinfo.header_offset = self.fp.tell() # Start of header bytes
- self._writecheck(zinfo)
- self._didModify = True
- zinfo.CRC = crc32(bytes) & 0xffffffff # CRC-32 checksum
- if zinfo.compress_type == ZIP_DEFLATED:
- co = zlib.compressobj(zlib.Z_DEFAULT_COMPRESSION,
- zlib.DEFLATED, -15)
- bytes = co.compress(bytes) + co.flush()
- zinfo.compress_size = len(bytes) # Compressed size
- else:
- zinfo.compress_size = zinfo.file_size
- zip64 = zinfo.file_size > ZIP64_LIMIT or \
- zinfo.compress_size > ZIP64_LIMIT
- if zip64 and not self._allowZip64:
- raise LargeZipFile("Filesize would require ZIP64 extensions")
- self.fp.write(zinfo.FileHeader(zip64))
- self.fp.write(bytes)
- if zinfo.flag_bits & 0x08:
- # Write CRC and file sizes after the file data
- fmt = '<LQQ' if zip64 else '<LLL'
- self.fp.write(struct.pack(fmt, zinfo.CRC, zinfo.compress_size,
- zinfo.file_size))
- self.fp.flush()
- self.filelist.append(zinfo)
- self.NameToInfo[zinfo.filename] = zinfo
- def __del__(self):
- """Call the "close()" method in case the user forgot."""
- self.close()
- def close(self):
- """Close the file, and for mode "w" and "a" write the ending
- records."""
- if self.fp is None:
- return
- try:
- if self.mode in ("w", "a") and self._didModify: # write ending records
- pos1 = self.fp.tell()
- for zinfo in self.filelist: # write central directory
- dt = zinfo.date_time
- dosdate = (dt[0] - 1980) << 9 | dt[1] << 5 | dt[2]
- dostime = dt[3] << 11 | dt[4] << 5 | (dt[5] // 2)
- extra = []
- if zinfo.file_size > ZIP64_LIMIT \
- or zinfo.compress_size > ZIP64_LIMIT:
- extra.append(zinfo.file_size)
- extra.append(zinfo.compress_size)
- file_size = 0xffffffff
- compress_size = 0xffffffff
- else:
- file_size = zinfo.file_size
- compress_size = zinfo.compress_size
- if zinfo.header_offset > ZIP64_LIMIT:
- extra.append(zinfo.header_offset)
- header_offset = 0xffffffffL
- else:
- header_offset = zinfo.header_offset
- extra_data = zinfo.extra
- if extra:
- # Append a ZIP64 field to the extra's
- extra_data = struct.pack(
- '<HH' + 'Q'*len(extra),
- 1, 8*len(extra), *extra) + extra_data
- extract_version = max(45, zinfo.extract_version)
- create_version = max(45, zinfo.create_version)
- else:
- extract_version = zinfo.extract_version
- create_version = zinfo.create_version
- try:
- filename, flag_bits = zinfo._encodeFilenameFlags()
- centdir = struct.pack(structCentralDir,
- stringCentralDir, create_version,
- zinfo.create_system, extract_version, zinfo.reserved,
- flag_bits, zinfo.compress_type, dostime, dosdate,
- zinfo.CRC, compress_size, file_size,
- len(filename), len(extra_data), len(zinfo.comment),
- 0, zinfo.internal_attr, zinfo.external_attr,
- header_offset)
- except DeprecationWarning:
- print >>sys.stderr, (structCentralDir,
- stringCentralDir, create_version,
- zinfo.create_system, extract_version, zinfo.reserved,
- zinfo.flag_bits, zinfo.compress_type, dostime, dosdate,
- zinfo.CRC, compress_size, file_size,
- len(zinfo.filename), len(extra_data), len(zinfo.comment),
- 0, zinfo.internal_attr, zinfo.external_attr,
- header_offset)
- raise
- self.fp.write(centdir)
- self.fp.write(filename)
- self.fp.write(extra_data)
- self.fp.write(zinfo.comment)
- pos2 = self.fp.tell()
- # Write end-of-zip-archive record
- centDirCount = len(self.filelist)
- centDirSize = pos2 - pos1
- centDirOffset = pos1
- requires_zip64 = None
- if centDirCount > ZIP_FILECOUNT_LIMIT:
- requires_zip64 = "Files count"
- elif centDirOffset > ZIP64_LIMIT:
- requires_zip64 = "Central directory offset"
- elif centDirSize > ZIP64_LIMIT:
- requires_zip64 = "Central directory size"
- if requires_zip64:
- # Need to write the ZIP64 end-of-archive records
- if not self._allowZip64:
- raise LargeZipFile(requires_zip64 +
- " would require ZIP64 extensions")
- zip64endrec = struct.pack(
- structEndArchive64, stringEndArchive64,
- 44, 45, 45, 0, 0, centDirCount, centDirCount,
- centDirSize, centDirOffset)
- self.fp.write(zip64endrec)
- zip64locrec = struct.pack(
- structEndArchive64Locator,
- stringEndArchive64Locator, 0, pos2, 1)
- self.fp.write(zip64locrec)
- centDirCount = min(centDirCount, 0xFFFF)
- centDirSize = min(centDirSize, 0xFFFFFFFF)
- centDirOffset = min(centDirOffset, 0xFFFFFFFF)
- endrec = struct.pack(structEndArchive, stringEndArchive,
- 0, 0, centDirCount, centDirCount,
- centDirSize, centDirOffset, len(self._comment))
- self.fp.write(endrec)
- self.fp.write(self._comment)
- self.fp.flush()
- finally:
- fp = self.fp
- self.fp = None
- if not self._filePassed:
- fp.close()
- 复制代码
- 复制代码
- class TarFile(object):
- """The TarFile Class provides an interface to tar archives.
- """
- debug = 0 # May be set from 0 (no msgs) to 3 (all msgs)
- dereference = False # If true, add content of linked file to the
- # tar file, else the link.
- ignore_zeros = False # If true, skips empty or invalid blocks and
- # continues processing.
- errorlevel = 1 # If 0, fatal errors only appear in debug
- # messages (if debug >= 0). If > 0, errors
- # are passed to the caller as exceptions.
- format = DEFAULT_FORMAT # The format to use when creating an archive.
- encoding = ENCODING # Encoding for 8-bit character strings.
- errors = None # Error handler for unicode conversion.
- tarinfo = TarInfo # The default TarInfo class to use.
- fileobject = ExFileObject # The default ExFileObject class to use.
