数据预处理以及探索性分析(EDA)
1.根据某个列进行groupby,判断是否存在重复列。
# Count the unique variables (if we got different weight values,
# for example, then we should get more than one unique value in this groupby)
all_cols_unique_players = df.groupby('playerShort').agg({col:'nunique' for col in player_cols})
其中针对.agg函数:
DataFrame.agg(self, func, axis=0, *args, **kwargs)[source]
Aggregate using one or more operations over the specified axis.
例子:
>>> df = pd.DataFrame([[1, 2, 3],
... [4, 5, 6],
... [7, 8, 9],
... [np.nan, np.nan, np.nan]],
... columns=['A', 'B', 'C']) >>> df.agg({'A' : ['sum', 'min'], 'B' : ['min', 'max']})
A B
max NaN 8.0
min 1.0 2.0
sum 12.0 NaN
2.获取一个字表
其主要实现的是: """Helper function that creates a sub-table from the columns and runs a quick uniqueness test."""
player_index = 'playerShort'
player_cols = [#'player', # drop player name, we have unique identifier
'birthday',
'height',
'weight',
'position',
'photoID',
'rater1',
'rater2',
]
def get_subgroup(dataframe, g_index, g_columns):
"""Helper function that creates a sub-table from the columns and runs a quick uniqueness test."""
g = dataframe.groupby(g_index).agg({col:'nunique' for col in g_columns})
if g[g > 1].dropna().shape[0] != 0:
print("Warning: you probably assumed this had all unique values but it doesn't.")
return dataframe.groupby(g_index).agg({col:'max' for col in g_columns})
players = get_subgroup(df, player_index, player_cols)
players.head()
3.将整理出的字表存储至CSV文件
def save_subgroup(dataframe, g_index, subgroup_name, prefix='raw_'):
save_subgroup_filename = "".join([prefix, subgroup_name, ".csv.gz"])
dataframe.to_csv(save_subgroup_filename, compression='gzip', encoding='UTF-8')
test_df = pd.read_csv(save_subgroup_filename, compression='gzip', index_col=g_index, encoding='UTF-8')
# Test that we recover what we send in
if dataframe.equals(test_df):
print("Test-passed: we recover the equivalent subgroup dataframe.")
else:
print("Warning -- equivalence test!!! Double-check.")
4.数据具体指标查看---缺失值查看
import missingno as msno
import pandas_profiling
