spring源码解析--上
本文是作者原创,版权归作者所有.若要转载,请注明出处.
首先是配置类
package com.lusai.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.lusai.service")
public class SpringConfig { }
然后是IndexService
package com.lusai.service; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service
public class IndexService { public void hello(){
System.out.println("IndexService");
} }
然后是测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);//从这里开始看
IndexService indexService = (IndexService) applicationContext.getBean("indexService");
indexService.hello();
}
看结果
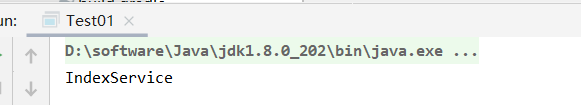
可以看到,IndexService 已经交给spring管理了,我们就开始学习源码吧
/**
* 这个构造方法需要传入一个配置类
* 然后会把这个被注解了的类通过注解读取器读取,继而解析
* Create a new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext, deriving bean definitions
* from the given annotated classes and automatically refreshing the context.
* @param annotatedClasses one or more annotated classes,
* e.g. {@link Configuration @Configuration} classes
*/
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) {
//annotatedClasses ---> 配置类的class对象
//这里由于他有父类,故而会先调用父类的构造方法,然后才会调用自己的构造方法
//在自己构造方法中初始一个读取器和扫描器
this();//进这里看
register(annotatedClasses);
refresh();
}
继续看this()
/**
* 初始化一个bean的读取器和扫描器
* 何谓读取器和扫描器参考上面的属性注释
* 默认构造函数,如果直接调用这个默认构造方法,需要在稍后通过调用其register()
* 去注册配置类(javaconfig),并调用refresh()方法刷新容器,
* 触发容器对注解Bean的载入、解析和注册过程
* Create a new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext that needs to be populated
* through {@link #register} calls and then manually {@linkplain #refresh refreshed}.
*/
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() {
/**
* 父类的构造方法
* 创建一个读取注解的Bean定义读取器
* 什么是BeanDefinition
*/
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
//可以用来扫描包或者类,继而转换成BeanDefinition
//但是实际上我们扫描包工作不是scanner这个对象来完成的
//是spring自己new的一个ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner
//这里的scanner仅仅是为了程序员能够在外部调用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象的scan方法
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
我们看一下this.reader
/**
* 这个类顾名思义是一个reader,一个读取器
* 读取什么呢?还是顾名思义:AnnotatedBeanDefinition意思是读取一个被加了注解的BeanDefinition
* 这个类在构造方法中实例化的
*/
private final AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader reader;
我们再看一下AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 的定义
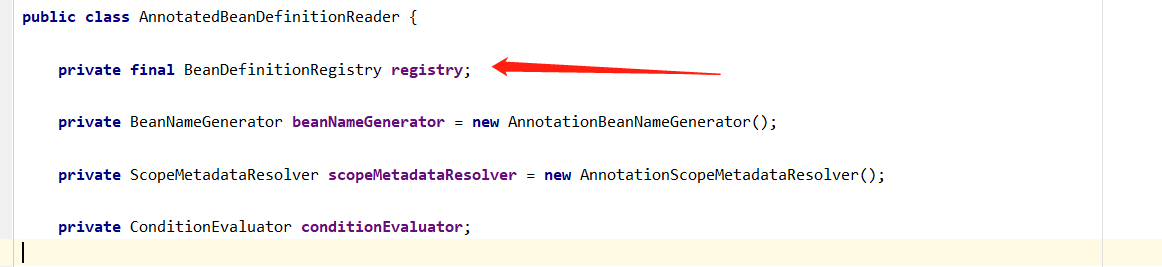
可以看出有个BeanDefinitionRegistry,看这个名字应该是BeanDefinition的注册器,那么BeanDefinition是什么呢,看一下
/**
* BeanDefinition描述了一个bean实例
* A BeanDefinition describes a bean instance, which has property values,
* constructor argument values, and further information supplied by
* concrete implementations.
*
* <p>This is just a minimal interface: The main intention is to allow a
* {@link BeanFactoryPostProcessor} such as {@link PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer}
* to introspect and modify property values and other bean metadata.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Rob Harrop
* @since 19.03.2004
* @see ConfigurableListableBeanFactory#getBeanDefinition
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.ChildBeanDefinition
*/
public interface BeanDefinition extends AttributeAccessor, BeanMetadataElement { /**
* 单例作用域的作用域标识符:“singleton”。
* Scope identifier for the standard singleton scope: "singleton".
* <p>Note that extended bean factories might support further scopes.
* @see #setScope
*/
String SCOPE_SINGLETON = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON; /**
* 非单例作用域的作用域标识符:“prototype”。
* Scope identifier for the standard prototype scope: "prototype".
* <p>Note that extended bean factories might support further scopes.
* @see #setScope
*/
String SCOPE_PROTOTYPE = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE; /**
* 还没搞懂 权限的值
* Role hint indicating that a {@code BeanDefinition} is a major part
* of the application. Typically corresponds to a user-defined bean.