- def __init__(self, name=None, mode="r", fileobj=None, format=None,
- tarinfo=None, dereference=None, ignore_zeros=None, encoding=None,
- errors=None, pax_headers=None, debug=None, errorlevel=None):
- """Open an (uncompressed) tar archive `name'. `mode' is either 'r' to
- read from an existing archive, 'a' to append data to an existing
- file or 'w' to create a new file overwriting an existing one. `mode'
- defaults to 'r'.
- If `fileobj' is given, it is used for reading or writing data. If it
- can be determined, `mode' is overridden by `fileobj's mode.
- `fileobj' is not closed, when TarFile is closed.
- """
- modes = {"r": "rb", "a": "r+b", "w": "wb"}
- if mode not in modes:
- raise ValueError("mode must be 'r', 'a' or 'w'")
- self.mode = mode
- self._mode = modes[mode]
- if not fileobj:
- if self.mode == "a" and not os.path.exists(name):
- # Create nonexistent files in append mode.
- self.mode = "w"
- self._mode = "wb"
- fileobj = bltn_open(name, self._mode)
- self._extfileobj = False
- else:
- if name is None and hasattr(fileobj, "name"):
- name = fileobj.name
- if hasattr(fileobj, "mode"):
- self._mode = fileobj.mode
- self._extfileobj = True
- self.name = os.path.abspath(name) if name else None
- self.fileobj = fileobj
- # Init attributes.
- if format is not None:
- self.format = format
- if tarinfo is not None:
- self.tarinfo = tarinfo
- if dereference is not None:
- self.dereference = dereference
- if ignore_zeros is not None:
- self.ignore_zeros = ignore_zeros
- if encoding is not None:
- self.encoding = encoding
- if errors is not None:
- self.errors = errors
- elif mode == "r":
- self.errors = "utf-8"
- else:
- self.errors = "strict"
- if pax_headers is not None and self.format == PAX_FORMAT:
- self.pax_headers = pax_headers
- else:
- self.pax_headers = {}
- if debug is not None:
- self.debug = debug
- if errorlevel is not None:
- self.errorlevel = errorlevel
- # Init datastructures.
- self.closed = False
- self.members = [] # list of members as TarInfo objects
- self._loaded = False # flag if all members have been read
- self.offset = self.fileobj.tell()
- # current position in the archive file
- self.inodes = {} # dictionary caching the inodes of
- # archive members already added
- try:
- if self.mode == "r":
- self.firstmember = None
- self.firstmember = self.next()
- if self.mode == "a":
- # Move to the end of the archive,
- # before the first empty block.
- while True:
- self.fileobj.seek(self.offset)
- try:
- tarinfo = self.tarinfo.fromtarfile(self)
- self.members.append(tarinfo)
- except EOFHeaderError:
- self.fileobj.seek(self.offset)
- break
- except HeaderError, e:
- raise ReadError(str(e))
- if self.mode in "aw":
- self._loaded = True
- if self.pax_headers:
- buf = self.tarinfo.create_pax_global_header(self.pax_headers.copy())
- self.fileobj.write(buf)
- self.offset += len(buf)
- except:
- if not self._extfileobj:
- self.fileobj.close()
- self.closed = True
- raise
- def _getposix(self):
- return self.format == USTAR_FORMAT
- def _setposix(self, value):
- import warnings
- warnings.warn("use the format attribute instead", DeprecationWarning,
- 2)
- if value:
- self.format = USTAR_FORMAT
- else:
- self.format = GNU_FORMAT
- posix = property(_getposix, _setposix)
- #--------------------------------------------------------------------------
- # Below are the classmethods which act as alternate constructors to the
- # TarFile class. The open() method is the only one that is needed for
- # public use; it is the "super"-constructor and is able to select an
- # adequate "sub"-constructor for a particular compression using the mapping
- # from OPEN_METH.
- #
- # This concept allows one to subclass TarFile without losing the comfort of
- # the super-constructor. A sub-constructor is registered and made available
- # by adding it to the mapping in OPEN_METH.
- @classmethod
- def open(cls, name=None, mode="r", fileobj=None, bufsize=RECORDSIZE, **kwargs):
- """Open a tar archive for reading, writing or appending. Return
- an appropriate TarFile class.
- mode:
- 'r' or 'r:*' open for reading with transparent compression
- 'r:' open for reading exclusively uncompressed
- 'r:gz' open for reading with gzip compression
- 'r:bz2' open for reading with bzip2 compression
- 'a' or 'a:' open for appending, creating the file if necessary
- 'w' or 'w:' open for writing without compression
- 'w:gz' open for writing with gzip compression
- 'w:bz2' open for writing with bzip2 compression
- 'r|*' open a stream of tar blocks with transparent compression
- 'r|' open an uncompressed stream of tar blocks for reading
- 'r|gz' open a gzip compressed stream of tar blocks
- 'r|bz2' open a bzip2 compressed stream of tar blocks
- 'w|' open an uncompressed stream for writing
- 'w|gz' open a gzip compressed stream for writing
- 'w|bz2' open a bzip2 compressed stream for writing
- """
- if not name and not fileobj:
- raise ValueError("nothing to open")
- if mode in ("r", "r:*"):
- # Find out which *open() is appropriate for opening the file.
- for comptype in cls.OPEN_METH:
- func = getattr(cls, cls.OPEN_METH[comptype])
- if fileobj is not None:
- saved_pos = fileobj.tell()
- try:
- return func(name, "r", fileobj, **kwargs)
- except (ReadError, CompressionError), e:
- if fileobj is not None:
- fileobj.seek(saved_pos)
- continue
- raise ReadError("file could not be opened successfully")
- elif ":" in mode:
- filemode, comptype = mode.split(":", 1)
- filemode = filemode or "r"
- comptype = comptype or "tar"
- # Select the *open() function according to
- # given compression.
- if comptype in cls.OPEN_METH:
- func = getattr(cls, cls.OPEN_METH[comptype])
- else:
- raise CompressionError("unknown compression type %r" % comptype)
- return func(name, filemode, fileobj, **kwargs)
- elif "|" in mode:
- filemode, comptype = mode.split("|", 1)
- filemode = filemode or "r"
- comptype = comptype or "tar"
- if filemode not in ("r", "w"):
- raise ValueError("mode must be 'r' or 'w'")
- stream = _Stream(name, filemode, comptype, fileobj, bufsize)
- try:
- t = cls(name, filemode, stream, **kwargs)
- except:
- stream.close()
- raise
- t._extfileobj = False
- return t
- elif mode in ("a", "w"):
- return cls.taropen(name, mode, fileobj, **kwargs)
- raise ValueError("undiscernible mode")
- @classmethod
- def taropen(cls, name, mode="r", fileobj=None, **kwargs):
- """Open uncompressed tar archive name for reading or writing.