msno.matrix(players.sample(500),
figsize=(16, 7),
width_ratios=(15, 1))
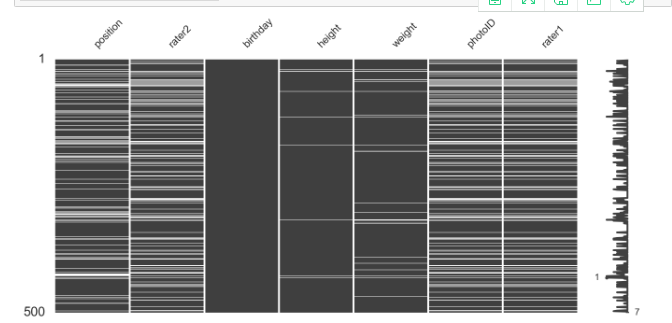
msno.heatmap(players.sample(500),
figsize=(16, 7),)

5.数据透视表
转至https://blog.csdn.net/Dorisi_H_n_q/article/details/82288092
透视表概念:pd.pivot_table()
透视表是各种电子表格程序和其他数据分析软件中一种常见的数据汇总工具。它根据一个或多个键对数据进行聚合,并根据行和列上的分组键将数据分配到各个矩形区域中。
透视表:根据特定条件进行分组计算,查找数据,进行计算
pd.pivot_table(df,index=['hand'],columns=['male'],aggfunc='min')
交叉表概念:pd.crosstab(index,colums)
交叉表是一种用于计算分组频率的特殊透视图,对数据进行汇总。
pd.crosstab(players.rater1, players.rater2)
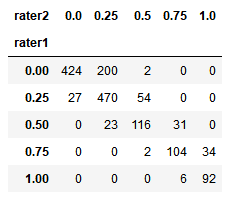
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 8))
sns.heatmap(pd.crosstab(players.rater1, players.rater2), cmap='Blues', annot=True, fmt='d', ax=ax)
ax.set_title("Correlation between Rater 1 and Rater 2\n")
fig.tight_layout()
创建一个新列,新列的值是另外两列的平均值
players['skintone'] = players[['rater1', 'rater2']].mean(axis=1)
players.head()
6.对离散category数值进行处理
#连续变量离散化
weight_categories = ["vlow_weight",
"low_weight",
"mid_weight",
"high_weight",
"vhigh_weight",
] players['weightclass'] = pd.qcut(players['weight'],
len(weight_categories),
weight_categories)
(Create higher level categories)
position_types = players.position.unique()
position_types
“”“
array(['Center Back', 'Attacking Midfielder', 'Right Midfielder',
'Center Midfielder', 'Goalkeeper', 'Defensive Midfielder',
'Left Fullback', nan, 'Left Midfielder', 'Right Fullback',
'Center Forward', 'Left Winger', 'Right Winger'], dtype=object)
”“” defense = ['Center Back','Defensive Midfielder', 'Left Fullback', 'Right Fullback', ]
midfield = ['Right Midfielder', 'Center Midfielder', 'Left Midfielder',]
forward = ['Attacking Midfielder', 'Left Winger', 'Right Winger', 'Center Forward']
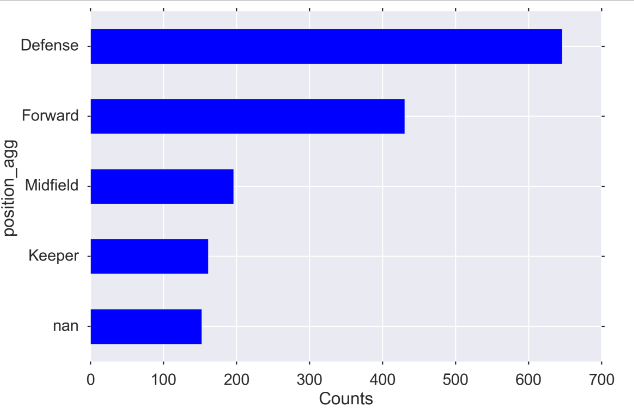
keeper = 'Goalkeeper' # modifying dataframe -- adding the aggregated position categorical position_agg
players.loc[players['position'].isin(defense), 'position_agg'] = "Defense"
players.loc[players['position'].isin(midfield), 'position_agg'] = "Midfield"