*/
int ROLE_APPLICATION = 0; /**
* Role hint indicating that a {@code BeanDefinition} is a supporting
* part of some larger configuration, typically an outer
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ComponentDefinition}.
* {@code SUPPORT} beans are considered important enough to be aware
* of when looking more closely at a particular
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ComponentDefinition},
* but not when looking at the overall configuration of an application.
*/
int ROLE_SUPPORT = 1; /**
* Role hint indicating that a {@code BeanDefinition} is providing an
* entirely background role and has no relevance to the end-user. This hint is
* used when registering beans that are completely part of the internal workings
* of a {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ComponentDefinition}.
* 就是我这Bean是Spring自己的,和你用户没有一毛钱关系
*/
int ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE = 2; // Modifiable attributes /**
* 设置父BeanDefinition的名字
* Set the name of the parent definition of this bean definition, if any.
*/
void setParentName(@Nullable String parentName); /**
* 获得父BeanDefinition的名字
* Return the name of the parent definition of this bean definition, if any.
*/
@Nullable
String getParentName(); /**
* 指定此BeanDefinition的bean类名
* Specify the bean class name of this bean definition.
* <p>The class name can be modified during bean factory post-processing,
* typically replacing the original class name with a parsed variant of it.
* @see #setParentName
* @see #setFactoryBeanName
* @see #setFactoryMethodName
*/
void setBeanClassName(@Nullable String beanClassName); /**
* 获取此BeanDefinition的bean类名
* Return the current bean class name of this bean definition.
* <p>Note that this does not have to be the actual class name used at runtime, in
* case of a child definition overriding/inheriting the class name from its parent.
* Also, this may just be the class that a factory method is called on, or it may
* even be empty in case of a factory bean reference that a method is called on.
* Hence, do <i>not</i> consider this to be the definitive bean type at runtime but
* rather only use it for parsing purposes at the individual bean definition level.
* @see #getParentName()
* @see #getFactoryBeanName()
* @see #getFactoryMethodName()
*/
@Nullable
String getBeanClassName(); /**
*设置此BeanDefinition的scope的类型
* Override the target scope of this bean, specifying a new scope name.
* @see #SCOPE_SINGLETON
* @see #SCOPE_PROTOTYPE
*/
void setScope(@Nullable String scope); /**
* 获取此BeanDefinition的scope的类型
* Return the name of the current target scope for this bean,
* or {@code null} if not known yet.
*/
@Nullable
String getScope(); /**
* 设置懒加载
* Set whether this bean should be lazily initialized.
* <p>If {@code false}, the bean will get instantiated on startup by bean
* factories that perform eager initialization of singletons.
*/
void setLazyInit(boolean lazyInit); /**
* 获取是否懒加载
* Return whether this bean should be lazily initialized, i.e. not
* eagerly instantiated on startup. Only applicable to a singleton bean.
*/
boolean isLazyInit(); /**
* 设置dependsOn,将首先初始化这些bean
* Set the names of the beans that this bean depends on being initialized.
* The bean factory will guarantee that these beans get initialized first.
*/
void setDependsOn(@Nullable String... dependsOn); /**
* 获取被dependsOn的beans的名字
* Return the bean names that this bean depends on.
*/
@Nullable
String[] getDependsOn(); /**
* 设置是否参与自动装配的候选,与autowire-candidate有关
* Set whether this bean is a candidate for getting autowired into some other bean.
* <p>Note that this flag is designed to only affect type-based autowiring.
* It does not affect explicit references by name, which will get resolved even
* if the specified bean is not marked as an autowire candidate. As a consequence,
* autowiring by name will nevertheless inject a bean if the name matches.
*/
void setAutowireCandidate(boolean autowireCandidate); /**
* 获取是否参与自动装配的候选
* Return whether this bean is a candidate for getting autowired into some other bean.
*/
boolean isAutowireCandidate(); /**
* 设置@Primay注解
* Set whether this bean is a primary autowire candidate.
* <p>If this value is {@code true} for exactly one bean among multiple
* matching candidates, it will serve as a tie-breaker.
*/
void setPrimary(boolean primary); /**
* 获取该bean是否被@Primay注解
* Return whether this bean is a primary autowire candidate.
*/
boolean isPrimary(); /**
* Specify the factory bean to use, if any.
* This the name of the bean to call the specified factory method on.
* @see #setFactoryMethodName
*/
void setFactoryBeanName(@Nullable String factoryBeanName); /**
* Return the factory bean name, if any.
*/
@Nullable
String getFactoryBeanName(); /**
* 与bean标签的factory-method有关
* Specify a factory method, if any. This method will be invoked with
* constructor arguments, or with no arguments if none are specified.
* The method will be invoked on the specified factory bean, if any,
* or otherwise as a static method on the local bean class.
* @see #setFactoryBeanName
* @see #setBeanClassName
*/
void setFactoryMethodName(@Nullable String factoryMethodName); /**
* Return a factory method, if any.
*/
@Nullable
String getFactoryMethodName(); /**
* 存放构造方法的参数和顺序等 constructor-arg标签的index和name等属性
* Return the constructor argument values for this bean.
* <p>The returned instance can be modified during bean factory post-processing.