- """
- if mode not in ("r", "a", "w"):
- raise ValueError("mode must be 'r', 'a' or 'w'")
- return cls(name, mode, fileobj, **kwargs)
- @classmethod
- def gzopen(cls, name, mode="r", fileobj=None, compresslevel=9, **kwargs):
- """Open gzip compressed tar archive name for reading or writing.
- Appending is not allowed.
- """
- if mode not in ("r", "w"):
- raise ValueError("mode must be 'r' or 'w'")
- try:
- import gzip
- gzip.GzipFile
- except (ImportError, AttributeError):
- raise CompressionError("gzip module is not available")
- try:
- fileobj = gzip.GzipFile(name, mode, compresslevel, fileobj)
- except OSError:
- if fileobj is not None and mode == 'r':
- raise ReadError("not a gzip file")
- raise
- try:
- t = cls.taropen(name, mode, fileobj, **kwargs)
- except IOError:
- fileobj.close()
- if mode == 'r':
- raise ReadError("not a gzip file")
- raise
- except:
- fileobj.close()
- raise
- t._extfileobj = False
- return t
- @classmethod
- def bz2open(cls, name, mode="r", fileobj=None, compresslevel=9, **kwargs):
- """Open bzip2 compressed tar archive name for reading or writing.
- Appending is not allowed.
- """
- if mode not in ("r", "w"):
- raise ValueError("mode must be 'r' or 'w'.")
- try:
- import bz2
- except ImportError:
- raise CompressionError("bz2 module is not available")
- if fileobj is not None:
- fileobj = _BZ2Proxy(fileobj, mode)
- else:
- fileobj = bz2.BZ2File(name, mode, compresslevel=compresslevel)
- try:
- t = cls.taropen(name, mode, fileobj, **kwargs)
- except (IOError, EOFError):
- fileobj.close()
- if mode == 'r':
- raise ReadError("not a bzip2 file")
- raise
- except:
- fileobj.close()
- raise
- t._extfileobj = False
- return t
- # All *open() methods are registered here.
- OPEN_METH = {
- "tar": "taropen", # uncompressed tar
- "gz": "gzopen", # gzip compressed tar
- "bz2": "bz2open" # bzip2 compressed tar
- }
- #--------------------------------------------------------------------------
- # The public methods which TarFile provides:
- def close(self):
- """Close the TarFile. In write-mode, two finishing zero blocks are
- appended to the archive.
- """
- if self.closed:
- return
- if self.mode in "aw":
- self.fileobj.write(NUL * (BLOCKSIZE * 2))
- self.offset += (BLOCKSIZE * 2)
- # fill up the end with zero-blocks
- # (like option -b20 for tar does)
- blocks, remainder = divmod(self.offset, RECORDSIZE)
- if remainder > 0:
- self.fileobj.write(NUL * (RECORDSIZE - remainder))
- if not self._extfileobj:
- self.fileobj.close()
- self.closed = True
- def getmember(self, name):
- """Return a TarInfo object for member `name'. If `name' can not be
- found in the archive, KeyError is raised. If a member occurs more
- than once in the archive, its last occurrence is assumed to be the
- most up-to-date version.
- """
- tarinfo = self._getmember(name)
- if tarinfo is None:
- raise KeyError("filename %r not found" % name)
- return tarinfo
- def getmembers(self):
- """Return the members of the archive as a list of TarInfo objects. The
- list has the same order as the members in the archive.
- """
- self._check()
- if not self._loaded: # if we want to obtain a list of
- self._load() # all members, we first have to
- # scan the whole archive.
- return self.members
- def getnames(self):
- """Return the members of the archive as a list of their names. It has
- the same order as the list returned by getmembers().
- """
- return [tarinfo.name for tarinfo in self.getmembers()]
- def gettarinfo(self, name=None, arcname=None, fileobj=None):
- """Create a TarInfo object for either the file `name' or the file
- object `fileobj' (using os.fstat on its file descriptor). You can
- modify some of the TarInfo's attributes before you add it using
- addfile(). If given, `arcname' specifies an alternative name for the
- file in the archive.
- """
- self._check("aw")
- # When fileobj is given, replace name by
- # fileobj's real name.
- if fileobj is not None:
- name = fileobj.name
- # Building the name of the member in the archive.
- # Backward slashes are converted to forward slashes,
- # Absolute paths are turned to relative paths.
- if arcname is None:
- arcname = name
- drv, arcname = os.path.splitdrive(arcname)
- arcname = arcname.replace(os.sep, "/")
- arcname = arcname.lstrip("/")
- # Now, fill the TarInfo object with
- # information specific for the file.
- tarinfo = self.tarinfo()
- tarinfo.tarfile = self
- # Use os.stat or os.lstat, depending on platform
- # and if symlinks shall be resolved.
- if fileobj is None:
- if hasattr(os, "lstat") and not self.dereference:
- statres = os.lstat(name)
- else:
- statres = os.stat(name)
- else:
- statres = os.fstat(fileobj.fileno())
- linkname = ""
- stmd = statres.st_mode
- if stat.S_ISREG(stmd):
- inode = (statres.st_ino, statres.st_dev)
- if not self.dereference and statres.st_nlink > 1 and \
- inode in self.inodes and arcname != self.inodes[inode]:
- # Is it a hardlink to an already
- # archived file?
- type = LNKTYPE
- linkname = self.inodes[inode]
- else:
- # The inode is added only if its valid.
- # For win32 it is always 0.
- type = REGTYPE
- if inode[0]:
- self.inodes[inode] = arcname
- elif stat.S_ISDIR(stmd):
- type = DIRTYPE
- elif stat.S_ISFIFO(stmd):
- type = FIFOTYPE
- elif stat.S_ISLNK(stmd):
- type = SYMTYPE
- linkname = os.readlink(name)
- elif stat.S_ISCHR(stmd):
- type = CHRTYPE
- elif stat.S_ISBLK(stmd):
- type = BLKTYPE
- else:
- return None
- # Fill the TarInfo object with all
- # information we can get.
- tarinfo.name = arcname
- tarinfo.mode = stmd
- tarinfo.uid = statres.st_uid
- tarinfo.gid = statres.st_gid
- if type == REGTYPE:
- tarinfo.size = statres.st_size
- else:
- tarinfo.size = 0L
- tarinfo.mtime = statres.st_mtime
- tarinfo.type = type
- tarinfo.linkname = linkname
- if pwd:
- try:
- tarinfo.uname = pwd.getpwuid(tarinfo.uid)[0]
- except KeyError:
- pass
- if grp:
- try:
- tarinfo.gname = grp.getgrgid(tarinfo.gid)[0]
- except KeyError:
- pass
- if type in (CHRTYPE, BLKTYPE):
- if hasattr(os, "major") and hasattr(os, "minor"):
- tarinfo.devmajor = os.major(statres.st_rdev)
- tarinfo.devminor = os.minor(statres.st_rdev)
- return tarinfo
- def list(self, verbose=True):
- """Print a table of contents to sys.stdout. If `verbose' is False, only
- the names of the members are printed. If it is True, an `ls -l'-like
- output is produced.