players.loc[players['position'].isin(forward), 'position_agg'] = "Forward"
players.loc[players['position'].eq(keeper), 'position_agg'] = "Keeper"
绘制value_counts()图片
MIDSIZE = (12, 8)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=MIDSIZE)
players['position_agg'].value_counts(dropna=False, ascending=True).plot(kind='barh', ax=ax)
ax.set_ylabel("position_agg")
ax.set_xlabel("Counts")
fig.tight_layout()
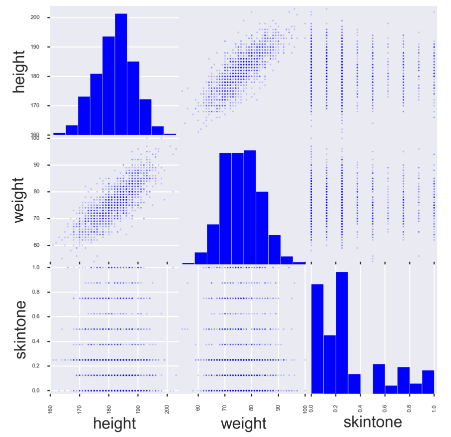
7.绘制多变量之间的关系图
from pandas.plotting import scatter_matrix
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 10))
scatter_matrix(players[['height', 'weight', 'skintone']], alpha=0.2, diagonal='hist', ax=ax);
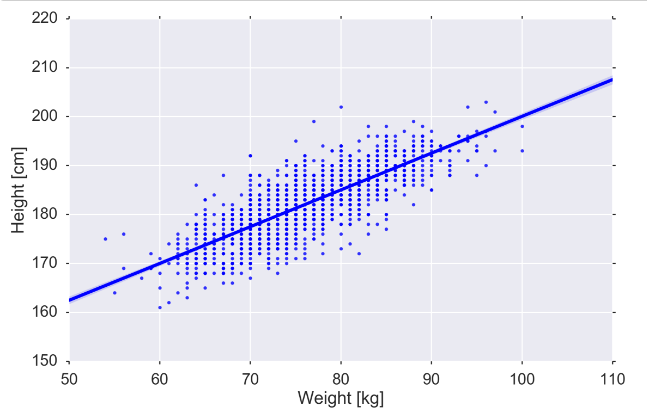
# Perhaps you want to see a particular relationship more clearly
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=MIDSIZE)
sns.regplot('weight', 'height', data=players, ax=ax)
ax.set_ylabel("Height [cm]")
ax.set_xlabel("Weight [kg]")
fig.tight_layout()
8.连续变量离散化(Create quantile bins for continuous variables)
weight_categories = ["vlow_weight",
"low_weight",
"mid_weight",
"high_weight",
"vhigh_weight",
] players['weightclass'] = pd.qcut(players['weight'],
len(weight_categories),
weight_categories)
9.数据报表查看
pandas_profiling.ProfileReport(players)

10.出生日期等时间格式处理
players['birth_date'] = pd.to_datetime(players.birthday, format='%d.%m.%Y')
players['age_years'] = ((pd.to_datetime("2013-01-01") - players['birth_date']).dt.days)/365.25
players['age_years']
//选择特定列
players_cleaned_variables = players.columns.tolist()
players_cleaned_variables
player_dyad = (clean_players.merge(agg_dyads.reset_index().set_index('playerShort'),
left_index=True,
right_index=True))
//groupby+sort_values+rename
(tidy_dyads.groupby(level=1)
.sum()
.sort_values('redcard', ascending=False)
.rename(columns={'redcard':'total redcards received'})).head()
针对时间统计可以分别列出,年、月、日以及相应的小时等数据,查看年的、月的、季度的、每天时间段的各个统计量。
11.数据偏度与峰度
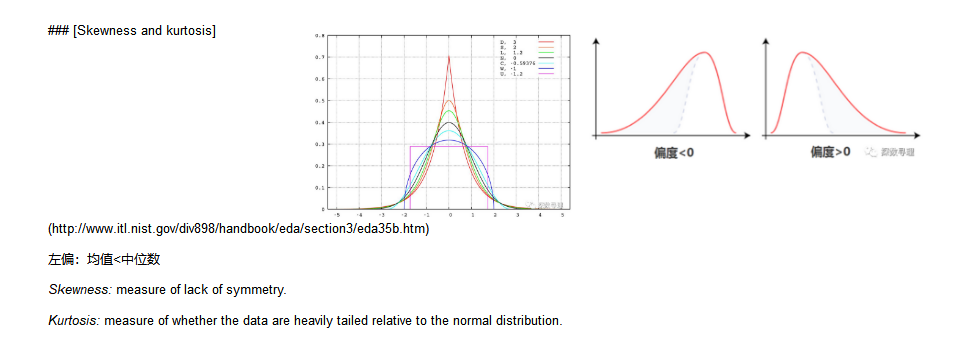
正态分布的偏度应为零。负偏度表示偏左,正偏表示右偏。
峰度也是一个正态分布和零只能是积极的。我们肯定有一些异常值!
