Java规则引擎 Easy Rules
1. Easy Rules 概述
Easy Rules是一个Java规则引擎,灵感来自一篇名为《Should I use a Rules Engine?》的文章
规则引擎就是提供一种可选的计算模型。与通常的命令式模型(由带有条件和循环的命令依次组成)不同,规则引擎基于生产规则系统。这是一组生产规则,每条规则都有一个条件(condition)和一个动作(action)———— 简单地说,可以将其看作是一组if-then语句。
精妙之处在于规则可以按任何顺序编写,引擎会决定何时使用对顺序有意义的任何方式来计算它们。考虑它的一个好方法是系统运行所有规则,选择条件成立的规则,然后执行相应的操作。这样做的好处是,很多问题都很自然地符合这个模型:
if car.owner.hasCellPhone then premium += 100;
if car.model.theftRating > 4 then premium += 200;
if car.owner.livesInDodgyArea && car.model.theftRating > 2 then premium += 300;规则引擎是一种工具,它使得这种计算模型编程变得更容易。它可能是一个完整的开发环境,或者一个可以在传统平台上工作的框架。生产规则计算模型最适合仅解决一部分计算问题,因此规则引擎可以更好地嵌入到较大的系统中。
你可以自己构建一个简单的规则引擎。你所需要做的就是创建一组带有条件和动作的对象,将它们存储在一个集合中,然后遍历它们以评估条件并执行这些动作。
Easy Rules它提供Rule抽象以创建具有条件和动作的规则,并提供RuleEngine API,该API通过一组规则运行以评估条件并执行动作。
Easy Rules简单易用,只需两步:
首先,定义规则,方式有很多种
方式一:注解
@Rule(name = "weather rule", description = "if it rains then take an umbrella")
public class WeatherRule { @Condition
public boolean itRains(@Fact("rain") boolean rain) {
return rain;
} @Action
public void takeAnUmbrella() {
System.out.println("It rains, take an umbrella!");
}
}
方式二:链式编程
Rule weatherRule = new RuleBuilder()
.name("weather rule")
.description("if it rains then take an umbrella")
.when(facts -> facts.get("rain").equals(true))
.then(facts -> System.out.println("It rains, take an umbrella!"))
.build();
方式三:表达式
Rule weatherRule = new MVELRule()
.name("weather rule")
.description("if it rains then take an umbrella")
.when("rain == true")
.then("System.out.println(\"It rains, take an umbrella!\");");
方式四:yml配置文件
例如:weather-rule.yml
name: "weather rule"
description: "if it rains then take an umbrella"
condition: "rain == true"
actions:
- "System.out.println(\"It rains, take an umbrella!\");"
MVELRuleFactory ruleFactory = new MVELRuleFactory(new YamlRuleDefinitionReader());
Rule weatherRule = ruleFactory.createRule(new FileReader("weather-rule.yml"));
接下来,应用规则
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// define facts
Facts facts = new Facts();
facts.put("rain", true);
// define rules
Rule weatherRule = ...
Rules rules = new Rules();
rules.register(weatherRule);
// fire rules on known facts
RulesEngine rulesEngine = new DefaultRulesEngine();
rulesEngine.fire(rules, facts);
}
}
入门案例:Hello Easy Rules
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jeasy</groupId>
<artifactId>easy-rules-core</artifactId>
<version>4.0.0</version>
</dependency>
通过骨架创建maven项目:
mvn archetype:generate \
-DarchetypeGroupId=org.jeasy \
-DarchetypeArtifactId=easy-rules-archetype \
-DarchetypeVersion=4.0.
默认给我们生成了一个HelloWorldRule规则,如下:
package com.cjs.example.rules; import org.jeasy.rules.annotation.Action;
import org.jeasy.rules.annotation.Condition;
import org.jeasy.rules.annotation.Rule; @Rule(name = "Hello World rule", description = "Always say hello world")
public class HelloWorldRule { @Condition
public boolean when() {
return true;
} @Action
public void then() throws Exception {
System.out.println("hello world");
} }

2. 规则定义
2.1. 定义规则
大多数业务规则可以用以下定义表示:
- Name : 一个命名空间下的唯一的规则名称
- Description : 规则的简要描述
- Priority : 相对于其他规则的优先级
- Facts : 事实,可立即为要处理的数据
- Conditions : 为了应用规则而必须满足的一组条件
- Actions : 当条件满足时执行的一组动作
Easy Rules为每个关键点提供了一个抽象来定义业务规则。
在Easy Rules中,Rule接口代表规则
public interface Rule {
/**
* This method encapsulates the rule's conditions.