- """
- self._check()
- for tarinfo in self:
- if verbose:
- print filemode(tarinfo.mode),
- print "%s/%s" % (tarinfo.uname or tarinfo.uid,
- tarinfo.gname or tarinfo.gid),
- if tarinfo.ischr() or tarinfo.isblk():
- print "%10s" % ("%d,%d" \
- % (tarinfo.devmajor, tarinfo.devminor)),
- else:
- print "%10d" % tarinfo.size,
- print "%d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d" \
- % time.localtime(tarinfo.mtime)[:6],
- print tarinfo.name + ("/" if tarinfo.isdir() else ""),
- if verbose:
- if tarinfo.issym():
- print "->", tarinfo.linkname,
- if tarinfo.islnk():
- print "link to", tarinfo.linkname,
- def add(self, name, arcname=None, recursive=True, exclude=None, filter=None):
- """Add the file `name' to the archive. `name' may be any type of file
- (directory, fifo, symbolic link, etc.). If given, `arcname'
- specifies an alternative name for the file in the archive.
- Directories are added recursively by default. This can be avoided by
- setting `recursive' to False. `exclude' is a function that should
- return True for each filename to be excluded. `filter' is a function
- that expects a TarInfo object argument and returns the changed
- TarInfo object, if it returns None the TarInfo object will be
- excluded from the archive.
- """
- self._check("aw")
- if arcname is None:
- arcname = name
- # Exclude pathnames.
- if exclude is not None:
- import warnings
- warnings.warn("use the filter argument instead",
- DeprecationWarning, 2)
- if exclude(name):
- self._dbg(2, "tarfile: Excluded %r" % name)
- return
- # Skip if somebody tries to archive the archive...
- if self.name is not None and os.path.abspath(name) == self.name:
- self._dbg(2, "tarfile: Skipped %r" % name)
- return
- self._dbg(1, name)
- # Create a TarInfo object from the file.
- tarinfo = self.gettarinfo(name, arcname)
- if tarinfo is None:
- self._dbg(1, "tarfile: Unsupported type %r" % name)
- return
- # Change or exclude the TarInfo object.
- if filter is not None:
- tarinfo = filter(tarinfo)
- if tarinfo is None:
- self._dbg(2, "tarfile: Excluded %r" % name)
- return
- # Append the tar header and data to the archive.
- if tarinfo.isreg():
- with bltn_open(name, "rb") as f:
- self.addfile(tarinfo, f)
- elif tarinfo.isdir():
- self.addfile(tarinfo)
- if recursive:
- for f in os.listdir(name):
- self.add(os.path.join(name, f), os.path.join(arcname, f),
- recursive, exclude, filter)
- else:
- self.addfile(tarinfo)
- def addfile(self, tarinfo, fileobj=None):
- """Add the TarInfo object `tarinfo' to the archive. If `fileobj' is
- given, tarinfo.size bytes are read from it and added to the archive.
- You can create TarInfo objects using gettarinfo().
- On Windows platforms, `fileobj' should always be opened with mode
- 'rb' to avoid irritation about the file size.
- """
- self._check("aw")
- tarinfo = copy.copy(tarinfo)
- buf = tarinfo.tobuf(self.format, self.encoding, self.errors)
- self.fileobj.write(buf)
- self.offset += len(buf)
- # If there's data to follow, append it.
- if fileobj is not None:
- copyfileobj(fileobj, self.fileobj, tarinfo.size)
- blocks, remainder = divmod(tarinfo.size, BLOCKSIZE)
- if remainder > 0:
- self.fileobj.write(NUL * (BLOCKSIZE - remainder))
- blocks += 1
- self.offset += blocks * BLOCKSIZE
- self.members.append(tarinfo)
- def extractall(self, path=".", members=None):
- """Extract all members from the archive to the current working
- directory and set owner, modification time and permissions on
- directories afterwards. `path' specifies a different directory
- to extract to. `members' is optional and must be a subset of the
- list returned by getmembers().
- """
- directories = []
- if members is None:
- members = self
- for tarinfo in members:
- if tarinfo.isdir():
- # Extract directories with a safe mode.
- directories.append(tarinfo)
- tarinfo = copy.copy(tarinfo)
- tarinfo.mode = 0700
- self.extract(tarinfo, path)
- # Reverse sort directories.
- directories.sort(key=operator.attrgetter('name'))
- directories.reverse()
- # Set correct owner, mtime and filemode on directories.
- for tarinfo in directories:
- dirpath = os.path.join(path, tarinfo.name)
- try:
- self.chown(tarinfo, dirpath)
- self.utime(tarinfo, dirpath)
- self.chmod(tarinfo, dirpath)
- except ExtractError, e:
- if self.errorlevel > 1:
- raise
- else:
- self._dbg(1, "tarfile: %s" % e)
- def extract(self, member, path=""):
- """Extract a member from the archive to the current working directory,
- using its full name. Its file information is extracted as accurately
- as possible. `member' may be a filename or a TarInfo object. You can
- specify a different directory using `path'.
- """
- self._check("r")
- if isinstance(member, basestring):
- tarinfo = self.getmember(member)
- else:
- tarinfo = member
- # Prepare the link target for makelink().
- if tarinfo.islnk():
- tarinfo._link_target = os.path.join(path, tarinfo.linkname)
- try:
- self._extract_member(tarinfo, os.path.join(path, tarinfo.name))
- except EnvironmentError, e:
- if self.errorlevel > 0:
- raise
- else:
- if e.filename is None:
- self._dbg(1, "tarfile: %s" % e.strerror)
- else:
- self._dbg(1, "tarfile: %s %r" % (e.strerror, e.filename))
- except ExtractError, e:
- if self.errorlevel > 1:
- raise
- else:
- self._dbg(1, "tarfile: %s" % e)
- def extractfile(self, member):
- """Extract a member from the archive as a file object. `member' may be
- a filename or a TarInfo object. If `member' is a regular file, a
- file-like object is returned. If `member' is a link, a file-like
- object is constructed from the link's target. If `member' is none of
- the above, None is returned.