* @return the ConstructorArgumentValues object (never {@code null})
*/
ConstructorArgumentValues getConstructorArgumentValues(); /**
* 判断构造方法有没有参数值
* Return if there are constructor argument values defined for this bean.
* @since 5.0.2
*/
default boolean hasConstructorArgumentValues() {
return !getConstructorArgumentValues().isEmpty();
} /**
* bean标签的property属性
* Return the property values to be applied to a new instance of the bean.
* <p>The returned instance can be modified during bean factory post-processing.
* @return the MutablePropertyValues object (never {@code null})
*/
MutablePropertyValues getPropertyValues(); /**
* Return if there are property values values defined for this bean.
* @since 5.0.2
*/
default boolean hasPropertyValues() {
return !getPropertyValues().isEmpty();
} /**
* Set the name of the initializer method.
* @since 5.1
*/
void setInitMethodName(@Nullable String initMethodName); /**
* Return the name of the initializer method.
* @since 5.1
*/
@Nullable
String getInitMethodName(); /**
* Set the name of the destroy method.
* @since 5.1
*/
void setDestroyMethodName(@Nullable String destroyMethodName); /**
* Return the name of the destroy method.
* @since 5.1
*/
@Nullable
String getDestroyMethodName(); /**
* Set the role hint for this {@code BeanDefinition}. The role hint
* provides the frameworks as well as tools with an indication of
* the role and importance of a particular {@code BeanDefinition}.
* @since 5.1
* @see #ROLE_APPLICATION
* @see #ROLE_SUPPORT
* @see #ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
*/
void setRole(int role); /**
* Get the role hint for this {@code BeanDefinition}. The role hint
* provides the frameworks as well as tools with an indication of
* the role and importance of a particular {@code BeanDefinition}.
* @see #ROLE_APPLICATION
* @see #ROLE_SUPPORT
* @see #ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
*/
int getRole(); /**
* @Description注解,描述,无太大意义
* Set a human-readable description of this bean definition.
* @since 5.1
*/
void setDescription(@Nullable String description); /**
* Return a human-readable description of this bean definition.
*/
@Nullable
String getDescription(); // Read-only attributes /**
* Return whether this a <b>Singleton</b>, with a single, shared instance
* returned on all calls.
* @see #SCOPE_SINGLETON
*/
boolean isSingleton(); /**
* Return whether this a <b>Prototype</b>, with an independent instance
* returned for each call.
* @since 3.0
* @see #SCOPE_PROTOTYPE
*/
boolean isPrototype(); /**
* 判断是否是抽象类,为什么可以是抽象类
* Return whether this bean is "abstract", that is, not meant to be instantiated.
*/
boolean isAbstract(); /**
* 对文件的描述
* Return a description of the resource that this bean definition
* came from (for the purpose of showing context in case of errors).
*/
@Nullable
String getResourceDescription(); /**
* Return the originating BeanDefinition, or {@code null} if none.
* Allows for retrieving the decorated bean definition, if any.
* <p>Note that this method returns the immediate originator. Iterate through the
* originator chain to find the original BeanDefinition as defined by the user.
*/
@Nullable
BeanDefinition getOriginatingBeanDefinition(); }
BeanDefinition描述了一个bean实例,可以理解为:我们定义的对象交给spring管理以后会变成一个个BeanDefinition
好了,看看下一个
//可以用来扫描包或者类,继而转换成BeanDefinition
//但是实际上我们扫描包工作不是scanner这个对象来完成的
//是spring自己new的一个ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner
//这里的scanner仅仅是为了程序员能够在外部调用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象的scan方法
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
这里的scanner 我们也不深究,姑且认为是一个扫描器
继续看构造方法
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) {
//annotatedClasses ---> 配置类的class对象
//这里由于他有父类,故而会先调用父类的构造方法,然后才会调用自己的构造方法
//在自己构造方法中初始一个读取器和扫描器
this();
register(annotatedClasses);//进这里看
refresh();
}
看register方法
/**
* 注册单个bean给容器
* 比如有新加的类可以用这个方法
* 但是注册注册之后需要手动调用refresh方法去触发容器解析注解
*
* 有两个意思
* 他可以注册一个配置类
* 他还可以单独注册一个bean
* Register one or more annotated classes to be processed.
* <p>Note that {@link #refresh()} must be called in order for the context
* to fully process the new classes.
* @param annotatedClasses one or more annotated classes,
* e.g. {@link Configuration @Configuration} classes
* @see #scan(String...)