对于分布超级不均衡的数据,采用log变换的方式,将变量的统计部分变为正常。
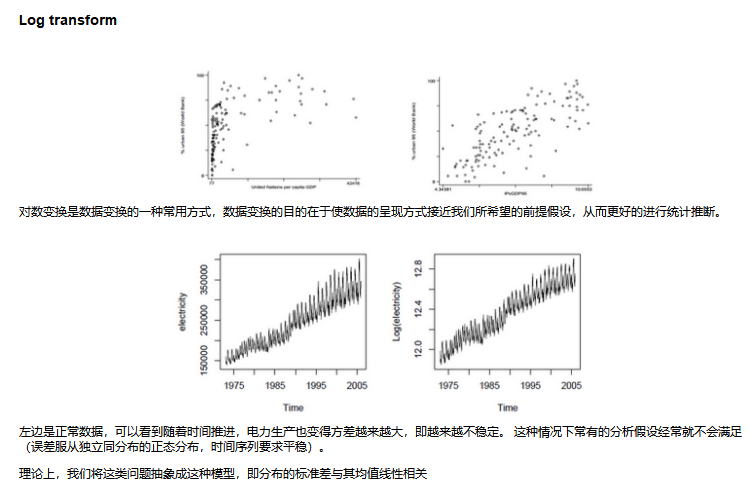
具体的代码采用的是np.log
recent[['total_pop']].apply(np.log).apply(scipy.stats.skew)
//绘图函数
def plot_hist(df, variable, bins=20, xlabel=None, by=None,
ylabel=None, title=None, logx=False, ax=None): if not ax:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12,8))
if logx:
if df[variable].min() <=0:
df[variable] = df[variable] - df[variable].min() + 1
print('Warning: data <=0 exists, data transformed by %0.2g before plotting' % (- df[variable].min() + 1)) bins = np.logspace(np.log10(df[variable].min()),
np.log10(df[variable].max()), bins)
ax.set_xscale("log") ax.hist(df[variable].dropna().values, bins=bins); if xlabel:
ax.set_xlabel(xlabel);
if ylabel:
ax.set_ylabel(ylabel);
if title:
ax.set_title(title); return ax
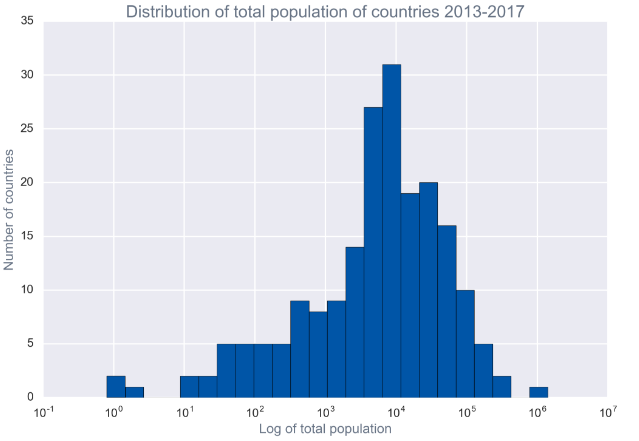
plot_hist(recent, 'total_pop', bins=25, logx=True,
xlabel='Log of total population', ylabel='Number of countries',
title='Distribution of total population of countries 2013-2017');

查看单个变量之间的变化规律时,在出现变量数值不均衡,有的数值很大,有的很小时,可以采用变量的增长速度比率进行表示,查看其变化情况。例子:
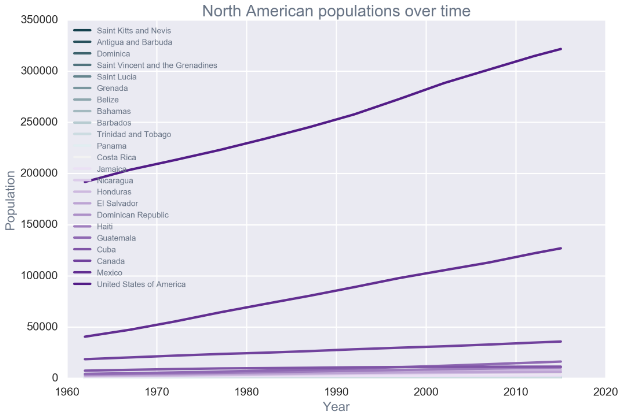
原数据
with sns.color_palette(sns.diverging_palette(220, 280, s=85, l=25, n=23)):
north_america = time_slice(subregion(data, 'North America'), '1958-1962').sort_values('total_pop').index.tolist()
for country in north_america:
plt.plot(time_series(data, country, 'total_pop'), label=country);
plt.xlabel('Year');
plt.ylabel('Population');
plt.title('North American populations over time');
plt.legend(loc=2,prop={'size':10});
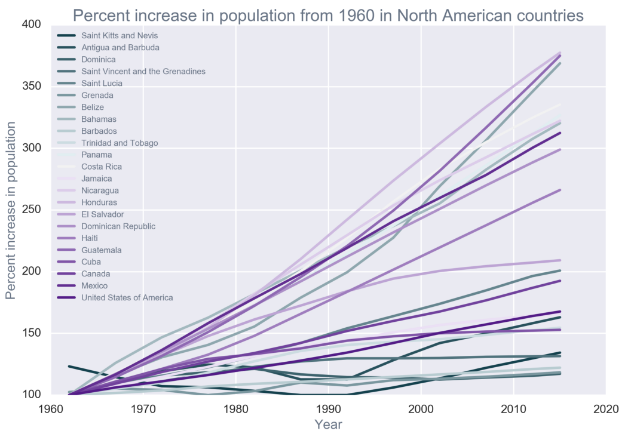
比率处理后的数据可视化
with sns.color_palette(sns.diverging_palette(220, 280, s=85, l=25, n=23)):
for country in north_america:
ts = time_series(data, country, 'total_pop')
ts['norm_pop'] = ts.total_pop/ts.total_pop.min()*100
plt.plot(ts['norm_pop'], label=country);