- The file-like object is read-only and provides the following
- methods: read(), readline(), readlines(), seek() and tell()
- """
- self._check("r")
- if isinstance(member, basestring):
- tarinfo = self.getmember(member)
- else:
- tarinfo = member
- if tarinfo.isreg():
- return self.fileobject(self, tarinfo)
- elif tarinfo.type not in SUPPORTED_TYPES:
- # If a member's type is unknown, it is treated as a
- # regular file.
- return self.fileobject(self, tarinfo)
- elif tarinfo.islnk() or tarinfo.issym():
- if isinstance(self.fileobj, _Stream):
- # A small but ugly workaround for the case that someone tries
- # to extract a (sym)link as a file-object from a non-seekable
- # stream of tar blocks.
- raise StreamError("cannot extract (sym)link as file object")
- else:
- # A (sym)link's file object is its target's file object.
- return self.extractfile(self._find_link_target(tarinfo))
- else:
- # If there's no data associated with the member (directory, chrdev,
- # blkdev, etc.), return None instead of a file object.
- return None
- def _extract_member(self, tarinfo, targetpath):
- """Extract the TarInfo object tarinfo to a physical
- file called targetpath.
- """
- # Fetch the TarInfo object for the given name
- # and build the destination pathname, replacing
- # forward slashes to platform specific separators.
- targetpath = targetpath.rstrip("/")
- targetpath = targetpath.replace("/", os.sep)
- # Create all upper directories.
- upperdirs = os.path.dirname(targetpath)
- if upperdirs and not os.path.exists(upperdirs):
- # Create directories that are not part of the archive with
- # default permissions.
- os.makedirs(upperdirs)
- if tarinfo.islnk() or tarinfo.issym():
- self._dbg(1, "%s -> %s" % (tarinfo.name, tarinfo.linkname))
- else:
- self._dbg(1, tarinfo.name)
- if tarinfo.isreg():
- self.makefile(tarinfo, targetpath)
- elif tarinfo.isdir():
- self.makedir(tarinfo, targetpath)
- elif tarinfo.isfifo():
- self.makefifo(tarinfo, targetpath)
- elif tarinfo.ischr() or tarinfo.isblk():
- self.makedev(tarinfo, targetpath)
- elif tarinfo.islnk() or tarinfo.issym():
- self.makelink(tarinfo, targetpath)
- elif tarinfo.type not in SUPPORTED_TYPES:
- self.makeunknown(tarinfo, targetpath)
- else:
- self.makefile(tarinfo, targetpath)
- self.chown(tarinfo, targetpath)
- if not tarinfo.issym():
- self.chmod(tarinfo, targetpath)
- self.utime(tarinfo, targetpath)
- #--------------------------------------------------------------------------
- # Below are the different file methods. They are called via
- # _extract_member() when extract() is called. They can be replaced in a
- # subclass to implement other functionality.
- def makedir(self, tarinfo, targetpath):
- """Make a directory called targetpath.
- """
- try:
- # Use a safe mode for the directory, the real mode is set
- # later in _extract_member().
- os.mkdir(targetpath, 0700)
- except EnvironmentError, e:
- if e.errno != errno.EEXIST:
- raise
- def makefile(self, tarinfo, targetpath):
- """Make a file called targetpath.
- """
- source = self.extractfile(tarinfo)
- try:
- with bltn_open(targetpath, "wb") as target:
- copyfileobj(source, target)
- finally:
- source.close()
- def makeunknown(self, tarinfo, targetpath):
- """Make a file from a TarInfo object with an unknown type
- at targetpath.
- """
- self.makefile(tarinfo, targetpath)
- self._dbg(1, "tarfile: Unknown file type %r, " \
- "extracted as regular file." % tarinfo.type)
- def makefifo(self, tarinfo, targetpath):
- """Make a fifo called targetpath.
- """
- if hasattr(os, "mkfifo"):
- os.mkfifo(targetpath)
- else:
- raise ExtractError("fifo not supported by system")
- def makedev(self, tarinfo, targetpath):
- """Make a character or block device called targetpath.
- """
- if not hasattr(os, "mknod") or not hasattr(os, "makedev"):
- raise ExtractError("special devices not supported by system")
- mode = tarinfo.mode
- if tarinfo.isblk():
- mode |= stat.S_IFBLK
- else:
- mode |= stat.S_IFCHR
- os.mknod(targetpath, mode,
- os.makedev(tarinfo.devmajor, tarinfo.devminor))
- def makelink(self, tarinfo, targetpath):
- """Make a (symbolic) link called targetpath. If it cannot be created
- (platform limitation), we try to make a copy of the referenced file
- instead of a link.
- """
- if hasattr(os, "symlink") and hasattr(os, "link"):
- # For systems that support symbolic and hard links.
- if tarinfo.issym():
- if os.path.lexists(targetpath):
- os.unlink(targetpath)
- os.symlink(tarinfo.linkname, targetpath)
- else:
- # See extract().
- if os.path.exists(tarinfo._link_target):
- if os.path.lexists(targetpath):
- os.unlink(targetpath)
- os.link(tarinfo._link_target, targetpath)
- else:
- self._extract_member(self._find_link_target(tarinfo), targetpath)
- else:
- try:
- self._extract_member(self._find_link_target(tarinfo), targetpath)
- except KeyError:
- raise ExtractError("unable to resolve link inside archive")
- def chown(self, tarinfo, targetpath):
- """Set owner of targetpath according to tarinfo.
- """
- if pwd and hasattr(os, "geteuid") and os.geteuid() == 0:
- # We have to be root to do so.
- try:
- g = grp.getgrnam(tarinfo.gname)[2]
- except KeyError:
- g = tarinfo.gid
- try:
- u = pwd.getpwnam(tarinfo.uname)[2]
- except KeyError:
- u = tarinfo.uid
- try:
- if tarinfo.issym() and hasattr(os, "lchown"):
- os.lchown(targetpath, u, g)
- else:
- if sys.platform != "os2emx":
- os.chown(targetpath, u, g)
- except EnvironmentError, e:
- raise ExtractError("could not change owner")
- def chmod(self, tarinfo, targetpath):
- """Set file permissions of targetpath according to tarinfo.
- """
- if hasattr(os, 'chmod'):
- try:
- os.chmod(targetpath, tarinfo.mode)
- except EnvironmentError, e:
- raise ExtractError("could not change mode")
- def utime(self, tarinfo, targetpath):
- """Set modification time of targetpath according to tarinfo.
- """
- if not hasattr(os, 'utime'):
- return
- try:
- os.utime(targetpath, (tarinfo.mtime, tarinfo.mtime))
- except EnvironmentError, e:
- raise ExtractError("could not change modification time")
- #--------------------------------------------------------------------------
- def next(self):
- """Return the next member of the archive as a TarInfo object, when
- TarFile is opened for reading. Return None if there is no more
- available.
