【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—编程作业 Programming Exercise 2——逻辑回归
作业说明
Exercise 2,Week 3,使用Octave实现逻辑回归模型。数据集 ex2data1.txt ,ex2data2.txt
实现 Sigmoid 、代价函数计算Computing Cost 和 梯度下降Gradient Descent。

文件清单
- ex2.m - Octave/MATLAB script that steps you through the exercise
- ex2 reg.m - Octave/MATLAB script for the later parts of the exercise
- ex2data1.txt - Training set for the first half of the exercise
- ex2data2.txt - Training set for the second half of the exercise
- submit.m - Submission script that sends your solutions to our servers
- mapFeature.m - Function to generate polynomial features
- plotDecisionBoundary.m - Function to plot classifier’s decision boundary
- [*] plotData.m - Function to plot 2D classification data
- [*] sigmoid.m - Sigmoid Function
- [*] costFunction.m - Logistic Regression Cost Function
- [*] predict.m - Logistic Regression Prediction Function
- [*] costFunctionReg.m - Regularized Logistic Regression Cost
* 为必须要完成的
结论
正则化不涉及第一个 θ0
逻辑回归
背景:大学管理员,想要根据两门课的历史成绩记录来每个是否被允许入学。
ex2data1.txt ,前两列是两门课的成绩,第三列是y值 0 和 1。
一、绘制数据图
plotData.m:
positive = find(y == );
negative = find(y == ); plot(X(positive,),X(positive,),'k+','MarkerFaceColor','g',
'MarkerSize',);
hold on;
plot(X(negative,),X(negative,),'ko','MarkerFaceColor','y',
'MarkerSize',);
运行效果如下:

二、sigmoid 函数
function g = sigmoid(z)
% Instructions: Compute the sigmoid of each value of z (z can be a matrix,
% vector or scalar).
g = ./ ( + exp(-z));
end
三、代价函数
costFunction.m:
function [J, grad] = costFunction(theta, X, y) m = length(y); % number of training examples part1 = - * y' * log(sigmoid(X * theta));
part2 = ( - y)' * log(1 - sigmoid(X * theta));
J = / m * (part1 - part2); grad = / m * X' *((sigmoid(X * theta) - y)); end
四、预测函数
输入X和theta,返回预测结果向量。每个值是 0 或 1
function p = predict(theta, X)
%PREDICT Predict whether the label is or using learned logistic
%regression parameters theta
% p = PREDICT(theta, X) computes the predictions for X using a
% threshold at 0.5 (i.e., if sigmoid(theta'*x) >= 0.5, predict 1) m = size(X, ); % Number of training examples % 最开始没有四舍五入,导致错误
p = round(sigmoid(X * theta)); end
五、进行逻辑回归
ex1.m 中的调用:
加载数据:
data = load('ex2data1.txt');
X = data(:, [, ]); y = data(:, );
[m, n] = size(X);
% Add intercept term to x and X_test
X = [ones(m, ) X];
initial_theta = zeros(n + , );
调用 fminunc 函数
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', );
[theta, cost] = ...
fminunc(@(t)(costFunction(t, X, y)), initial_theta, options);
四、绘制边界线
plotDecisionBoundary.m
function plotDecisionBoundary(theta, X, y)
%PLOTDECISIONBOUNDARY Plots the data points X and y into a new figure with
%the decision boundary defined by theta
% PLOTDECISIONBOUNDARY(theta, X,y) plots the data points with + for the
% positive examples and o for the negative examples. X is assumed to be
% a either
% ) Mx3 matrix, where the first column is an all-ones column for the
% intercept.