* @see #refresh()
*/
public void register(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) {
Assert.notEmpty(annotatedClasses, "At least one annotated class must be specified");
this.reader.register(annotatedClasses);//被注解的类
}
我们把配置类的扫描注释掉看下
@Configuration
//@ComponentScan("com.lusai.service")
public class SpringConfig { }
运行测试类,看下结果
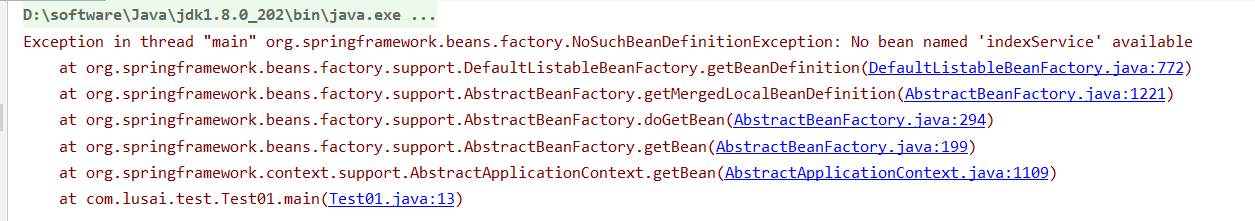
扫描不到报错,我们改成如下形式再试一下
public static void main(String[] args) {
//AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(IndexService.class);
IndexService indexService = (IndexService) applicationContext.getBean("indexService");
indexService.hello();
}
看结果
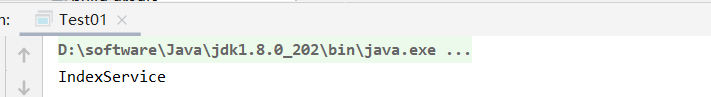
ok,可以看出register方法有两个意思:1.他可以注册一个配置类2.他还可以单独注册一个bean
好了,继续点进去看源码
/**
* Register one or more annotated classes to be processed.
* <p>Calls to {@code register} are idempotent; adding the same
* annotated class more than once has no additional effect.
* @param annotatedClasses one or more annotated classes,
* e.g. {@link Configuration @Configuration} classes
*/
public void register(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) {
for (Class<?> annotatedClass : annotatedClasses) {
registerBean(annotatedClass);
}
}
继续看registerBean
/**
* Register a bean from the given bean class, deriving its metadata from
* class-declared annotations.
* @param annotatedClass the class of the bean
*/
public void registerBean(Class<?> annotatedClass) {
doRegisterBean(annotatedClass, null, null, null);
}
继续看doRegisterBean
/**
* Register a bean from the given bean class, deriving its metadata from
* class-declared annotations.
* @param annotatedClass the class of the bean
* @param instanceSupplier a callback for creating an instance of the bean
* (may be {@code null})
* @param name an explicit name for the bean
* @param qualifiers specific qualifier annotations to consider, if any,
* in addition to qualifiers at the bean class level
* @param definitionCustomizers one or more callbacks for customizing the
* factory's {@link BeanDefinition}, e.g. setting a lazy-init or primary flag
* @since 5.0
*/
<T> void doRegisterBean(Class<T> annotatedClass, @Nullable Supplier<T> instanceSupplier, @Nullable String name,
@Nullable Class<? extends Annotation>[] qualifiers, BeanDefinitionCustomizer... definitionCustomizers) { /**
* 根据指定的bean创建一个AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition
* 这个AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition可以理解为一个数据结构
* AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition包含了类的其他信息,比如一些元信息
* scope,lazy等等.
* 此时因为传入的注解,所以new AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition
*/
AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition abd = new AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(annotatedClass);
/**
* 判断这个类是否需要跳过解析
* 通过代码可以知道spring判断是否跳过解析,主要判断类有没有加注解
*/
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(abd.getMetadata())) {
return;
} abd.setInstanceSupplier(instanceSupplier);
/**
* 得到类的作用域 singleton
*/
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(abd);
/**
* 把类的作用域添加到数据结构结构中
*/
abd.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
/**
* 生成类的名字通过beanNameGenerator
*/
String beanName = (name != null ? name : this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(abd, this.registry));
/**
* 处理类当中的通用注解
* 分析源码可以知道他主要处理
* Lazy DependsOn Primary Role等等注解
* 处理完成之后processCommonDefinitionAnnotations中依然是把他添加到数据结构当中
*/
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(abd);
if (qualifiers != null) {//qualifiers总是为null
for (Class<? extends Annotation> qualifier : qualifiers) {
//如果配置了@Primary注解,如果加了则作为首选
if (Primary.class == qualifier) {
abd.setPrimary(true);
}
//懒加载,前面加过
else if (Lazy.class == qualifier) {
abd.setLazyInit(true);
}
else {
//如果使用了除@Primary和@Lazy以外的其他注解,则为该Bean添加一个根据名字自动装配的限定符
//这里难以理解,后面会详细介绍
abd.addQualifier(new AutowireCandidateQualifier(qualifier));
}
}
}
//自定义注解
for (BeanDefinitionCustomizer customizer : definitionCustomizers) {
customizer.customize(abd);
} /**
* 这个BeanDefinitionHolder也是一个数据结构,这个对象放入了BeanDefinition和beanName,可以理解为一个map
*/
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(abd, beanName);