- """
- self._check("ra")
- if self.firstmember is not None:
- m = self.firstmember
- self.firstmember = None
- return m
- # Read the next block.
- self.fileobj.seek(self.offset)
- tarinfo = None
- while True:
- try:
- tarinfo = self.tarinfo.fromtarfile(self)
- except EOFHeaderError, e:
- if self.ignore_zeros:
- self._dbg(2, "0x%X: %s" % (self.offset, e))
- self.offset += BLOCKSIZE
- continue
- except InvalidHeaderError, e:
- if self.ignore_zeros:
- self._dbg(2, "0x%X: %s" % (self.offset, e))
- self.offset += BLOCKSIZE
- continue
- elif self.offset == 0:
- raise ReadError(str(e))
- except EmptyHeaderError:
- if self.offset == 0:
- raise ReadError("empty file")
- except TruncatedHeaderError, e:
- if self.offset == 0:
- raise ReadError(str(e))
- except SubsequentHeaderError, e:
- raise ReadError(str(e))
- break
- if tarinfo is not None:
- self.members.append(tarinfo)
- else:
- self._loaded = True
- return tarinfo
- #--------------------------------------------------------------------------
- # Little helper methods:
- def _getmember(self, name, tarinfo=None, normalize=False):
- """Find an archive member by name from bottom to top.
- If tarinfo is given, it is used as the starting point.
- """
- # Ensure that all members have been loaded.
- members = self.getmembers()
- # Limit the member search list up to tarinfo.
- if tarinfo is not None:
- members = members[:members.index(tarinfo)]
- if normalize:
- name = os.path.normpath(name)
- for member in reversed(members):
- if normalize:
- member_name = os.path.normpath(member.name)
- else:
- member_name = member.name
- if name == member_name:
- return member
- def _load(self):
- """Read through the entire archive file and look for readable
- members.
- """
- while True:
- tarinfo = self.next()
- if tarinfo is None:
- break
- self._loaded = True
- def _check(self, mode=None):
- """Check if TarFile is still open, and if the operation's mode
- corresponds to TarFile's mode.
- """
- if self.closed:
- raise IOError("%s is closed" % self.__class__.__name__)
- if mode is not None and self.mode not in mode:
- raise IOError("bad operation for mode %r" % self.mode)
- def _find_link_target(self, tarinfo):
- """Find the target member of a symlink or hardlink member in the
- archive.
- """
- if tarinfo.issym():
- # Always search the entire archive.
- linkname = "/".join(filter(None, (os.path.dirname(tarinfo.name), tarinfo.linkname)))
- limit = None
- else:
- # Search the archive before the link, because a hard link is
- # just a reference to an already archived file.
- linkname = tarinfo.linkname
- limit = tarinfo
- member = self._getmember(linkname, tarinfo=limit, normalize=True)
- if member is None:
- raise KeyError("linkname %r not found" % linkname)
- return member
- def __iter__(self):
- """Provide an iterator object.
- """
- if self._loaded:
- return iter(self.members)
- else:
- return TarIter(self)
- def _dbg(self, level, msg):
- """Write debugging output to sys.stderr.
- """
- if level <= self.debug:
- print >> sys.stderr, msg
- def __enter__(self):
- self._check()
- return self
- def __exit__(self, type, value, traceback):
- if type is None:
- self.close()
- else:
- # An exception occurred. We must not call close() because
- # it would try to write end-of-archive blocks and padding.
- if not self._extfileobj:
- self.fileobj.close()
- self.closed = True
- # class TarFile
七、ConfigParser
用于对特定的配置进行操作,当前模块的名称在 python 3.x 版本中变更为 configparser。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
# 注释1; 注释2[section1]k1 = v1k2:v2[section2]k1 = v1 |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
import ConfigParserconfig = ConfigParser.ConfigParser()config.read('i.cfg')# ########## 读 ###########secs = config.sections()#print secs#options = config.options('group2')#print options#item_list = config.items('group2')#print item_list#val = config.get('group1','key')#val = config.getint('group1','key')# ########## 改写 ###########sec = config.remove_section('group1')#config.write(open('i.cfg', "w"))#sec = config.has_section('wupeiqi')#sec = config.add_section('wupeiqi')#config.write(open('i.cfg', "w"))#config.set('group2','k1',11111)#config.write(open('i.cfg', "w"))#config.remove_option('group2','age')#config.write(open('i.cfg', "w")) |
八、logging
用于便捷记录日志且线程安全的模块
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
import logginglogging.basicConfig(filename='log.log', format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s -%(module)s: %(message)s', datefmt='%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S %p', level=10)logging.debug('debug')logging.info('info')logging.warning('warning')logging.error('error')logging.critical('critical')logging.log(10,'log') |
对于等级:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
CRITICAL = 50FATAL = CRITICALERROR = 40WARNING = 30WARN = WARNINGINFO = 20DEBUG = 10NOTSET = 0 |
只有大于当前日志等级的操作才会被记录。
对于格式,有如下属性可是配置:

九、time
时间相关的操作,时间有三种表示方式:
- 时间戳 1970年1月1日之后的秒,即:time.time()
- 格式化的字符串 2014-11-11 11:11, 即:time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
- 结构化时间 元组包含了:年、日、星期等... time.struct_time 即:time.localtime()
- #_*_coding:utf-8_*_
- __author__ = 'Alex Li'
- import time
- # print(time.clock()) #返回处理器时间,3.3开始已废弃 , 改成了time.process_time()测量处理器运算时间,不包括sleep时间,不稳定,mac上测不出来
- # print(time.altzone) #返回与utc时间的时间差,以秒计算\