% ) MxN, N> matrix, where the first column is all-ones % Plot Data
plotData(X(:,:), y);
hold on if size(X, ) <=
% Only need points to define a line, so choose two endpoints
plot_x = [min(X(:,))-, max(X(:,))+]; % Calculate the decision boundary line
plot_y = (-./theta()).*(theta().*plot_x + theta()); % Plot, and adjust axes for better viewing
plot(plot_x, plot_y) % Legend, specific for the exercise
legend('Admitted', 'Not admitted', 'Decision Boundary')
axis([, , , ])
else
% Here is the grid range
u = linspace(-, 1.5, );
v = linspace(-, 1.5, ); z = zeros(length(u), length(v));
% Evaluate z = theta*x over the grid
for i = :length(u)
for j = :length(v)
z(i,j) = mapFeature(u(i), v(j))*theta;
end
end
z = z'; % important to transpose z before calling contour % Plot z =
% Notice you need to specify the range [, ]
contour(u, v, z, [, ], 'LineWidth', )
end
hold off end

正则化逻辑回归
背景:预测来自制造工厂的微芯片是否通过质量保证(QA)。 在QA期间,每个微芯片都经过两个测试以确保其正常运行。
ex2data2.txt ,前两列是测试结果的成绩,第三列是y值 0 和 1。
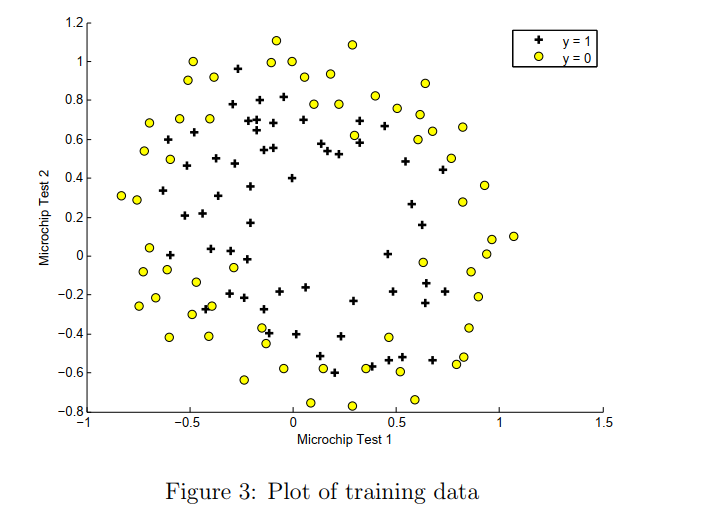
只有两个feature,使用直线不能划分。
为了让数据拟合的更好,使用mapFeature函数,将x1,x2两个feature扩展到六次方。
六次方曲线复杂,容易造成过拟合,所以需要正则化。
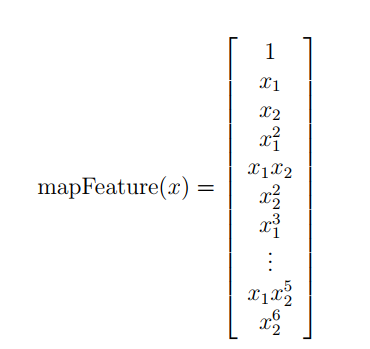
mapFeature.m
function out = mapFeature(X1, X2)
% MAPFEATURE Feature mapping function to polynomial features
%
% MAPFEATURE(X1, X2) maps the two input features
% to quadratic features used in the regularization exercise.
%
% Returns a new feature array with more features, comprising of
% X1, X2, X1.^, X2.^, X1*X2, X1*X2.^, etc..