plt.xlabel('Year');
plt.ylabel('Percent increase in population');
plt.title('Percent increase in population from 1960 in North American countries');
plt.legend(loc=2,prop={'size':10});
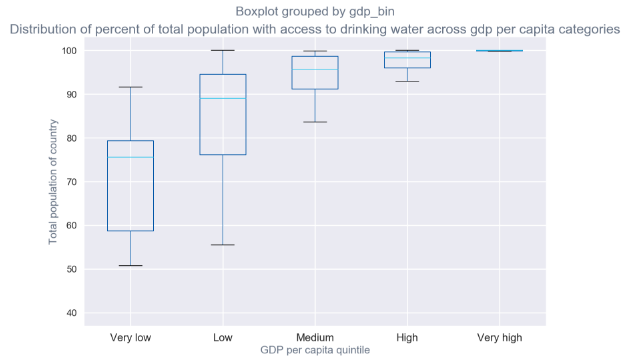
recent[['gdp_bin','total_pop_access_drinking']].boxplot(by='gdp_bin');
# plt.ylim([0,100000]);
plt.title('Distribution of percent of total population with access to drinking water across gdp per capita categories');
plt.xlabel('GDP per capita quintile');
plt.ylabel('Total population of country');
12.对特定列进行处理
simple_regions ={
'World | Asia':'Asia',
'Americas | Central America and Caribbean | Central America': 'North America',
'Americas | Central America and Caribbean | Greater Antilles': 'North America',
'Americas | Central America and Caribbean | Lesser Antilles and Bahamas': 'North America',
'Americas | Northern America | Northern America': 'North America',
'Americas | Northern America | Mexico': 'North America',
'Americas | Southern America | Guyana':'South America',
'Americas | Southern America | Andean':'South America',
'Americas | Southern America | Brazil':'South America',
'Americas | Southern America | Southern America':'South America',
'World | Africa':'Africa',
'World | Europe':'Europe',
'World | Oceania':'Oceania'
}
data.region = data.region.apply(lambda x: simple_regions[x])
数据预处理以及探索性分析(EDA)的更多相关文章
- ubuntu之路——day3(本来打算做pytorch的练习 但是想到前段时间的数据预处理的可视化分析 就先总结一下)
首先依托于一个场景来进行可视化分析 直接选了天池大数据竞赛的新人赛的一个活跃题目 用的方式也是最常用的数据预处理方式 [新人赛]快来一起挖掘幸福感!https://tianchi.aliyun.com ...
- Next generation sequencing (NGS)二代测序数据预处理与分析
二代测序原理: 1.DNA待测文库构建. 超声波把DNA打断成小片段,一般200--500bp,两端加上不同的接头2.Flowcell.一个flowcell,8个channel,很多接头3.桥式PCR ...
- 第七篇:数据预处理(四) - 数据归约(PCA/EFA为例)
前言 这部分也许是数据预处理最为关键的一个阶段. 如何对数据降维是一个很有挑战,很有深度的话题,很多理论书本均有详细深入的讲解分析. 本文仅介绍主成分分析法(PCA)和探索性因子分析法(EFA),并给 ...