/**
* ScopedProxyMode 这个知识点比较复杂,需要结合web去理解
* 可以暂时放一下,等说道springmvc的时候再说
* 或者看情况现在说也是一样的
*/
definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
/**
* 把上述的这个数据结构注册给registry
* registy就是AnnotatonConfigApplicationContext
* AnnotatonConfigApplicationContext在初始化的時候通過調用父類的構造方法
* 實例化了一个DefaultListableBeanFactory
* *registerBeanDefinition里面就是把definitionHolder这个数据结构包含的信息注册到
* DefaultListableBeanFactory这个工厂
*/
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
看下这行的源码
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(abd);
继续
public static void processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(AnnotatedBeanDefinition abd) {
processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(abd, abd.getMetadata());
}
继续
/**
* 检查常用的注解
* @param abd
* @param metadata
*/
static void processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(AnnotatedBeanDefinition abd, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
//检查Lazy注解,如果有将它放入AnnotatedBeanDefinition
AnnotationAttributes lazy = attributesFor(metadata, Lazy.class);
if (lazy != null) {
abd.setLazyInit(lazy.getBoolean("value"));
}
else if (abd.getMetadata() != metadata) {
lazy = attributesFor(abd.getMetadata(), Lazy.class);
if (lazy != null) {
abd.setLazyInit(lazy.getBoolean("value"));
}
}
//检查Primary注解,如果有将它放入AnnotatedBeanDefinition
if (metadata.isAnnotated(Primary.class.getName())) {
abd.setPrimary(true);
}
//检查DependsOn注解,如果有将它放入AnnotatedBeanDefinition
AnnotationAttributes dependsOn = attributesFor(metadata, DependsOn.class);
if (dependsOn != null) {
abd.setDependsOn(dependsOn.getStringArray("value"));
}
//检查Role注解,如果有将它放入AnnotatedBeanDefinition
AnnotationAttributes role = attributesFor(metadata, Role.class);
if (role != null) {
abd.setRole(role.getNumber("value").intValue());
}
//检查Description注解,如果有将它放入AnnotatedBeanDefinition
AnnotationAttributes description = attributesFor(metadata, Description.class);
if (description != null) {
abd.setDescription(description.getString("value"));
}
}
分析源码可以知道他主要处理Lazy DependsOn Primary Role等等注解
处理完成之后是把他添加到AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition数据结构当中
继续看下面
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(abd, beanName);
看下BeanDefinitionHolder 的定义
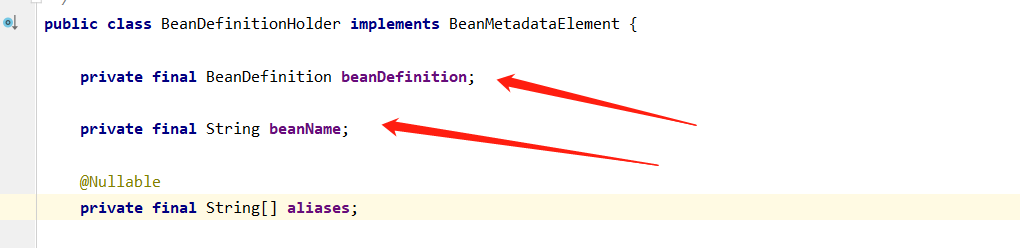
这个BeanDefinitionHolder也是一个对象,这个对象放入了BeanDefinition和beanName
好了,我们看最后一行关键代码:
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
点进去
public static void registerBeanDefinition(
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { // Register bean definition under primary name.
String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName();//获取beanName
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition());//关键代码 //别名,先不看
// Register aliases for bean name, if any.
String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases();
if (aliases != null) {
for (String alias : aliases) {
registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias);
}
}
}
看那行关键代码
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { //DefaultListableBeanFactory
this.beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
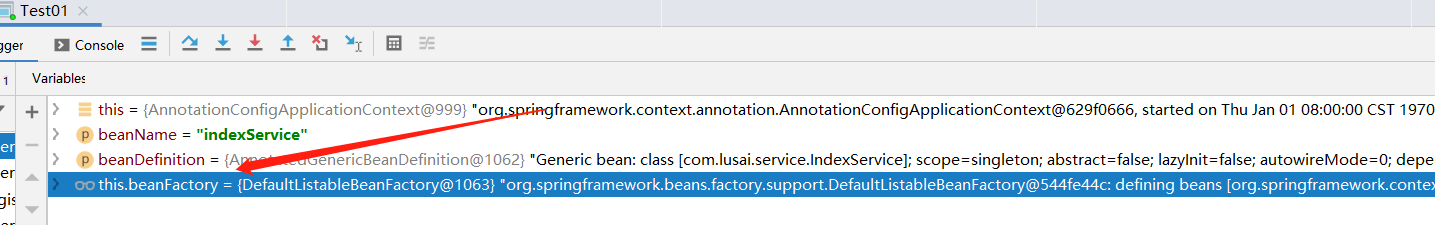
这里的this.beanFactory是DefaultListableBeanFactory,这个是默认的bean工厂
再点进去看
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null"); if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {//验证
try {
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
} BeanDefinition existingDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (existingDefinition != null) {
if (!isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionOverrideException(beanName, beanDefinition, existingDefinition);
}
else if (existingDefinition.getRole() < beanDefinition.getRole()) {
// e.g. was ROLE_APPLICATION, now overriding with ROLE_SUPPORT or ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Overriding user-defined bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a framework-generated bean definition: replacing [" +
existingDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else if (!beanDefinition.equals(existingDefinition)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a different definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with an equivalent definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