%
% Inputs X1, X2 must be the same size
% degree = ;
out = ones(size(X1(:,)));
for i = :degree
for j = :i
out(:, end+) = (X1.^(i-j)).*(X2.^j);
end
end end
二、代价函数
注意:θ0不参与正则化。
正则化逻辑回归的代价函数如下,分为三项:
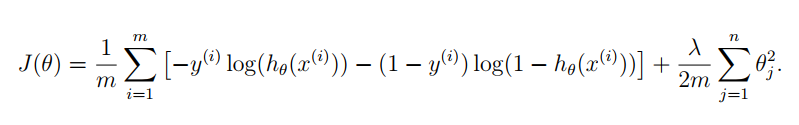
梯度下降算法如下:


coatFunctionReg.m 如下:
function [J, grad] = costFunctionReg(theta, X, y, lambda)
m = length(y); % number of training examples
% theta0 不参与正则化。直接让变量等于theta,将第一个元素置为0,再参与和 λ 的运算
t = theta; t() = ; % 第一项
part1 = -y' * log(sigmoid(X * theta));
% 第二项
part2 = ( - y)' * log(1 - sigmoid(X * theta)); % 正则项
regTerm = lambda / / m * t' * t;
J = / m * (part1 - part2) + regTerm; % 梯度
grad = / m * X' *((sigmoid(X * theta) - y)) + lambda / m * t; end
em2_reg.m 里的调用
% 加载数据
data = load('ex2data2.txt');
X = data(:, [, ]); y = data(:, );
% mapfeature
X = mapFeature(X(:,), X(:,)); % Initialize fitting parameters
initial_theta = zeros(size(X, ), );
lambda = ;
% 调用 fminunc方法
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', );
[theta, J, exit_flag] = ...
fminunc(@(t)(costFunctionReg(t, X, y, lambda)), initial_theta, options);
三、参数调整
(1)使用正则化之前,决策边界曲线如下,可以看到存在过拟合现象:
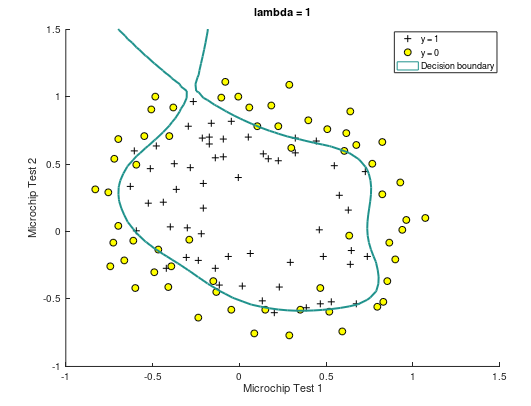
(2)当 λ = 1,决策边界曲线如下。此时训练集预测准确率为 83.05%

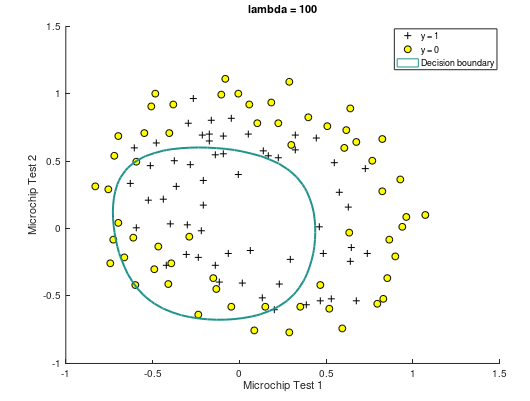
(3)当 λ = 100,曲线如下。此时训练集预测准确率为 61.01%
https://github.com/madoubao/coursera_machine_learning/tree/master/homework/machine-learning-ex2/ex2
【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—编程作业 Programming Exercise 2——逻辑回归的更多相关文章
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—编程作业 Programming Exercise 4—反向传播神经网络
课程笔记 Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—课程笔记 Lecture 9_Neural Networks learning 作业说明 Exercise 4,Week 5,实现反向传播 ba ...
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—编程作业 Programming Exercise 1 线性回归
作业说明 Exercise 1,Week 2,使用Octave实现线性回归模型.数据集 ex1data1.txt ,ex1data2.txt 单变量线性回归必须实现,实现代价函数计算Computin ...
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—编程作业 Programming Exercise 3—多分类逻辑回归和神经网络
作业说明 Exercise 3,Week 4,使用Octave实现图片中手写数字 0-9 的识别,采用两种方式(1)多分类逻辑回归(2)多分类神经网络.对比结果. (1)多分类逻辑回归:实现 lrCo ...