- # print(time.asctime()) #返回时间格式"Fri Aug 19 11:14:16 2016",
- # print(time.localtime()) #返回本地时间 的struct time对象格式
- # print(time.gmtime(time.time()-800000)) #返回utc时间的struc时间对象格式
- # print(time.asctime(time.localtime())) #返回时间格式"Fri Aug 19 11:14:16 2016",
- #print(time.ctime()) #返回Fri Aug 19 12:38:29 2016 格式, 同上
- # 日期字符串 转成 时间戳
- # string_2_struct = time.strptime("2016/05/22","%Y/%m/%d") #将 日期字符串 转成 struct时间对象格式
- # print(string_2_struct)
- # #
- # struct_2_stamp = time.mktime(string_2_struct) #将struct时间对象转成时间戳
- # print(struct_2_stamp)
- #将时间戳转为字符串格式
- # print(time.gmtime(time.time()-86640)) #将utc时间戳转换成struct_time格式
- # print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S",time.gmtime()) ) #将utc struct_time格式转成指定的字符串格式
- #时间加减
- import datetime
- # print(datetime.datetime.now()) #返回 2016-08-19 12:47:03.941925
- #print(datetime.date.fromtimestamp(time.time()) ) # 时间戳直接转成日期格式 2016-08-19
- # print(datetime.datetime.now() )
- # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(3)) #当前时间+3天
- # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(-3)) #当前时间-3天
- # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(hours=3)) #当前时间+3小时
- # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(minutes=30)) #当前时间+30分
- #
- # c_time = datetime.datetime.now()
- # print(c_time.replace(minute=3,hour=2)) #时间替换
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
print time.time()print time.mktime(time.localtime()) print time.gmtime() #可加时间戳参数print time.localtime() #可加时间戳参数print time.strptime('2014-11-11', '%Y-%m-%d') print time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d') #默认当前时间print time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d',time.localtime()) #默认当前时间print time.asctime()print time.asctime(time.localtime())print time.ctime(time.time()) import datetime'''datetime.date:表示日期的类。常用的属性有year, month, daydatetime.time:表示时间的类。常用的属性有hour, minute, second, microseconddatetime.datetime:表示日期时间datetime.timedelta:表示时间间隔,即两个时间点之间的长度timedelta([days[, seconds[, microseconds[, milliseconds[, minutes[, hours[, weeks]]]]]]])strftime("%Y-%m-%d")'''import datetimeprint datetime.datetime.now()print datetime.datetime.now() - datetime.timedelta(days=5) |
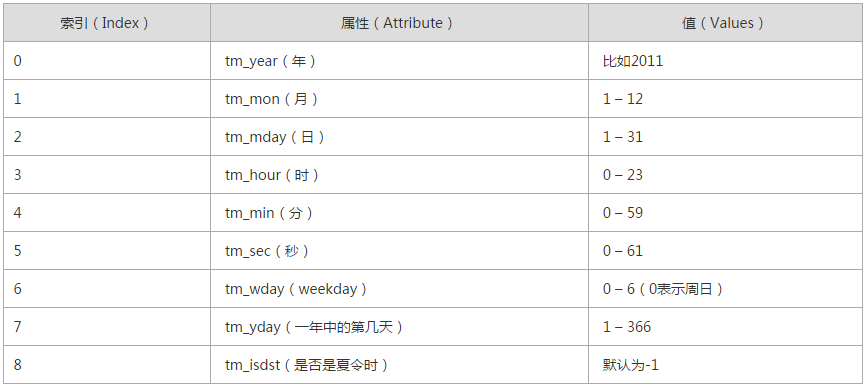
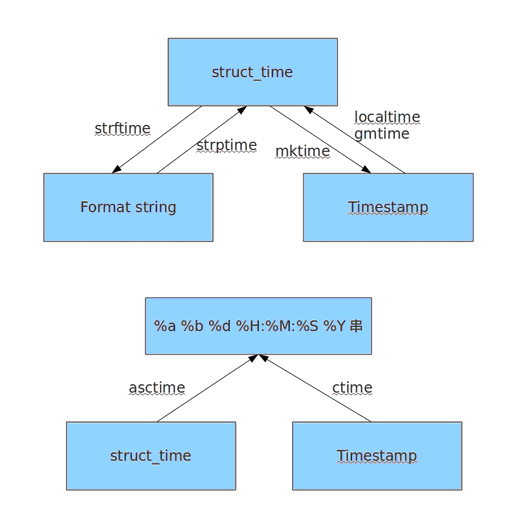
十、re
re模块用于对python的正则表达式的操作。
字符:
. 匹配除换行符以外的任意字符
\w 匹配字母或数字或下划线或汉字
\s 匹配任意的空白符
\d 匹配数字
\b 匹配单词的开始或结束
^ 匹配字符串的开始
$ 匹配字符串的结束
次数:
* 重复零次或更多次
+ 重复一次或更多次
? 重复零次或一次
{n} 重复n次
{n,} 重复n次或更多次
{n,m} 重复n到m次
- IP:
- ^(25[0-5]|2[0-4]\d|[0-1]?\d?\d)(\.(25[0-5]|2[0-4]\d|[0-1]?\d?\d)){3}$
- 手机号:
- ^1[3|4|5|8][0-9]\d{8}$
1、match(pattern, string, flags=0)
从起始位置开始根据模型去字符串中匹配指定内容,匹配单个
- 正则表达式
- 要匹配的字符串
- 标志位,用于控制正则表达式的匹配方式
- import re
- obj = re.match('\d+', '123uuasf')
- if obj:
- print obj.group()
- # flags
- I = IGNORECASE = sre_compile.SRE_FLAG_IGNORECASE # ignore case
- L = LOCALE = sre_compile.SRE_FLAG_LOCALE # assume current 8-bit locale
- U = UNICODE = sre_compile.SRE_FLAG_UNICODE # assume unicode locale
- M = MULTILINE = sre_compile.SRE_FLAG_MULTILINE # make anchors look for newline
- S = DOTALL = sre_compile.SRE_FLAG_DOTALL # make dot match newline
- X = VERBOSE = sre_compile.SRE_FLAG_VERBOSE # ignore whitespace and comments
- flags
2、search(pattern, string, flags=0)
根据模型去字符串中匹配指定内容,匹配单个
- import re
- obj = re.search('\d+', 'u123uu888asf')
- if obj:
- print obj.group()
3、group和groups

- a = "123abc456"
- print re.search("([0-9]*)([a-z]*)([0-9]*)", a).group()
- print re.search("([0-9]*)([a-z]*)([0-9]*)", a).group(0)
- print re.search("([0-9]*)([a-z]*)([0-9]*)", a).group(1)
- print re.search("([0-9]*)([a-z]*)([0-9]*)", a).group(2)
- print re.search("([0-9]*)([a-z]*)([0-9]*)", a).groups()

4、findall(pattern, string, flags=0)
上述两中方式均用于匹配单值,即:只能匹配字符串中的一个,如果想要匹配到字符串中所有符合条件的元素,则需要使用 findall。
- import re
- obj = re.findall('\d+', 'fa123uu888asf')
- print obj
5、sub(pattern, repl, string, count=0, flags=0)
用于替换匹配的字符串
- content = "123abc456"
- new_content = re.sub('\d+', 'sb', content)
- # new_content = re.sub('\d+', 'sb', content, 1)
- print new_content
相比于str.replace功能更加强大
6、split(pattern, string, maxsplit=0, flags=0)
根据指定匹配进行分组
- content = "'1 - 2 * ((60-30+1*(9-2*5/3+7/3*99/4*2998+10*568/14))-(-4*3)/(16-3*2) )'"
- new_content = re.split('\*', content)
- # new_content = re.split('\*', content, 1)
- print new_content
- content = "'1 - 2 * ((60-30+1*(9-2*5/3+7/3*99/4*2998+10*568/14))-(-4*3)/(16-3*2) )'"
- new_content = re.split('[\+\-\*\/]+', content)
- # new_content = re.split('\*', content, 1)
- print new_content
- inpp = '1-2*((60-30 +(-40-5)*(9-2*5/3 + 7 /3*99/4*2998 +10 * 568/14 )) - (-4*3)/ (16-3*2))'
- inpp = re.sub('\s*','',inpp)
- new_content = re.split('\(([\+\-\*\/]?\d+[\+\-\*\/]?\d+){1}\)', inpp, 1)
- print new_content
相比于str.split更加强大
实例:计算器源码
十一、random
随机数
|
1
2
3
4
|
mport randomprint random.random()print random.randint(1,2)print random.randrange(1,10) |
随机验证码实例:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
import randomcheckcode = ''for i in range(4): current = random.randrange(0,4) if current != i: temp = chr(random.randint(65,90)) else: temp = random.randint(0,9) checkcode += str(temp)print checkcode |
Python全栈开发:模块的更多相关文章
- Python全栈开发【模块】
Python全栈开发[模块] 本节内容: 模块介绍 time random os sys json & picle shelve XML hashlib ConfigParser loggin ...