else {
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) {
// Cannot modify startup-time collection elements anymore (for stable iteration)
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
List<String> updatedDefinitions = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1);
updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames);
updatedDefinitions.add(beanName);
this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions;
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
}
else {//关键代码
// Still in startup registration phase
//这里的beanDefinitionMap是一个map,存放beanName,beanDefinition
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
//这里的beanDefinitionNames是一个list,存放beanName
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
} if (existingDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
}
看我注释的地方,那里就是关键代码
这里的this.beanDefinitionMap看一下
/** Map of bean definition objects, keyed by bean name. */
private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
这里我们debug一下
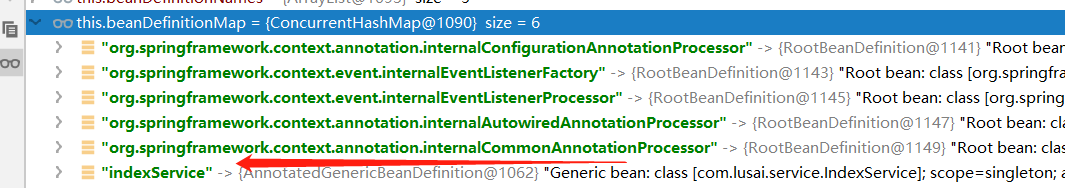
可以看到除了indexService之外很多内置的bean,那么这些类是什么时候注册的,都有什么用呢?我们后面再研究
我们register看完了,现在看refresh方法
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) {
//annotatedClasses ---> 配置类的class对象
//这里由于他有父类,故而会先调用父类的构造方法,然后才会调用自己的构造方法
//在自己构造方法中初始一个读取器和扫描器
this();
register(annotatedClasses);
refresh();//进这里看
}
点进去
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
////准备工作包括设置启动时间,是否激活标识位,
// 初始化属性源(property source)配置
prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
//返回一个factory 为什么需要返回一个工厂
//因为要对工厂进行初始化
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
//准备工厂
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. //这个方法在当前版本的spring是没用任何代码的
//可能spring期待在后面的版本中去扩展吧
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
//在spring的环境中去执行已经被注册的 factory processors
//设置执行自定义的ProcessBeanFactory 和spring内部自己定义的
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
//注册beanPostProcessor
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context.
//初始化应用事件广播器
initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
} // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
} finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
看看下面这行
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
点进去
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
refreshBeanFactory();
return getBeanFactory();
}
继续看getBeanFactory()方法
@Override
public final ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() {
return this.beanFactory;
}
这里的this.beanFactory就是上文提到的DefaultListableBeanFactory
private final DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
好,下面我们看这行
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
点进去
/**
*
* 配置其标准的特征,比如上下文的加载器ClassLoader和post-processors回调
* Configure the factory's standard context characteristics,
* such as the context's ClassLoader and post-processors.
* @param beanFactory the BeanFactory to configure
* 此处的beanFactory参数等于DefaultListableFactory
*/
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc.
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
//bean表达式解释器,后面说 能够获取bean当中的属性在前台页面
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
//对象与string类型的转换 <property red="dao">
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment())); // Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
//添加一个后置管理器
//ApplicationContextAwareProcessor
// 能够在bean中获得到各种*Aware(*Aware都有其作用)
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));//核心代码 beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class); // BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.
// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this); // Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners.
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this)); // Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
} //意思是如果自定义的Bean中没有名为"systemProperties"和"systemEnvironment"的Bean,
// 则注册两个Bena,Key为"systemProperties"和"systemEnvironment",Value为Map,
// 这两个Bean就是一些系统配置和系统环境信息
// Register default environment beans.