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—课程笔记 Lecture 6_Logistic Regression 逻辑回归
Lecture6 Logistic Regression 逻辑回归 6.1 分类问题 Classification6.2 假设表示 Hypothesis Representation6.3 决策边界 ...
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—Week 3 习题—Logistic Regression 逻辑回归
课上习题 [1]线性回归 Answer: D A 特征缩放不起作用,B for all 不对,C zero error不对 [2]概率 Answer:A [3]预测图形 Answer:A 5 - x1 ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习编程作业:Logistic Regression
编程作业文件: machine-learning-ex2 1. Logistic Regression (逻辑回归) 有之前学生的数据,建立逻辑回归模型预测,根据两次考试结果预测一个学生是否有资格被大 ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习编程作业: Linear Regression
编程作业有两个文件 1.machine-learning-live-scripts(此为脚本文件方便作业) 2.machine-learning-ex1(此为作业文件) 将这两个文件解压拖入matla ...
- Andrew NG 机器学习编程作业3 Octave
问题描述:使用逻辑回归(logistic regression)和神经网络(neural networks)识别手写的阿拉伯数字(0-9) 一.逻辑回归实现: 数据加载到octave中,如下图所示: ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习编程作业:Support Vector Machines
作业: machine-learning-ex6 1. 支持向量机(Support Vector Machines) 在这节,我们将使用支持向量机来处理二维数据.通过实验将会帮助我们获得一个直观感受S ...
随机推荐
- 静态嵌套类(Static Nested Class)和内部类(Inner Class)的不同?
Static Nested Class是被声明为静态(static)的内部类,它可以不依赖于外部类实例被实例化.而通常的内部类需要在外部类实例化后才能实例化,其语法看起来挺诡异的,如下所示. /** ...
- Java 面试/笔试题神整理 [Java web and android]
Java 面试/笔试题神整理 一.Java web 相关基础知识 1.面向对象的特征有哪些方面 1.抽象: 抽象就是忽略一个主题中与当前目标无关的那些方面,以便更充分地注意与当前目标有关的方面.抽象并 ...
- Android数据库代码优化(1) - 从Google的数据库guide说起
假如我们没有任何在Android上使用SQLite的经验,现在要开始在工作中用SQLite存储一些数据.OK, 我们去看google的官方培训文档吧,http://developer.android. ...
- vim自动打开跳到上次的光标位置
只需要vimrc里面加一个稍微复杂一点的autocmd就搞定了: if has("autocmd") au BufReadPost * && line(" ...
- 11.求二元查找树的镜像[MirrorOfBST]
[题目] 输入一颗二元查找树,将该树转换为它的镜像,即在转换后的二元查找树中,左子树的结点都大于右子树的结点.用递归和循环两种方法完成树的镜像转换. 例如输入: 8 / \ 6 1 ...
- Grunt 新手一日入门
var sassStyle = 'expanded'; grunt.initConfig({ pkg: grunt.file.readJSON('package.json'), sass: { out ...
- java md5 函数
private static final String md5(final String s) { final String MD5 = "MD5"; try { // Creat ...
- datasnap的初步
datasnap的初步-回调函数 服务器端 TServerMethods1 =class(TComponent) private { Private declarations } public { P ...
- 有趣的java小项目------猜拳游戏
package com.aaa; //总结:猜拳游戏主要掌握3个方面:1.人出的动作是从键盘输入的(System.in)2.电脑是随机出的(Random随机数)3.双方都要出(条件判断) import ...
- 杂项:WiKi
ylbtech-杂项:WiKi Wiki是一种在网络上开放且可供多人协同创作的超文本系统,由沃德·坎宁安于1995年首先开发,这种超文本系统支持面向社群的协作式写作,同时也包括一组支持这种写作.沃德· ...