- python全栈开发中级班全程笔记(第二模块、第四章(三、re 正则表达式))
python全栈开发笔记第二模块 第四章 :常用模块(第三部分) 一.正则表达式的作用与方法 正则表达式是什么呢?一个问题带来正则表达式的重要性和作用 有一个需求 : 从文件中读取所有联 ...
- python全栈开发中级班全程笔记(第二模块、第四章)(常用模块导入)
python全栈开发笔记第二模块 第四章 :常用模块(第二部分) 一.os 模块的 详解 1.os.getcwd() :得到当前工作目录,即当前python解释器所在目录路径 impor ...
- python全栈开发之正则表达式和python的re模块
正则表达式和python的re模块 python全栈开发,正则表达式,re模块 一 正则表达式 正则表达式(Regular Expression)是一种文本模式,包括普通字符(例如,a 到 z 之间的 ...
- python全栈开发中级班全程笔记(第二模块、第三章)(员工信息增删改查作业讲解)
python全栈开发中级班全程笔记 第三章:员工信息增删改查作业代码 作业要求: 员工增删改查表用代码实现一个简单的员工信息增删改查表需求: 1.支持模糊查询,(1.find name ,age fo ...
- Python全栈开发【面向对象进阶】
Python全栈开发[面向对象进阶] 本节内容: isinstance(obj,cls)和issubclass(sub,super) 反射 __setattr__,__delattr__,__geta ...
- Python全栈开发【面向对象】
Python全栈开发[面向对象] 本节内容: 三大编程范式 面向对象设计与面向对象编程 类和对象 静态属性.类方法.静态方法 类组合 继承 多态 封装 三大编程范式 三大编程范式: 1.面向过程编程 ...
- Python全栈开发【基础三】
Python全栈开发[基础三] 本节内容: 函数(全局与局部变量) 递归 内置函数 函数 一.定义和使用 函数最重要的是减少代码的重用性和增强代码可读性 def 函数名(参数): ... 函数体 . ...
- Python全栈开发【基础一】
Python全栈开发[第一篇] 本节内容: Python 的种类 Python 的环境 Python 入门(解释器.编码.变量.input输入.if流程控制与缩进.while循环) if流程控制与wh ...
- python全栈开发-Day2 布尔、流程控制、循环
python全栈开发-Day2 布尔 流程控制 循环 一.布尔 1.概述 #布尔值,一个True一个False #计算机俗称电脑,即我们编写程序让计算机运行时,应该是让计算机无限接近人脑,或者说人 ...
随机推荐
- favicon.ico请求处理
favicon.ico 图标用于收藏夹图标和浏览器标签上的显示,如果不设置,浏览器会请求网站根目录的这个图标,如果网站根目录也没有这图标会产生 404. 出于优化的考虑,要么就有这个图标,要么就禁止产 ...
- [JZOJ 5697] 农场
题目大意:将 n 个数 ai分成若干连续的段,使得每段的和都相等,求最多可以分成多少段. 思路: 考虑ai的和为sum,那么每一段的和就是约数. 对于每一个d,考虑其是否合法. 1e6之内用桶统计不会 ...
- hdu多校第五场1006 (hdu6629) string matching Ex-KMP
题意: 给你一个暴力匹配字符串公共前缀后缀的程序,为你对于某个字符串,暴力匹配的次数是多少. 题解: 使用扩展kmp构造extend数组,在扩展kmp中,设原串S和模式串T. extend[i]表示T ...
- POJ2226-Muddy Fields-二分图*
目录 目录 思路: (有任何问题欢迎留言或私聊 && 欢迎交流讨论哦 目录 题意:传送门 原题目描述在最下面. 一个nm的矩阵,有坑有草,可以用1x长度的木板盖住坑,但不能盖到草. ...
- [zz]winform 窗体关闭事件
注册窗体关闭事件: 在Form1.Designer.cs 文件中添加: this.FormClosing += new System.Windows.Forms.FormClosingEventHan ...
- drools原生drl规则文件的使用
在初识drools中对drl文件进行了简单的介绍.这里举个例子来具体说明下.主要是写了规则之后我们如何用java代码来run起来. drl文件内容如下: rule "ageUp12" ...
- 2019.2.23VScode的c++配置详细方法
根据个人经验,最新的c++配置方法. 主要的步骤: 安装Vscode 在Vscode类安装c++插件 安装编译调试环境 修改Vscode配置文件. 安装Vscode的步骤省略 如何配置Vscode中文 ...
- Sublime Text自定制代码片段(Code Snippets)
在编写代码的整个过程中,开发人员经常会一次又一次的改写或者重用相同的代码段,消除这种重复过程的方法之一是把我们经常用到的代码保存成代码片段(snippets),这使得我们可以方便的检索和使用它们. 为 ...
- 常用Oracle操作语句
--常用的字段类型有:varchar2,char,nchar,date,long,number,float,BLOB,CLOB --添加表字段 ); --修改表字段 ); --删除表字段 alter ...
- [TJOI 2018]游园会
题意:求NOI的合法串... 思路: 首先这个似乎和后缀自动机没关系(话说TJ不考后缀自动机??),其实就是一个\(DP\)套\(DP\),考虑如果不看兑奖串就是一个LCS,当出现时多记一维即可. # ...