- Python做数据预处理
在拿到一份数据准备做挖掘建模之前,首先需要进行初步的数据探索性分析(你愿意花十分钟系统了解数据分析方法吗?),对数据探索性分析之后要先进行一系列的数据预处理步骤.因为拿到的原始数据存在不完整.不一致. ...
- 借助 SIMD 数据布局模板和数据预处理提高 SIMD 在动画中的使用效率
原文链接 简介 为发挥 SIMD1 的最大作用,除了对其进行矢量化处理2外,我们还需作出其他努力.可以尝试为循环添加 #pragma omp simd3,查看编译器是否成功进行矢量化,如果性能有所提升 ...
- 对数据预处理的一点理解[ZZ]
数据预处理没有统一的标准,只能说是根据不同类型的分析数据和业务需求,在对数据特性做了充分的理解之后,再选择相关的数据预处理技术,一般会用到多种预处理技术,而且对每种处理之后的效果做些分析对比,这里面经 ...
- 【深度学习系列】PaddlePaddle之数据预处理
上篇文章讲了卷积神经网络的基本知识,本来这篇文章准备继续深入讲CNN的相关知识和手写CNN,但是有很多同学跟我发邮件或私信问我关于PaddlePaddle如何读取数据.做数据预处理相关的内容.网上看的 ...
- [数据预处理]-中心化 缩放 KNN(一)
据预处理是总称,涵盖了数据分析师使用它将数据转处理成想要的数据的一系列操作.例如,对某个网站进行分析的时候,可能会去掉 html 标签,空格,缩进以及提取相关关键字.分析空间数据的时候,一般会把带单位 ...
- 数据准备<3>:数据预处理
数据预处理是指因为算法或者分析需要,对经过数据质量检查后的数据进行转换.衍生.规约等操作的过程.整个数据预处理工作主要包括五个方面内容:简单函数变换.标准化.衍生虚拟变量.离散化.降维.本文将作展开介 ...
随机推荐
- 【JZOJ4878】【NOIP2016提高A组集训第10场11.8】时空传送
题目描述 经过旷久的战争,ZMiG和707逐渐培养出了深厚的感♂情.他们逃到了另一块大陆上,决定远离世间的纷争,幸福地生活在一起.钟情707的neither_nor决心要把他们拆散,他要动用手中最大杀 ...
- HDU_2035:人见人爱A^B
Problem Description 求A^B的最后三位数表示的整数. 说明:A^B的含义是“A的B次方” Input 输入数据包含多个测试实例,每个实例占一行,由两个正整数A和B组成(1< ...
- 阿里云数据库自研产品亮相国际顶级会议ICDE 推动云原生数据库成为行业标准
4月9日,澳门当地时间下午4:00-5:30,阿里云在ICDE 2019举办了主题为“云时代的数据库”的专场分享研讨会. 本次专场研讨会由阿里巴巴集团副总裁.高级研究员,阿里云智能数据库产品事业部负责 ...
- @codeforces - 444A@ DZY Loves Physics
目录 @description@ @solution@ @accepted code@ @details@ @description@ 给定一个 n 点 m 边的图,边有边权,点有点权. 找到一个连通 ...
- linux下arm平台Qt编译环境搭建与解析
一.概述: 我们知道QTcreator.这仅仅是个IDE,他包含了一个编译器--qmake.这两者的关系与codeblocks和g++的关系一样,首先要明确这些. 而我们在linu ...
- python 字符串(str)
- Python 变量赋值
- LeetCode Weekly Contest 6
leetcode现在每周末举办比赛,这是今天上午参加的比赛的题解.题目难度不算大,两个easy,一个medium,一个hard.hard题之前接触过,所以做得比较顺利. 1. Sum of Left ...
- 2018-2-13-win10-uwp-如何让WebView标识win10手机
title author date CreateTime categories win10 uwp 如何让WebView标识win10手机 lindexi 2018-2-13 17:23:3 +080 ...
- hdu 5744 Keep On Movin (2016多校第二场)
Keep On Movin Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)Tot ...