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}
我们看一下核心的那行代码
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));//核心代码
打断点
@Override
public void addBeanPostProcessor(BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor) {
Assert.notNull(beanPostProcessor, "BeanPostProcessor must not be null");
// Remove from old position, if any
this.beanPostProcessors.remove(beanPostProcessor);
// Track whether it is instantiation/destruction aware
if (beanPostProcessor instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
this.hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors = true;
}
if (beanPostProcessor instanceof DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
this.hasDestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors = true;
}
// Add to end of list
this.beanPostProcessors.add(beanPostProcessor);//核心代码
}
我们看一下this.beanPostProcessors是什么
/** BeanPostProcessors to apply in createBean. */ private final List<BeanPostProcessor> beanPostProcessors = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
BeanPostProcessor就是传说中的后置处理器,通过实现BeanPostProcessor接口,程序员就可插手bean实例化的过程
我们试一下
@Service
public class IndexService { public IndexService(){
System.out.println("IndexService 构造方法");
} @PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("IndexService init方法");
} public void hello(){
System.out.println("IndexService");
} }
配置类
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.lusai")
public class SpringConfig { }
实现BeanPostProcessor接口的类
@Component
public class TestBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { /**
* 在bean初始化之前执行
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (beanName.equals("indexService")){
System.out.println("indexService postProcessBeforeInitialization");
}
//这里也可以产生代理对象 Proxy.newProxyInstance()
return bean;
} /**
* 初始化之后
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (beanName.equals("indexService")){
System.out.println("indexService postProcessAfterInitialization");
}
return bean;
}
}
测试类
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
//AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(IndexService.class);
IndexService indexService = (IndexService) applicationContext.getBean("indexService");
indexService.hello();
}
看下结果
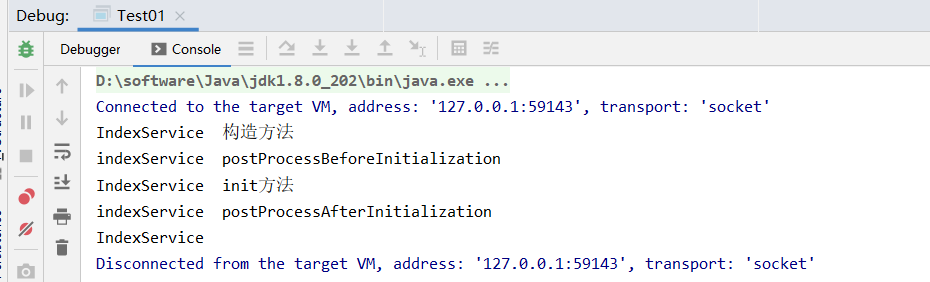
插手成功
好了,我们继续这行代码
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));//核心代码
我们看下此处的ApplicationContextAwareProcessor,这个类实现了BeanPostProcessor 接口,重写了postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
class ApplicationContextAwareProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
@Nullable
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(final Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
AccessControlContext acc = null;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null &&
(bean instanceof EnvironmentAware || bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware ||
bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware || bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware ||
bean instanceof MessageSourceAware || bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware)) {
acc = this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory().getAccessControlContext();
}
if (acc != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareInterfaces(bean);
return null;
}, acc);
}
else {
invokeAwareInterfaces(bean);//看这行
}
return bean;
}
}
看下那行代码
private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware) {//EnvironmentAware用于获取配置文件
//比如this.applicationContext.getEnvironment().getProperty("url")
//ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.applicationContext.getEnvironment();
((EnvironmentAware) bean).setEnvironment(this.applicationContext.getEnvironment());
}
if (bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) {
((EmbeddedValueResolverAware) bean).setEmbeddedValueResolver(this.embeddedValueResolver);
}
if (bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) {
((ResourceLoaderAware) bean).setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware) {
((ApplicationEventPublisherAware) bean).setApplicationEventPublisher(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof MessageSourceAware) {
((MessageSourceAware) bean).setMessageSource(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {//实现ApplicationContextAware接口,可以在spring管理的单例bean中中使用原型依赖bean
((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
}
}
我们测试一下ApplicationContextAware接口
@Service
public class IndexService implements ApplicationContextAware { private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public IndexService(){
System.out.println("IndexService 构造方法");
} @PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("IndexService init方法");
} public void hello(){
System.out.println("IndexService");
} @Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext=applicationContext;
System.out.println(applicationContext);
}
}
运行测试类,看下结果
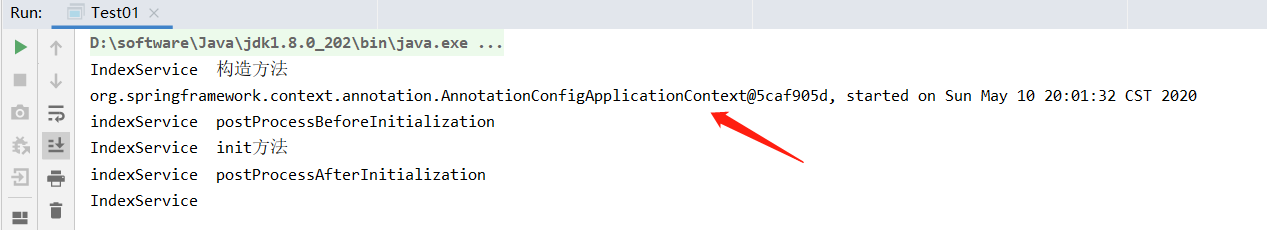
好了,我们继续看源码
//目前是空方法,留给后续扩展
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); //完成扫描和解析(类--->beanDefinition) beanDefinitionMap
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
第一个是空方法,看第二行
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
//先看下getBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime
// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)
if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}
先看下getBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法
public List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> getBeanFactoryPostProcessors() {
return this.beanFactoryPostProcessors;
}
这里的this.beanFactoryPostProcessors就是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的集合,如下
private final List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
那么BeanFactoryPostProcessor是什么?有什么用呢?