* @return true if the rule should be applied given the provided facts, false otherwise
*/
boolean evaluate(Facts facts);
/**
* This method encapsulates the rule's actions.
* @throws Exception if an error occurs during actions performing
*/
void execute(Facts facts) throws Exception;
//Getters and setters for rule name, description and priority omitted.
}
evaluate方法封装了必须计算结果为TRUE才能触发规则的条件。execute方法封装了在满足规则条件时应该执行的动作。条件和操作由Condition和Action接口表示。
定义规则有两种方式:
- 通过在POJO类上添加注解
- 通过RuleBuilder API编程
可以在一个POJO类上添加@Rule注解,例如:
@Rule(name = "my rule", description = "my rule description", priority = 1)
public class MyRule { @Condition
public boolean when(@Fact("fact") fact) {
//my rule conditions
return true;
} @Action(order = 1)
public void then(Facts facts) throws Exception {
//my actions
} @Action(order = 2)
public void finally() throws Exception {
//my final actions
} }
@Condition注解指定规则条件
@Fact注解指定参数
@Action注解指定规则执行的动作
RuleBuilder支持链式风格定义规则,例如:
Rule rule = new RuleBuilder()
.name("myRule")
.description("myRuleDescription")
.priority(3)
.when(condition)
.then(action1)
.then(action2)
.build();
组合规则
CompositeRule由一组规则组成。这是一个典型地组合设计模式的实现。
组合规则是一个抽象概念,因为可以以不同方式触发组合规则。
Easy Rules自带三种CompositeRule实现:
- UnitRuleGroup : 要么应用所有规则,要么不应用任何规则(AND逻辑)
- ActivationRuleGroup : 它触发第一个适用规则,并忽略组中的其他规则(XOR逻辑)
- ConditionalRuleGroup : 如果具有最高优先级的规则计算结果为true,则触发其余规则
复合规则可以从基本规则创建并注册为常规规则:
//Create a composite rule from two primitive rules
UnitRuleGroup myUnitRuleGroup = new UnitRuleGroup("myUnitRuleGroup", "unit of myRule1 and myRule2");
myUnitRuleGroup.addRule(myRule1);
myUnitRuleGroup.addRule(myRule2); //Register the composite rule as a regular rule
Rules rules = new Rules();
rules.register(myUnitRuleGroup); RulesEngine rulesEngine = new DefaultRulesEngine();
rulesEngine.fire(rules, someFacts);
每个规则都有优先级。它代表触发注册规则的默认顺序。默认情况下,较低的值表示较高的优先级。可以重写compareTo方法以提供自定义优先级策略。
2.2. 定义事实
在Easy Rules中,Fact API代表事实
public class Fact<T> {
private final String name;
private final T value;
}

举个栗子:
Fact<String> fact = new Fact("foo", "bar");
Facts facts = new Facts();
facts.add(fact);
或者,也可以用这样简写形式
Facts facts = new Facts();
facts.put("foo", "bar");
用@Fact注解可以将Facts注入到condition和action方法中
@Rule
class WeatherRule { @Condition
public boolean itRains(@Fact("rain") boolean rain) {
return rain;
} @Action
public void takeAnUmbrella(Facts facts) {
System.out.println("It rains, take an umbrella!");
// can add/remove/modify facts
} }
2.3. 定义规则引擎
Easy Rules提供两种RulesEngine接口实现:
- DefaultRulesEngine : 根据规则的自然顺序应用规则
- InferenceRulesEngine : 持续对已知事实应用规则,直到不再适用任何规则为止
创建规则引擎:
RulesEngine rulesEngine = new DefaultRulesEngine(); // or RulesEngine rulesEngine = new InferenceRulesEngine();
然后,注册规则
rulesEngine.fire(rules, facts);
规则引擎有一些可配置的参数,如下图所示:
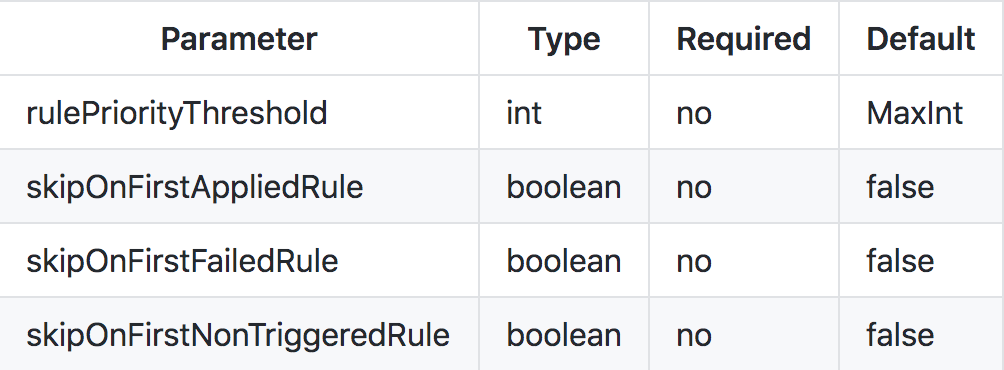
举个栗子:
RulesEngineParameters parameters = new RulesEngineParameters()
.rulePriorityThreshold(10)
.skipOnFirstAppliedRule(true)
.skipOnFirstFailedRule(true)
.skipOnFirstNonTriggeredRule(true); RulesEngine rulesEngine = new DefaultRulesEngine(parameters);
2.4. 定义规则监听器
通过实现RuleListener接口
public interface RuleListener {
/**
* Triggered before the evaluation of a rule.
*
* @param rule being evaluated
* @param facts known before evaluating the rule
* @return true if the rule should be evaluated, false otherwise
*/
default boolean beforeEvaluate(Rule rule, Facts facts) {
return true;
}
/**
* Triggered after the evaluation of a rule.
*
* @param rule that has been evaluated
* @param facts known after evaluating the rule
* @param evaluationResult true if the rule evaluated to true, false otherwise
*/
default void afterEvaluate(Rule rule, Facts facts, boolean evaluationResult) { }
/**
* Triggered on condition evaluation error due to any runtime exception.
*
* @param rule that has been evaluated
* @param facts known while evaluating the rule
* @param exception that happened while attempting to evaluate the condition.
*/
default void onEvaluationError(Rule rule, Facts facts, Exception exception) { }
/**
* Triggered before the execution of a rule.
*
* @param rule the current rule
* @param facts known facts before executing the rule
*/
default void beforeExecute(Rule rule, Facts facts) { }
/**
* Triggered after a rule has been executed successfully.
*
* @param rule the current rule
* @param facts known facts after executing the rule
*/
default void onSuccess(Rule rule, Facts facts) { }
/**
* Triggered after a rule has failed.
*
* @param rule the current rule
* @param facts known facts after executing the rule
* @param exception the exception thrown when attempting to execute the rule
*/
default void onFailure(Rule rule, Facts facts, Exception exception) { }
}
3. 示例
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.cjs.example</groupId>
<artifactId>easy-rules-quickstart</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jeasy</groupId>
<artifactId>easy-rules-core</artifactId>
<version>4.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jeasy</groupId>
<artifactId>easy-rules-support</artifactId>
<version>4.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jeasy</groupId>
<artifactId>easy-rules-mvel</artifactId>
<version>4.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-simple</artifactId>
<version>1.7.30</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>

4. 扩展
规则本质上是一个函数,如y=f(x1,x2,..,xn)
规则引擎就是为了解决业务代码和业务规则分离的引擎,是一种嵌入在应用程序中的组件,实现了将业务决策从应用程序代码中分离。
还有一种常见的方式是Java+Groovy来实现,Java内嵌Groovy脚本引擎进行业务规则剥离。
https://github.com/j-easy/easy-rules/wiki
Java规则引擎 Easy Rules的更多相关文章
- JAVA规则引擎JSR-94笔札
JAVA规则引擎JSR-94笔札 JSR-94 是由JCP(Java Community Process)组织所制定的java规则引擎API的java请求规范.它主要定义了规则引擎在java运行时的一 ...