BeanFactoryPostProcessor是spring的扩展点之一
* 实现该接口,可以在spring的bean创建之前修改bean的定义属性。
* spring允许BeanFactoryPostProcessor在容器实例化任何其它bean之前读取配置元数据,
* 并可以根据需要进行修改,例如可以把bean的scope从singleton改为prototype,也可以把property的值给修改掉。
* 可以同时配置多个BeanFactoryPostProcessor,并通过设置'order'属性来控制各个BeanFactoryPostProcessor的执行次序。
* BeanFactoryPostProcessor是在spring容器加载了bean的定义文件之后,在bean实例化之前执行的
来测试一下这个功能
@Component
public class TestBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
BeanDefinition indexService = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("indexService");
String scope = indexService.getScope();
System.out.println(scope);
indexService.setScope("prototype");
System.out.println(scope);
}
}
这篇就先到这里吧
spring源码解析--上的更多相关文章
- Spring源码解析 - AbstractBeanFactory 实现接口与父类分析
我们先来看类图吧: 除了BeanFactory这一支的接口,AbstractBeanFactory主要实现了AliasRegistry和SingletonBeanRegistry接口. 这边主要提供了 ...
- spring 源码解析
1. [文件] spring源码.txt ~ 15B 下载(167) ? 1 springн┤┬вио╬Ш: 2. [文件] spring源码分析之AOP.txt ~ 15KB 下载( ...
- Spring源码解析-ioc容器的设计
Spring源码解析-ioc容器的设计 1 IoC容器系列的设计:BeanFactory和ApplicatioContext 在Spring容器中,主要分为两个主要的容器系列,一个是实现BeanFac ...
- Spring源码解析系列汇总
相信我,你会收藏这篇文章的 本篇文章是这段时间撸出来的Spring源码解析系列文章的汇总,总共包含以下专题.喜欢的同学可以收藏起来以备不时之需 SpringIOC源码解析(上) 本篇文章搭建了IOC源 ...
- Spring源码解析之BeanFactoryPostProcessor(三)
在上一章中笔者介绍了refresh()的<1>处是如何获取beanFactory对象,下面我们要来学习refresh()方法的<2>处是如何调用invokeBeanFactor ...
- Spring源码解析之ConfigurationClassPostProcessor(二)
上一个章节,笔者向大家介绍了spring是如何来过滤配置类的,下面我们来看看在过滤出配置类后,spring是如何来解析配置类的.首先过滤出来的配置类会存放在configCandidates列表, 在代 ...
- Spring源码解析之八finishBeanFactoryInitialization方法即初始化单例bean
Spring源码解析之八finishBeanFactoryInitialization方法即初始化单例bean 七千字长文深刻解读,Spirng中是如何初始化单例bean的,和面试中最常问的Sprin ...
- Spring源码解析——循环依赖的解决方案
一.前言 承接<Spring源码解析--创建bean>.<Spring源码解析--创建bean的实例>,我们今天接着聊聊,循环依赖的解决方案,即创建bean的ObjectFac ...
- Spring源码解析之PropertyPlaceholderHelper(占位符解析器)
Spring源码解析之PropertyPlaceholderHelper(占位符解析器) https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39471249/article/details/7 ...
随机推荐
- docker 概览 (1)
Docker Docker 是一个开源的应用容器引擎,让开发者可以打包他们的应用以及依赖包到一个可移植的镜像中,然后发布到任何流行的 Linux或Windows 机器上,也可以实现虚拟化.容器是完全使 ...
- python之elasticsearch查询
下载所需模块 python安装好的情况下,通过pip install elasticsearch进行es模块的安装 安装完成后通过pip list命中查询 导入模块 from elasticsearc ...
- 使用mysqlbinlog查看二进制日志
(一)mysqlbinlog工具介绍 binlog类型是二进制的,也就意味着我们没法直接打开看,MySQL提供了mysqlbinlog来查看二进制日志,该工具类似于Oracle的logminer.my ...
- redis:String字符串类型(三)
字符串拼接(如果key不存在则创建):append name " applesnt" 获取字符串的长度:strlen name 127.0.0.1:6379> set nam ...
- Linux-LAMP虚拟主机配置
1.配置用户认证 <Directory /data/discuz/passwd> AllowOverride AuthConfig AuthName "自定义的" Au ...
- java 递归及其经典应用--求阶乘、打印文件信息、计算斐波那契数列
什么是递归 我先看下百度百科的解释: 一种计算过程,如果其中每一步都要用到前一步或前几步的结果,称为递归的.用递归过程定义的函数,称为递归函数,例如连加.连乘及阶乘等.凡是递归的函数,都是可计算的,即 ...
- wget下载整个网站---比较实用--比如抓取Smarty的document
wget下载整个网站可以使用下面的命令 wget -r -p -k -np http://hi.baidu.com/phps, -r 表示递归下载,会下载所有的链接,不过要注意的是,不要单独使用这个参 ...
- js html生成图片
我自己分装好的方法,外链自己去下: /** * !!!使用前请导入jq文件!!! 海报生成, 二维码链接生成 */ document.write('<script src="/Publ ...
- 文件读取的时候要留意 -- 序列化serialize()与反序列化unserialize():
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/little_rabbit_baby/article/details/53840543 序列化serialize()与反序列化unserialize( ...
- QT踩坑记录1-多线程信号与槽
QT踩坑记录1-多线程信号与槽 QTC++Bugs 错误输出 无错误输出, 但是声明了信号的连接,但是无法使用 程序中就是无命令 介绍 QT 典型程序 #include <QObject> ...