- Java规则引擎及JSR-94[转]
规则引擎简介 Java规则引擎是推理引擎的一种,它起源于基于规则的专家系统. Java规则引擎将业务决策从应用程序代码中分离出来,并使用预定义的语义模块编写业务决策.Java规则引擎接 ...
- [Drools]JAVA规则引擎 -- Drools- 转http://blog.csdn.net/quzishen/article/details/6163012
[Drools]JAVA规则引擎 -- Drools 标签: java引擎exceptiongetterstringsetter 2011-01-25 14:33 113340人阅读 评论(35) 收 ...
- 【java规则引擎】之规则引擎解释
转载:http://www.open-open.com/lib/view/open1417528754230.html 现实生活中,规则无处不在.法律.法规和各种制度均是:对于企业级应用来说,在IT技 ...
- JAVA规则引擎 -- Drools
Drools是一个基于java的规则引擎,开源的,可以将复杂多变的规则从硬编码中解放出来,以规则脚本的形式存放在文件中,使得规则的变更不需要修正代码重启机器就可以立即在线上环境生效. 本文所使用的de ...
- [Drools]JAVA规则引擎 -- Drools 2
上一篇文章 http://blog.csdn.net/quzishen/archive/2011/01/25/6163012.aspx 描述了一些常用的drools的语法标签和一个模拟实例即发送积分的 ...
- [Drools]JAVA规则引擎 -- Drools
Drools是一个基于Java的规则引擎,开源的,可以将复杂多变的规则从硬编码中解放出来,以规则脚本的形式存放在文件中,使得规则的变更不需要修正代码重启机器就可以立即在线上环境生效. 本文所使用的de ...
- java 规则引擎资料汇集
1. ibm的developworks中较早的一篇关于规则引擎的文章 https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-java-rules/ 2. 一篇硕士论 ...
- 【java规则引擎】drools6.5.0版本中kmodule.xml解析
kmodule.xml文件存放在src/main/resources/META-INF/文件夹下. <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UT ...
随机推荐
- spark机器学习从0到1特征抽取–Word2Vec(十四)
一.概念 Word2vec是一个Estimator,它采用一系列代表文档的词语来训练word2vecmodel.该模型将每个词语映射到一个固定大小的向量.word2vecmodel使用文档中每个词 ...
- node的fs模块
node的file system模块提供的api有同步和异步两种模式(大多数情况下都是用的异步方法,毕竟异步是node的特色,至于提供同步方法,可能应用程序复杂的时候有些场景使用同步会比较合适).异步 ...
- MySQL索引及查询优化
mysql 索引 1.索引介绍 索引按数据结构分可分为哈希表,有序数组,搜索树,跳表: 哈希表适用于只有等值查询的场景 有序数组适用于有等值查询和范围查询的场景,但有序数组索引的更新代价很大,所以最好 ...
- Java switch case语句
switch case 语句判断一个变量与一系列值中某个值是否相等,每个值称为一个分支. switch case 语句语法格式如下: switch(expression){ case value : ...
- linux高级管理第十二章--rsync
实验部分 1.安装rsync 2.配置文件 3.配置密码 4.后续 5.为了测试,创建几个文件 配置实时同步 1.调整inotify内核参数 安装inotify-tools 测试同步 编写脚本 验证 ...
- vue-cli2 使用cdn资源
vue-cli2 引入固定cdn资源操作记录 vue引入cdn也不是什么神奇的操作,但是自己之前一直没有尝试过,这次正好项目优化需要,所以,实操一波,特此记录 本次cnd引入了如下资源 vue vue ...
- python 比较常见的工具方法
下面是一些工作过程中比较常见的工具方法,但不代表最终答案.希望能对你有所帮助,如果您有更好更多的方法工具,欢迎推荐! 1. 按行读取带json字符串的文件 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- ...
- 大数据平台比较-CDH,HDP
主要的不同点 apache Ambari ClouderaManager Express(免费版) 配置版本控制和历史记录 支持 不支持 二次开发 支持 不支持 集成 支持 no (不支持redis. ...
- Python对象组合
一个类的对象作为另一个类的对象的属性,称为类的组合. 即 class1.instance1.property = class2.instance 组合也是代码重用的重要方式之一. 先定义三个类:人.汽 ...
- 计划任务工具-windows
计划任务工具根据自己设定的具体时间,频率,命令等属性来规定所要执行的计划. 代码 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Module implement ...
